September 9, 2022 Rhinopharyngitis or nasopharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, pharynx and their lymphoid formations.
Our upper respiratory tract has no clear boundaries. All boundaries between the pharynx, larynx, nose and other parts of the respiratory system are very conditional.
In this regard, inflammation of the pharynx almost always, regardless of the cause, spreads to neighboring areas of the respiratory tract.
The nasal cavity serves as the main entry point for infection. From the nasal cavity, viruses, bacteria, fungi and other pathogens very quietly and quickly penetrate the pharynx and spread through the respiratory tract.3
Causes of nasopharyngitis
Rhinopharyngitis is predominantly an infectious disease. In more than 80% of cases, especially in the autumn-winter period, it is caused by viruses - rhinovirus, adenoviruses, influenza viruses, etc. Bacterial nasopharyngitis occurs slightly less frequently. In this case, the causative agents of the disease are chlamydia, mycoplasma, streptococcus and staphylococcus.
Separately, we can distinguish allergic rhinopharyngitis, which develops under the influence of allergens that penetrate the upper respiratory tract - plant pollen, animal hair, tobacco smoke, household chemicals, etc.
Risk factors for developing a runny nose: hypothermia, weak immunity, the presence of chronic ENT diseases or pathologies of internal organs.
Symptoms of nasopharyngitis
The disease develops acutely:
- the nasal mucosa swells;
- copious watery or mucous discharge appears;
- nasal breathing becomes difficult;
- there is a burning and itching sensation in the nose;
- your throat starts to hurt;
- body temperature rises.
Swelling of the mucous membrane contributes to nasal congestion, which leads to a decrease or loss of smell, a change in the timbre of the voice (a specific nasal sound appears). The patient often sneezes and his head begins to hurt. The mucus formed in the nose flows down the back wall of the throat, causing a reflex cough. Lymph nodes in the neck may become enlarged.
Rhinopharyngitis in children has a similar clinical picture. In addition, children are often capricious and refuse to eat.
If left untreated, chronic nasopharyngitis develops. Nasal congestion occurs periodically, most often it occurs on the half of the nose on the side of which the person is lying (left - on the left side and vice versa). When lying on your back, nasal breathing becomes completely difficult. Other symptoms characteristic of the acute form of the disease are usually absent. If atrophic rhinitis develops, patients complain of dryness and itching in the nasal cavity, and crusts with an unpleasant odor form in the nose. In the case of hypertrophic chronic rhinitis, the nose is constantly blocked.
Prevention
There are several rules to strengthen your immune system and prevent disease.
- Wash your hands often and teach your children to do it correctly, especially after blowing their nose.
- Do not share personal items such as glasses, dishes, or a sick person's towel.
- Protect your mouth when you cough or sneeze with a disposable tissue. If you don’t have a disposable tissue, cough into the crease of your elbow rather than into your palm.
- Don't overheat the house, keep the room temperature between 18 C and 20 C to keep the air humid. Too dry air makes symptoms worse.
- Ventilate the room regularly, even when it’s cold.
- Get enough sleep and avoid stressful situations.
- Consume vitamin C and honey daily in preventative doses.
Good to know! Rhinopharyngitis remains contagious for a long time, in some cases up to 21 days.
How to treat nasopharyngitis?
Considering the main symptom of nasopharyngitis, treatment is almost always accompanied by the use of vasoconstrictor drops or sprays that relieve swelling and normalize nasal breathing. These drugs contain mainly oxymetazoline, phenylephrine, naphazoline or xylometazoline as active substances - Galazolin, Nazik, Snoop, Xilen, Sanorin, Tizin, Nazivin, DLYANOS, Babyfrin, etc. Depending on the dosage, the drugs can be used for the treatment of acute nasopharyngitis in children and adults.
If the disease is caused by a viral infection, it is recommended to use interferon-based nasal agents - Nazoferon, Grippferon, Genferon light. The drug based on the natural components of ARVI Active has an immunostimulating and indirect local antiviral effect.
If the disease is bacterial in nature, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs for nasopharyngitis, taking into account the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to the antibiotic.
If rhinorrhea is caused by allergies, antihistamines such as loratadine, suprastin, fexofenadine, levocetirizine or cetirizine are required.
To eliminate pain and sore throat, antiseptic medications for nasopharyngitis are used - Ingalipt, Grammidin, Agisept, Strepsils.
Modern approaches to the treatment of acute nasopharyngitis in children
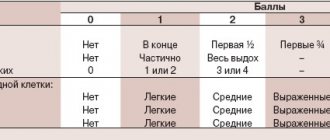
The highest incidence of acute respiratory infections occurs in young children, preschoolers and primary schoolchildren. The maximum incidence traditionally occurs in the autumn-winter period and the beginning of spring. Factors influencing the increased incidence of ARVI in children include: anatomical and physiological characteristics of the respiratory tract (narrow airway lumens, insufficient development of elastic tissue, etc.), delayed maturation of the immune system, living conditions (nutrition, living conditions) and etc. Particularly noteworthy is passive smoking, which leads to a decrease in local immunity of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and an increase in allergenicity of the body. One of the important factors influencing the frequency of colds is living in environmentally unfavorable areas. An increase in the content of various xenobiotics in air, water, and food is accompanied by their accumulation in the body, which leads to changes in cellular metabolism, disorders of homeostasis and immune defense [3]. The main causative agents of acute infections of the upper respiratory tract are viruses. One of the most relevant is rhinovirus. It is the cause of at least 25–40% of all acute respiratory infections. Along with rhinoviruses, the causes of acute respiratory diseases (ARI) are adenoviruses, parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial (RS) virus, and during epidemic outbreaks - influenza viruses. In recent years, considerable attention has been paid to metapneumoviruses, the most common cause of acute respiratory infections in children of the first year of life; human bocaviruses, which most often infect children in the 2nd–3rd year of life [4]. In Table 1 [V.K. Tatochenko, 1987] lists the main syndromes of damage to the upper respiratory tract depending on the viruses that cause diseases of the respiratory tract.
One of the manifestations of ARVI is acute infectious rhinopharyngitis (isolated acute infectious rhinitis in children is extremely rare). Laboratory diagnostic methods play a decisive role in monitoring a sick child only in cases of severe or complicated nasopharyngitis, when the child is admitted to a hospital [5]. Among them are methods for identifying the pathogen (antigen) and detecting an increase in the titer of specific antibodies in the dynamics of the disease. In recent years, the most reliable method for identifying the pathogen is the polymerase chain reaction method [6, 7]. It allows you to identify most viruses, as well as mycoplasma, chlamydia and a number of other bacteria. The immunofluorescence method is a universal method that combines accurate morphological analysis with high specificity and resolution [6, 7]. It is easy to perform, highly sensitive and allows you to get a positive result within a few hours from the start of the study in relation to any antigenic substance of a viral, bacterial or other nature.
The incubation period for acute nasopharyngitis is usually from 1 to 4 days. Often the first symptoms of nasopharyngitis are sore throat and sore throat. The pharynx is rich in nerve receptors, as it receives sensitive, motor and autonomic innervation from the pharyngeal plexus. This plexus, located on the outer surface of the middle sphincter under the buccal-pharyngeal fascia, is formed by the branches of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, as well as sympathetic fibers of the superior cervical ganglion. Sensitive innervation of the pharynx is mainly carried out by the glossopharyngeal nerve, but in the area of the pharyngeal openings of the auditory tubes there are nerve connections with the second branch of the trigeminal nerve. The superior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve, also takes part in the innervation of the laryngopharynx. The richness of nerve connections explains the irradiation of pain in diseases of the pharynx to the ear, lower jaw, etc.
The first hours of the clinical picture are characterized by: nasal congestion, nasal breathing disturbances; then rhinorrhea and sneezing appear. A nighttime cough may appear (usually at the beginning of the night), which occurs due to mucus draining down the back of the throat (the so-called drip syndrome). Other common symptoms are hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane of the pharynx in the area of the back wall of the pharynx, some pain when swallowing, which sometimes causes the child to refuse to eat and even the urge to vomit. Rhinopharyngitis may be accompanied by a febrile reaction. General malaise and cough are noted due to irritation and dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa when breathing through the mouth [7].
In children of the first year of life, acute nasopharyngitis can be quite severe due to the narrowness of the nasal passages and the small vertical size of the nasal cavity. This causes severe disruption of nasal breathing, shortness of breath, anxiety, refusal to suck, regurgitation, which can lead to the development of aspiration [7]. Infants become restless, capricious, their sleep is disturbed, and their appetite worsens. The average duration of the disease in uncomplicated cases is 5–10 days. Usually on the 3rd–5th day, nasal discharge becomes mucopurulent, nasal breathing improves, nasal discharge gradually decreases, and recovery occurs.
With mycoplasma and chlamydial etiology, the disease tends to be protracted - over 2 weeks, often accompanied by the development of tracheitis and/or bronchitis. A complication of nasopharyngitis is the addition of a bacterial infection, usually caused by microflora colonizing the child’s upper respiratory tract, with the development of sinusitis, bronchitis, acute otitis media, and pneumonia. This is observed in weakened and immunocompromised children. Another complication of nasopharyngitis is exacerbation of chronic pulmonary pathology: decompensation of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, etc. [7]. Typically, differential diagnosis of acute rhinopharyngitis is required only when it is protracted, when it is necessary to exclude the non-infectious nature of the disease: allergic and vasomotor rhinitis, hay fever, a foreign body in the nasal cavity, and also (extremely rarely) nasal diphtheria. In this case, the collection of anamnesis and examination by an ENT doctor, including endoscopy of the nasal cavity, X-ray of the nose, and sometimes the nasopharynx (fiberoscopy), and ultrasound scanning are of primary importance [7]. A child up to a certain age may not present specific complaints, so first of all, objective manifestations are taken into account: changes in the color of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, refusal of dense foods or the appearance of moodiness when taking them.
Pharyngoscopy reveals hyperemia, swelling and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall, palatine arches and soft palate. With lateral pharyngitis, hyperemia and swelling of the lateral ridges of the pharynx are observed. The degree of hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa can vary: from mild to severe inflammation with plaque or purulent exudate. Fever, cervical lymphadenopathy, and leukocytosis are observed in both viral and bacterial pharyngitis. Basic principles of treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity in children: reducing the severity of symptoms of the disease, preventing the development of purulent and non-purulent complications due to bacterial infection, reducing the incidence of side effects of treatment. Antibiotics for the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections are indicated only for the development of bacterial complications: sinusitis, otitis media, pneumonia, bronchitis. At the same time, data from numerous studies both in our country and abroad indicate that in 50–70% of cases of acute nasopharyngitis, tracheitis, and bronchitis in children, despite their predominantly viral etiology, antibiotics are prescribed. Although the results of clinical studies MEDLINE and SCIELO (from January 2000 to October 2006), concerning the diagnosis and treatment of nasopharyngitis and sinusitis in pediatric practice, showed that the positive dynamics of most of these diseases without antibiotics is observed after 2-3 days. Moreover, antibacterial drugs may simply be ineffective [8–10]. Also, the above-mentioned drugs do not have anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. Even more significant is that, by destroying both pathogenic and non-pathogenic microflora of the oropharynx, they reduce the immunological status of the child, increase the number of relapses of inflammatory diseases of the pharynx, contribute to the development of allergic reactions, the emergence of resistant strains of microorganisms, dysbiosis of the oral cavity, oropharynx and intestines. Moreover, the severity of the side effects of irrational antibiotic therapy sometimes exceeds the severity of the pharyngeal disease for which antibiotics are prescribed. Therefore, experts today pay attention to the excessive use of systemic antibiotics in the treatment of acute respiratory infections, recommending symptomatic treatment with a low risk of complications. And only if there is a clear clinical picture of bacterial infection of the nasopharynx, ineffectiveness of symptomatic therapy, or deterioration of the child’s condition, immediate prescription of antibiotics is necessary. Currently, in the treatment of nasopharyngitis in children, it is proposed to use local medications that affect the main parts of the pathological process: inflammatory, edematous, pain. Therapeutic measures for acute pharyngitis include: • a gentle diet: warm broths, thin cereals. During the acute period of the disease, it is necessary to exclude hot, cold, sour, and spicy foods. You should drink more than usual; • gargling with antiseptic solutions with sea salt, herbs, eucalyptus solution, etc. 3-4 times a day, preferably after meals; • irrigation of the pharynx with antiseptic or aerosols containing antibacterial agents, 2–3 doses 2–4 times/day; • resorption of tablets or lozenges with antiseptic, analgesic, softening effects; • for bacterial pharyngitis, systemic antibiotics must be prescribed. Antitussive expectorants and enveloping drugs are prescribed only in cases where the disease is accompanied by an unproductive, painful, painful cough, leading to disturbances in the child’s sleep and appetite. Expectorant medications are indicated if the cough is not accompanied by the presence of thick, viscous sputum, but its separation is difficult. The drugs are prescribed for severe cough for 7-10 days. It must be said that expectorants are used very widely, although there have been practically no rigorous clinical studies of these drugs. Electrical procedures (ultrahigh-frequency, ultra-high-frequency therapy, diathermy) are indicated for complicated nasopharyngitis, but the effectiveness of “warming up” the chest and electrophoresis of drugs, which are still widely used in our country, have not been proven, so they should not be used. The effect of ultraviolet irradiation of the pharynx with tube-quartz is also questionable. The use of mustard plasters, cups, burning patches and rubbing is painful, fraught with burns and allergic reactions. When treating acute rhinitis, the stages of the disease should be taken into account: 1) dry (irritation stage); 2) serous discharge; 3) mucopurulent discharge (resolution stage). In the first phase, various oil preparations are used, which are injected into the nasal cavity. Aerosols may be used. A good effect is achieved from local administration of immune and antiviral drugs, such as interferon [11]. It is possible to use hot baths, rubbing, and thermal procedures. In addition, it is necessary to rinse the nasal cavity with saline solutions, which promote better cleansing of the nasal mucosa and elimination of the virus. It is believed that the content of microelements such as Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Cu in the nasal rinsing solution helps to increase the motor activity of cilia, activate reparative processes in the cells of the nasal mucosa and normalize the function of its glands [12]. The listed microelements are contained in preparations made from mineral spring water, which has medicinal properties, and preparations prepared from sea water, sterilizing it and bringing the salt content to isotonic concentration. These products help thin mucus and facilitate its removal from the nose, increasing the resistance of the nasal mucosa to pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In the stage of serous exudation, it is recommended to use local astringents (Collargol and Protargol), isotonic solutions for rinsing the nose, decongestants in the form of a gel or nasal drops. If there are severe general symptoms, antipyretic drugs and plenty of fluids are prescribed.
In the third stage, isotonic solutions for rinsing the nose and vasoconstrictors are also used. It should be remembered that due to the danger of the formation of drug-induced rhinitis (rebound syndrome), the period of use of local decongestants in children is approximately 2 times less than in adults, and is 3-5 days. For young children, it is advisable to use short-acting drugs due to the danger of prolonged ischemia not only of the nasal mucosa, but also of the brain, which can provoke general convulsions [13]. Antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are used. Antihistamine therapy is also possible. When choosing medications for children, it is especially important to focus on drugs with the lowest risk of side effects. Today, there is many years of experience in the successful use of Protargol for acute runny nose in any phase, from nasal congestion and runny discharge to thick mucous discharge. Protargol, or silver proteinate, is a silver-containing protein compound that has an astringent, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Silver has long been used as a powerful antiseptic, capable of destroying many bacteria that cause diseases. Protargol is a brownish-yellow or brown odorless powder, soluble in water, and has a slightly bitter astringent taste. Its silver content is 7.8–8.3%. 1–5% solutions are prepared from the powder in pharmacies, which are used for external use.
Unlike vasoconstrictor drops, Protargol fights the cause of the infectious-inflammatory process in the ENT organs, suppresses the vital activity of infectious agents and reduces the inflammatory process. The vasoconstrictor effect of Protargol is mild, there are no complications from blood vessels, so it can be used for a long time. Unlike other effective antibacterial chemotherapeutic drugs, Protargol has not only antimicrobial, but also antiviral and immunostimulating properties. As a result of a study of Protargol solution in various concentrations on cell culture, inhibition of the reproduction of viruses causing infectious rhinotracheitis and viral diarrhea was noted at a concentration of 0.25–0.5% [14]. For acute rhinitis, children under 6 years old take 1-2 drops of Protargol 3 times a day, adults and children over 6 years old - 2-3 drops 3 times a day. Adults and children over 6 years old can also use the spray (1 injection 3 times a day). Usually a weekly course of treatment with Protargol is sufficient, but for chronic runny nose the drug is prescribed in courses of 14 days or more. In this case, it gently affects the blood vessels of the nasal cavity, narrowing them, which reduces the flow of blood to the mucous membrane. The lack of additional nutrition contributes to the fact that the growth of the mucous membrane decreases or stops. Protargol has bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects on strains that cause acute respiratory infections, such as Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Moraxella spp. etc. Thus, the use of Protargol, which has an active antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, promotes early recovery and prevention of complications of acute rhinitis. Many years of experience in the clinical use of Protargol indicate its good effectiveness and high safety profile in the treatment of children with acute rhinitis in any phase.
Literature 1. On strengthening measures to prevent influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 25 of January 27, 1998 2. Ratnikova L.I., Stenko E.A. A new approach to the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza // Polyclinic. 2009. No. 2. P. 70–72. 3. Klyuchnikov S. O. Treatment of cough during ARVI in frequently ill children // RMZh. 2012. No. 2 (Pediatrics). pp. 68–72. 4. Kazulina I.S. New infectious agents – metapneumovirus and human bocavirus: Abstract of thesis. dis. ...cand. honey. Sci. M., 2010. 5. Acute respiratory diseases in children: treatment and prevention. Scientific and practical program of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. M.: International Foundation for Mother and Child Health, 2002. 6. Klyuchnikov S.O., Zaitseva O.V., Osmanov I.M. and others. Acute respiratory diseases in children. Manual for doctors // Ros. Vestn. perinatology and pediatrics. 2008. No. 3. P. 1–36. 7. Samsygina G.A., Bogomilsky M.R. Upper respiratory tract infections. Pediatrics. National leadership. T. 2. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. pp. 56–62. 8. Battist N. The evaluation of the analgesic and antiinflammatory effects of flurbiprofen mouth wash and 100 mg tablets in oral medicine // Minerva Stomatol. 1994. Vol. 43. No. 4. R. 141–144. 9. Benzimoj SI, Langford JH, Homan HD et al. Efficacy and safety of the anti-inflammatory throat lozenge flurbiprofen 8.75 mg in the treatment of sore throat // Fundament. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999. Vol. 13. R. 189. 10. Benzimoj SI, Langford JH, Christian J. et al. Efficacy and tolerability of the anti-inflammatory throat lozenge Flurbiprofen 8.75 mg in the treatment of sore throat // Clin. Drug Invest. 2001. Vol. 21. No. 3. R. 183–193. 11. Klyuchnikov S.O., Zaitseva O.V., Osmanov I.M., Krapivkin A.I., Keshishyan E.S., Blinova O.V., Bystrova O.V. Acute respiratory diseases in children. A manual for doctors // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics. 2008. No. 3. P. 1–36. 12. Lopatin A.S., Ovchinnikov A.Yu., Svistushkin V.M., Nikiforova G.N. Topical drugs for the treatment of acute and chronic rhinitis // Russian Medical Journal. 2003. T. 11. No. 8. P. 446–448. 13. Garashchenko T. I. Modern therapy of allergic rhinitis in children // Russian Medical Journal. 2002. T. 10. No. 5. P. 273–278. 14. Krasochko P.A. The use of T-activin and protargol for the treatment of respiratory diseases in calves / P.A. Krasochko, T.I. Pomirko, P.I. Yarovoy // Veterinary medicine. 1990. No. 11. pp. 22–23.
Complications
If acute nasopharyngitis is not treated, it can become chronic.
There is also a risk of developing the following complications:
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- laryngitis;
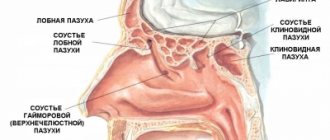
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- tracheitis;
- inflammation of the middle ear (which can lead to hearing loss);
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia.
Respiratory infections can cause exacerbation of existing chronic diseases, such as bronchial asthma.