Characteristics of the drug
Metformin is a hypoglycemic drug. The product can be purchased in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The cost of the medicine is 93 – 465 rubles. The active substance of the drug is metformin hydrochloride.
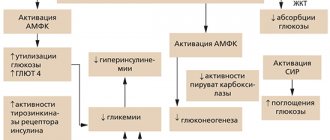
The medication effectively reduces gluconeogenesis, reduces the synthesis of fatty acids, and inhibits the oxidation of fat molecules. The drug can increase the sensitivity of insulin receptors located in the periphery. The product accelerates the utilization of glucose molecules. The drug does not affect the concentration of insulin in the blood, but can change the hemodynamics of insulin molecules.
The drug increases the formation of glycogen. Against the background of the drug's action, the capacity of carriers of glucose molecules increases and the rate of penetration of glucose through the intestinal walls decreases. The number of lipid molecules decreases. The patient's weight decreases or remains stable.
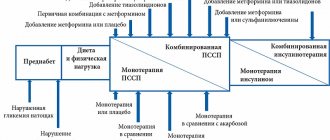
According to the instructions, the medicine is used to treat diabetic patients. The drug is used if diet and physical therapy do not help. For adults, the drug can be used with other medications that reduce blood sugar, as well as with insulin. In children, Metformin is prescribed from the age of 10 as the only hypoglycemic drug or combined with insulin.
Restrictions on the use of the drug:
- metabolic acidosis;
- comatose, precomatous state, ketoacidosis in diabetics;
- kidney dysfunction;
- severe infectious pathology;
- hypoxic conditions (heart pathologies, changes in respiratory function);
- intravenous administration of iodine-containing drugs for X-ray examination and computed tomography;
- poisoning from alcohol-containing drinks;
- allergy to Metformin.
The drug is used carefully in elderly patients over 60 years of age who engage in heavy physical labor (high probability of lactic acidosis). Metformin should be prescribed with caution to nursing mothers and patients 10-12 years of age. Use the medicine carefully in patients with kidney pathology.
The effect of Metformin is not completely known when used in pregnant patients. There is evidence that the drug does not increase the risk of developing defects in a child. When pregnancy occurs or is planned, it is better to discontinue the medicine so as not to have a negative effect on the body of the mother and baby.
The medicine should not be prescribed together with iodine-containing drugs. There is no need to combine Metformin with alcohol. It is not recommended to use the drug simultaneously with glucocorticosteroid hormones, diuretics, Danazol, Chlorpromazine, blood pressure medications, β2-adrenergic agonists and other drugs.
The drug cannot be used independently, as it has a large number of undesirable effects. When using the drug, lactic acidosis and megaloblastic anemia (decreased absorption of vitamin B12) are possible. Patients experience a change in the sense of taste, dyspepsia, allergies (skin reactions), increased levels of liver enzymes, and the development of hepatitis.
When using high dosages of the drug, lactic acidosis is possible. The patient experiences respiratory disorders: drowsiness, dyspepsia, decreased blood pressure and body temperature, and decreased rhythm frequency. Muscle cramps and impaired consciousness may occur.
If symptoms of lactic acidosis appear, the patient requires urgent hospitalization. This will allow you to quickly relieve the symptoms of lactic acidosis. To relieve symptoms of overdose, hemodialysis is performed.
Metformin Long - start of therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus
One of the most common diseases in modern society is diabetes mellitus (DM). The medical and social significance of diabetes is determined by the steady increase in the number of patients, the high risk of macro- and microvascular complications, as well as the impact of the disease on the quality and life expectancy of patients. A similar global trend of steady growth in the number of people with diabetes mellitus also occurs in the Republic of Belarus. Over the past 10 years, the number of such patients in Belarus has increased from 150 thousand to 336 thousand people, 94% of whom suffer from type 2 diabetes (data as of 01/01/2019). And every year there are more patients with type 2 diabetes in the country. Currently, the drug metformin occupies a central place in all current recommendations for the management of type 2 diabetes.
Thus, the 2022 consensus algorithm of the American and European Diabetes Associations (ADA/EASD) strongly recommends the use of metformin as a first-line agent (in the absence of contraindications or intolerance), immediately upon diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, in addition to image correction life (dietary recommendations and exercise). The preference given to this drug is not accidental: the effectiveness and safety of metformin have a huge evidence base, its cost is low, the drug reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular complications, helps reduce body weight, and the risk of hypoglycemia when taking it is minimal. In 2022, the American Diabetes Association released new recommendations that metformin remains the preferred drug for initiating glucose-lowering therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes (Evidence Level A). However, unfortunately, the tolerability of metformin is limited by side effects from the gastrointestinal tract, which, according to some data, develop in almost 25% of patients, which leads to discontinuation of the drug in 5-10% of patients. In addition, splitting up metformin intake throughout the day and a large number of tablets, if necessary, to take other drugs to treat concomitant diseases, creates additional inconvenience for patients. Insufficiently good tolerability from the gastrointestinal tract and the need to take it more than once a day leads to decreased adherence to metformin therapy in some patients. The new extended-release dosage form of metformin has been designed to provide sustained release of the drug to improve tolerability and ensure prolonged action of the drug. This dosage form helps slow down the transit of the tablet from the stomach through the pylorus, thereby significantly increasing the time the drug remains in the stomach. In vitro studies have shown that 90% of metformin in the conventional dosage form is released within 30 minutes. In contrast, extended-release metformin releases 90% of the drug within 10 hours, relatively independent of gastrointestinal pH and motility. Thus, the dosage form of Metformin Long provides a slower, smoother and longer delivery of the drug without an initial rapid increase in the concentration of the drug in the plasma. When prescribed in the evening with food, due to its dosage form, Metformin Long acts synchronously with natural physiological processes, when gastrointestinal emptying slows down at night. This leads to prolonged absorption of metformin and justifies the administration once a day.
However, patients should be aware and warned that the inactive portion of the metformin extended-release tablet is excreted unchanged. Otherwise, this may lead to erroneous conclusions and unmotivated refusal to use this dosage form. The hypoglycemic effect of modified-release metformin is comparable to that of immediate-release metformin. Thus, modified-release metformin, having all the advantages of the conventional form of the drug, is devoid of a significant part of its disadvantages: taking extended-release metformin once a day significantly simplifies the treatment regimen and, together with a decrease in the frequency of side effects, increases patient adherence to treatment. Metformin Long, the first long-acting generic metformin in the Republic of Belarus, is produced by the Borisov Medical Preparations Plant Open Joint Stock Company in dosages of 500 mg, 750 mg and 1000 mg. The indication for the use of drugs Metformin Long 500, 750, 1000 is type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults (especially in overweight patients) with ineffective diet therapy and exercise, as monotherapy or in combination with other oral hypoglycemic agents or together with insulin . When used as monotherapy or combination therapy in combination with other oral hypoglycemic agents, Metformin Long is used as follows:
- The recommended initial dose is 1 tablet of Metformin Long 500 per day.
- After 10-15 days of treatment, the dose must be adjusted in accordance with the results of measurements of glucose levels in the blood serum. Slowly increasing the dose helps reduce gastrointestinal side effects. The maximum recommended dose is 4 Metformin Long 500 tablets per day (2000 mg).
- It is recommended to take the dose of the drug once a day with meals in the evening, increasing by 500 mg every 10-15 days to a maximum dose of 2000 mg. If, when using Metformin Long at a maximum dose of 2000 mg 1 time per day, the required level of glycemia cannot be achieved, the dose taken can be divided into 2 doses (morning and evening during meals). If the required glycemic level is not achieved after this, metformin immediate-release tablets can be used at the maximum recommended dose of 3000 mg per day.
- For patients already taking metformin, the starting dose of Metformin Long should be equivalent to the immediate-release tablet dose. For patients taking metformin at a dose above 2000 mg, switching to Metformin Long is not recommended.
- If you switch to Metformin Long, you must stop taking the other antidiabetic drug.
- Metformin Long 750 and Metformin Long 1000 are intended for patients already receiving metformin immediate-release tablets.
- Doses of Metformin Long 750 or Metformin Long 1000 should be equivalent to the daily dose of metformin immediate-release tablets with a maximum dose of 1500 mg or 2000 mg, respectively, taken in the evening with meals.
In combination therapy in combination with insulin, Metformin Long is used as follows:
- To achieve better control of blood glucose levels, metformin and insulin can be used in combination therapy. Typically, the initial dose of Metformin Long 500 is 1 tablet per day with meals in the evening; the dose of insulin must be adjusted in accordance with the results of measuring blood glucose levels.
- For patients already receiving metformin and insulin in combination therapy, the dose of Metformin Long 750 or Metformin Long 1000 should be equivalent to the daily dose of metformin with a maximum dose of 1500 mg or 2000 mg, respectively, in the evening with meals, while the insulin dose is adjusted to based on blood glucose measurements.
- For elderly patients and patients with reduced renal function, the dose is adjusted based on assessment of renal function, which should be carried out regularly.
- Due to the lack of data on use, Metformin Long should not be used in children under 18 years of age.
- Medicines Metformin Long 500, Metformin Long 750, Metformin Long 1000 are available with a doctor's prescription.
Drug analogues
Metformin has structural and non-structural analogues. Structural substitutes for Metformin also have a medicinal substance. They are also called generics or synonyms. Non-structural analogues may differ in composition, but have a similar effect on the body.
Drugs similar to Metformin are often used if Metformin is relatively expensive for a particular patient or is not suitable for the patient. If the reason for replacing the drug is price, then it is better to look for structural analogues. If the medicine is not suitable, then a non-structural analogue is more often prescribed.
Types of similar products
The number of similar drugs is quite large. Many of them have a similar composition. The cost of medications may vary, but not significantly.
Metformin has analogues (structural):
| Russian analogues | Imported analogues of Metformin |
|
|
Similar analogues of Metformin include Reduxin Met. It has a slightly different composition. It is more often used for the treatment of obesity, especially in patients with diabetes and prediabetes.
Analogs produced in Russia
Bagomet
The Russian substitute for the drug Metformin is Bagomet. The active component of the drug is metformin hydrochloride. It helps reduce the absorption of glucose molecules in the intestinal tube and reduce gluconeogenesis in the liver tissue.
The drug does not increase the formation of insulin and does not provoke hypoglycemia. The analogue is in the form of tablets (500 mg, 750 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The limitations and side effects of the drug are the same as those of Metformin.
The price for the analogue is 38 - 428 rubles. It is slightly cheaper than Metformin.
Formetin
A cheap analogue of Metformin is Formetin. The drug contains metformin hydrochloride. The drug is produced in tablet forms (500 mg, 750 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The cost of the analogue is 57-229 rubles (in some pharmacies it may be a little more expensive).
The pharmacokinetics and undesirable effects of the drug are the same as Metformin. The drug is not prescribed to a pregnant patient and a child under 18 years of age. During breastfeeding I use the analogue very carefully.
Novoformin
A similar remedy is Novoformin. The drug can be purchased in pharmacies in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg). The price of the medicine is 49-153 rubles. The medicinal component of the drug is metformin hydrochloride. The drug has similar limitations. The analogue is not used in pregnant and lactating patients. The drug is prescribed to children only according to indications.
Metformin-Richter
Metformin-Richter is an analogue that is produced in Russia. The drug is in the form of tablets (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The medicinal component is the same as Metformin. The drug is not used during pregnancy. Carefully prescribe the drug to children 10-12 years of age. The analogue should not be used on a child under 10 years of age or a nursing mother. The price of the drug is 89-186 rubles.
Merifatin
Merifatin is considered a good analogue of Metformin. It is also produced in our country. The drug can be purchased in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The medicinal component is metformin hydrochloride. The medicine is not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The drug can be used in pediatric practice. Carefully prescribe medicine to elderly patients. The cost of the analogue is 169-283 rubles.
Gliformin
You can replace Metformin with Gliformin. The drug is in the form of tablets (250 mg, 500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The medicine does not differ from Metformin in pharmacokinetics, restrictions and undesirable effects. The product costs 93-216 rubles. The drug may be a little more expensive.
Foreign drugs
Siofor
A more famous foreign analogue is Siofor. The product is produced in Germany. The medicine can be purchased in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). It is carefully used in children's practice (10-12 years of age). In children 10-18 years of age, the drug is indicated as monotherapy or together with insulin.
The dosage of insulin is adjusted according to the level of glucose in the bloodstream. The drug is indicated for children under 10 years of age. The analogue should not be used in pregnant patients and nursing mothers. The drug is carefully prescribed to patients over 60 years of age. The price for Siofor is 212 – 477 rubles.
Nova Met
It is allowed to take Nova Met instead of Metformin . Swiss analogue. The medicine is sold in pharmacies in the form of tablets (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The therapeutic component of the analogue is metformin hydrochloride. The product can be used in patients over 10 years of age. The drug is not indicated for pregnant and lactating patients.
Formin Pliva
Formin Pliva is another foreign analogue. The manufacturer of the drug is considered to be Germany, the representative is Israel. The medicine is sold in tablet form (850, 1000 mg). The dosages of the analogue are large, so it is not used in pediatric practice. The drug is not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The analogue cannot be prescribed to patients with kidney pathology.
Glucophage
An analogue of Metformin is Glucophage. It can be produced by Germany, Russia or France. The drug is sold in tablet form (500 mg, 750 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The drug is not indicated for use in pediatric practice, since the drug has not been sufficiently studied in children.
The drug is carefully prescribed in patients with insufficiency of renal function with a creatinine clearance of 45-59 ml per minute. It is permissible to use the analogue cautiously in nursing patients and persons over 60 years of age, but only according to indications. The cost of the drug is 107 – 729 rubles.
Sophamet
Sophamet is the Bulgarian analogue . It also contains Metformin. The drug is produced in tablet forms (850 mg). The cost of the analogue is from 100 rubles. The medicine is approved for use in children over 10 years of age. The drug is not indicated for severe damage to the liver and kidneys. Use the medicine carefully in patients over 60 years of age. The analogue is not prescribed during pregnancy or breastfeeding, since it has not been fully studied in this group of patients.
Metformin Teva
Metformin-Teva is an Israeli substitute for Metformin . The drug can be purchased at a pharmacy in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The medicine has an average cost of 168-284 rubles.
The product should not be used in patients under 18 years of age, since clinical studies on children have not been completed. The analogue should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. When planning a child, the drug should be discontinued if it was taken previously.
Metfogamma
Metfogamma is a Germanic analogue. The drug can be bought at the pharmacy in the form of tablets (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The medicine is indicated for diabetics. Its cost is from 134 rubles. The product is not used in pediatrics. The analogue cannot be prescribed during pregnancy and lactation. The drug is not indicated for serious pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
Metformin Zentiva
Metformin Zentiva is an analogue that is produced in Slovakia. The drug is produced in tablet form (500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg). The product is approved for use in children over 10 years of age.
The drug is carefully prescribed to children 10-12 years of age (as monotherapy or in combination with insulin). Use the product carefully when breastfeeding, with moderate kidney pathology, and in elderly patients over 60 years of age. The medicine is not indicated during pregnancy and pregnancy planning. The cost of the drug is 99-212 rubles.
Metformin
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a rare but serious (high mortality unless promptly treated) complication, most often occurring in the setting of acute deterioration of renal function, cardiopulmonary disease or sepsis. Accumulation of metformin against the background of acute deterioration of renal function increases the risk of lactic acidosis.
If dehydration occurs (severe diarrhea or vomiting, fever or decreased fluid intake), you should temporarily stop treatment with metformin and consult a doctor.
Treatment of patients taking metformin with drugs that can acutely worsen renal function (such as antihypertensive drugs, diuretics or NSAIDs) should be initiated with caution.
Other associated risk factors for lactic acidosis should be considered, such as decompensated diabetes mellitus, ketosis, prolonged fasting, alcoholism, liver failure and any other condition associated with severe hypoxia, as well as concomitant use with drugs that can lead to lactic acidosis (see. sections “Contraindications” and “Interaction with other drugs”). This may help reduce the incidence of lactic acidosis.
Patients and/or caregivers should be informed of the risk of lactic acidosis.
Lactic acidosis is characterized by acidotic shortness of breath, abdominal pain, muscle cramps, severe asthenia and hypothermia followed by coma. If suspicious symptoms occur, the patient should stop taking metformin and seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnostic laboratory parameters are a decrease in blood pH (less than 7.35), lactate content in the blood plasma over 5 mmol/l, increased anion gap and lactate/pyruvate ratio.
Doctors should warn patients about the risk of developing and symptoms of lactic acidosis.
Administration of iodinated contrast agents
Intravascular administration of iodinated contrast agents can lead to nephropathy and accumulation of metformin, which increases the risk of developing lactic acidosis. The use of metformin should be stopped 48 hours before such a procedure and resumed no earlier than 48 hours after it, provided that the examination did not reveal renal dysfunction (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
Surgical operations
The use of metformin should be discontinued 48 hours before elective surgery under general, spinal or epidural anesthesia and can be continued no earlier than 48 hours after surgery, provided that the examination did not reveal impaired renal function.
Kidney function
Since metformin is excreted by the kidneys, it is necessary to determine CC before starting treatment and regularly thereafter:
- at least once a year in patients with normal renal function;
- every 3-6 months in patients with CC 45-59 ml/min and every 3 months with CC 30-44 ml/min.
When CC is less than 30 ml/min, the use of metformin is contraindicated. Treatment with metformin should be suspended in the presence of conditions that may affect renal function.
Particular caution should be exercised in case of possible impairment of renal function in elderly patients (due to the asymptomatic nature), with simultaneous use of antihypertensive drugs, diuretics or NSAIDs.
Heart failure
Patients with heart failure have a higher risk of developing hypoxia and renal failure. Patients with chronic heart failure should have cardiac and renal function monitored regularly while taking metformin.
Taking metformin in heart failure with unstable hemodynamic parameters is contraindicated.
Children and teenagers
The diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus must be confirmed before starting treatment with metformin.
In clinical studies lasting 1 year, metformin was shown to have no effect on growth and puberty. However, due to the lack of long-term data, careful monitoring of the subsequent effects of metformin on these parameters in children, especially during puberty, is recommended. Clinical experience with metformin in children aged 10 to 12 years is limited, so the most careful monitoring is necessary in children in this age group.
Other Precautions
- Patients are advised to continue to follow a diet with even carbohydrate intake throughout the day. Overweight patients are recommended to continue to follow a hypocaloric diet (but not less than 1000 kcal/day).
— Patients should inform the doctor about any treatment being carried out and any infectious diseases.
— It is recommended that routine laboratory tests be performed regularly to monitor diabetes mellitus.
— Metformin in monotherapy does not cause hypoglycemia, however, it is recommended to exercise caution when using it in combination with insulin or other hypoglycemic agents (for example, sulfonylurea derivatives, repaglinide, etc.).
The use of metformin is recommended for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in persons with prediabetes and additional risk factors for the development of overt type 2 diabetes mellitus, such as:
- age less than 60 years;
- body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2;
- history of gestational diabetes mellitus;
- family history of diabetes in first-degree relatives;
- increased concentration of triglycerides;
- reduced concentration of HDL cholesterol;
- arterial hypertension.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia include weakness, headache, dizziness, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, blurred vision, or difficulty concentrating.
Metformin did not affect fertility in male or female rats when administered at doses three times the maximum recommended daily dose for humans.