Basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) is the most common type of skin cancer. It grows from epidermal cells called keratinocytes, which are located near the basal layer of the dermis. The tumor grows extremely slowly and practically does not metastasize, which is why it is called semi-malignant. However, basal cell carcinoma is characterized by infiltrative growth, so it can penetrate into the underlying tissue. With severe destruction and persistent relapses, basal cell skin cancer metastasizes and can lead to the death of the patient.
- Causes of malignant skin tumors
- Types of basal cell skin cancer
- Skin Cancer Symptoms
- Methods for diagnosing basal cell tumors of the skin
- Treatment options for basal cell skin cancer
- Possibility of recurrence of basal cell carcinoma
- Prognosis and prevention of basal cell carcinoma
- Related operations and techniques
Typically, basal cell carcinoma occurs in people with fair skin on areas of the body exposed to sunlight (face and hands).
In the head and face area, basalioma is usually localized in natural folds:
- Wings of the nose.
- Nasolabial folds.
- Lips and corners of the mouth.
- Corners of the eyes.
Causes of malignant skin tumors
The development of basal cell carcinoma can be triggered by the following factors:
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation - tanning under the influence of solar radiation or a solarium.
- Exposure to ionizing radiation - a history of radiation therapy courses, work with open sources of radiation, etc.
- Immunodeficiencies, both primary and secondary.
- Chronic traumatic injury to the skin, such as chafing from uncomfortable clothing.
- Exposure to carcinogenic factors of a chemical nature - work in hazardous production conditions, contact with household chemicals.
In addition, there is a genetic predisposition - basal cell nevus syndrome or Gorlin syndrome. It is characterized by the formation of multiple foci of basal cell carcinoma in young people in combination with endocrine pathology, mental disorders and skeletal lesions.
At the moment, there are two most common forms: superficial and nodular
Superficial (newly identified) BCC:
- most often develops on the skin of the trunk and limbs;
- less common: head and neck;
- in younger patients, with a predominance of women.
Important!
The main development factor is genetic - this is a hereditary mutation that is transmitted to descendants or arises in connection with environmental or other adverse effects of the external environment. Nodular form (first identified) of BCC:
- most often develops on the scalp
- in elderly and senile patients
Types of basal cell skin cancer
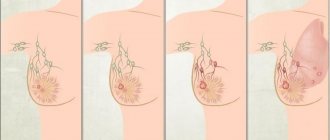
- Nodular-ulcerative form of skin cancer. The onset of the disease is characterized by the appearance of dense areas on the skin that have clear boundaries (nodules). New growths may have a gray, pinkish or yellowish color. Gradually, the skin over them becomes thin and acquires a pearlescent hue. The nodules merge with each other and form a plaque with a depression inside. Over time, an ulcer covered with a crust forms in the center of this plaque. It spreads to the sides and deep into the plaque, as a result the latter becomes like a crater. The bottom of the ulcer is uneven, covered with scabs and crusts, the edges are very dense, almost like cartilage tissue. The process lasts several months. If basalioma is not removed, it will grow into the underlying tissue, affecting the subcutaneous tissue, muscles and even bones.
- Large nodular basalioma develops from a single node. It gradually increases in size and becomes rounded. Its diameter can exceed 3 cm. The surface of the node is usually smooth, but can be covered with scales. The color of the tumor may not differ from healthy skin, but may acquire a pinkish tint. An ulcer forms in the center of the node, from which ichor oozes.
- The perforating form of skin cancer is characterized by initially infiltrative growth. The tumor grows inside the tissue, has no clear boundaries, and over time an ulcer appears on its surface.
- The warty form of cancer looks like papillomas with keratinizations tightly adjacent to them.
- The superficial form of basal cell carcinoma begins with the formation of a pale pink spot. At first it does not exceed 5 mm, then it begins to peel off and acquire clear contours. After some time, its edges thicken and nodules form on them, which then merge into a roller. The center of the formation sinks and becomes dark pink or brown. The tumor gradually increases in size and can sometimes grow into the underlying tissue.
- The scleroderma-like form of basal cell skin cancer begins with the formation of an inconspicuous yellowish-whitish plaque. Periodically, erosions form along its edges, covered with a thin crust. These crusts are easily separated, revealing a reddish inflammation underneath. Gradually, cysts form in the tumor, in which crystals of calcium salts can be found.
- The fibrous form of skin basalioma begins with the formation of a dense nodule, which gradually grows, flattens and turns into a plaque. Blood vessels are visible through the layer of epidermis.
- Cylinderoma, or turban skin tumor, is most often localized on the scalp. It consists of hemispherical nodes of a violet-red color; spider veins can be visible in them. The size of one node in diameter can reach 10 cm. Usually there are several such nodes.
During a general examination of the patient, an oncodermatologist
EVERYONE is watching! Skin on the torso, face, neck, limbs, mucous membranes, scalp.
- Dermatoscope.
- SIAscopically.
- Cytologically.
- Histologically!!
Biopsy of a skin tumor
A mandatory diagnostic step for skin tumors is morphological verification of the process; for this, a biopsy
. The oncologist takes cells or tissues from the site of the tumor and submits them for examination to pathologists, who form their conclusion.
The morphological report contains information about the tumor:
- localization of the process (where the tumor is located);
- diameter (what size is the tumor);
- growth type;
- characteristics of the resection margin (the tumor was completely removed or not).
The oncologist makes a final diagnosis and forms a treatment plan only after receiving the results of the biopsy.
Skin Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma are extremely variable and depend on the form of the disease. The tumor manifests itself with the following manifestations:
- Shiny pink nodules with visible blood vessels.
- Papules or nodules covered with ulcers.
- Plaques. Dense, scar-like.
- Psoriasis-like plaques.
Stages of basal cell skin tumor:
- Stage 1 - the tumor is no more than 2 cm in greatest dimension.
- Stage 2 - the size of the tumor exceeds 2 cm, but there is no germination (invasion) into the underlying tissue.
- Stage 3 - Skin cancer has grown into underlying structures, such as muscles or bones. Or a less invasive tumor, but with regional metastases.
- Stage 4 - the tumor gives distant metastases.
2.What does basal cell carcinoma look like?
Basal cell carcinoma usually begins as a small, dome-shaped lump, often with small superficial blood vessels. The skin in this area may look shiny and translucent, as if pearlescent. Some basal carcinomas contain the pigment melanin, and because of this they appear dark rather than shiny. Because of these variations, it can be difficult to distinguish basal cell carcinoma from benign skin lesions without a biopsy.
Basal cell skin cancer grows slowly. It may take months or even years before it reaches a serious stage. Although basal cell carcinoma metastasizes to other organs and tissues very rarely, skin changes can damage or disfigure the eye, ear, or nose if the tumor grows nearby.
Visit our Oncology page
Methods for diagnosing basal cell tumors of the skin
Diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma involves a thorough examination of the skin. The Photofinder digital dermoscopic system allows you to perform a more detailed examination. Its effectiveness is tens of times greater than that of standard dermatoscopy, since it records all nevi and skin tumors larger than 0.9 mm and allows you to monitor the dynamics of their changes.
To confirm the diagnosis, a laboratory histological examination of a piece of tumor tissue is performed. This piece is obtained in one of the following ways:
- Incisional biopsy. Using a scalpel, a small marginal fragment of the neoplasm is excised within visually unchanged skin. This method is indicated for large tumor sizes.
- Excisional biopsy. The entire tumor is excised within healthy tissue. The resulting wound is sutured with cosmetic sutures. Such a study is possible for tumor sizes up to 1 cm on the body and limbs and less than 0.5 cm on the face.
A biopsy is not always possible, especially if the skin cancer is located on the face. In this case, a cytological examination of scrapings or impression smears from the tumor is indicated. If the surface of the tumor is not changed, a puncture is performed with aspiration of the tumor tissue.
Additional diagnostic methods are used to examine lymph nodes for the presence of metastases. For this purpose, ultrasound, CT or MRI is used. If there is a suspicion of damage to the lymph nodes, they are punctured and the resulting material is subjected to microscopic examination.
Diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma
The diagnosis is made based on histological examination
. Differential diagnosis of basalioma is carried out with:
- molluscum contagiosum,
- hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands,
- amelanoma
, _ - intradermal melanocytic nevus,
- Merkel cell carcinoma,
- trichoepithelioma,
- squamous cell carcinoma
- keratoacanthoma,
- inflammatory dermatoses (psoriasis and eczema),
- actinic keratosis,
- Bowen's disease
- morphea (focal scleroderma),
- dermatofibrosarcoma,
- scar.
Treatment options for basal cell skin cancer
The choice of treatment options for basal cell carcinoma is determined by the location of the tumor and the stage of the disease. Preference is given to surgical removal methods. If their use is impossible, radiation therapy is performed. Additional treatment methods can also be used, for example, cryodestruction, local chemotherapy, etc.
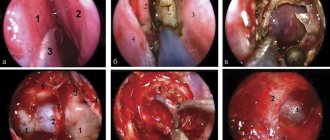
Surgery
Surgical treatment is more preferable because it allows you to control the radicality of the operation by examining the cutting edges for the presence of malignant cells.
- The classic method is excision of the tumor with a scalpel within healthy tissue. The wound is closed with cosmetic stitches, and the tumor is sent to the laboratory. If there are no tumor cells at the cutting edges, it is considered that the tumor has been radically removed and no other treatment methods are required. Surgical excision cannot be performed when basal cell carcinoma is localized in the folds of the face, since a pronounced defect will remain.
- The second option for the operation is curettage followed by electrocoagulation. First, the basal cell carcinoma is removed using a curette (a surgical instrument with a tip in the form of a ring with a sharp edge). Then the wound is cauterized with an electrocoagulator. If there is a high risk of relapse, the procedure is repeated to destroy any malignant cells remaining in the wound. A whitish scar remains at the site of removal.
Radiation therapy for cancer
Radiation therapy gives fairly good results in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Its effectiveness reaches 90%. Treatment is carried out in courses over several weeks. Sometimes the protocol involves daily radiation therapy sessions.
Indications:
- Senile age of the patient.
- High risks of surgical intervention.
- Impossibility of surgery due to the “inconvenient” location of the tumor - nose, ears, eyelids.
- The patient's serious condition.
- As part of combined treatment for high risks of relapse after surgical excision.
Chemotherapy
Treatment of superficial forms of cancer is possible with the help of local chemotherapy drugs. For this, an ointment based on 5-fluorouracil or other cytostatics is used. If regional metastases are present, they are surgically removed. As a rule, the operation involves excision of subcutaneous fat in a volume corresponding to the nature of the lesion.
Other methods
In addition, alternative methods of treating basal cell carcinoma are used, which provide good clinical and aesthetic results. Photodynamic therapy is most effective in this regard. It is performed as follows: a special drug is applied to the surface of the basal cell carcinoma - a photosensitizer, which accumulates in malignant cells in increased quantities. After this, the tumor is exposed to laser radiation of a given wavelength. This leads to the activation of the photosensitizer and the launch of a cascade of chemical reactions that destroy tumor cells. Immediately after irradiation, swelling develops at the site of exposure, and within 24 hours the tissue begins to become necrotic.
After a few days, a dense scab forms at the site of the tumor, fused to the underlying tissues. As it heals, the scab falls off and an epithelialized wound remains in its place. In general, the cosmetic result is satisfactory. Photodynamic therapy in our clinic is used to treat superficial forms of basal cell cancer located in the face and hands.
Other alternative treatments are less effective, but may be used under certain conditions:
- Cryodestruction is the destruction of a tumor using low temperatures. The cooling agent is applied to the skin by application or applied using an aerosol. This method is rarely used because it gives worse treatment results. However, its use may be justified in patients suffering from bleeding disorders (propensity to bleed).
- Laser surgery has not received official approval for the treatment of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, so it is used in cases where other methods have exhausted their possibilities. The essence of the treatment is layer-by-layer evaporation of the tumor using heating under the influence of laser radiation.
Combination treatment of basal cell carcinoma
Combined treatment is carried out for large invasive tumors that cannot be removed to the required extent, as well as in the presence of metastases. Surgical excision of the tumor is used, followed by irradiation of its location (for locally advanced cancers), or surgery followed by systemic chemotherapy.
Systemic drug treatment for disseminated forms of basal cell carcinoma
Invasive and metastatic forms of basal cell carcinoma require systemic therapy. Targeted drugs are indicated that block the molecular processes that ensure the functioning of the tumor.
In 85% of basal cell carcinoma cases, there are mutations in genes encoding proteins of the Hedgehog signaling cascade, which is of great importance during embryonic development. In particular, it affects the specialization of cells in the process of organ formation. In adults, its work is very limited.
Normally, the signaling pathway is triggered by the action of the Sonic Hedgehog SHH protein, which is named after the video game character Sonic the Hedgehog (in a study on fruit flies, turning off SHH resulted in the embryos becoming like spiky balls). But with basalioma, the process began without it, with the help of another protein called SMO.
The drug Vismodegib suppresses the action of SMO, thereby blocking the entire uncontrolled Hedgehog cascade. This therapy is indicated for locally advanced and metastatic forms of basal cell carcinoma, as well as in cases where other forms of treatment (surgery or radiation therapy) are impossible or impractical.
Reviews about the treatment of basal cell carcinoma
Maria Alexandrovna, 57 years old “ Around the end of the summer of 2022, a reddish spot the size of a pea, with jagged edges, appeared on my right cheek. Over time, the spot began to increase in size and peel off. This alarmed me and I went to the clinic to see a surgeon, who examined me and did not give me a clear answer that it was he who did not give me. He prescribed me ointments, but they had no effect. As time passed, the spot became inflamed and turned into a weeping wound, which began to get worse. I was tired of all this and on the Internet I came across the LazerVita clinic and made an appointment with a surgeon. On the day of the appointment, the surgeon Gafarov Sarkhan Vidadievich saw me, examined the wound, he immediately did not like it and took cytology. After explaining everything to me and reassuring me, he made an appointment with oncologist Violetta Aleksandrovna Purtskhvanidze in 3 days, by which time the cytology will be ready. He prescribed me to treat with antiseptic solutions and antibiotics for now. Three days later, I came to see Violetta Alexandrovna. After examining the wound, she diagnosed Basal cell carcinoma, which was confirmed cytologically. She explained my diagnosis to me in detail, reassured me, and explained to me all the treatment options. Then, on the same day, Dr. Sarkhan Vidadievich performed an operation on me: laser removal. The operation went without complications, everything healed perfectly. I want to express my gratitude to the entire LazerVit team, and especially to doctor oncologist V.A. Purtskhvanidze. and doctor surgeon S.V. Gafarov Thank you very much!
» All reviews about the treatment of basal cell carcinoma and other diseases.
Prognosis and prevention of basal cell carcinoma
The extremely slow growth of the tumor and the low probability of metastasis of basal cell carcinoma give a good prognosis in terms of complete recovery. Metastatic forms of basal cell carcinoma are extremely rare, so it is difficult to talk about accurate survival prognosis here. According to world literature, the average life expectancy of such patients is 4.5 years.
Prevention of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma involves regular protective measures against the aggressive effects of carcinogenic factors:
- Do not expose your skin to direct sunlight. At a minimum, use creams with sunscreen properties. Do not overuse tanning or visiting a solarium.
- When working with chemical irritants in hazardous production conditions, use personal protective equipment - clothing, gloves, masks.
- Do not neglect protective equipment when working with household chemicals.
In order to detect skin cancer in time and carry out treatment with minimal losses, it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations using dermatoscopy.
At Euroonko, this procedure is carried out using special German PhotoFinder technology. It involves drawing up a map of moles and neoplasms of the entire body, followed by tracking the dynamics of their changes. The resolution of the optical system allows visualization of skin tumors measuring only 0.9 mm.
When basal cell carcinoma is detected, we use treatment methods recommended by modern protocols. They give good clinical and cosmetic results. If you have any questions, please contact our specialists.
| Price : | |
| Oncologist consultation | 5100 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy | 4600 rub. |
| Histological examination | 5200 rub. |
| PDT without contrast cost | 39600 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Causes of degeneration of basal keranocytes
The tumor received the name “basal cell carcinoma” because of the similarity of its cells to the cells of the basal layer of the skin - the lowest layer of the epidermis. It is not surprising, since basalioma develops from keratinocytes just near the basal layer.
Epidermal stem cells, which exist in the body throughout its life, contribute to the constant renewal of the skin. A genetic malfunction in the cell division mechanism leads to the appearance of neoplasms. Damage to a cell's DNA can be caused by a number of reasons.
The main and most common cause of basal cell carcinoma is exposure of exposed skin to direct sunlight or UV radiation in a solarium. It is no coincidence that the favorite place for basal cell carcinoma is the human face, which is exposed to UV radiation more often and longer.