Dextrose is used in medicine and industry for the manufacture of food products and sports/dietary nutrition, and at home to soften the taste of moonshine. The product has many beneficial properties, including improving the taste of dishes. It invigorates and adds energy, and is therefore recommended for people exposed to regular physical activity.
Let's consider what dextrose is, indications/contraindications for use, benefits and harms, who should refrain from using it, how much to add to moonshine to soften the taste?
Dextrose
What is dextrose
Dextrose (Dextrosum genus Dextrosi) is a monohydrate that has the same structure as glucose. This carbohydrate is the main “fast” source of energy in the body. In the food industry it is used as a taste regulator and food additive (sweet substitute for losing weight). In the confectionery industry it is used to make waffles, soft candies, cakes, etc. Dextrose is often used by athletes and people who need to enhance brain activity, as well as those who have an insufficiently balanced diet.
In medicine, dextrose (glucose monohydrate) is used for intravenous infusions to restore metabolism and normalize blood sugar levels. In pharmaceuticals, the substance is used for the manufacture of antibiotics and the production of vitamin C, and in the microbiological industry - as a nutrient medium for the cultivation of beneficial microorganisms.
Types of sugar:
- simple (contains 1 molecule, monosaccharide);
- complex (consists of several long molecular chains interconnected).
Dextrose is a simple one. It is made primarily from corn sugar/syrup. The substance is easily absorbed and enters the bloodstream, making it a quick source of energy for the body.
When to take:
- To improve the absorption of nutrients after exercise. Athletes add dextrose to their post-workout drink to restore energy and carbohydrate levels.
- When performing exercises that require endurance of the body. A small amount of dextrose strengthens the body, allowing you to achieve your goal.
- Lack of energy. Dextrose is necessary if active physical/mental stress is expected against the background of an unbalanced diet.
- Low blood sugar levels.
- Disturbed metabolism.
Dextrose in small quantities helps people with low energy. It improves mood, adds energy, activates the brain and cardiovascular system.
Who to accept
Dextrose helps absorb other molecules, such as amino acids. It is recommended in moderate quantities for every person who has no contraindications for use.
It is especially needed:
- athletes;
- workers in production;
- loaders;
- office workers (to stimulate the brain);
- people with medical indications for use.
Note! Even for preventive purposes, use the monosaccharide under the supervision of your doctor. Before use, take a urine and blood test.
Harmful effects of dextrose on the body
Dextrose itself is not a harmful, dangerous or toxic substance. If taken in moderate doses. At the same time, it can be noted that it is not at all necessary to replace regular sugar with dextrose. It does not contain vitamins, minerals, micro- and macronutrients. If dextrose is abused, it can lead to the development of various diseases and painful conditions, such as:
- obesity;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- indigestion;
- skin problems: various rashes, acne, premature aging;
- feeling tired, lethargic, wanting to sleep;
- increase in biological age;
- cellulite.
Properties and benefits of dextrose
During mental/physical stress, energy reserves (glycogen) are consumed and muscle fiber proteins are destroyed. Fats and proteins take several hours to be converted into clean energy, so athletes and people with increased mental activity need to consume dextrose about an hour before exercise. It is instantly absorbed and distributed throughout the body, restoring glycogen levels and adding energy.
pharmachologic effect
The monosaccharide is actively involved in redox and metabolic metabolic processes. Dextrose accelerates the removal of toxins from the liver and helps normalize water balance (against the background of excessive vomiting or diarrhea).
Penetrating into the body, dextrose is converted into glucose-6-phosphate, phosphorylated and completely absorbed by the body. The presence of even a small amount of dextrose in urine indicates a hidden progressive pathology.
Oral consumption of the powder, a monosaccharide dissolved in water, invigorates, stimulates thinking, and normalizes muscle activity.
Hypertonic essence 10% stabilizes blood pressure, myocardial contractility and liver functional activity. The solution improves vascular permeability and normalizes metabolism.
Isotonic essence 5% has a detoxifying and metabolism-restoring effect. It helps replenish energy reserves.
Benefits of Dextrose
The optimal amount of monosaccharide is responsible for the balance of substances necessary for the body, which improves overall well-being, improves mood and physical activity, as well as:
- stimulates energy tone,
- increases concentration;
- prevents diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system.
- stimulates brain activity;
- increases reaction speed.
Dextrose for daily use is useful for truck drivers. Their lifestyle, unfortunately, practically excludes a properly balanced diet, but their work requires increased attentiveness and speed of reaction.
In the food industry:
- increases the nutritional value of baby cereals and formulas;
- improves the taste of products, but does not change it;
- gives baked goods porosity and slows down the hardening;
- lowers the freezing point of ice cream, improving the structure of the finished dessert.
It is used for preservation, preparation of alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, flour products, yoghurts, dairy desserts, etc.
Glucose in ampoules, can I drink it?
Glucose can be taken orally, as its regular solution does not contain substances that can be harmful. The medicinal liquid tastes quite pleasant, reminiscent of ordinary sweet water.
You can drink glucose in ampoules if there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure or if a diabetic has exceeded the dosage of insulin. However, for these problems, it is wiser to drink strong, sweet tea.
In case of poisoning, glucose is often prescribed, but its oral use during intoxication can provoke additional vomiting.
Glucose and dextrose
Dextrose and glucose are components of regular sugar. Their difference is in optical isomers: L (glucose) and D (dextrose). The differences are minimal, due to the rotation of the polarization of light L to the left, and D to the right, similar to the specular reflection of an object.
L (glucose) is found predominantly in human blood. It is extracted in the laboratory from plant fruits in small quantities. D – found in many berries, vegetables, cereals, and in the form of starch. Easily obtained in the laboratory. It is this isomer that quickly spreads throughout the body, nourishing brain cells and muscle tissue.
Buildings made from bricks
Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of galactose and glucose. It tastes almost not sweet, and therefore the milk is not sweet either, although each glass contains about 2 spoons of lactose sugar (8-10 g). In the digestive tract, it breaks down into the original “building blocks” - galactose and lactose. And they are already absorbed into the blood. Disaccharides are not absorbed. If a person does not have the enzyme lactase, which breaks down this milk sugar, it begins to ferment in the intestines, causing flatulence (excessive gas formation) and diarrhea. This is lactose intolerance.
Sucrose is the most famous sugar. Even if this chemical name is unknown to you, you know it very well and consume it almost every day. This is the same “white death” that is sold in the form of sand or pieces of refined sugar and which is added to tea, coffee, porridge, and used in cooking. We simply call it “sugar.” This is a common name. The “ose” particle at the end of sucrose in the language of chemistry means that this substance belongs to sugars. Remember the names of other sugars: glucose, fructose... It is from these two “building blocks” that ordinary sugar consists, and it breaks down into them during digestion.
Question answer
Is it possible to completely give up sweets? Maltose is a less familiar disaccharide. It consists of two identical “bricks” of glucose. It got its name from barley malt (malt), which contains the most of it. Fans of real Scotch whiskey probably already think that this drink contains the most maltose, because Single malt whiskey is made only from this malt. In fact, maltose does not reach either the barrel or the bottle. A significant part of it disintegrates during fermentation, and the remainder goes to waste during distillation. But it’s in beer (it’s not distilled). And we consume the most maltose in beer and products with added malt (most often baked goods).
There are also polysaccharides - long chains of glucose “building blocks”, branched and tangled. This is starch, it is found in plants. Animal starch synthesized in the liver is called glycogen.
And if these “bricks” of glucose are connected in such a special way that our enzymes cannot separate (digest) them, then this is already fiber (cellulose) - dense dietary fiber. They make up the membranes of plant cells, which play a useful role in digestion. They trap some toxins and harmful substances, and without them we would suffer from severe constipation.
Table. Glycemic index and degree of sweetness of different sugars
| Name of sugar | Glycemic index (GI) | Sweetness |
| Maltose | 105 | 32,5 |
| Glucose | 100* | 74,3 |
| Sucrose (table sugar) | 65 | 100** |
| Lactose | 46 | 16 |
| Galactose | 23 | 32,1 |
| Fructose | 19 | 173 |
Note: * Glucose GI is taken as 100, all others are assessed in comparison with it
** The sweetness of sucrose is taken as 100, and the sweetness of other sugars is compared with this standard
Indications for use
Any person who has insufficient physical or mental activity can use dextrose in moderation.
For medicinal purposes it is prescribed for:
- liver diseases (up to atrophy and partial dysfunction of the organ);
- hypoglycemia;
- dehydration (dehydration due to vomiting or diarrhea);
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- shocked;
- collapse;
- general intoxication of the body.
Monohydrate has a general strengthening effect. It stimulates the absorption of nutrients and provides a flow of energy, helping the body recover faster.
Classic dextrose moonshine recipe
The monosaccharide dextrose is used in moonshine, observing the same proportions of ingredients as for sugar mash.
- 1 kg dextrose
- 4 liters of water
- 70 grams of pressed yeast or 20 grams of dry yeast
- The monosaccharide must be well dissolved in water and mixed in a clean container with yeast “fermented” in a separate container
- The container with the wort is closed and a water seal is installed
- The temperature inside the vessel must be maintained in the optimal range from 18˚C to 25˚C. If the temperature drops lower, the fermentation process will go slower; at a more severe temperature, the yeast will lose its activity and may die
- At the end of the fermentation process, begin distillation.
- After the first distillation, you can further purify the resulting raw alcohol with activated carbon by passing it through a carbon column; this is not necessary because during the second fractional distillation you will remove all unnecessary impurities
- Be sure to distill twice a second time, separating the head and tail fractions
- Dilute the finished moonshine to 40% alcohol content
- To soften moonshine, add 1–1.5 tablespoons of dextrose to it for every 7–8 liters of drink
Instructions for use
D-glucose for athletes is available in powder form. Packaging contains 1000-2000 g. An hour before training, dissolve 1 scoop of product or 50 g in a glass of 300-500 ml of warm milk/water. Have a drink.
To improve metabolism, drink ½ or 1/3 of a scoop of the drug, after dissolving it in 1 glass of water (daily).
Important! Please consult your doctor first about the possibility of preventive treatment with dextrose. Check the required dosage. Self-medication is unacceptable!
For therapeutic purposes, the following is prescribed intravenously (drip) to adults:
| % solution | Maximum feed rate, up to cap/min | Maximum 24 hour dose/ml, up to ml/min | Maximum 24 hour dose/ml |
| 5% | 150 | 7 | 2000 |
| 10% | 60 | 3 | 1000 |
| 20% | 40 | 2 | 500 |
| 40% | 30 | 1,5 | 250 |
Intravenous (stream) essences 5% and 10%, volume up to 50 ml:
| Dosage | Max. feed speed | Peculiarities | |
| For adults | 250-450 g at the rate of 4-6g/kg | 0.25-.5 g/kg/h. If metabolism deteriorates, 0.125-0.25 g/kg/hour. | If metabolism deteriorates, the daily norm is reduced to 200-300 g. |
| For children | Initially 6 g/kg/day. Further up to 15 g/kg/day. | 0.5 g/kg/h. For 5% essence 200 drops/min. | Body weight up to 10 kg – 100-165 ml/kg. Weight 10-40 kg 45-100 ml/kg/day. |
To maximize the absorption of monohydrate, administered in large quantities, insulin is additionally prescribed at a dosage of 4-5 g of D-glucose/1 unit. insulin.
Insulin-dependent patients receiving the drug require regular laboratory monitoring of urine and blood. Monohydrate can only be used for medical reasons.
Sources
The monosaccharide is found in animal muscle glycogen, starch, berries and fruits. A person receives 50% of the energy needed by the body from glycogen (deposited in the liver and muscle tissue) and the consumption of glucose-containing foods.
The main natural source of the compound is honey (80%), it also contains another healthy carbohydrate - fructose.
Nutritionists recommend stimulating the body to extract saccharides from food, avoiding refined sugar.
Table No. 1 “What contains glucose”
| Product name | Monosaccharide content per 100 grams, grams |
| Rafinated sugar | 99,7 |
| Bee Honey | 80,1 |
| Marmalade | 79,2 |
| Gingerbread | 77,6 |
| Pasta | 70,5 |
| Sweet straw | 69,1 |
| Dates | 69,0 |
| Pearl barley | 66,8 |
| Dried apricots | 66,1 |
| Raisin | 65,6 |
| Apple jam | 65,0 |
| Chocolate | 63,2 |
| Rice | 62,2 |
| Oatmeal | 61,7 |
| Corn | 61,3 |
| Buckwheat | 60,3 |
| White bread | 52,8 |
| Rye bread | 44,2 |
| Ice cream | 21,2 |
| Potato | 8,0 |
| Apples | 7,8 |
| Grape | 7,7 |
| Beet | 6,6 |
| Carrot | 5,6 |
| Cherry | 5,4 |
| Cherries | 5,4 |
| Milk | 4,4 |
| Gooseberry | 4,3 |
| Pumpkin | 4,1 |
| Legumes | 4,1 |
| Cabbage | 4,0 |
| Raspberries | 3,8 |
| Tomatoes | 3,3 |
| Cottage cheese | 3,2 |
| Sour cream | 3,0 |
| Plums | 3,0 |
| Liver | 2,7 |
| Strawberry | 2,6 |
| Cranberry | 2,4 |
| Watermelon | 2,3 |
| Oranges | 2,3 |
| Apricots | 2,1 |
| Tangerines | 2,0 |
| Cheese | 2,0 |
| Peaches | 2,0 |
| Pear | 1,7 |
| Black currant | 1,4 |
| cucumbers | 1,2 |
| Oil | 0,4 |
| Eggs | 0,3 |
Harm and overdose
The monosaccharide is non-toxic and very important for the normal functioning of the body, but its excess provokes:
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- stroke;
- acute left ventricular failure;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- hypervolemia;
- fever;
- glucosuria;
- hyperglycemia;
- decreased brain activity.
Such consequences appear with unreasonable regular use of the monosaccharide or overdose.
Treatment of drug poisoning is carried out by stopping the intake of dextrose and urgently administering insulin in combination with symptomatic therapy.
Benefit
The daily intake of saccharide is from 120 to 140 grams. When consumed within reasonable limits, dextrose has a purely positive effect on the athlete’s body:
- Increased attention
- Improved ability to concentrate,
- Increased endurance,
- Acceleration of recovery processes,
- Improving stress resistance.
Taking dextrose during periods of intense physical activity within reasonable limits does not cause harm to the body , however, if the recommended daily doses are repeatedly and regularly exceeded, this substance can cause problems.
Contraindications
The use of monohydrate in the presence of certain diseases leads to their exacerbation.
Dextrose is contraindicated for:
- exacerbation of left ventricular failure;
- cerebral edema;
- pulmonary edema;
- hyperglycemia;
- hyperosmolar coma;
- overhydration;
- impaired glucose utilization;
- hyperlactic acidemia;
- individual intolerance to monohydrate.
The drug is used with caution when:
- chronic renal failure;
- diabetes mellitus;
- decompensated heart failure;
- hyponatremia;
- pregnancy/breastfeeding.
Important! Diseases often develop in an asymptomatic form, so before consuming, undergo a comprehensive examination of the body.
Measuring instruments
Monitoring the parameters of the future drink using the following precise measuring instruments will ensure its high quality:
Thermometer
The device will be needed to determine the optimal water temperature for dissolving monosaccharides (T=29–30˚С) and the temperature of the mash inside the container during fermentation (T=18–25˚С)
Refractometer
To control the sugar content in the mash before the start of fermentation and after its completion. Fermentation is complete when the Brix refractometer shows zero. If you know the initial and final density of the wort, you can determine the final strength of the mash, see the article.
pH meter
The acidity of the environment is a determining factor that positively affects the intensity of fermentation and negatively affects the development of undesirable microflora. Its optimal level at the fermentation stage is pH = 4.0–4.5. The wort is acidified (at a higher pH) with citric acid.
Application in special cases
There are a number of cases when dextrose should be taken with caution or completely eliminated from the diet.
Dextrose for vegetarians
Dextrose is a natural dietary supplement obtained primarily from corn. It can be consumed by vegans and people who prefer exclusively healthy foods.
When losing weight
Dextrose does not increase body weight, and is often used as a sweetener by people trying to lose extra pounds.
Pregnancy and lactation
The use of dextrose during a delicate period is not prohibited if there are no problems with metabolism and there are no contraindications. Reception is possible only under the supervision of the attending physician, and only in an individually selected dosage.
Treatment for diabetes
Therapy for insulin-dependent patients with dextrose is carried out as prescribed by a doctor if there are medical indications. For control, daily blood and urine tests are performed. To improve metabolism, fructose is most often prescribed to diabetics as a sweetener.
Dextrose for children
Dextrose can be given to children for medical reasons, according to an individually selected dosage.
Effect on reaction speed and attention
The drug does not “inhibit” the psychomotor reaction and does not have a negative effect on concentration. Permitted to drivers and people working at potentially dangerous objects that require timely reaction and care.
Dextrose to soften moonshine
To soften the taste of moonshine, use any form of dextrose: powder, ready-made solution or tablets. The latter must be crushed to prepare the essence. It is most convenient to use a solution made by dissolving the powder in distilled or purified water. For 1 l. 5-30 ml of 20-40% liquid is needed.
Prepare a solution from the powder:
- Weigh out 2-4 g of dextrose.
- Stir in 100 ml of water.
You can use dry dextrose without dissolving. Pour 1-3 g per 1 liter. moonshine.
Important! The best way not to overdo it with softening is to add the prepared liquid or powder to the moonshine a little at a time, then taste it.
Softening moonshine with dextrose step by step
The distillate initially obtained is passed through activated coconut/charcoal. The process eliminates large molecules from moonshine (inevitable flaws in home production). Only drinks made from ordinary mash are filtered. Berry and fruit products are not subjected to such cleaning in order to preserve the taste and aroma.
- Make moonshine 2-3° stronger than required (42°-43°). The introduced solution neutralizes excess strength.
- Pour 100 ml of the drink with a ladle.
- Add 1 ml dextrose.
- Try the drink after 3-4 minutes.
- If the taste is not mild enough, add another 1 ml until you get the desired result.
- Calculate how much dextrose is needed per 100 ml. Recalculate how much ready-made solution you will need for the required volume of moonshine.
- Mix with the drink, leave to infuse for 2-4 days in a cool place (2-4° C).
Since the moonshine will be of different hardness each time it is brewed, this recipe will help you accurately determine the right amount of dextrose for each batch.
Why is Glucose useful?
Glucose is widely used for the treatment of various pathologies, as it has a good effect on metabolic processes.
Pregnant women are prescribed glucose:
- If you suspect that the intrauterine fetus is smaller than the required size
- To reduce the chance of miscarriage
- To prevent premature birth
After consuming glucose, you feel better and fatigue goes away.
During pregnancy and lactation, it is necessary to constantly monitor plasma sugar levels.
Where can I buy
Dextrose is widely distributed and available, but not every form is suitable for use, therefore:
- The powder is sold in sports stores along with special nutrition, in pharmacies and online stores;
- Tablets and solution can be purchased exclusively in pharmacies.
Thanks to modern technologies, you can purchase any type of dextrose on the Internet (online store or on the website of a pharmacy). You can receive your order by mail, courier or self-pickup. Some pharmacies give the buyer the opportunity to reserve the medicine and then pick it up themselves. The goods must be paid for in cash or by card upon receipt. Others allow you to buy medications online. They are sent to the buyer in a convenient way, making payments by prepayment or cash on delivery.
Dextrose in food
Dextrose occurs naturally in corn and some other plants. In commercial production, it is often added to baked goods, as well as other products that contain sweeteners - various sweets, breakfast cereals, frozen desserts. Don't be surprised if adding dextrose to your post-workout shake makes it even sweeter—you're increasing your sugar intake!
How much does dextrose cost?
There is no fixed cost for D-glucose. The price is affected by:
- release form;
- weight;
- the locality where you are buying;
- pharmacy or store;
- private/public point of sale.
The larger the city, the more expensive the cost of the product. For example, in a large city, in a private store, an entrepreneur has the right to set a price for a product convenient for his business, so the cost may differ significantly from dextrose purchased at a state pharmacy. On average, the cost of a solution for infusion of 5% 500 ml is 50 rubles, 200 ml of 10% is 35 rubles, powder is 65-70 rubles/1 kg, tablets 500 mg are 25 rubles/1 plate.
Composition, release form and analogues
The drug Dextrose is produced in the form of a 5% and 10% solution for infusion in bottles or vials of 100 ml.
Analogs of Dextrose in terms of the active substance are the medications Glucose and Glucosteril. In some cases, one of the drug analogues that has a similar therapeutic effect is prescribed: Infuzolipol, Aminoven, Hymix, Aminosol-Neo, Aminocrovin, Dipeptiven, Hydramin, Infusamine, Kabiven, Aminotrof, Lipofundin, Nephrotect, SMOFlipid, Omegaven, Polyamine, Fibrinosol, Oliclinomel.
Shelf life and storage conditions
D-glucose must be stored in a dry place, away from children. The air temperature should not exceed 10-25° C. The shelf life is 3 years. Expired dextrose should not be used! Damaged or opened packaging of the solution must be thrown away!
Dextrose is useful for every person, but do not forget about side effects and contraindications. Do not use dextrose for self-medication! Before use, contact your local physician for a referral for testing. Their results will help you choose a dosage that is safe for your body and consistent with regular mental and physical activity.
| The article was verified by medical expert Vladimir Aleksandrovich Plisov |
Composition of the drug
One tablet of the drug contains 1 g of glucose monohydrate. The auxiliary ingredients are:
- Calcium stearate
- Potato starch
- Talc
- Stearic acid
Glucose tablets are produced in a round shape, their surface is flat.
If the drug is produced in a “set” with ascorbic acid, a chamfer and a dash are applied to the tablets.
The drug is placed in 10 pieces in blister packs. The cardboard package may contain 1 or 2 blisters and instructions for use.
Significance in the life of animals and humans
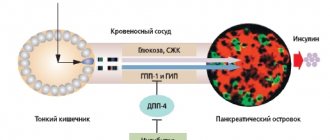
Why is glucose so important in the body and why is it needed? In nature, this chemical is involved in the process of photosynthesis.
This is because glucose is able to bind and transport energy to cells. In the body of living beings, glucose, due to the energy produced, plays an important role in metabolic processes. Main benefits of glucose:
- Grape sugar is an energy fuel that allows cells to function smoothly.
- 70% of glucose enters the human body through complex carbohydrates, which, when entering the gastrointestinal tract, are broken down into fructose, galactose and dextrose. Otherwise, the body produces this chemical, using its own stored reserves.
- Glucose penetrates into the cell, saturates it with energy, due to which intracellular reactions develop. Metabolic oxidation and biochemical reactions occur.
Many cells in the body are capable of producing grape sugar on their own, but not the brain. An important organ cannot synthesize glucose, so it receives nutrition directly through the blood.
The level of glucose in the blood, for normal functioning of the brain, should not be lower than 3.0 mmol/l.