The metacarpal bones are located in the hand between the finger bones and the wrist bones. Fractures of the metacarpal bones usually occur due to direct impact - for example, hitting a hard object with a fist, falling on the hand. Based on location, fractures of the base of the metacarpal bone (the most proximal part, located near the bones of the wrist), the head of the metacarpal bone (near the metacarpophalangeal joints), and the diaphysis of the metacarpal bone (its middle part) are distinguished. Fractures can be either with displacement of bone fragments or without displacement.
For fractures without displacement of bone fragments, conservative treatment in a plaster cast is indicated. If there is displacement and unsatisfactory reposition (comparison of fragments), surgical treatment is necessary. This is due to the fact that such fractures can significantly affect the function of the hand (preservation of pain, decreased grip strength of the hand). Particular attention is paid to fractures of the head of the metacarpal bone, which is part of the metacarpophalangeal joint. Surgical treatment for fractures of the metacarpal bones with displacement of fragments contributes to the fastest and most complete restoration of hand function.
Diagnostics
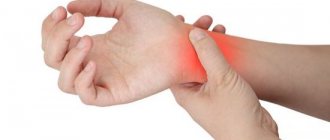
Symptoms of any fracture are pain, swelling, dysfunction, and limited movement in adjacent joints. The hand is very characterized by rapidly growing swelling, especially if 2 or more bones are broken. Due to swelling, the deformation caused by the displacement of fragments is often not noticeable, so some patients consider such injuries to be simply severe bruises and put off seeing a doctor. The standard test to detect a fracture is an x-ray. Computed tomography (CT) can be used to more accurately determine the position of fragments or identify intra-articular fractures of the base of the metacarpal bones.
Publications in the media
Fractures of the hand bones account for 35% of all fractures. Classification • Fracture of the carpal bones •• Fracture of the scaphoid bone •• Fracture of the lunate bone •• Fractures of other bones of the wrist • Fractures of the metacarpal bones • Fractures of the phalanges of the fingers. Fracture of the scaphoid • Causes: fall on an outstretched, extended arm, direct blow to the palmar surface of the hand • Pathomorphology . The scaphoid bone breaks at the tubercle area. The peculiarities of the blood supply determine poor healing of the fracture • Clinical picture : swelling in the area of the anatomical snuffbox, limitation of movements in the dorsoradial direction, inability to clench the hand into a fist. To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is performed in three projections: direct, lateral and oblique • Treatment: plaster cast for 6–8 weeks in the position of thumb abduction and slight dorsal extension (150–160°). If the fracture heals poorly, surgical treatment is required.
Fracture of the lunate bone • Causes : fall on the hand abducted to the ulnar side • Clinical picture . Swelling in the middle of the wrist joint on the back side, retraction in the area of the third metacarpal bone when clenching the hand into a fist, pain with axial load on the third and fourth fingers • Treatment . Plaster cast for 6–10 weeks. Surgical treatment - for false joints and aseptic necrosis.
Fracture of the metacarpal bones . The most commonly observed fracture is the base of the first finger • Pathomorphology •• Bennett's fracture is a longitudinal fracture at the palmar-ulnar edge of the base of the first finger, while the triangular fragment is held by ligaments, the metacarpal bone is displaced in the proximal direction •• Roland's fracture is a comminuted fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone • Clinical picture: pain, deformation and swelling of the metacarpal joint area; pain occurs with axial load on the finger. With a fracture of the first metacarpal bone, the thumb is adducted and slightly bent • Treatment. Accurate comparison of fragments, plaster cast with thumb abduction. For Roland's fracture - arthrodesis, transosseous remote osteosynthesis.
Fracture of the phalanges of the fingers • Causes: direct and indirect injuries • Pathomorphology: displacement with the formation of an angle open to the back • Clinical picture : deformation, shortening and swelling of the finger, subcutaneous hematoma, pathological mobility, pain with axial load • Treatment: reposition, plaster cast for 4–5 weeks, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, skeletal traction on a Beller splint, osteosynthesis with a Kirschner wire.
ICD-10 • S62 Fracture at the level of the wrist and hand
Treatment of metacarpal fractures
For the first stage of self-care, the main goals are pain relief and swelling prevention. To do this, give your hand a comfortable position, apply ice, try to hold your hand as high as possible. You should not delay seeking qualified help for more than 2-3 days. After taking x-rays, you can decide on treatment tactics.
Most metacarpal fractures can be treated conservatively or by closed reduction using wires. Sometimes, especially for intra-articular fractures, mini-implants are used: plates, screws, special rods.
Conservative treatment
If the displacement of the fragments is considered insignificant, then immobilization with plaster or other materials can be used. Minor displacement is a somewhat vague concept, this means that there is no large shortening, angular deformation, displacement along the articular surface, or rotational displacement. The latter is determined to a greater extent not by x-rays, but by the position of the fingers when they are bent. For metacarpal fractures, you should always ask the patient to try to make a fist to avoid crossing the fingers. A sunken knuckle or a small bump on the back of the hand is much less of a hassle than crossing your fingers.
Immobilization is applied from the proximal interphalangeal joints to the middle third of the forearm in a position of flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints of 70-90 degrees and extension at the wrist of about 45 degrees. This position is the most physiological; it is important that the fingertips remain mobile. The immobilization period is usually about 4 weeks. The most convenient, lightweight and comfortable immobilization is obtained from micro-perforated low-temperature Orfit NS plastic with a thickness of 1.6 or 2 mm.
What are the possible treatment options for brachymetacarpy and how does it work?
To lengthen the bones of the hand, there are three main options for operations: one-stage bone grafting, two-stage bone grafting and distraction osteosynthesis according to G.A. Ilizarov. The method of choice in the treatment of brachymetacarpy is the third option - distraction osteosynthesis or lengthening with a distraction device according to the method of G.A. Ilizarov. With brachymetacarpy, the shortening of the metacarpal bone always exceeds 1 cm, and one-stage bone grafting does not eliminate the shortening of the metacarpal bone by more than 1 cm at a time, so the choice of this technique for the treatment of brachymetacarpy is not the most competent decision. Two-stage bone grafting can be used to treat this pathology, however, lacking the advantages of one-stage bone grafting (only one operation and a relatively short recovery period), it has the same disadvantage - the need for bone grafting from another area. Lengthening with a distraction device allows one to avoid significant postoperative scars and does not require trauma to the donor area, despite the rather long period of wearing the device (about 3 months), and therefore this technique is the operation of choice for brachymetacarpy.
Scaphoid fracture
A fracture of the scaphoid bone, as a rule, occurs when falling on an outstretched hand, with a direct blow to the palmar surface of the hand, etc. The peculiarity of the blood supply to the scaphoid bone determines various treatment options for fractures of this bone.
Clinical picture of a fracture of the scaphoid: in most cases, examination reveals swelling in the area of the anatomical snuffbox, movements in the dorsoradial direction are limited by pain, the patient usually cannot clench the hand into a fist. Diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture includes an X-ray examination in three projections (direct, lateral and oblique), in some cases CT and MRI are performed.
Treatment of scaphoid fractures . When treating scaphoid fractures, it is used conservatively with a plaster cast (the hand is fixed for 6–8 weeks in the position of thumb abduction and dorsal extension of 150–160°). So is surgery, in case of non-union of a fracture or formation of a false joint.
Advantages of modern orthoses
Conventional plaster splints crumble and crumble; due to their low reliability, it is necessary to increase the thickness and length of the bandage. In addition, there is often no opportunity to observe the condition of the fingers, namely, pathological rotation of the finger is a sign of an improperly healing fracture.
Light and comfortable immobilizing thermoplastic splints can be used as an option for fixing the hand bones. After heating with a hairdryer, the doctor has the opportunity to model the necessary and suitable shape of the bandage in each individual case. Durable straps, soft breathable lining, anatomical placement of the splint provide maximum wearing comfort. At the same time, there is a full opportunity to monitor the healing of the postoperative wound and care for the skin of the hand and fingers.
Ease of use is of particular importance for fractures of the base of the 1st metacarpal bone, since the period of fixation of these fractures can be more than 2 months. Light plastic orthoses with fixation of the 1st finger can replace plaster for fractures of the 1st metacarpal bone. These products are lighter, more comfortable, and safer than traditional bandages. Breathable material, a reliable plastic splint, and the ability to adjust and adapt to different volumes of the limb make such orthoses increasingly popular.
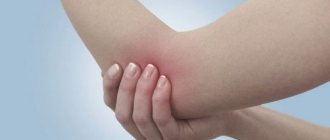
Bruises of the hand
Classic contusion of the soft tissues of the hand occurs very often in the practice of traumatologists. It is accompanied by redness of the tissue, moderate pain and swelling, and a local increase in temperature. and no serious treatment is required in this case. Specialists limit themselves to local anesthetics that help quickly relieve swelling and relieve pain.
If, in addition to a bruise, a violation of tissue integrity is detected, it is necessary to use antiseptics, and, if necessary, antibacterial agents. This will prevent the spread of infection. In some cases, it is necessary to immobilize the limb until the diagnosis is clarified.
The quality of primary antiseptic treatment directly affects the purity of infectious complications. Many patients do not pay attention to the need to disinfect the injury site before meeting with a traumatologist. After treatment with an antiseptic and applying a bandage, it is recommended to apply dry cold to reduce the risk of bleeding and the formation of a large hematoma.
Lunate fracture
A fracture of the lunate bone in most cases occurs from a fall on the hand, which is abducted to the ulnar side.
Clinical picture. Upon examination, swelling of the soft tissues in the area of the wrist joint is revealed; retraction in the area of the third metacarpal bone can be detected when the hand is clenched into a fist. With axial load, pain is detected in the third and fourth fingers.
Treatment of fractures of the bones of the hand (lunate bone) is conservative - with a plaster cast for 6-10 weeks, in some cases surgically.
First aid for bruises and other injuries to the hand
Immediately after the injury, the patient must make sure that he received a minor bruise and that no bone remains are visible at the site of the injury. The wound is washed with warm water and soap, gently dried and treated with antiseptic. Then you need to apply dry ice for 5-10 minutes. After this time, the hand must be examined again, finger activity and range of motion checked.
In case of damage to the hand with a violation of the integrity of the skin, it is necessary to apply a bandage of a sterile bandage. When applied correctly, the bandage completely covers the damaged tissue, does not hinder movement and does not cause any pain. Make sure that the bandage does not squeeze the skin. If the tissues begin to turn blue and sensitivity decreases, this indicates that the bandage urgently needs to be loosened or replaced.
Dry ice must be applied every hour for 5-10 minutes. Usually this is enough to reduce pain and prevent the appearance of a hematoma. Intermittent cold therapy is an effective treatment for minor bruises and injuries. More serious injuries require specialist consultation and a comprehensive examination.
The main tasks of first aid for hand injuries:
- immobilization of the limb to prevent the development of complications;
- stopping bleeding from a wound;
- antiseptic treatment for prophylactic purposes;
- reduction of swelling, pain, signs of an inflammatory reaction.
Patients are not always able to provide first aid for hand injuries, especially if the wound is bleeding and there is severe pain. If you cannot adequately assess the complexity of the situation and your condition, it is recommended to immediately contact medical professionals. They will carry out antiseptic treatment themselves, relieve pain and, if necessary, use immobilization.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to restore the anatomy and function of the hand.
- Antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis are treatment options for open fractures according to standard guidelines.
- Treatment will vary depending on the integrity of the skin (open or closed fracture), number of finger/metacarpal fractures, degree of bone fragmentation, displacement, rotation, etc.
- The general practitioner/specialist, after assessing the patient's condition, should perform gentle tests and imaging to determine whether surgery is required.
- If surgery is not required, a physical therapist will create a special splint that will keep the joint in the correct position while it heals.
Fracture of the phalanges of the fingers
Fractures of the phalanges of the fingers often occur with direct and indirect injuries. As a rule, with fractures of the diaphysis, a displacement is formed with an angle open to the rear. The clinical picture is characteristic of most fractures - swelling, deformation, subcutaneous hematoma, pathological mobility, pain with axial load. You can read about injuries to the knee meniscus, clavicle fracture and dislocation of the clavicle, and arthroscopic plastic surgery in the appropriate sections.
Treatment. Closed manual reduction is performed, fixation with plaster casts or orthoses for 4–5 weeks. In cases where the displacement cannot be eliminated conservatively, surgical treatment of the fracture is resorted to.
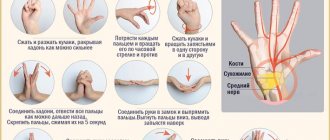
Rehabilitation after hand injuries
Rehabilitation is a mandatory stage in the treatment of hand injuries. Rehabilitation measures may include physiotherapeutic techniques, massage, spa therapy, physical therapy, warming compresses, and the use of medicinal ointments. The patient’s motor activity and quality of life in the future depend on the effectiveness of rehabilitation. It is forbidden to subject the hand to increased physical stress in the first months after the end of treatment.
In our Clinic in Yaroslavl you will receive the necessary assistance with hand injuries of any complexity. We are ready to answer all your questions and provide high-quality information support.
If you have any questions or make an appointment with a specialist, please call: (4852) 37-00-85 Daily from 8:00 to 20:00
Sign up for a consultation