A person makes many movements with his hands every day. The hands are the most functional part of the upper limb; they rest only when a person sleeps. It is not surprising that with increased activity, the hands experience greater stress and become susceptible to various injuries and diseases. Pain occurs of various types, and sometimes the patient does not know what to do or how to help himself in such a situation.
If a person’s arm hurts from the elbow to the hand, then this can be caused by a number of diseases or injuries. Discomfort in the hand appears for the following reasons:
- inflammation of joint elements;
- intense stress on the hands;
- pathological processes in muscles and bones;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- mechanical damage in the elbow or hand;
- spinal pathologies.
Each of these diseases provokes unpleasant painful sensations in the upper extremities. To cope with pain, you first need to find out the specific cause of the discomfort.
Arthrosis of the elbow joint
Arthrosis of the elbow joint is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology, which has a second name - epicondylosis. A typical place for the appearance of pathological changes in cartilage tissue is the supracondylar zone. During the course of the disease, the joint space between the elements of the joints significantly decreases and pain occurs when moving the arm.
To be fair, it is worth noting that arthrosis quite rarely affects the elbow joint. Much more often, signs of arthrosis can be found in the knee and hip joints. However, patients over forty-five years of age are at constant risk of developing elbow arthrosis if they do not spare their hands.
REFERENCE! Arthrosis of the elbow joint usually occurs in athletes and those people whose profession involves stress on the upper limbs.
The reasons for the development of arthrosis can be identified as follows:
- elbow injuries, both fresh and old;
- metabolic disorders leading to a deficiency of nutrients needed by tissues;
- lack of fluid in the body;
- the presence of a focus of rheumatoid arthritis in the body, which can spread to the elbow joint;
- inflammatory processes in the joint capsule;
- the influence of external factors on a person;
- serious intoxication;
- hereditary factor;
- age-related degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- frequent cases of hypothermia, previously suffered from acute respiratory viral infections.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the elbow joint are typical. There are three stages of elbow arthrosis. At the initial stage, the pathology is not so pronounced, so you can only notice episodic discomfort that occurs only from time to time. As the pathology progresses, the pain will intensify and be present even at rest. When moving the elbow, patients hear a crunching sound. It is caused by rough friction of the joint elements of the left or right hand against each other.
As pathological processes worsen, the elbow joint is affected by spines, and muscle spasms occur more and more often. All these signs provoke difficulty in movement in the joint. During diagnosis, the doctor checks the joint for mobility. Thompson's syndrome and Wetl's syndrome are most often found. As osteophytes grow, deformation of the elbow joint can be noticed. In this case, a diagnosis of “deforming arthrosis” is made.
Deforming arthrosis occurs in approximately half of all cases of arthrosis. A characteristic complaint of patients with deforming arthrosis is the appearance of severe pain in the elbow and its increase during the course of the pathological process. Intra-articular osteophytes that cause pain in the arm are removed surgically.
Epicondylitis is a complication of arthrosis. An inflammatory disease. The epicondyles, which experience significant mechanical stress, are predominantly affected. Pain is felt between the elbow and hand, and the shoulder joint suffers. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by pain in the upper limb when moving the shoulder, when shaking hands, when trying to clench or unclench the hand.
Conservative treatment of the disease is possible only at the initial stage of arthrosis development. Patients are advised to spare the hand, relieve it from increased stress, and also recommend a number of chondroprotectors (Structum, glucosamine sulfate, Ostenil, Artra) to restore cartilage tissue. When an inflammatory process occurs, the drugs Ortofen, Diclofenac, Voltaren are recommended.
In advanced cases, if conservative therapy does not produce results, surgical treatment is performed. After surgery, patients are recommended to perform exercises to develop the elbow joint and maintain the usual range of motion. Physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed for rehabilitation after surgery.
How to prevent shoulder pain
To prevent pain from occurring, the following conditions must be observed:
- lead an active lifestyle, move more, engage in feasible sports;
- Avoid prolonged periods with your arms raised above your head, as well as movements associated with unilateral load on the shoulder joint; At risk are weightlifters, tennis players, and miners; If a representative of one of these groups feels persistent pain in the shoulder, perhaps he should change his occupation or at least reduce his exposure to harmful factors as much as possible.
Gout
Of course, all people have heard about gout - a painful disease with a typical bunion on the foot. But few people know that the elbow joint is also susceptible to gout, which means that the pathological process can develop here too. The disease is associated with the accumulation of urate in the elbow joint.
The immediate cause of gout is metabolic disorders characterized by excess uric acid in the body. It is deposited in any joints, including the elbow. With a significant amount of salts, patients develop characteristic gouty bumps and granulomas, and after this an inflammatory process develops.
At the initial stage, gout does not make itself felt, and attacks are felt already when the inflammatory process joins. Usually the disease occurs in males over forty years of age, but gout of the elbow can also develop in women during menopause.
Risk factors for the development of elbow gout are poor diet, alcohol abuse, physical inactivity, excess weight, metabolic diseases, and diabetes. When exposed to these factors, the disease worsens. The elbow begins to hurt, turns red, and pain appears when straightening and bending the arm. Characterized by the presence of muscle pain. Patients try to spare their hand.
Attacks of gout disappear on their own within a week, but with chronic, protracted development of the disease, complications can arise. Patients develop so-called tophi - nodular neoplasms that can take the form of fistulas.
Treatment of the disease consists of normalizing uric acid metabolism. Among the drugs of conservative therapy, Allopurinol and Uralit showed themselves to be the best. For symptomatic therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. For severe pain, Kenalog is injected directly into the elbow joint. Treatment is carried out against the background of mandatory diet.
Diagnostic methods
To differentiate pain in the shoulder of the left arm, hardware diagnostic methods are used:
- Radiography . Determines severe damage, curvature, and other bone deformations.
- Arthrography . Detects joint diseases.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Aimed at identifying pathological processes in the soft tissues of the shoulder girdle.
- Computed tomography (CT) . Diagnoses structural changes and functional condition of the shoulder joint of the left hand.
X-ray will reveal obvious damage to the shoulder
To determine inflammatory diseases, a CCA (general clinical analysis) of blood is prescribed.
Bursitis
The causes of pain in the arm from the elbow to the hand itself can be caused by the development of bursitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the synovial bursa located in the elbow joint. Since the neurovascular bundle is located in close proximity, the pain with bursitis is quite noticeable; patients feel it not only in the elbow, but also in the muscles of the arm.
Typically, bursitis is diagnosed in young and middle-aged people who may overload their upper limbs. Athletes and loaders suffer from bursitis; the disease is aggravated by existing arthritis or gout.
IMPORTANT! Bursitis, as such, is not particularly dangerous, but it can lead to a number of complications - osteomyelitis, lymphadenitis, phlegmon.
Inflammation of the bursa is associated with increased mechanical stress on the elbow joint. In response to mechanical irritation, fluid production in the synovial bursa increases, and with intra-articular hemorrhage, hemorrhagic bursitis is formed. Pain appears in the forearm and wrist.
When pathogenic microorganisms penetrate inside, the contents of the synovial bursa suppurate, which threatens the transition of the inflammatory process to the surrounding tissues. Prolonged, low-grade inflammation can be complicated by adhesions, necrotic foci and calcification.
The causes of bursitis may be the following:
- mechanical elbow injuries;
- salt deposition in the joint;
- daily microtraumas;
- the presence of arthritis of the elbow joint;
- erysipelas;
- stagnation of blood and lymph;
- diabetes;
- immunodeficiency states;
- metabolic disorders;
- allergic reactions of the body to foods, toxic substances;
- autoimmune processes.
A typical symptom of serous non-purulent bursitis is swelling in the elbow area; you can visually notice an enlargement of the elbow and the appearance of a soft lump on it. In most cases, acute bursitis ends in cure of the disease, but with residual effects there is a risk of transition to the chronic stage.
With chronic bursitis, patients do not have the typical swollen elbow, but patients complain of continued pain when moving, hardening in the elbow joint. Patients can flex and extend their arm almost exactly as they did before the disease.
If the bursitis is septic, then the symptoms become more complicated - characteristic twitching sensations appear in the elbow, directly proportional to the intensity of the pathological process. Redness of the skin is detected. The elbow becomes hot when touched, the skin at the site of bursitis becomes shiny and acquires a characteristic shine. Movement of the upper limb is limited, the muscles of the forearm become stiff and twitchy. Any attempt to straighten or bend the arm causes pain.
Diagnosing bursitis is not difficult for a surgeon. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe a puncture. Content analysis will help determine sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Treatment of non-purulent bursitis is conservative. Patients are given a tight bandage to immobilize the elbow, and cold can be applied to reduce swelling. It is recommended to take one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For purulent bursitis, the patient is punctured, the purulent contents are removed and the cavity is washed with antibacterial liquids. In some cases, drainage is installed. If therapy is ineffective or frequent relapses, it is recommended to remove the bursa.
Treatment
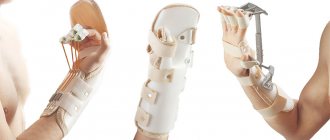
In a condition where the arm hurts when raising the arm, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis. If it is discovered that this symptom indicates diseases of the internal organs, then treatment of the underlying disease is carried out. Rheumatoid arthritis is treated by a rheumatologist. In case of injuries, the joint is immobilized using special devices to ensure tissue regeneration, or surgery is performed. In the acute phase of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, drug therapy is carried out:
- To relieve inflammation and pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in various forms: injection solutions, capsules, tablets, ointments.
- Glucocorticosteroids are used to relieve autoimmune inflammation and prevent joint destruction. They can be inserted directly into the joint cavity.
- To eliminate muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed.
- To activate blood circulation in the affected shoulder joint, warming ointments are used.
If the inflammatory disease is caused by an infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. For osteoarthritis, the doctor prescribes chondroprotectors; for neurological diseases, B vitamins are used.
After the inflammatory process has been relieved, massage and various physiotherapeutic procedures are added to the treatment: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, electrical myostimulation, etc. During the period of remission, so that the shoulder no longer hurts when raising the arm, it is recommended to regularly perform a set of physical exercises.
If it is impossible to solve problems with the shoulder joint with therapeutic methods, surgical treatment is indicated. It can be prescribed to restore the integrity of ligaments and bones after injuries, remove pathological fluids by puncture, replace the affected joint with an endoprosthesis, etc. The most modern and effective joint treatment can be performed in our clinic.
Traumatic injuries
Elbow injuries occur quite often. Signs of traumatic injury are obvious - patients have pain in their arm from the elbow to the wrist, the pain can rise higher to the shoulder. Severe discomfort prevents you from making normal hand movements.
With a dislocation or fracture, the elbow joint may visually shift; with a fracture of the wrist bone, these symptoms are observed along the path from the wrist to the elbow at the site of direct injury. The hand swells, a hematoma appears, and an open fracture is accompanied by bleeding and damage to the integrity of the soft tissues.
The types of traumatic injuries of the upper limb are as follows:
- bruise - damage to the hand, in which the blow falls on soft tissues, but their integrity is not damaged;
- compression of soft tissues - prolonged compression of muscles, resulting in necrosis;
- damage to the ligamentous apparatus - this can be sprains or complete ruptures of the ligaments;
- dislocation - displacement of bone elements relative to each other;
- fracture - a violation of the integrity of the bone.
In some cases, fractures are complicated by other injuries, for example, a fracture of the forearm or collarbone, or spinal bruise, which greatly complicates the treatment of injuries. Therapy is either conservative or surgical, depending on the type of damage.
What to do if your left shoulder hurts?
If your shoulder hurts after physical activity, warming medications for external use will help eliminate the symptoms. For constant pain, lumbago, or heaviness in the shoulder area, treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment with drugs
To eliminate pain, topical medications, tablet analgesics and muscle relaxants are used.
Ortofen is an anti-inflammatory drug that relieves pain
Table: Medicines for external use
| Group of drugs | Action | Indications | External means |
| anti-inflammatory | relieve inflammation, eliminate pain | glenohumeral periarthrosis, myalgia, bursitis, synovitis, rheumatism, neuritis, capsulitis | Indomethacin, Viprosal, Diclofenac, Voltaren, Ortrofen |
| warming and locally irritating | normalize blood circulation, restore muscle fibers, improve innervation, structure of nerve fibers, relieve pain | bruises, dislocations, osteochondrosis, sprains, neuralgia, myalgia, muscle spasms, | Turpentine ointment, Viprosal, Nayatox, Finalgon, Capsicam, Apizartron, Arthro-Active |
| chondroprotectors | regenerate joint tissues, inhibit joint destruction | arthrosis, rheumatism, fractures and cracks of bones | Dona, Chondroflex, Teraflex, Honda, Sabelnik |
| painkillers | eliminate symptoms | pain syndrome of various etiologies | Nise, Ketonal, |
Tramadol is a non-steroidal pain reliever
Tablets for pain relief:
- muscle relaxants : Mydocalm, Tolperil, Tisanil
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Tramadol.
For destructive diseases, injections of hormonal drugs, hyaluronic acid, and ampoule chondroprotectors are given into the shoulder joint.
Folk remedies
It is permissible to treat pain syndrome at home in the absence of displaced bone fractures or suppuration in the joint capsule.
An infusion of dried thyme and vodka is used for rubbing
Recipe examples:
- Dried thyme herb - 3 tbsp. l. pour 200 ml of vodka over the top. Keep in a dark place for 14 days. Use as a daily rub.
- Melt 100 g of lard and cool. 2 tsp. Grind dried St. John's wort and cinquefoil into powder. Mix lard with herbs, add 1 tsp. ground red pepper. Stir thoroughly. Rub the sore spot before going to bed. Store the ointment in the refrigerator.
- Mix honey (liquid), dry mustard and sunflower oil in equal parts until smooth. Heat the resulting pulp, place it on gauze, and apply it to the sore area. Secure the top with cling film and a warm scarf. Carry out the procedure at night.
- Wash the burdock leaves, dry them, and generously spread the dark side with liquid honey. Apply to the shoulder, secure with a dressing.
- 2 tbsp. Pour tablespoons of dry cinquefoil grass into a liter thermos and brew with boiling water. Leave for 3 hours, filter and drink in small portions between meals.
- Sew small bags from natural fabric and fill them with coarse salt. Before the procedure, heat the bags in a frying pan to the optimal temperature. Apply and keep until completely cool.
The use of honey is contraindicated if you are allergic to bee products. Before warming the shoulder for bursitis and synovitis, make sure there is no suppuration.
Other therapies
Auxiliary methods of therapy include massage, physiotherapy, and physical therapy.
Massage sessions
A warming massage relieves tightness, warms up muscles, accelerates blood circulation and lymphatic drainage.
Massage sessions will relieve tightness; it is recommended to visit a specialist even in the absence of pain
Sessions are contraindicated in the acute period of the disease, with purulent inflammation, or with bone damage. It is better to entrust the procedure to a specialist, especially if the child’s shoulder hurts.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy speeds up the rehabilitation process after injury and helps prevent relapses of chronic joint diseases.
For the shoulder girdle use:
- electrophoresis - exposure to direct voltage current in combination with medicinal solutions;
- magnetotherapy - the use of magnetic waves of constant and alternating fields;
- ozokerite – thermal effect of natural material – natural wax.
Laser treatment is considered the most effective. Laser therapy sessions in most clinics are carried out on a paid basis.
Exercise therapy
A referral for exercise therapy (physical therapy) is prescribed by the attending physician. Group classes are held in the clinic.
The doctor refers you to exercise therapy if necessary.
You can independently supplement treatment with special exercises to restore the function of the shoulder girdle.
Shoulder surgery
Surgical intervention is carried out:
- for severe injuries (fractures, dislocations);
- for purulent inflammation (synovitis, bursitis);
- for grade 3 arthrosis, joint replacement is performed.
The type of operation (arthroscopy or arthrotomy) is determined by the surgeon individually in each individual case.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis of the upper extremities is much less common than the lower extremities, but brings no less suffering to the patient. The disease begins with the deposition of small amounts of lipids on the walls of blood vessels. In the initial stage of development of atherosclerosis, these symptoms are invisible, but when more than half of the lumen of the vessel is blocked, patients begin to feel obvious signs of the disease.
IMPORTANT! A complication of the disease is blood clots. Blood elements are retained in lipid formation, which provokes a blood clot. When a blood clot breaks off, it easily reaches vital vessels and can lead to death.
If the vessels of the upper extremities affected by cholesterol plaques do not allow sufficient blood to pass through, then the nervous and muscle tissues suffer. Symptoms of atherosclerosis include the following:
- In the first, compensated stage, patients experience only minor deviations in health. Hands can freeze in the cold; they are overly sensitive to temperature changes.
- In the second stage, symptoms become more pronounced. The reaction to cold may be accompanied by cramps in the hands. They quickly get tired of even minor work.
- The third stage is manifested by a significant deterioration in the functioning of the upper extremities. The skin on the arms and in the area of the hands becomes thinner, the vessels become translucent and characteristic blue vessels protrude. The patient suffers from pain in the arms from the hand to the elbow, cramps, and numbness.
- In the last stage, severe symptoms of the disease appear. Atherosclerosis of blood vessels leads to tissue death and gangrene. Hands become more and more blue and cold. Trophic ulcers may appear. It is extremely difficult for patients to perform the most common operations, and the pain appears not only in the hand area - the forearm and the area under the collarbone hurt.
As a treatment for atherosclerosis, patients will be recommended tableted blood thinners. Doctors insist on including ten minutes of hand exercises in your daily schedule. It is necessary to give up bad habits, normalize weight if necessary, and take vitamins.
Which doctor should I contact?
Pain in the shoulder muscles due to intense loads or poor positioning of the body goes away on its own and does not require a visit to the doctor.
If pain occurs, consult a physician first
- If pain suddenly appears in the left shoulder area, caused by dislocations, bruises, or fractures, a traumatologist will help.
- Finding out the cause of pain, both during movement and at rest, is the therapist’s task. If necessary, refer the patient for examination to specialized medical specialists.
- Discomfort in the shoulder and under the collarbone, accompanied by stabbing pain in the heart, burning behind the sternum, high blood pressure, shortness of breath requires attention from a cardiologist.
- Spontaneous shooting in combination with aching pain may indicate myalgia or neuralgia; treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
- The treatment of rheumatism, periarthrosis, and capsulitis is carried out comprehensively. Consultation with a neurologist or rheumatologist is necessary.
- In severe forms of synovitis and bursitis, surgical intervention is resorted to.
- An orthopedist can help treat pain in the shoulder and shoulder blade caused by arthrosis and scoliosis.
- If a pain symptom occurs after eating, you should check the functioning of the digestive organs with a gastroenterologist.