Home prevention methods
Preventing colds should begin in the summer. The condition of the body depends on nutrition and the intake of vitamins. A healthy lifestyle and balanced diet will help support your immune system. To do this, you need to include vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, and a sufficient amount of lean meat and fish in your menu.
Traditional methods of preventing ARVI recommend medicinal plants and products with an immunostimulating effect. These include:
- ginger;
- garlic;
- onion;
- lemon;
- mint;
- echinacea;
- birch mushroom.
An effective method of preventing colds is staying hydrated. An adult needs 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day. This volume supports the functioning of the kidneys, helps them quickly filter the blood and remove toxic substances, viruses and metabolic products.
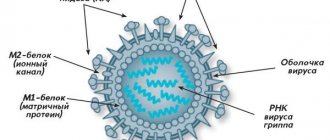
Causes of viral diseases
Each virus, entering the human body, finds exactly those cells on which it can parasitize and attaches to them. Most viruses remain latent in the body, as they are controlled by the immune system. However, when it decreases significantly, control also weakens. The virus enters the cell, divides inside it and leaves the membrane. Most often, the cell dies¹.
The process of virus division and the death of a large number of cells is accompanied by the release of toxic substances into the body. They cause inflammation, fever and other specific reactions, for example, skin rashes, the appearance of benign neoplasms on the skin or mucous membranes.
When a viral infection is activated, the immune system begins to release antibodies in response. They attach to the virus and prevent it from entering cells. However, with weak immunity or significant infection, this protection is not enough. We need antiviral drugs that are effective against the particular virus that attacks the body.
Figure 1. Classification of viruses. Image: Thomas Splettstoesser (www.scistyle.com) / Wikipedia (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Daily routine and hardening
Colds and flu can be prevented with the help of hardening procedures, which begin in the summer. In childhood and untrained people, you can wipe with a damp towel, pour cool water over your feet, gradually lowering the temperature. Hardening helps improve thermoregulation; the body will not react to hypothermia with a cold.
But hardening procedures do not give an effect immediately and only when carried out regularly. If you stop dousing, after a few weeks the body will again become susceptible to disease.
To prevent colds, it is important to follow a daily routine and avoid stress. During sleep, the hormone melatonin is produced, which is involved in regulating the function and coordinated functioning of the nervous, endocrine and immune systems. An important condition is to go to bed before 23:00, do not watch TV before bed and do not use gadgets. Melatonin is produced only in complete darkness.
Types of antiviral agents
With all the diversity of viruses, the choice of drugs with proven effectiveness is relatively small. Some of them stimulate the patient’s own immunity. Others act on the principle of antibodies, preventing infection from entering the cell. Still others block the virus at a certain stage of its life cycle. Based on their purpose, the following medications are distinguished:
- anti-influenza;
- antiherpetic;
- anticytomegalovirus;
- antiretroviral (against HIV infection);
- drugs with an extended spectrum of action (interferons, lamivudine, ribavirin).
Based on the methods of influencing a viral infection, drugs are divided into large groups of local and systemic action⁶.
- Chemotherapy drugs are the most studied and widespread. They suppress the stages of virus reproduction without significantly affecting the cells themselves.
- Interferons are distinguished by their versatility, broad action and maximum safety for the body.
- Inducers of interferon synthesis - stimulate the formation of interferon in the body and have a wide spectrum of action.
- Immunomodulators - improve the insufficient functions of immunocytes (cells of the immune system).
The World Health Organization allocates only antiherpetic, antiretroviral, hepatitis and other drugs, which include ribavirin, valganciclovir³.
There are plenty of antiviral drugs in pharmacies, but not all of them are effective. Don't get carried away with self-medication! Photo: alfexe / Depositphotos
How to avoid getting sick in the fall
When the seasonal increase in the incidence of influenza and colds begins, it is necessary to move on to active preventive measures. They are mandatory for children and adults:
- wash your hands as often as possible - after returning home, before eating, after visiting a public toilet;
- avoid large crowds of people and travel on public transport;
- do not touch your face, nose or eyes with your hands, especially outside the home;
- ventilate the apartment several times a day;
- do regular wet cleaning.
A good way to avoid getting the flu is to get vaccinated. The vaccine is approved for use in children over 6 months of age. It is recommended for patients at risk who have weakened immune systems or who frequently come into contact with other people at work. The flu shot is given at the end of September or at the beginning of October so that immunity to the virus develops within 3 weeks. But vaccination does not prevent the development of other colds.
An effective method of prevention is rinsing the nose with salt water. It helps both prevent colds and cleanse the mucous membrane of dust particles. For rinsing, you can purchase ready-made sea salt solutions. They are available in the form of a spray, which can also be used in children.
What are acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections?
Both diseases are acute inflammations of various organs of the respiratory system, caused by various infections. Acute respiratory disease - acute respiratory disease - a broader name that is used when the viral component has not been established. And ARVI is an acute respiratory viral disease - when the clinical picture is clear and it is known for sure that the infection is caused by a virus. There are several such viruses: influenza, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial infection, rhinovirus and adenovirus infection and others. Most often, the disease begins with an elevated temperature. Then it may be supplemented by headache, general weakness, fatigue, aching bones, redness of the pharyngeal mucosa, pain when swallowing, dry cough and nasal congestion. Among the troubles that accompany acute respiratory infections is the addition of a bacterial infection to the disease, which causes complications.
Medicines to prevent colds
The development of colds is prevented by special medications that help strengthen the immune system. You can increase the body's overall resistance with multivitamins. They improve metabolism, the reproduction of protective cells and accelerate tissue repair. Vitamins are taken in courses of several weeks with a break of 1 month.
Antiviral drugs effectively prevent the disease. They belong to the group of immunomodulators and immunostimulants and are available in the form of tablets, solutions and suppositories. To prevent colds in children, it is convenient to take syrup.
You can buy the following medications in pharmacies:
- Arbidol;
- Kagocel;
- Anaferon;
- Aflubin;
- Rimantadine;
- Kipferon;
- Oscillococcinum;
- Genferon;
- Viferon;
- Lycopid;
- Amiksin;
- Lavomax;
Tablets for the prevention of ARVI increase the production of your own interferon and antibodies, which are necessary to suppress the viral infection. Medicines should be used before contact with a person with a cold occurs and symptoms of the disease appear. This will prepare the body and avoid illness.
Types of viral diseases
A person comes into contact with thousands of viruses. To date, only a portion of them have been classified. They are mainly grouped according to the systems and organs they affect¹.
- Respiratory. These are diseases of the upper respiratory tract - from the nasopharynx to the lungs. These diseases are caused by influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses and others. They are transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets and cause a runny nose and cough.
- Gastrointestinal. They are transmitted orally and cause vomiting and diarrhea. Rotaviruses, astroviruses, and adenoviruses are especially dangerous for children, and noroviruses for adults.
- Exanthematous. Infection most often occurs by airborne droplets. Viruses are also carried by insects. They cause skin lesions and diseases such as measles, rubella, scarlet fever, typhoid, and chickenpox.
- Neurological. A viral infection affects the nervous system. The most well-known disease is encephalitis. The most common carriers are mosquitoes and ticks.
- Liver infections. The most common are 5 types of hepatitis. Viruses are transmitted through blood, secretions, and orally and cause severe damage to liver tissue and disruption of its functions.
- Dermatotropic. Affects the skin and mucous membranes. The most common viruses are herpes and papilloma. They are dangerous because they can cause cancer.
Do antibiotics help against viruses?
No! These medications are designed specifically to fight bacteria, while special antiviral drugs are needed to treat viral infections. Bacteria are much larger and more complex than viruses; they are microorganisms of a completely different nature.
What to do at the first sign of a cold
If it was not possible to prevent infection, you need to adopt methods that will help avoid severe disease and stop the replication of viruses. Antiviral drugs can be taken early in the course of the disease. They are effective from the moment the virus enters the body until the first signs of infection appear. Doctors recommend taking immunostimulants for 3-4 days after the onset of illness.
To protect others from infection, you need to stay at home and maintain bed rest. Rest will help the body use energy sparingly and fight infection. Ventilation of the room where the patient is located and frequent wet cleaning prevent the spread of viruses.
For early treatment, drinking plenty of warm fluids is recommended. It increases blood circulation in the kidneys, helps remove viruses and toxic metabolic products through sweat and urine. To reduce signs of inflammation, drink tea from medicinal plants: chamomile, thyme, linden, calendula. They are also used for gargling. If a sore throat begins or pain bothers you, use lozenges and other means to reduce symptoms.
At a later stage or when the condition worsens, cough is added, expectorants and tablets with antibacterial action are needed. They must be prescribed by a doctor.
How and how to treat ARVI and influenza in adults?
Regardless of the severity of the disease, all patients are recommended1:
- bed rest;
- easily digestible food;
- drinking plenty of fluids.
If you have a cold, you should try to drink more fluids throughout the day. You can drink weakly brewed tea with milk, honey, jam, as well as rosehip decoction, freshly prepared fruit and berry juices, compotes, alkaline mineral waters 1.
At the same time, it is important to remember what not to do during ARVI. You should not drink alcohol1, intense physical activity1 is unacceptable, and you should also not ignore the doctor’s recommendations and self-medicate1.
Only a doctor can decide what adults should take and what regimen they should take. And timely initiation of therapy significantly improves the prognosis10.
For ARVI in adults, the doctor may prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- Antiviral drugs
are most effective when prescribed in the first 2 days of acute respiratory viral infections, including influenza9. - Antipyretics
- taken when body temperature rises above 38.5 ° C or severe discomfort (headache, muscle-joint pain, impaired consciousness)1. - Vasoconstrictor drops and sprays
- recommended for use for a runny nose for no longer than 5 days1. - Means for relieving sore throat
- local anesthetics in the form of spray, lozenges, lozenges1.
If necessary, the doctor may additionally prescribe mucolytics, antitussives and bronchodilators. The need for antibacterial therapy can only be assessed by a specialist1.
Antibiotics are not used for influenza; the doctor prescribes them when he assumes that the causative agent is not a virus, but a bacterium, or in case of bacterial complications.1.
Anaferon®9, a domestic drug used to treat ARVI for more than 15 years, has antiviral activity against respiratory viruses, including influenza viruses. The active ingredient of lozenges is technologically processed antibodies to gamma interferon11.
The use of the drug as part of complex therapy helps reduce the duration of the main symptoms of the disease by more than a third compared to placebo12. Studies show that more than half of patients with a confirmed diagnosis of ARVI during treatment with Anaferon® recover on the 4th day, which is 2 times more compared to placebo therapy12.
For ARVI, the drug acts as follows11:
- reduces the concentration of viral particles in tissues;
- stimulates the production of interferons (the body’s own proteins that limit the spread of viruses);
- activates all parts of the immune system;
- enhances the production of antibodies (secretory IgA).
The favorable safety profile allows the use of Anaferon® by elderly people and people with concomitant diseases. According to clinical studies, the drug is well tolerated, and there are no cases of drug incompatibility11.
Up to contents
How to bring down the temperature when you have a cold
An early sign of a cold is a rapid rise in temperature to 38-39°C. A distinctive feature is that with the flu it rises to 41°C, and there are no other symptoms. To reduce the temperature, you can use tablets, but at the stage of a slight rise, various methods of cooling the body are often sufficient.
In young children, fever can be reduced by removing clothes and diapers. Heat transfer through the skin will increase and the child will cool down. But this method works well if it is applied early, before the temperature rises to 38.5°C. Later it is used as an auxiliary method.
For children and adults, wiping the forehead, neck, and elbows with a damp cloth is effective. But if this does not help and the temperature continues to rise, you need to take an antipyretic drug. Children are allowed drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen; others can use any medicine from this group.
Colds begin after a cold snap. Using prevention methods, you can reduce the risk of developing pathology. But in order not to delay the start of treatment and avoid complications, it is better to buy the main drugs for prevention in advance.
Oseltamivir
The trade names of this flu medicine are Tamiflu, Nomides, Oseltamivir phosphate. Oseltamivir acts on the influenza virus in the same way as the previous drug. When using it, the illness lasts 2 days less. Oseltamivir can be prescribed to adults and children over 1 year of age. For children from one to 8 years old, it is better to use a suspension.
Possible side effects include dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Contraindications to the use of oseltamivir: individual intolerance and renal failure. This flu medicine is available by prescription.
Oseltamivir
Sources
- Virology. Methodological materials: Textbook. method. aid for students biol. fak. / Authors-comp. E. V. Glinskaya, E. S. Tuchina, S. V. Petrov. — Saratov. — 2013.
- Mechanisms of transmission of pathogens and ecological and epidemiological classification of infectious and parasitic human diseases. / V. I. Sergevnin. — Epidemiology and vaccine prevention. — No. 2(63). — 2012.
- Approximate list of essential medicines. 21st list, 2022—Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe, 2020.
- Samoshchenkova I.F., Garankina R.Yu., Bobkova E.A., Omelchenko A.A. Study of the range of antiviral drugs with in-depth product analysis of the drug Normomed // Bulletin of the North-Eastern Federal University named after. M.K. Amosova. Series "Medical Sciences". — 2022. — No. 1 (22). — P. 41-51.
- Telnova E.A., Shchepin V.O., Zagoruichenko A.A. Antiviral drugs: from creation to the present time // Bulletin of the National Research Institute of Public Health named after. ON THE. Semashko. - 2022. - No. 4. - P. 108-119.
- Shestakova I.V. Antiviral drugs // Infectious diseases: news, opinions, training. - 2015. - No. 1. - P. 77-86.