Flu
– an acute viral infection caused by the influenza virus.
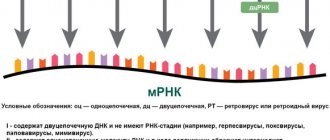
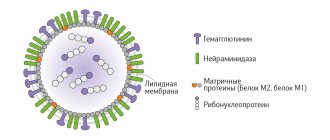
There are 3 types of the virus - A, B and C. Types A and B annually cause the development of seasonal epidemics, type C is rare and does not cause epidemics. Influenza type A is divided into different subtypes (H1N1, H3N2, H5N1, H7N9). The letters indicate the types of proteins on the surface of the virus (H - hemagglutinins, N - neurominedase), and the number indicates the order of their discovery. With the help of these proteins, the virus attaches to human cells. These H and N proteins are constantly changing, resulting in a different virus. If the type B virus affects only humans, then the type A virus circulates among people and many animals (waterfowl and poultry, horses, pigs). Currently, only 2 subtypes of the A virus are spread from person to person - H1N1 (swine flu) and H3N2. In 2015, the bird flu virus (H7N9) was identified; people were infected with it from domestic chickens, while the chickens themselves did not get sick and the virus was not transmitted from person to person. The avian influenza virus was characterized by a severe course in children.
Seasonal outbreaks are typical for places with a temperate climate during the transition to winter. Apparently, a decrease in ambient temperature leads to a decrease in immunity and a weakening of the body’s defenses, which is a predisposing factor in the development of the epidemic.
Main route of infection
– airborne. The influenza virus attaches to the surface cells of the respiratory tract, penetrates them and multiplies, leading to death. Massive cell death leads to local inflammation of the airways, weakening their protective properties. All this causes secondary complications with the development of deadly pneumonia. When you cough and sneeze, millions of viruses spread into the air and infect people.
During an epidemic, there is a high chance of getting sick while in public places. You can also become infected through household contact; the patient’s secretions on the hands and household items (table, pens and pencils, handrails in transport, door handles, telephone handsets and other gadgets) are dangerous. The virus remains active on these objects for 2 hours. That is why the basic rules for preventing infection are:
- Avoid crowded places during an epidemic;
- Wash your hands, face, and blow your nose more often and thoroughly;
- Use disposable disinfectant wipes;
- Ventilate the room;
- Wear individual disposable masks (it should be noted that the confined space they create can be a negative factor; it is recommended to replace masks every 4 hours)
Flu symptoms
Flu symptoms
are high temperature (
up to 38-39
), general weakness, lethargy, pain in muscles and joints. The so-called respiratory syndrome develops - coughing, sneezing, feeling of lack of air, sore throat. Symptoms of pneumonia (pneumonia) are rapid breathing (about 40 respiratory movements when the norm is 20), severe cough, shortness of breath, and blue discoloration of the skin. In these cases, hospitalization and inpatient treatment are recommended. To confirm pneumonia, an x-ray of the lungs is usually performed.
Flu symptoms usually last 7-10 days
, then pass on their own. Why most people have a mild form of the disease, and some have a severe form with the development of complications, scientists have not yet figured out.
Diagnosis is based on the presence of characteristic complaints (increase in temperature to 39 degrees and severe intoxication syndrome - general weakness, drowsiness, body aches, on the 2-3rd day respiratory syndrome - cough, runny nose) during the period of seasonal exacerbation. Laboratory diagnostics to determine the type of virus are not carried out in everyday life due to the lack of prognostic significance.
Ways to get a respiratory infection
Respiratory viruses are a large family of ultramicroscopic intracellular parasites. Some of them become noticeably more active during the demi-season, causing epidemics of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection). These are paramyxoviruses, picornaviruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, influenza A, B, C.
Pathogens of infectious respiratory diseases are highly contagious (infectious), but they can only enter the body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The main method of infection is aerogenic or airborne droplets. Viral particles fly through the air with droplets of liquid that escape from the mouth of a sick person when sneezing or coughing. The second method of infection is through household contact. The direct route is through a handshake with a carrier of the infection, the indirect route is through contaminated (infected) surfaces. Having picked up the virus in your hands, it is easy to carry it into your nose, your mouth is the “entrance gate” of ARVI.
Flu treatment
It is advisable to adhere to home bed or semi-bed rest. This is especially true for “business” people who constantly work and prefer to endure the flu “on their feet.” Firstly, in doing so they infect their surroundings, and secondly, the chances of developing complications with further hospitalization increase significantly.
Drugs with proven antiviral activity against influenza are oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza). However, for their effective use, they should be taken in the first hours of the development of symptoms, maximum during the first 24 hours. The World Health Organization does not confirm the effectiveness of the domestic drug Arbidol and does not recommend its use as an antiviral agent.
The same can be said about a large group of immunostimulants and immunomodulators (cycloferon, amiksin, galavit, diucifon, imunofan, thymogen, viferon, kipferon, ribomunil, bronchomunal, oscillococcinum, etc.). Their effectiveness is zero and does not exceed the placebo effect. As a rule, all of them are not registered at all and are not used in European countries and the USA. Unfortunately, lubricating the nose with oxolinic ointment also does not protect us from the influenza virus.
The vast majority of people heal on their own at home within 5-10 days. Here you can remember the old saying: “If you treat the flu, it goes away within 7 days, if you don’t treat it, it will go away within a week.”
Thus, when the temperature rises above 38.0 degrees, it is recommended to give antipyretic drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen). For children, there are forms of these drugs in rectal suppositories and powders.
For cough symptoms, drugs from the mucolytic group are used, which help thin and remove mucus. If you are bothered by a painful dry “barking” cough, you can use central antitussive drugs.
In general, in most cases of persistent cough, a symptom indicating the presence of bronchitis, in order to eliminate it and prevent the development of pneumonia, it is necessary to use penicillin or macrolide antibiotics. To do this, you need to consult a doctor.
Etiotropic drugs
Etiotropic drugs have a direct effect on the influenza pathogen. They reduce the activity of the virus and lead to its death. The most effective medications are:
- Arbidol - helps suppress pathogen activity and stimulates the immune response. Used to treat influenza A and B. Recommended for adults and children over 3 years of age. Available in the form of tablets for oral administration. The therapeutic dose and course duration are determined by the doctor.
- Grippferon is an interferon-based antiviral agent for the treatment and prevention of influenza infection. Used in the form of nasal drops. The therapeutic effect is determined by the inhibition of the vital activity of the pathogen and the creation of a protective barrier for pathogenic flora. The drug is a new release, approved for adults, children and pregnant women.
- Remantadine is a drug in the form of tablets and syrup. Effective against viruses A and B. The course of treatment is 5-14 days, depending on the patient’s condition. It has contraindications and can cause an allergic process. Used as prescribed by a doctor.
- Neovir is an anti-flu drug for injection and oral administration. It is a derivative of interferon. Has immunostimulating and antiviral effects. The maximum duration of the course is no more than 2 weeks. Not dispensed without a medical prescription.
- Tamiflu is intended only for the treatment of influenza and is not used for preventive purposes. The medicine is effective against different types of virus and is used for adults and children. The product is highly toxic and should not be used without a doctor's prescription.
When to call a doctor if you have the flu?
For children, the reason to call a doctor is frequent and difficult breathing, bluish skin tint, lethargy and drowsiness, refusal to drink and eat, repeated vomiting, high temperature (39 or more).
For adults – shortness of breath, worsening during the day, chest pain, repeated vomiting, severe weakness and dizziness, high fever.
In order for the efforts of doctors to be effective, you need to seek help from doctors in a timely manner, i.e. immediately when the above symptoms appear.
What to do if you get sick?
Fever, weakness, soreness, lacrimation are early signs of infection. When they appear, it is not recommended to leave the house. Firstly, so as not to spread viruses, and secondly, so as not to worsen your health. You can call a therapist or pediatrician by phone. In case of extreme temperatures, it is better to call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, the sick person must be put to bed and given warm tea (fruit juice). It is advisable to put a medical mask on the patient, provide him with a separate room, dishes, and hygiene items. To prevent complications, it is important to follow medical prescriptions - take medications, drink plenty of fluids, ventilate the room, eat foods rich in vitamins, phytoncides, and protein. In the first days of illness it is necessary to observe bed rest. If you have the flu, physical activity can trigger the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome, an extremely life-threatening condition.
How to avoid getting the flu?
The most effective way to specifically prevent influenza is vaccination!!! Its safety and effectiveness have been confirmed by 50 years of use by progressive doctors around the world. 70-90% of those who got vaccinated in October-November (Influvac, Influenza) can rest easy during the seasonal epidemic; they will not get the flu. Even if the types of influenza virus in the vaccine do not match the type that caused the epidemic, the severity of the disease in the vaccinated person will be several times less, and the possibility of developing complications is sharply reduced.
WHO recommends that the following groups of people be vaccinated annually:
- pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy
- children from 6 months to 5 years
- seniors 65 years and older
- people with chronic illnesses
- healthcare workers
Summarizing all of the above, we can draw the following conclusions:
- The most effective way to reduce morbidity and mortality from influenza is to get vaccinated annually
- Immunostimulants and oxolinic ointment are ineffective against influenza
- If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs should be given
- You should call a doctor if: the temperature rises above 39.0 degrees, with a constant and debilitating cough, rapid and difficult breathing, shortness of breath, vomiting, dizziness, refusal to drink and eat in children.
Vitamins to strengthen the immune system
Special blood tests help determine which vitamins the body lacks. The main marker of stable immune function is considered to be normal levels of vitamin D hormone. It enters the body with food and is synthesized by skin cells under the influence of sunlight. Considering the deficiency of ultraviolet radiation in most Russian regions, it is recommended to take the vitamin hormone in the form of a dietary supplement. To prevent respiratory diseases, the immune system needs B vitamins, ascorbic acid, and fat-soluble vitamins A and E.
Products that contain vitamins for the prevention of ARVI and influenza
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
- sauerkraut
- bell pepper
- citrus
- cranberry
- currant
- rose hip
Group B:
- nuts
- milk
- legumes
- buckwheat
- oats
- tomatoes
Tocopherol (E):
- sea buckthorn
- spinach
- broccoli
- bran
- eggs
- vegetable oils
Retinol (A):
- carrot
- green onions
- parsley
- peaches
- apricots
- melon
Replenishing vitamin reserves through nutrition alone is an impossible task. To maintain the immune system in a state of combat readiness, an additional source is needed - pharmacy vitamin complexes:
• Supradin Immuno Forte; • Doctor More; • Multi-tabs Immuno Plus; • Pediakid syrup; • Superum Echinacea Vitamin C Complex.
The most modern and effective means for strengthening the immune system can be ordered with home delivery.
Useful information about the influenza virus
The most common misconception is that flu symptoms go away after three days, but this is not at all true. Of course, the human body will fight the disease, but recovery will not come so soon. It will take three days for the body to begin to develop immunity, but only after six to seven days does it begin to fight the influenza virus.
Another common misconception among patients is that flu can be cured even without the use of special medications. Tablets must be present during the treatment of a viral disease. Of course, you can try to rely on the body’s good immunity, but do not forget about possible serious complications. Damage to internal organs, disruption of their functioning, or even death are just a few possible complications.
Sign up
| January 2022 | ||||||
| Mon | W | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Complications of influenza: what are the dangers and how to recognize them
The most vulnerable groups of the population include children under 6 years of age, the elderly, pregnant women and people with chronic diseases (diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases). It is they who often experience the flu with complications.
The most common complications include pneumonia. Complications such as viral encephalitis, meningitis, myocarditis are also possible.
If you notice any of the following symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- breathing problems (frequent, noisy, a person can only breathe in one body position);
- pain in the ribs, intensifying or appearing when coughing;
- headaches with nausea, loss of consciousness, behavioral disturbances;
- the temperature does not drop after taking various antipyretic drugs (according to the scheme);
- convulsions due to high fever.
In addition, you should call a doctor at home if the body temperature remains high on the 4th day of illness or there is a decrease to 37-37.5℃ with a subsequent rise to 38℃.
The first thing a person should do when sick is stay home. You should not work “heroically” or study while barely standing. Such behavior will not bring any benefit, but will only undermine your health and those around you. Right:
- Call a doctor at home.
- Follow the doctor's recommendations and do not self-medicate.
Prevention of influenza and ARVI
With the onset of the autumn-winter period, people spend more and more time indoors: at home, in educational institutions, clinics, entertainment centers, and shopping centers. Effective prevention of ARVI should work in different directions:
- limiting visits to crowded places, especially at the first signs of ill health;
- washing hands after places, using handkerchiefs when coughing and sneezing;
- regular ventilation of premises, air humidification;
- taking care of your health: proper nutrition, protection from hypothermia, avoiding stress.
Timely annual vaccination is considered the most effective way of prevention. Specific prevention has been developed to combat seasonal influenza. Vaccination is primarily important for vulnerable groups of the population: preschool children, pensioners and people with chronic diseases, the course of which may worsen after an infection.
When refusing vaccination “out of conviction,” you should remember that even in the absence of a clear clinical picture, a person who has contracted the flu spreads the virus among family and friends. Including those who have medical contraindications to vaccination.
Methods of nonspecific prevention include:
- regular hand washing;
- avoiding crowded places during seasonal epidemics;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- hardening;
- playing sports;
- prolonged exposure to fresh air;
- proper nutrition;
- full sleep.