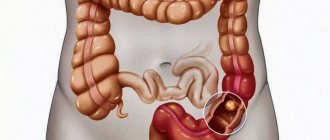
Rectal cancer has an ICD 10 code - C18. One type of rectal cancer is adenocarcinoma. The tumor develops from epithelial cells and is located in the final part of the digestive tract. Most often, this disease is diagnosed in people of the older age group. The exact causes of colorectal cancer have not been established. The risk of developing pathology increases significantly after reaching the age of fifty.
The advantages of treating patients for a malignant tumor of the rectum at the Yusupov Hospital are:
- Timely and accurate diagnosis;
- Examination using the latest techniques;
- Gentle, effective surgical interventions;
- Application of the latest chemotherapy drugs and radiation techniques using modern equipment;
- Attentive care and monitoring of each patient.
The comfort of the rooms at the oncology clinic corresponds to the European level. Patients are provided with individual personal hygiene products and dietary nutrition. All complex cases of cancer are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council, in which professors and doctors of the highest category take part. Leading oncologists in Moscow draw up an individual treatment plan for each patient suffering from rectal cancer. If a patient is diagnosed with stage 4 rectal cancer with metastases, he is provided with palliative medical care.
Symptoms of adenocarcinoma and sarcoma of the rectum
Most often, patients suffering from a malignant tumor of the rectum present the following complaints:
- Lack of appetite;
- Unreasonable increases in body temperature;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- Decrease in body weight over a short period of time;
- Frequent bloating;
- Pain and discomfort during bowel movements;
- Unexplained constipation and diarrhea;
- The presence of blood and large amounts of mucus in the stool.
Patients suffering from rectal carcinoma are concerned about general weakness. Pallor of the skin is noted.
Rectal sarcoma occurs in approximately 1% of rectal cancer cases. They can come from connective tissue elements, lymphatic tissue, and the endothelium of blood vessels. Based on various elements of the intestinal wall and located under the epithelial cover, sarcoma in the initial period of growth consists of nodes of various sizes, covered with an intact mucous membrane. They are painless on palpation and do not fall off when pressed.
Located in the thickness of the rectal wall, simple sarcomas do not cause discomfort to patients for a long time. Symptoms of rectal sarcomas depend on the location, growth pattern and histological structure of the tumor. The main symptoms of sarcomas are:
- Moderate pain;
- Pathological discharge from the rectum (just bloody discharge or mucus with blood);
- Defecation disorder.
These are signs that characterize rectal cancer.
Among women
Most often, colon cancer occurs in women. Cancer usually appears after the age of forty, as the body prepares for menopause. Very often, cancer arises from the degeneration of polyps. Hereditary predisposition and poor nutrition play a very important role here.
The main symptoms appear after two years. Usually these are abdominal pain, problems with stool, and bloating. When metastasis occurs, the lymph nodes, vagina, and other pelvic organs are affected. In the later stages, the pain intensifies, intestinal incontinence occurs, the patient vomits, the composition of his urine changes, the kidneys are affected, urogenital fistulas occur, and the menstrual cycle may change.
Diagnosis of rectal adenocarcinoma
How to identify colorectal cancer? The diagnosis of rectal cancer at the Yusupov Hospital is made based on the results of a comprehensive examination of patients suffering from rectal malignant neoplasms. In the case of rectal adenocarcinoma, treatment begins with a detailed diagnosis. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture, each patient uses a set of various diagnostic techniques:
- Blood test - allows you to identify characteristic hematological and biochemical changes, determine the concentration of tumor markers characteristic of colon cancer;
- Testing stool for blood—helps doctors identify early signs of occult bleeding;
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic study aimed at visualizing changes in the surface of the mucous membrane of the final sections of the intestine;
- Colonoscopy is the most informative examination of the intestines, which allows you to examine the rectum, sigmoid and colon;
- Ultrasound examination - with the help of this non-invasive examination, doctors determine some features of tumor growth, assess the condition of the abdominal organs (depending on the characteristics of the clinical course of the disease, they perform a transabdominal or endorectal ultrasound);
- Biopsy - allows you to confirm the diagnosis of colon adenocarcinoma (performed during an endoscopic examination of the intestine or during surgery).
Computer, magnetic resonance, positron emission computed tomography, scintigraphy are used to clarify the structural features and location of the tumor relative to other organs and tissues, and to identify signs of cancer metastasis. Tumor markers for colon and rectal cancer allow one to suspect a malignant neoplasm before the first symptoms of cancer appear.
What does colon cancer look like?
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital collect material from a rectal tumor during an endoscopic examination or surgery and send it to the histology laboratory. Laboratory assistants determine the histological type of the tumor based on what colorectal cancer looks like.
Rectal adenocarcinoma consists of atypical cells that originate from glandular epithelial tissue and are formed into tubular, papillary and other structures. The cellular structure can have varying degrees of differentiation: highly differentiated neoplasms have cytological signs of maternal epithelial tissue, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas only vaguely resemble the original material. They are highly aggressive, grow and spread faster.
Mucous adenocarcinoma is a group of cells that are surrounded by mucus. Tumors of the mucous type can be poorly differentiated and highly differentiated. Mucus accumulates in tumor structures in the form of “lakes” of varying sizes
Signet ring cell carcinoma gets its name due to the shape of the cells, which, due to an excess of mucus in them and the displacement of nuclei towards the membranes, take on the appearance of a ring. The mucous substance that occupies the space of cells is a specific protein mucin. Signet ring cell tumors of the rectum are quite aggressive.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum consists of atypical cells. They belong to the squamous intestinal epithelium. Pathological lesions contain intercellular bridges and keratin. Rectal squamous cell tumors can be keratinizing or non-keratinizing.
Glandular squamous adenocarcinoma is a rare type of rectal cancer. Such neoplasms are represented by adenocarcinoma, in combination with squamous cell carcinoma. Under a microscope, histologists see small fragments of squamous cell transformation.
Undifferentiated rectal tumors consist of atypical cells of epithelial tissue that do not form glandular structures and do not produce mucus. These cells represent different cytological structures. They form sheets or cords that are separated by a scant stroma of connective tissue.
Scirrhus is a cancerous tumor in which the connective tissue predominates over the stroma. Cytological structures in scirra are cubic cells collected in strands or small cells. Sometimes there are neoplasms in the rectum that do not fit into any histological type. In this case, oncologists talk about unclassified rectal cancer.
Neuroendocrine tumors of the rectum originate from cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system. They have a well-developed fibrous stroma and are histologically different from adenocarcinomas.
The difference between hemorrhoids and rectal cancer
Hemorrhoids and rectal cancer are proctological diseases that occur most often. How to distinguish hemorrhoids from colorectal cancer? You can independently determine the nature of the disease by the symptoms, but it is best to seek advice from the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital. Oncologists will conduct a comprehensive examination and differential diagnosis.
Hemorrhoids and rectal cancer have very similar symptoms and are well camouflaged. For a long period of time they do not manifest themselves in any way. A characteristic difference is the color of the blood. With hemorrhoidal bleeding, the blood is bright scarlet in color and practically does not mix with the feces. In cases of colorectal cancer, dark blood appears during bowel movements. It is evenly distributed in the feces.
Cancer and hemorrhoids are manifested by characteristic discharge. With pathological inflammation of hemorrhoidal veins, the mucus is transparent and does not have a pungent odor. A sign of rectal cancer is the presence of a foul-smelling, purulent substance in the stool, which appears not only during bowel movements.
With hemorrhoids, stool does not change shape. The growth of a malignant tumor, the gradual narrowing of the lumen of the anus contributes to the formation of ribbon-like feces. With hemorrhoids, patients deliberately refuse to eat because of pain during constipation or bowel movements, while they experience hunger and lethargy. With rectal cancer, the patient does not complain of poor appetite, but rapidly loses body weight.
Benign tumors of the rectum
Tubular adenoma of the rectum is a benign neoplasm. The tumor develops from the glandular cells of the intestine. This type of adenoma is small in size with a smooth, even surface. A large adenoma has a lobular structure.
There are 3 degrees of dysplasia for tubular intestinal adenomas. Moderate dysplasia is characterized by thickening of the basal layer of the intestinal epithelium. The cell nucleus contains little chromatin, and the number of mitoses (cell division) is increased. Tubular adenoma of the colon with grade 2 dysplasia has the following features: the epithelial layer is blurred, pronounced proliferation is observed in the growth zone of cells. The elements themselves differ in shape and size. The pronounced degree of dysplasia is the terminal stage. The cells are characterized by an increased chromatin content and a variety of shapes. The number of changed elements varies from 0.5 to 1% of the epithelial tissue.
Villous tumor of the rectum is a benign neoplasm. It is a spongy pinkish-red formation on a thick stalk or wide base, clearly demarcated from unchanged surrounding tissues. The surface is covered with thin fringed villi, which consist of connective tissue fibers covered with a layer of epithelial cells. The stroma of a villous tumor of the colon is represented by connective tissue, which is penetrated by a large number of thin-walled blood vessels.
Reasons for the development of pathology
- Age over 50 years.
- Overweight.
- Lack of vitamin D in the body.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Wrong diet: excess fried foods and red meat, low consumption of vegetables and fruits.
- Bad habits (alcoholism, smoking).
- Bad heredity (accounts for about 30% of all cases).
Adenocarcinomas often develop against the background of other proctological diseases. Most often - with Crohn's disease, colon polyps and ulcerative colitis.
Treatment of rectal adenocarcinoma
With rectal adenocarcinoma, metastases appear quite early. For this reason, after establishing an accurate diagnosis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital immediately begin treatment. The earlier the disease is detected, the better the prognosis for the patient. Differentiated rectal adenocarcinoma is more treatable. The consequences of undifferentiated cancer are more severe. Each patient with this diagnosis in the oncology clinic is provided with an individual approach and high-quality medical care.
Currently, preference is given to combined treatment of rectal adenocarcinoma. During the operation, surgeons eliminate the main focus of tumor growth. Using other treatment methods, surviving cancer cells are destroyed.
Depending on the extent of the tumor process, the volume of surgical intervention is determined. Extirpation and resection of the rectum are complemented by excision of regional lymph nodes and soft tissues. When performing such operations, oncological surgeons follow all the principles of ablastics and antiblastics. This can significantly reduce the risk of cancer cells spreading throughout the body. In some patients, surgery is performed in several stages. Patients who have undergone a colostomy for rectal cancer are provided with all the necessary materials. Medical staff provides hygienic care for her.
Radiation therapy techniques used in the treatment of rectal cancer in some cases can suppress the progression of the tumor process. Radiotherapy sessions are performed for weakened patients who have contraindications to surgical treatment or have been diagnosed with an inoperable tumor.
The use of modern cytotoxic drugs for chemotherapy makes it possible to destroy cancer cells in all tissues of the patient’s body. The risk of developing relapses of the pathological process is reduced and the prognosis for patients with rectal tumors is improved. You can get a consultation with an oncologist or proctologist by making an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Treatment of intestinal cancer in the department of thoracoabdominal surgery and oncology
Treatment in the department is carried out according to the compulsory medical insurance, voluntary medical insurance, high medical insurance programs, as well as on a paid basis. Our department has highly qualified surgeons, modern equipment, comfortable hospital conditions and attentive staff. Read how to get treatment at the Department of Thoracoabdominal Surgery and Oncology of the Russian Scientific Center for Surgery.
To schedule a consultation, call:
+7 (499) 248 13 91 +7 (903) 728 24 52 +7 (499) 248 15 55
Submit a request for a consultation by filling out the form on our website and attaching the necessary documents.