Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Metronidazole is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole, active against anaerobic protozoa and anaerobic bacteria. Metronidazole is effective against trichomonas vaginalis, giardia intestinalis, gardnerella vaginalis, entamoeba histolytica, lamblia spp., as well as obligate anaerobes: bacteroides spp. (b. fragilis, b. distasonis, b. thetaiotaomicron, b. vulgatus, b. ovatus), fusobacterium spp. and some gram-positive microorganisms: eubacterium spp., clostridium spp., peptostreptococcus spp., peptococcus spp. Metronidazole for external use has little antioxidant activity.
It has been established that metronidazole significantly reduces the production of active oxygen, hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide by neutrophils, which are potential oxidants and can harm tissues at the site of inflammation.
The mechanism of action of metronidazole is the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group of metronidazole by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group of metronidazole interacts with the DNA of microorganisms, inhibiting its synthesis, which leads to the death of microorganisms.
When applied topically, the drug is effective against acne, but the mechanism of this action has not been fully studied.
Pharmacokinetics. When used externally, absorption of the drug is minimal and only a small amount of the drug is determined in the blood plasma. Absorbed metronidazole penetrates the placental barrier and the BBB. Cmax in the blood reaches 66 mg/ml (if 1 g of gel is applied, which is equivalent to 7.5 mg of metronidazole).
Seborrheic dermatitis. Terminology
Seborrheic dermatitis
- a chronic inflammatory skin disease associated with an increase in the quantity and change in the quality of sebum, as well as with the influence of skin microflora.
The composition of sebum includes glycerides (more than 40%), free fatty acids (16%), wax esters (up to 25%) and cholesterol, squalene (12%) and cholesterol. Triglycerides in sebum are broken down into free fatty acids by bacteria. Some of them form volatile fatty acids that impart odor to the skin. Sebum itself has no odor.
The wide prevalence and constant increase in incidence determines various approaches to treatment, the main goal of which is to achieve a long-term positive result.
Manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis:
1) thickening of the stratum corneum, peeling;
2) oily sheen, seborrhea, sebostasis (stagnation of sebaceous secretion at the mouth of the hair follicle);
3) inflammation of the skin;
4) itching.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects those areas of the scalp and body where the sebaceous glands are most developed:
- scalp,
- anterior chest area and interscapular area,
- area of the ears,
- forehead,
- nasolabial triangle.
When the skin of the scalp is affected, thinning and thinning of the hair is observed. In severe cases, seborrheic dermatitis can have the character of a widespread exfoliative process up to erythroderma.
| Dandruff = seborrheic dermatitis | Brightness of blood vessels - inflammation |
special instructions
Avoid getting the drug into your eyes. If the gel gets into your eyes, you must immediately rinse them with plenty of water.
The gel should not be applied to areas close to the eyes. The affected area should be cleaned before applying Metrogyl gel. After applying the drug, you can use cosmetics.
For ordinary acne, the use of Metrogyl gel should be combined with oral antibiotics.
When applied to a large surface area of the skin or in case of prolonged use of Metrogyl gel, there is a possibility of developing systemic side effects.
The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with impaired hematopoietic function.
Metronidazole for topical use is not effective for the treatment of telangiectasia, which occurs with erythematosus.
Propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216) and methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), which are part of the drug, can cause an allergic reaction (possibly delayed).
Use during pregnancy and lactation.
When taken orally, metronidazole crosses the placental barrier into breast milk in very significant concentrations.
Despite the fact that when applied topically, the concentration of metronidazole in the blood is low, Metrogyl gel is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy, and in the second and third trimester it can be used if absolutely necessary.
Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
Children. Do not use in children.
The ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or operating machinery. The use of the drug at the indicated dose does not affect driving or working with potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Metrogyl®
Gastrointestinal disorders: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, stomatitis, metallic taste in the mouth, decreased appetite, anorexia, dry oral mucosa, constipation, pancreatitis (reversible cases), discoloration tongue / “coated tongue” (due to the growth of fungal microflora).
Immune system disorders: angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disorders: peripheral sensory neuropathy, headache, convulsions, dizziness, encephalopathy and subacute cerebellar syndrome (impaired coordination and synergism of movements, ataxia, dysarthria, gait disturbance, nystagmus, tremor) have been reported, which are reversible after discontinuation of metronidazole , aseptic meningitis.
Mental disorders: psychotic disorders, including confusion, hallucinations; depression, insomnia, irritability, increased excitability.
Visual disturbances: transient visual disturbances, such as diplopia, myopia, blurred contours of objects, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception; neuropathy/optic neuritis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: increased activity of liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), development of cholestatic or mixed hepatitis and hepatocellular liver damage, sometimes accompanied by jaundice; In patients treated with metronidazole in combination with other antibacterial agents, cases of liver failure requiring liver transplantation have been observed.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash, itching, skin flushing, urticaria, pustular skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: brownish-reddish coloration of urine due to the presence of a water-soluble metabolite of metronidazole in the urine, dysuria, polyuria, cystitis, urinary incontinence, candidiasis.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: fever, nasal congestion, arthralgia, weakness, thrombophlebitis (pain, hyperemia or swelling at the injection site).
Laboratory and instrumental data: flattening of the T wave on the electrocardiogram.
Interactions
When applied topically in recommended doses, no systemic interaction of Metrogyl gel with other drugs was detected. however, caution should be exercised when prescribing Metrogyl gel with certain medications.
Warfarin and other coumarin anticoagulants. Metronidazole enhances the anticoagulant effect, which leads to an increase in the time of prothrombin formation.
Phenobarbital. When used simultaneously with metronidazole, the antimicrobial activity of the latter decreases. The reason is the accelerated metabolism of metronidazole.
Disulfiram. Concomitant use increases the toxicity of the drugs, which can lead to the development of neurological symptoms.
Cimetidine. Suppresses the metabolism of metronidazole, which may lead to increased concentrations of metronidazole in the blood serum.
During systemic therapy with metronidazole, it is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol, since a disulfiram-like reaction is possible.
METROGYL (solution)
y follicles.
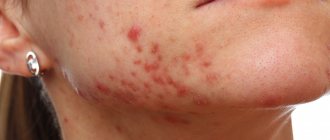
This mite lives on the skin of every person and, under certain circumstances and comfortable conditions for him, is activated and becomes an activator of the inflammatory process. Purely visually, demodicosis most often resembles acne or rosacea. And this is most often the mistake of a person who tries to treat acne and does not get any significant result.
The disease is actually extremely serious and requires great attention and long-term treatment. The tick is killed extremely reluctantly. You need to create truly uncomfortable conditions for his life in order to get rid of him from your skin. And not only drug therapy with metronidazole (Trichopolum), long-term use of certain skin products helps in this, but also strengthening the immune system, avoiding stress, and a special diet. That is, work in a complex!
Anything can trigger the appearance of demodicosis! Cosmetics, stress, malfunctions of the endocrine and digestive systems, etc. There are many reasons. And no one is safe from the fact that the tick will bypass it. Daily care has nothing to do with it. For example, all my life I paid close attention to my skin, took care of it and cared for it like a greenhouse plant), but this fate did not escape me.
The diagnosis is made only after examination of skin scrapings. ALTHOUGH experienced cosmetologists and dermatologists see it immediately by the appearance of the skin (they are nevertheless required to give a referral for analysis). Very often the mite does not manifest itself in full force, and the rashes are sporadic and rare.
The tick is afraid of birch tar like fire. That is why most often dermatologists prescribe Tar Soap for washing during the treatment of demodicosis (in general, the favorite treatment regimen for demodicosis by dermatologists is MEtronidazole (Trichopol) inside and Metrogyl gel outside). I conscientiously and regularly washed my face with it for 4 months, BUT the fear for my skin did not leave me. I didn’t wash my face with soap even as a teenager. Although the soap did not visually harm my oily skin, I still consider this product to be too aggressive.
At the next appointment, the dermatologist suggested using a Metrogyl solution instead of tar soap. Actually, this is a solution for intravenous administration with the same active substance, metronidazole, as in Metrogyl face and body gel and Metronidazole tablets.
The product is sold in this packaging:
Volume 100 ml, average cost from 23 to 27 rubles. The package contains instructions and the solution itself, placed in a dropper bottle. The dropper is additionally placed in the bag.
The dropper is made in the form of a bottle, which can be placed like this, it is stable:
There is a loop at the bottom of the bottle by which the bottle can be hung when it is used for intravenous administration:
WHAT is this drug used for? This is an antiprotozoal and antifungal drug used in the treatment of various infections, as well as for the prevention of postoperative complications and radiation therapy for patients with tumors.
BUT, I repeat, it was recommended to me as a lotion for washing or toning the face.
What can I say? Of course, this solution is much more gentle than tar soap. This is simple water, without any specific smell. I wash my face with it using a cotton pad, killing two birds with one stone: I cleaned the skin and poisoned the tick with a substance that it cannot tolerate. The solution does not leave marks on the skin, does not cause a burning sensation or any discomfort. The product is cheap, one bottle lasts me for a week. An excellent replacement for tar soap!
I can only recommend it to all demodecticists! Cheap and just what we need when treating our “joy”!
Well, I strongly advise anyone who has rashes, especially those aged far from adolescence, to get tested for ticks! In 90% of cases, it will be the cause of your rashes or redness! And don't be scared by photos from the Internet. Such advanced cases are rare. Much more often, it simply ruins life with isolated but frequent rashes.
Note!
The description of the drug Metrogyl gel tube 30g on this page is a simplified author’s version of the apteka911 website, created on the basis of the instructions for use.
Before purchasing or using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the manufacturer's original instructions (attached to each package of the drug). Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. Only a doctor can decide to prescribe the drug, as well as determine the dose and methods of its use.
Is it worth using Metrogyl gel?
If you survey those who have already used Metrogyl acne gel, the reviews will contain the following advantages:
- pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- improvement of the general condition of the skin;
- fewer rashes already in the first month of use;
- rapid healing of wounds and abrasions.
If there are no visible improvements within three weeks, contact your dermatologist; you may need to use additional products to enhance the effect of the gel or choose a different drug.
The result of treatment depends on many factors: the causes of the rash, the severity of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body and compliance with the rules of use.