Pharmacological properties of the drug Aspecard
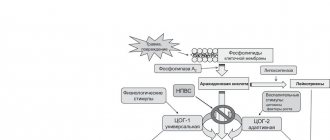
Aspecard has antithrombotic, as well as anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects, characteristic of acetylsalicylic acid. The mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid is based on the inactivation of the COX enzyme, as a result of which the synthesis of prostaglandins, prostacyclins and thromboxane is disrupted. Due to a decrease in the production of prostaglandins, their pyrogenic effect on thermoregulation centers is reduced. The sensitizing effect of prostaglandins on sensory nerve endings is reduced, which leads to a decrease in their sensitivity to pain mediators. An irreversible disruption of the synthesis of thromboxane A2 in platelets causes the antiplatelet effect of acetylsalicylic acid. Absorption of acetylsalicylic acid in the digestive tract occurs quickly and completely. The maximum level of concentration in blood plasma is reached after 10–20 minutes. The degree of binding to plasma proteins depends on the concentration and ranges from 49–70%. About 50% of acetylsalicylic acid is metabolized during the initial passage through the liver. Excreted in the form of metabolites in the urine. The half-life of salicylic acid is 20 minutes and increases with increasing dosage of the drug. Penetrates through the BBB into the CSF, synovial fluid, and breast milk.
Aspicard
When used simultaneously, ASA enhances the effect of the following drugs; If it is necessary to simultaneously prescribe ASA with the listed drugs, the need to reduce the dose of these drugs should be considered:
- methotrexate by reducing renal clearance and displacing it from protein binding; the use of the drug together with methotrexate is contraindicated if the dose of the latter exceeds 15 mg per week (see section “Contraindications”) and can be used with caution when the dose of methotrexate is less than 15 mg per week;
- heparin and indirect anticoagulants due to disruption of platelet function and displacement of indirect anticoagulants from binding with proteins;
- when used simultaneously with anticoagulants, thrombolytic and antiplatelet agents (ticlopidine), there is an increased risk of bleeding as a result of the synergistic action;
- when used simultaneously with drugs that have anticoagulant, thrombolytic or antiplatelet effects, an increased damaging effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is observed;
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which may lead to an increased risk of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (synergism with ASA);
- digoxin due to a decrease in its renal excretion, which can lead to an overdose;
— hypoglycemic agents for oral administration (sulfonylurea derivatives) and insulin due to the hypoglycemic properties of ASA itself in high doses and displacing sulfonylurea derivatives from binding with blood plasma proteins;
- when used simultaneously with valproic acid, its toxicity increases due to displacement from the connection with blood plasma proteins;
- NSAIDs and salicylic acid derivatives in high doses (increased risk of ulcerogenic effect and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract as a result of synergistic action);
- ethanol (increased risk of damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and prolongation of bleeding time as a result of the mutual enhancement of the effects of ASA and ethanol).
The simultaneous administration of ASA in high doses may weaken the effect of the drugs listed below. If it is necessary to simultaneously prescribe ASA with the listed drugs, you should consider the need to adjust the dose of the drugs listed below:
- diuretics (when used together with ASA in high doses, a decrease in glomerular filtration rate is observed as a result of a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys);
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (a dose-dependent decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is noted as a result of inhibition of prostaglandins that have a vasodilatory effect, respectively, weakening of the hypotensive effect. A clinically significant decrease in GFR is observed with a daily dose of ASA more than 160 mg. In addition, there is a decrease positive cardioprotective effect of ACE inhibitors prescribed to patients for the treatment of chronic heart failure. This effect is also manifested when used together with ASA in large doses;
- drugs with uricosuric action - benzbromarone, probenecid (reduced uricosuric effect due to competitive suppression of renal tubular excretion of uric acid).
When used simultaneously with ibuprofen, antagonism is observed against the irreversible platelet inhibition caused by the action of ASA, which leads to a decrease in the cardioprotective effects of ASA.
When used simultaneously with GCS (with the exception of hydrocortisone used for replacement therapy of Adison's disease), there is an increase in the elimination of salicylates and, accordingly, a weakening of their effect.
You should tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking. Aspicard can be used with other medications only if recommended by a doctor.
Use of the drug Aspecard
1 tablet 1 time per day after meals. For secondary prevention of myocardial infarction, the dose can be increased to 2-3 tablets per day for 2-3 months. The drug is intended for long-term use (from 1–2 months to 2 years), the duration of which is determined individually. To reduce the severity of the irritant effect of the drug on the gastric mucosa, Aspecard tablets are taken after meals with 1/2 glass of water or milk. The maximum daily dose is 300 mg.
Analogues and substitutes
The original Aspecard is temporarily unavailable on the Russian market. The drug is produced at the request of Stirolbiopharm Baltikum LLC at factories located in different countries.
There are imported analogues of medications on the market—medicines with identical composition and indications for use:
- Akard (Poland);
- "Anopyrin" (Slovakia);
- "Aspirin Cardio" (Germany, Switzerland);
- "Godasal" (Germany);
- "Reocard" (USA);
- "Trombopol" (Poland);
- "Ekorin" (India).
The cheapest substitute for Aspecard is Acetylsalicylic acid. To prevent cardiovascular complications, enteric forms of tablet coating have been developed. The main goal is to minimize the adverse effects of ASA on the inner lining of the stomach. “Acetylsalicylic acid” is a product without the necessary protective “capsule”.
If there is no effect or intolerance, you can purchase substitutes for Aspecard at the pharmacy (medicines with a different composition but similar effects):
- "Cardiomagnyl" (Austria). Magnesium hydroxide in the composition provides additional protection for the gastric mucosa.
- "Clopidogrel", "Agrel", "Clodia", "Lopirel", "Plavix". The active substance blocks platelet ADP receptors, providing an effect similar to Aspecard.
- "Dipyridamole", "Curantil". The drugs block platelet phosphodiesterase.
There are combinations of ASA with indirect anticoagulants: Clopidogrel (Aspigrel, Coplavix) or Dipyridamole (Agrenox). These drugs are expensive and are indicated for use in the acute period of TIA or after an ischemic stroke.
Side effects of the drug Aspecard
from the gastrointestinal tract: abdominal pain, microhemorrhages, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, discomfort in the epigastric region, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach, gastric bleeding, liver dysfunction; from the blood system: thrombocytopenia, anemia; from the urinary system: impaired renal function; allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria; from the side of metabolism : hypoglycemia.
Contraindications
Aspecard is not used for hemorrhagic diathesis (telangiectasia, von Willebrand disease , hemophilia), ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract, dissecting aortic aneurysm, severe damage to the renal and hepatic systems, vitamin K deficiency, initial hypoprothrombinemia, nephrolithiasis , hyperuricemia, thrombocytopenic purpura .
Aspecard is not used during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or in pediatrics (up to 14 years).
Special instructions for the use of the drug Aspecard
Aspecard is prescribed with caution and subject to constant medical supervision to patients with asthma, with simultaneous therapy with anticoagulants (coumarin or heparin derivatives), with drug allergies and a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers, with kidney diseases, severe liver dysfunction. Aspecard can provoke the development of asthma in patients with allergic diseases (hay fever, allergic rhinosinusitis, laryngitis, tracheobronchitis), as well as in the presence of chronic respiratory tract infections, with increased sensitivity to NSAIDs. When carrying out long-term therapy or using the drug in high doses, medical supervision and regular monitoring of blood clotting time, determination of the number of platelets, urea levels in the blood and urine, and stool analysis for occult blood are required. With prolonged uncontrolled use of analgesics, especially when combining several drugs, Aspecard can cause serious impairment of renal function, including nephropathy. You should inform your doctor about the use of Aspecard before surgery or dental surgery. In children and adolescents with fever of infectious-inflammatory origin, infectious-allergic myocarditis, pain syndrome of mild and moderate intensity, acetylsalicylic acid should be used under medical supervision for no more than 2 weeks.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The main active ingredient is acetylsalicylic acid . Aspecard has a pronounced antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effect, which is achieved through inhibition of cyclooxygenases 1,2. COX1 and COX2 regulate the production of prostaglandins , which are responsible for the formation of edema and pain. A decrease in the level of prostaglandins in the thermoregulation center is manifested by increased sweating and dilation of skin vessels, which leads to a decrease in body temperature.
The analgesic effect is achieved by both peripheral and central action of the drug.
Aspecard reduces adhesion and aggregation of platelets , suppresses the production of thromboxane in them, which leads to a decrease in thrombus formation. The antiplatelet effect after a single dose of the drug lasts a week (more pronounced in men than in women). When taking the drug, the risk of developing myocardial infarction with concomitant unstable angina , and mortality is reduced. Aspecard is used for primary and secondary prevention of myocardial infarction. A daily dosage of 6 grams increases prothrombin time , suppresses the production of prothrombin in the liver, enhances the fibrinolytic activity of plasma, stimulates the excretion of uric acid by disrupting its reabsorption in the tubules of the renal system.
Drug interactions Aspecard
Aspecard enhances the effect of anticoagulants, NSAIDs and antirheumatic drugs, oral hypoglycemic drugs (sulfonylurea derivatives), methotrexate, triiodothyronine. When used with GCS and ethanol, the likelihood of an ulcerogenic effect of the drug and the risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding increases. Aspecard increases the concentration of digoxin, barbiturates and lithium salts in the blood plasma. The drug weakens the effect of diuretics (spironolactone, furosemide), uricosurics (sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, etamide), antihypertensive drugs (captopril, atenolol, propranolol). It is not recommended to use together with antacid drugs.
Indications for use
Aspecard is used for rheumatoid arthritis , pericarditis , rheumatism , infectious-allergic myocarditis . Prescribed for the relief of pain ( lumbago , neuralgia , migraine , arthralgia, thoracic radicular syndrome, algodismenorrhea ), febrile syndrome.
As an antiplatelet agent, it is used for unstable angina, silent myocardial ischemia, stent installation, aortoarteritis , balloon coronary angioplasty, heart valve replacement, atrial fibrillation, pulmonary infarction , mitral valve prolapse , acute thrombophlebitis , recurrent pulmonary embolism, 's syndrome , Kawasaki disease , Takayasu .
In allergology and immunology, it is used in increasing dosages in patients with the “aspirin” triad and “aspirin” asthma.
Overdose of the drug Aspecard, symptoms and treatment
Mild intoxication may cause nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, tinnitus, dizziness, headache, decreased visual acuity and hearing (especially in children and elderly patients). With a significant overdose, incoherent thinking, confusion, drowsiness, collapse, tremor, shortness of breath, an attack of suffocation, severe dehydration of the body (decrease in the buffer capacity of tissue fluid), hyperthermia, coma, alkaline reaction of urine, impaired core function (first respiratory alkalosis, then metabolic alkalosis) are noted. acidosis), carbohydrate metabolism disorders (decreased blood glucose levels). The lethal dose of acetylsalicylic acid for adults is more than 10 g, for children - 3 g. Depending on the state of the core and electrolyte balance, infusion solutions of sodium bicarbonate, sodium citrate or sodium lactate are administered.
Side effects
Taking Aspecard may be accompanied by NSAID gastropathy, dizziness, tinnitus, leukopenia , thrombocytopenia , Reye's syndrome , bronchospasm , urticaria, aspirin-induced asthma, anemia, eosinophilic rhinitis, hyperplastic sinusitis.
Long-term use of the drug in large dosages leads to the development of prerenal azotemia, interstitial nephritis , nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis , aseptic meningitis , and acute renal failure.
There is an increase in the level of aminotransferases .
Interaction
Aspecard reduces renal clearance, toxicity, and effectiveness of methotrexate , NSAIDs, reserpine, thrombolytics, sulfonamides , indirect anticoagulants, heparin, and oral hypoglycemic drugs.
The drug reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive, diuretic (furosemide, spironolactone), uricouric (sulfinpyrazone, benzbromarone) drugs.
Aspecard increases the level of lithium salts, barbiturates , digoxin in the blood.
Myelotoxic drugs increase the hematotoxicity of the drug.
Overdose
Salicylic syndrome, convulsions, stupor, coma , severe dehydration, non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema , shock, and renal failure are noted.
Treatment: taking activated carbon, laxatives, provoking vomiting, alkalizing urine, inducing diuresis , restoring blood volume. Hemodialysis may be used.
For pulmonary edema, artificial ventilation of the lungs with an oxygen mixture is recommended; for cerebral edema, osmotic diuresis and pulmonary hyperventilation .
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Persantine
Aegitromb
Plavix
Coplavix
Chime
Cardiomagnyl
Polocard
Thrombo ACC
Brilinta
Magnicor
Plagril
Dipyridamole
Clopidogrel
Lopirel
Sylt
CardiASK
Aspirin Cardio
Acecardole
Aspinat
Aspicor
Analogs are the following drugs: Akard , Anopyrin , Aspenorm , Aspirin Cardio , Acecardin , Godasal , Cardisave , Lospirin , Polocard , Reocard , Thrombo Ass , Trombogard , Ecorin .