Influenza - Data from the World Health Organization (WHO)
Key Facts
- Influenza is an acute viral infection that is easily spread from person to person.
- Influenza circulates throughout the world and can affect anyone of any age group.
- Influenza causes annual seasonal epidemics that peak in winter in temperate climates.
- Influenza is a serious public health problem that causes severe illness and death in high-risk populations.
- The epidemic may have a negative impact on the economy through reduced labor productivity and place undue strain on health services.
- Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection.
- Antiviral drugs are available for treatment, but influenza viruses can develop drug resistance.
Review
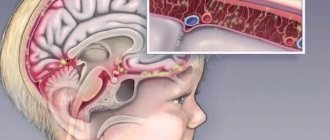
Seasonal influenza is an acute viral infection caused by the influenza virus.
There are three types of seasonal influenza - A, B and C. Influenza A viruses are divided into subtypes according to different types and combinations of surface proteins of the virus. Among the many subtypes of influenza A viruses, influenza A(H1N1) and A(H3N2) subtypes are currently circulating in humans. Influenza viruses circulate in all parts of the world. Cases of influenza type C are much less common compared to influenza types A and B. For this reason, seasonal flu vaccines contain only influenza A and B viruses.
Signs and symptoms
Seasonal influenza is characterized by a sudden onset of high fever, cough (usually dry), headache, muscle and joint pain, severe malaise (feeling unwell), sore throat and runny nose. Influenza can cause severe illness or death in people at higher risk. The period between infection and illness, known as the incubation period, lasts about two days.
Who is at risk?
Annual influenza epidemics can have a serious impact on all age groups, but children under age two, adults age 65 and older, and people of any age with certain medical conditions, such as chronic heart disease, lung disease, or kidney disease are at highest risk of complications. , blood and metabolic diseases (eg diabetes), or with a weakened immune system.
Transmission of infection
Seasonal influenza is easily transmitted and can spread quickly in schools, nursing homes, businesses and cities. When an infected person coughs, infected droplets become airborne. Another person can inhale them and become exposed to the virus. The virus can also be transmitted through hands infected with the virus. To prevent transmission, people should cover their mouth and nose when coughing with a handkerchief and wash their hands regularly.
Influenza has a global prevalence, with annual incidence rates estimated at 5%-10% among adults and 20%-30% among children. The disease can lead to hospitalization and death, mainly among high-risk groups (very young children, the elderly or chronically ill people).
Prevention
The most effective way to prevent the disease or its severe consequences is vaccination. Safe and effective vaccines have been available and used for more than 60 years. In healthy people, the influenza vaccine may provide moderate protection. However, among older adults, the influenza vaccine may be less effective at preventing illness, but may reduce the severity of illness and reduce complications and death.
Vaccination is especially important for people at higher risk of developing serious flu complications and for people who live with or care for people at high risk.
WHO recommends annual vaccination for the following population groups:
- pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy;
- children from 6 months to 5 years;
- seniors 65 years and older;
- people with chronic diseases;
- healthcare workers.
Influenza vaccination is most effective when circulating viruses closely match those in the vaccine. Influenza viruses are constantly changing, and the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network (GISN), a partnership of National Influenza Centers around the world, monitors influenza viruses circulating in people.
For many years, WHO has updated its vaccine composition recommendations twice a year, targeting the 3 most common circulating virus types (two subtypes A and one subtype B of influenza viruses).
World Health Organization (WHO) Fact Sheet No. 211 March 2014
Vaccine INFLUVAK® (Influvac)
Manufacturer: Solvay Biologicals BV, Netherlands
Influenza vaccine, subunit, inactivated
Dosage form:
suspension for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration
Compound:
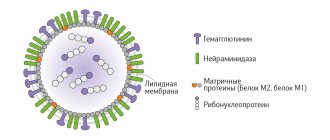
Influvac® is a trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine consisting of surface antigens (hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA)) of influenza viruses type A and B grown in chicken embryos. The antigenic composition of the influenza vaccine is updated annually according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization.
Active substances:
One dose of the vaccine (0.5 ml) contains GA and NA of the following viral strains:
| A/Brisbane/59/2007 / IVR-148, similar to A/Brisbane/59/2007 (H1N1) * | 15 mcg GA |
| A/Uruguay/716/2007 / NYMC X-175C, similar to A/Brisbane/10/2007 (H3N2) * | 15 mcg GA |
| B/Brisben/60/2008, similar to B/Brisben/60/2008* | 15 mcg GA |
* After the name of the strain, the name of the type recommended by WHO for the current epidemic influenza season is given.
Excipients:
potassium chloride, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride, calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, water for injection.
Immunological properties
The vaccine develops specific immunity to influenza viruses type A and B, which is fully formed, as a rule, 14 days after vaccination and lasts up to 1 year.
Purpose
Prevention of influenza in adults and children from 6 months. Vaccination is recommended for all persons and, first of all, for the following categories of the population who are at increased risk if influenza is combined with existing diseases: persons over 65 years of age, regardless of their health status; patients with respiratory diseases; patients with cardiovascular diseases of any etiology; patients with chronic renal failure; patients with diabetes mellitus; patients with immunodeficiency diseases (HIV infection, malignant blood diseases, etc.) and patients taking immunosuppressants, cytostatics, undergoing radiation therapy or receiving high doses of corticosteroids; children and adolescents (from 6 months to 18 years) who have been taking medications containing acetylsalicylic acid for a long time and, therefore, are at increased risk of developing Reye's syndrome due to influenza infection; pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. Pregnant women in high-risk categories should be vaccinated regardless of gestational age.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to chicken protein or any other component of the vaccine, severe fever or allergic reactions after previous vaccination with subunit influenza vaccines. Vaccination is postponed until the end of acute manifestations of the disease and exacerbation of chronic diseases. For mild ARVI, acute intestinal and other diseases, vaccination is carried out immediately after the patient has established a normal temperature.
Directions for use and dosage
Dose for adults and adolescents (from 14 years of age):
0.5 ml.
The vaccine is administered once. Dose for children from 6 months.
up to 3 years: 0.25 ml.
Dose for children from 3 to 14 years:
0.5 ml. The vaccine is administered once. For children who have not previously had influenza and have not previously been vaccinated, it is recommended that the vaccine be administered twice with an interval of 4 weeks. Patients with immunodeficiency are recommended to administer the vaccine twice with an interval of 4 weeks.
Mode of application.
Immunization is carried out annually in the autumn. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly or deeply subcutaneously.
Interaction with other drugs and other forms of interaction
Influvac® can be used simultaneously with other vaccines. In this case, vaccines should be administered to different parts of the body with different syringes.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Current experience shows that Influvac® does not have a teratogenic or toxic effect on the fetus. The Influvac® vaccine can be used during lactation.
Side effects
The vaccine has a high safety profile; allergic reactions, headaches, and decreased platelet levels in the blood are rarely observed. Local reactions may be observed: redness, swelling, pain, hardening at the injection site. There may be a short-term increase in temperature and malaise. Symptoms usually go away on their own without treatment.
Influence on the ability to drive a car and control machines and mechanisms
Influvac® does not affect the ability to drive a car or use machines and mechanisms.
Incompatibility
There are no known cases of incompatibility of Influvac® with other drugs.
Description
Immunization with Influvac vaccine prevents diseases caused by influenza A and B viruses and related strains. This vaccine does not contain live viruses. It is adapted to the mutations of influenza viruses that occur annually.
Children aged 6-36 months are given this vaccine in a dosage of 0.25 ml. Children over 3 years of age, adolescents and adults are given 0.5 ml of Influvac to prevent influenza. The seroprotective level of antibodies required to prevent the development of the disease is achieved within 10 days after vaccination. In this case, immunity lasts for 6-12 months. If a person has already been infected with the influenza virus when the vaccine is administered, the drug does not provide protection against the development of this disease.
Influvac, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly; subcutaneous administration is possible. The dose for adults is 0.5 ml, which is administered once. Persons with immunodeficiency are administered twice with an interval of a month. For children - 0.25 ml (6 months-3 years) and 0.5 ml (3-14 years) once. For those who have not previously been sick or vaccinated, it is administered twice at an interval of a month.
Before administration, warm the drug to room temperature, shake the syringe well, remove the cap and remove air from the syringe. During vaccination, it is necessary to have anti-shock medications. Immunization is carried out in the fall.
Special conditions
Influvac does not prevent upper respiratory tract diseases that are caused by viruses other than the influenza virus. This vaccine should be administered deep under the skin or intramuscularly. Under no circumstances should this drug be administered intravascularly. Therefore, the injection must be done with extreme caution to avoid the drug entering the vascular bed. The injection should warm to room temperature before administration. After vaccination, a person must remain under medical supervision for 30 minutes.
Additional Information
Is it possible to purchase Influvac from us or where to buy Influvac in Moscow?
Family Medical does not sell the Influvac vaccine, we provide vaccinations.
Where to get the Influvac vaccination in Moscow?
You can get vaccinated with Influvac at the Family Medical Center, the Influvac vaccine is available. Vaccination requires a mandatory examination before vaccination, the vaccination itself and observation after vaccination.
Call us, we will tell you everything in more detail
PricesSpecialistsSign upContacts
| Examination before vaccination | |
| Examination by a doctor before vaccination | 1600 |
| Name of service | |
| Vaxigrip - flu vaccination | 1000 |
| Influvac - flu vaccination | 1000 |
| Ultrix - flu vaccination | 1000 |
| Ultrix Quadri - flu vaccination | 1000 |
Call us, we will tell you everything in more detail
Drug interactions
The effectiveness of this vaccine may be reduced during immunosuppressive therapy and if the vaccine recipient has an immunodeficiency. This medicine should not be mixed with other medicines as its compatibility with other medicines has not been studied.
Immunization with Influvac can be done together with other vaccines, but injections must be given in different parts of the body. It should be borne in mind that the side effects of each of the vaccines administered to a person may be more acute.
Efficiency of Influvac
The Influvac vaccination is considered highly effective: more than 90% of those vaccinated receive a high level of immune protection for 12 months. To date, this vaccine is the most well studied. With its use, hundreds of studies have been conducted around the world, including the Russian Federation, in which patients of different ages with various histories of diseases took part.
The composition of the vaccine is updated annually in accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization, which identifies the viruses that are most active in the current period.
Influvac® is a subunit trivalent vaccine containing exclusively influenza surface antigens that have been specially purified and are responsible for creating immunity against influenza.
The drug contains no preservatives, which eliminates the development of allergic reactions and severe tolerability of the drug. Compared to split vaccines and whole virion preparations, Influvac is safer, but no less effective.
This became possible due to the fact that, unlike them, it does not contain elements of the lipid shell of the virus, group and internal antigens. They do not take part in the formation of immunity, but are quite capable of causing severe reactions to the vaccine.
From the second trimester, Influvac can be used even for pregnant women, while split vaccines and whole virion preparations can only be used if the risk of disease is high.
Indications
The indication for use of this vaccine is the prevention of influenza. Vaccination with this drug is recommended before the start of the epidemic influenza season. This vaccine can be used to immunize children from 6 months of age. Annual prevention of influenza using this vaccine is especially recommended for people who are in the following risk groups:
- age over 65 years;
- age from 6 months to 18 years;
- patients with chronic diseases of the respiratory system (including bronchial asthma), chronic renal failure, metabolic disorders (including diabetes mellitus);
- patients receiving radiation therapy, taking cytostatics or corticosteroids;
- patients with immunodeficiency conditions caused by diseases or medications;
- medical workers;
- schoolchildren and students;
- family members of persons at risk for influenza;
- children and adolescents who undergo long-term treatment with drugs containing acetylsalicylic acid.
Vaccine Influvac
Influvac (Ifluvac) is a vaccine for the prevention of influenza . It is a trivalent subunit inactivated influenza vaccine, consisting of surface antigens (hemagglutinin /HA/, neuraminidase /NA/), cultured on chicken embryos of healthy chickens, influenza viruses type A and B. The antigenic composition of the influenza vaccine is updated annually according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization.
The vaccine forms the development of specific immunity to influenza viruses type A and B, which usually occurs 14 days after immunization and lasts up to 1 year.
Indications for use of the drug INFLUVAK® Prevention of influenza in adults and children over 6 months. Vaccination is recommended for all individuals and, above all, for the following categories of the population who are at increased risk if influenza is combined with existing diseases: patients over 65 years of age, regardless of their health status; patients with respiratory diseases, including bronchial asthma; patients with cardiovascular diseases of any etiology; patients with chronic renal failure; patients with chronic metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus; patients with immunodeficiency diseases and patients receiving immunosuppressants, cytostatics, radiation therapy or corticosteroids in high doses; children and adolescents aged 6 months to 18 years who have been receiving medications containing acetylsalicylic acid for a long time and, therefore, are at increased risk of developing Reye's syndrome due to influenza infection.
Dosage regimen Adults and adolescents 14 years of age and older - 0.5 ml once. The dose for children aged 3 to 14 years is 0.5 ml once. Dose for children over 6 months of age. up to 3 years - 0.25 ml once. For children who have not previously been vaccinated, it is recommended to administer the vaccine twice with an interval of 4 weeks. Immunization is carried out annually in the autumn.
Rules for administering the vaccine Before administration, the vaccine must be warmed to room temperature. Shake the syringe immediately before injection. Then remove the protective cap from the needle and remove air from the syringe by holding it in a vertical position with the needle up and slowly pressing the plunger. When administering a dose of 0.25 ml, the movement of the syringe piston is stopped at the moment when its inner surface reaches the lower edge of the needle lock. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly or deeply subcutaneously. The injection should be carried out with caution to avoid the drug entering the intravascular bed. It is strictly forbidden to administer the drug intravenously!
Side effects From the central nervous system: often - headache. * Dermatological reactions: often - increased sweating. * From the musculoskeletal system: often - myalgia, arthralgia. * Local reactions: redness, swelling, pain, induration *, ecchymosis. Other: often - increased body temperature, malaise, chills, fatigue. * - reactions usually go away within 1-2 days and do not require treatment. Adverse reactions during post-marketing surveillance From the hematopoietic system: transient thrombocytopenia, transient lymphadenopathy. Allergic reactions: manifestations of allergic reactions; in some cases - angioedema, anaphylactic shock. From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: neuralgia, paresthesia, convulsions, encephalomyelitis, neuritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome. From the cardiovascular system: vasculitis in very rare cases accompanied by transient renal dysfunction. Dermatological reactions: generalized skin reactions, including itching, urticaria or nonspecific rash. Contraindications to the use of the drug INFLUVAK®: hypersensitivity to chicken protein or other components of the vaccine; hypersensitivity reactions to substances that may be contained in residual quantities - formaldehyde, CTAB, polysorbate-80 and gentamicin.
Vaccination of patients should be postponed until the end of acute manifestations of the disease and exacerbation of chronic diseases. For mild ARVI and acute intestinal diseases, vaccination is carried out immediately after the temperature has normalized.
Use of INFLUVAK® during pregnancy and breastfeeding Data on the use of the vaccine in pregnant women are limited. Available experience shows that Influvac does not have a teratogenic or toxic effect on the fetus. Influvac can be used from the second trimester of pregnancy. Pregnant women at risk should be vaccinated regardless of the stage of pregnancy. Influvac can be used during lactation (breastfeeding).
Use for renal impairment Possible use according to indications
Special instructions When carrying out vaccination, it is necessary to have all means for emergency treatment of anaphylactic shock (including epinephrine/adrenaline/, corticosteroids). In patients with endogenous or exogenous immunosuppression, the immune response may be insufficient. 1 dose of the vaccine should not contain more than 1 mcg of ovalbumin. After vaccination, it is possible to obtain false-positive results from serological tests based on the ELISA method (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) when determining antibodies against HIV (HIV1), hepatitis C, and human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV1). Laboratory diagnostics using the Western Blot method eliminates false-positive results from tests based on the ELISA method. Transient false-positive results may be due to IgM production after vaccination.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery Influvac does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate machines and mechanisms. All cases of post-vaccination complications must be reported to the national MIBP control body - FGUN, State Institute for Standardization and Control of Medical Immunobiological Preparations named after. L.A. Tarasevich Rospotrebnadzor (119002, Moscow, Sivtsev Vrazhek, 41, tel./fax: +7495-241-3922) and (tel.; fax: (495) 411-69-10).
Overdose There is no data on overdose of the Influvac vaccine.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies The vaccine in a package containing 1 syringe is available with a prescription. The vaccine in a package containing 10 syringes is distributed by medical institutions.
Conditions and periods of storage The vaccine should be stored and transported in a place protected from light at a temperature of 2° to 8°C; do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life: 1 year. The expiration date of the vaccine is June 30 of the year following the year of release. Transportation is allowed at a temperature of 25°C, but not more than 24 hours.
Project manager: Victoria Kolbineva +7 ext. 236 [email protected]
Section: Flu prevention | Manufacturer: Solvay Pharma Print | ↑ Up
Contraindications
There are the following contraindications to vaccination with Influvac:
- acute infectious disease;
- stage of exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- hypersensitivity to the substances included in the vaccine;
- allergy to egg white, which is used in the production of the vaccine;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- age up to 6 months;
- body temperature is above 37 degrees.
The effect of this vaccine on the fetus and pregnant women has not been sufficiently studied. The decision on the need to use this vaccine during lactation is made by the attending physician. For mild ARVI and acute intestinal disorders, the vaccine can be administered immediately after body temperature normalizes.
Side effects
After administration of the vaccine, the following side effects are possible:
- increased body temperature and general malaise, itching, rash, headache, redness and swelling at the site of vaccine administration - these symptoms disappear within 1-2 days;
- convulsions, vasculitis, neuralgia are manifestations that occur very rarely;
- anaphylactic shock – occurs extremely rarely.
Vaccination with Influvac may cause false positive results in serological tests when using the ELISA method, which are done to determine the presence of antibodies against hepatitis C and HIV-1, which is explained by the immune response to the vaccine.