In this article we will tell you:
- Causes of strabismus
- Symptoms of strabismus
- Types of strabismus
- Criteria for strabismus
- Diagnosis of strabismus
- Treatment of strabismus
- Conclusion
Strabismus is a disease, the characteristic feature of which is periodic or constant deviation of the visual axis of the eye in relation to the point of fixation and disorder of binocular vision (the ability to see well with both eyes at the same time). The defect has external manifestations, which consist in a violation of the position of the eyeballs. Violation often leads to headaches, dizziness, and general weakness. Depending on the nature of the course and severity, treatment of strabismus is based on the use of conservative correction options, including exercises and wearing glasses, as well as invasive methods - surgery, hardware techniques.
What causes squint?
Depending on the etiology of development, experts distinguish strabismus, which was present at birth and developed during life (for example, due to injury). In the first case, the defect is present at birth or develops during the first six months of the child’s life. It is difficult to establish the exact reason why a deviation appears during the period of intrauterine formation or the early stage of development of a child.
Pathology of the visual organs that arose later is called acquired strabismus. The reasons may be as follows:
- Diseases characterized by damage to the nervous system.
- Stress, nervous shock.
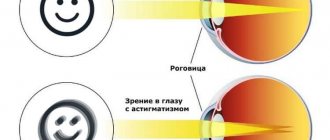
- Ophthalmological diseases of various etiologies and degrees of severity: optic nerve atrophy, eyesore, myopia, astigmatism.
- Pathology of development, injury and damage to the eye muscles.
- Paresis, as well as paralysis.
- Diseases of infectious etiology. Loss of vision, which can be either gradual or rapid.
- Somatic diseases (diseases of the body and internal organs).
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Frequent and prolonged visual stress on the eyes, as a result of which vision is noticeably reduced.
Strabismus can be fickle and acquired, but you should know that in adulthood, a defect in the organ of vision “pops up” solely against the background of provoking factors. It is important to make a diagnosis and determine the causes of strabismus; this approach allows us to eliminate the primary factors and simplify the treatment process.
Myth one
All newborns mow. False or true strabismus.
Up to 3-4 months, infants may have the impression of slanting due to structural features of the facial skull, for example, due to a skin fold at the corner of the eye or a wide bridge of the nose. If there are no oculomotor abnormalities, this condition is called false strabismus, and nothing needs to be done. A pediatric ophthalmologist must carry out a differentiated diagnosis between false and true strabismus using special research methods.
INSTRUCTION: Strabismus can be congenital or early acquired and develops into a serious functional and cosmetic pathology if parents do not begin treatment for the child in a timely manner.
Symptoms of strabismus
The symptoms accompanying strabismus vary significantly depending on the course, type and severity of the disease, as well as the age and general health of the person. A common clinical sign indicating the development of strabismus is decreased visual acuity.
The appearance of strabismus before the age of seven is accompanied by a number of the following symptoms:
- A characteristic turn of the head directed towards the squinting eye. The appearance of this sign is possible even against the background of the absence of externally expressed symptoms of eye disease.
- The appearance of problems with focusing the eyes, otherwise - strabismus. The occurrence of this sign (strabismus) is typical for all types of strabismus. Regardless of the reasons why strabismus occurs in children of a younger age category, the following variable symptom typically appears - when moving, the child may bump into various objects, which is due to impaired visual function of the eyes.
- Discrepancy in the synchrony of eye movements.
- Eye discrepancy, which can be determined by exposure to a direct light source.
Regardless of the causes of strabismus, the clinical picture in these cases includes the following signs in adolescents and adults:
- One of the main manifestations is a decrease in visual acuity during strabismus, which is expressed in the blurred perception of visual images by the eyes.
- Increased level of photosensitivity, with prolonged exposure to the sun or in a brightly lit room, vision decreases.
- General symptoms include headaches and systematic dizziness.
- Increased fatigue and blurred vision after short reading.
Parents often wonder whether strabismus can occur in young children and what to do in such cases. In babies less than four months old, eye movements are not synchronous. After reaching the specified age, the eyes take an anatomically correct position. If this does not happen, there is a possibility of developing eye disease.
Myths about operations
Surgeries to correct strabismus are traumatic and require long recovery
This is wrong. We perform operations while preserving the structures of the eye. We don't cut, we don't disconnect. We abandoned scalpels and scissors in favor of radio waves. Therefore, a long period of rehabilitation is not required; patients have the opportunity to be at home the very next day after the operation, and after three to four days return to their usual lifestyle - attending kindergarten or school. At the same time, there is no terrible swelling in the eyes and rapid healing is ensured. The rehabilitation period is greatly reduced in time - by 10 times! The child feels virtually no discomfort after such an operation.
No need to have surgery before school
This is an outdated opinion. As we have already said, our tactics showed complete justification for early treatment. It must begin during the period of formation and development of the basic human systems, and the main stages of rehabilitation must be completed before three or four years. If you do not ensure an absolutely symmetrical position of the eyes in a timely manner, then there will be no correct picture before the eyes, and the brain subsequently, after 3-4 years, will no longer be able to restructure itself and begin to correctly perceive information from the eyes. It is important to ensure the correct supply of information to the brain at the time of the onset of the disease and not waste time. Otherwise, the entire architecture of visual perception will be built on a crooked foundation, which is extremely difficult to change at an older age. In this sense, the early surgery we perform ensures a symmetrical position of the eyes, thereby creating optimal conditions for the development of vision and complete rehabilitation.
The operation will fix everything
Surgery is one of the important stages of complex treatment, which allows us to place the eyes symmetrically and make the gaze even. But it’s not the only one—surgery cannot provide high vision. To restore lost visual functions and complete rehabilitation, the child must be treated with therapeutic methods. The visual system is a complex mechanism. And if there is an eye pathology, its solution needs to be approached only in a comprehensive manner. Then success will be guaranteed. INTERRUPTION: Does strabismus have an age? No age. If strabismus is not cured in childhood, it can be eliminated in adult life, thereby significantly improving its quality.
Types of strabismus
Depending on how this ophthalmological pathology makes itself felt and what factors provoked the development of the eye disease, experts distinguish two main types of pathology: friendly and paralytic.
- Friendly. This type of disease is divided into 2 subtypes: accommodative (impaired visual perception of the affected eye, can be easily corrected with glasses), partially accommodative, non-accommodative (pathology that cannot be treated conservatively, is formed against the background of congenital anomalies). Typical manifestations of these forms of the disease are the following: absence of double vision in the perception of visual images, preservation of full mobility, identical strabismus angle of the affected eye to the healthy one.
- Paralytic. Caused by damage to certain parts of the brain and nervous system, this type of strabismus is characterized by disturbances of the vertical as well as torsion type (the direction of the affected eye upward or towards the temple), which is taken into account when choosing treatment tactics.
Depending on the characteristics of the involvement of the eyes in the pathological process, a monolateral or alternating type of the disease develops. In the first case, the position of one eye is disturbed. In the second case, there is a violation of the position of both one and the second eye.
Experts also identify the following forms of strabismus:
- Latent and compensated. Treatment with exercises in these cases is not mandatory; only measures that will help prevent complications are permissible. More often, these types of diseases of the visual organs are detected exclusively as part of preventive examinations and do not have external manifestations.
- Subcompensated. Against the background of this form of the disease, a person can control the movements of the eyeballs. External signs indicating that the patient is developing strabismus are barely noticeable. But over time, they become more pronounced; accordingly, it is necessary to correct vision and remove provoking factors as soon as possible, this is also done with the help of exercises.
- Decompensated. It is characterized by pronounced external manifestations and a lack of control regarding the movements of the eyeballs, which means a weakening of muscle tissue.
Treatment methods
Diagnosing pathology is possible only during a comprehensive ophthalmological examination. Specific tests allow you to evaluate the angle of deviation of the eye and impairment of binocular vision.
There are several basic methods for correcting the defect:
- spectacle correction
– prescription of special lenses; - hardware treatment
– a set of orthoptic exercises to develop the muscular structures of the organ of vision; - prismatic compensators
– special lenses for creating individual correction of the optical system for strabismus; - surgical treatment of divergent strabismus
- special operations that can normalize muscle function.
Often patients prefer to start with non-surgical therapy - the risks of surgery become discouraging factors when choosing a treatment method.
Orthoptic treatment of divergent strabismus shows good results. Special sets of exercises have been developed on hardware programs, on a synoptophore, with various lenses and prisms. Prismatic compensators can also be prescribed in the form of glasses - some companies and research institutes are creating glasses for permanent wear with prisms that form binocular vision in patients with strabismus. Courses of treatment are also recommended before surgery - only the readiness of the brain to perceive images from both eyes can reduce the risks of relapse of strabismus and repeated surgical interventions.
Criteria for strabismus
When treating strabismus, the criteria for the development of the disease are taken into account:
- In accordance with the characteristics and time of development of the disease, congenital and acquired forms are distinguished. Experts note that the most common is the first option.
- According to the stability of the deviation of the eyeball from the visual axis, unstable and constant forms are distinguished.
- Depending on how exactly the defect occurs, what manifestations it is accompanied by, for example, rapidly decreasing vision, friendly and paralytic forms are distinguished.
- Depending on how the pathology develops, why this happens, and in which direction the affected eye is deviated, forms of the disease are distinguished: mixed, vertical and horizontal.
Determining the type of disease should be considered as an important aspect, since the features of treatment of strabismus and the choice of medical tactics depend on the form of the pathology.
Complications
Strabismus does not go away on its own. Moreover, if left untreated, serious complications can develop. That is why, when the first signs of strabismus appear, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
With strabismus, work in almost all parts of the visual analyzer is disrupted, so treatment must be comprehensive.
In the squinting eye, visual acuity gradually decreases, that is, amblyopia develops. This, in turn, leads to even greater deviation from the norm. Thus, a vicious circle starts.
Read the material on how to restore vision at home.
- Strabismus in newborns: treatment methods, consequences of the disease
Diagnosis of strabismus includes:
Diagnosis of pathology includes a wide range of techniques, the most common of which are the following:
- Initial examination. In the later stages of development, external signs of pathology are clearly expressed; in the primary stages, when negative consequences can be avoided, only a specialist can see them. When the initial examination is carried out, the doctor notes the position of the head, as well as the location of the eyeballs.
- Checking visual acuity using special corrective lenses. This method allows you to determine whether the patient’s vision is deteriorating or whether these signs are absent; testing must be done over a period of time.
- Computer refractometry. This research method is necessary to determine the nature and characteristics of refraction - the process of refraction of light waves within the optical system of the eyeball; it should be done when identifying primary signs of the disease.
Additional examination of the patient is required if a paralytic form of the disease is detected.
How is strabismus treated?
Before starting treatment and getting rid of the defect, the patient will need to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures. Depending on why the pathology develops and the degree of its severity, the following treatment options can be chosen:
- Optical correction. To get rid of pathology in the early stages of formation, the patient is required to wear corrective lenses or glasses. Using this treatment method, almost any stage and type of strabismus is completely corrected. To correct the position of the eyeballs, children need to wear glasses on a regular basis.
- Pleoptic therapy (exercises). Using this method, pathology affecting only one eye is treated. The essence of the technique is to turn off the healthy eyeball from the visual process in order to train and correct the position of the affected one. Surgical intervention. Surgery is often used to treat patients under five years of age who do not respond to conservative treatment methods.
To improve results, vision correction during treatment with surgical intervention is carried out in combination with conservative methods of therapy. Doctors warn: in the case of strabismus, consistency in exercises is extremely important. Teach your children to do them regularly along with brushing their teeth.
Prevention
The main way to combat strabismus is early diagnosis. Required:
- mandatory early examinations of children, more frequent for children at risk (parents with visual impairments, birth trauma, etc.);
- annual medical examination;
- compliance with the norms and rules of visual hygiene.
Read about the rules of visual hygiene here.
If a child is prescribed glasses, they must be worn as recommended and visited an ophthalmologist every six months in order to promptly prevent the development of strabismus and amblyopia.