Data
Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is widely used and is one of the most common substances for poisoning. This happens during suicide attempts in adults and accidentally in children.
According to statistics, the frequency of ASA consumption is:
· Decreased due to association with the development of Reye's syndrome in children and the development of other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
· Increased due to the prevention of thrombosis of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Aspirin remains one of the most frequently used drugs by patients without a doctor's prescription.
How to treat warts with salicylic acid
Due to its antiseptic and antimicrobial effect, salicylic acid is used to remove papillomas. Use a solution and ointment of high concentration:
- Solution - take 5% or 10% product. Treat warts before going to bed once a day, avoiding getting the drug on healthy areas. In the morning, wash off with warm water.
- Ointment - used to treat papillomas of various shapes. Frequency of use: 1 time every 2 days. Recommended for adults and children over 2 years old.
The duration of taking salicylic acid is no more than a week.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Absorption and metabolism at acceptable dosage
· Aspirin is quickly absorbed into the stomach and duodenum.
· At therapeutic doses, 90% of salicylic acid is protein bound and therefore restricted to the vascular space.
· The maximum concentration of the substance in the blood serum is achieved within 60 minutes after administration.
Metabolism
Salicylic acid is metabolized in the liver in several ways:
· SC has a t½ of 2-4 hours in therapeutic doses.
· ASA is partially glucinated in the liver to salicylic acid, which is less toxic and is excreted more quickly through the kidneys.
· Only a small amount of ASA is excreted from the body without changes in the urine.
Absorption and metabolism in case of poisoning
· After an overdose, absorption and excretion change dramatically.
· When taking large doses, absorption of acid from the stomach and intestines may take more than 10 hours.
· The maximum concentration of the active substance is observed in the blood serum.
· Cleansing of the body slows down and takes up to 6-8 hours or even longer.
· In large doses, the half-life increases to 20-30 hours.
· As SA levels increase, protein binding decreases to 50% and hepatic detoxification becomes saturated. This way, more salicylic acid reaches the tissues.
Excretion
Since the liver's ability to degrade salicylic acid is saturated, the elimination of salicylic acid will depend on the rate of excretion by the kidneys.
· Therefore, t½ of the drug increases from 2-4 hours to 30 hours.
· Excretion in the kidneys slows down by 4 times with an increase in urine pH from 7 to 8 and by 10 times with an increase in pH from 5 to 8.
Instructions for use
Salicylic acid is used externally. The course of treatment is calculated according to the course of the diagnosis, skin condition and age of the patient.
Based on the instructions, the drug in the form of an alcohol solution should be applied no more than 3 times a day. The daily dose should not exceed 10 ml for adults and 1 ml for children. Duration of therapy is 1 week.
When using salicylic acid ointment, the skin must first be prepared. First, wash with soap and then dry. For better pharmacological action, the surface of the epidermis is treated with additional antimicrobial agents, then the area is lubricated with salicylic ointment with a concentration of 1% or 2%. The affected area is bandaged, and after 6 hours the bandage is replaced.
Hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet is eliminated with special powders containing the active substance. It should be used regularly, the course depends on the severity of symptoms.
For ear pathologies, drops based on salicylic acid are used. The duration of therapy is prescribed by the doctor.
Cellular and systemic effects
Respiratory alkalosis
The overall effect is that patients have respiratory alkalosis or a mixture of respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis—pure metabolic acidosis is rare in adults but can occur in children.
Respiratory acidosis should be suspected in the early stages if there is concomitant poisoning with a respiratory inhibitor.
· Inhibition of cyclooxygenase leads to a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxanes.
· Stimulation of chemoreceptors in the medulla leads to nausea and vomiting.
· Activation of the respiratory center in the medulla leads to respiratory alkalosis.
· Effect on cellular metabolism leads to metabolic acidosis.
Acid-base disorders
Various acid-base disorders can occur with ASA poisoning.
· Respiratory alkalosis (phase 1): Through rapid onset of respiratory center stimulation/hyperventilation, giving an early decrease in pCO2 and respiratory alkalosis.
· Metabolic acidosis (phase 2): Increased metabolism, accumulation of acidic metabolites and infusion of ASA from the intestine.
· Vomiting and electrolyte disturbances due to acid-base changes.
Indications for use
Salicylic acid is used in monotherapy and in combination with other drugs.
In dermatology, the main indications for use are infectious skin lesions (pyoderma, lichen, mycosis of the feet), including those caused by improper functioning of the sebaceous glands (acne, acne, seborrhea).
As a distraction and pain reliever, salicylic acid is used for gout, rheumatism, and arthritis.
Effective for the treatment of weeping wounds and the speedy healing of burns. Can be used for psoriasis, ichthyosis and chronic eczema.
In cosmetology it is used for hyperhidrosis and hyperkeratosis, to remove warts, calluses and corns.
Degree of influence and physiological principles of treatment
ASA is a weak acid. Treatments are aimed at increasing systemic pH, that is, reducing the concentration of H + ions, by adding sodium bicarbonate. Salicylic acid anions then enter the bloodstream and, to a lesser extent, cross the blood-brain barrier into the central nervous system.
Alkalinization also increases the secretion of salicylate in the kidneys.
Effect on the central nervous system:
· Salicylic acid may cause changes in mental status through three mechanisms: direct toxic effect in the central nervous system, cerebral edema and neuroglycopenia.
· Increased acidosis promotes the influx of salicylic acid into the central nervous system. SA reduces glucose levels in the central nervous system, so neuroglycopenia is observed despite normal blood glucose levels.
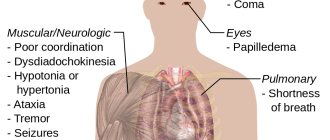
Mortality from ASA poisoning is closely related to CNS salicylic acid levels, and altered mental status due to poisoning is an absolute predictor of hemodialysis.
The effect of ASA poisoning on the lungs is expressed in pulmonary edema. Induced noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and acute lung injury are most common in elderly patients. The condition is treated with hemodialysis.
Release form
The drug is available in the form of a solution (in alcohol) and in the form of an ointment:
- In liquid form, it is bottled in glass bottles of 25 ml or 40 ml.
- Salicylic ointment is available in jars or aluminum tubes of 25 grams.
Less commonly supplied in the form of powder and medicinal paste, it can be included in medicinal plasters.
salicylic acid for acne
Diagnosis of the state of poisoning
Diagnostic criteria:
· Clinical suspicion.
· Taking ASA drugs in doses above toxic levels.
· Symptoms of hyperventilation.
· Metabolic acidosis without a known cause.
Diagnosis can only be made by measuring plasma concentrations of salicylic acid. Although there is no absolute correlation between plasma SA concentrations and symptoms, toxic reactions occur in most subjects at values above 3.0 mmol/L in adults and 2–3 mmol/L in children. The usual therapeutic level is 0.7-2.2 mmol/L.
Indications
Salicylic acid can be used as monotherapy and complex action. In both cases it is able to treat the following conditions:
- Psoriasis.
- Ichthyosis.
- Seborrhea.
- Warts.
- Pimples.
- Acne.
- Burns.
- Wound surface.
- High sweating of the lower extremities.
- Calluses, corns.
- Hair loss.
- Thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
History taking
A person who seeks help complains of a certain malaise. Early symptoms of ASA poisoning include ringing in the ears, fever, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Serious poisoning results in altered mental status, coma, noncardiac pulmonary edema, and death.
These questions are asked to the patient or his relatives during the initial examination:
1. How many tablets were taken?
2. What type of preparation? Gastroresistant?
3. When did the reception take place?
4. Was the drug consumed all at once or was there long-term consumption (chronic poisoning)?
5. Has the patient taken alcohol, drugs or other pills?
6. Has the patient vomited and is there a desire to vomit?
7.Did you use activated charcoal after this or take other measures to detoxify the body?
Answering these questions allows you to get a more accurate picture of your health and choose the appropriate treatment.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Mikonorm
Undecin
Gentian violet
Zinkundan
Exoderil
Exiter
Batrafen
Lotseril
Lamisil Dermgel
Lamisil Uno
Lamisil
Salicylic ointment
Keto Plus
Exifin
Fungoterbin
Mycoseptin
Thermikon
Nitrofungin
Sulsena
Baziron AS
Verrucatsid , Urgokor , Duofilm , Mozolin , Koplomak , Anti-callus ointment , Solcoderm , Sulfur-salicylic ointment .
Critical poisoning with acetylsalicylic acid
When using a critical dose of the drug, the following is observed:
· Respiratory depression, often after a period of hyperventilation.
· Effect on the central nervous system and mental changes: irritability, disorientation, speech disorders and hallucinations.
· Severe dehydration, especially in children.
· Low diuresis.
· Bloody vomiting.
· Bleeding, primarily cutaneous from the gastrointestinal tract.
· Increased body temperature, but the absence of fever cannot exclude the diagnosis.
· In the most severe cases, respiratory depression, convulsions and coma, often with cardiac arrest.
Changes in analyses:
· Therapeutic concentration is 0.7-2.2 mmol/L, values above 2.9 mmol/L may be associated with toxicity.
· Values above 7.2 mmol/L are associated with mortality and are considered an absolute value for hemodialysis.
Plasma values should be checked every two hours until the next two readings show decreasing values. An increase in plasma levels should not occur after 5-6 hours due to pylorospasm. When using enteric-coated tablets, it may take up to 35 hours to reach the maximum value.
Laboratory research
Monitoring plasma salicylic acid levels can assess response to treatment and the need for more aggressive action. Using laboratory tests, the following indicators are determined.
1. Creatinine. Knowledge of renal function in the form of serum creatinine is important since salicylate is excreted through the kidneys.
2. Potassium. Hypokalemia should be treated aggressively in patients with ASA toxicity because the condition reduces the ability to alkalinize the urine.
3. Coagulation. Overdose of ASA causes hepatotoxicity and disrupts vitamin K metabolism, leading to coagulopathy.
Clinically significant bleeding is rare, but if it occurs, the patient should seek immediate medical attention.
Signs of serious poisoning:
· Blood concentrations > 7 mmol/l are life-threatening. Serum concentrations should be assessed depending on the time of drug administration.
· Severe acidosis in the blood.
Salicylic acid, application in medicine and cosmetology.
Salicylic acid is known to many as a medicine for treating skin diseases. In addition, this same compound is the basis of the well-known Aspirin. Salicylates are salts of salicylic acid, found in many medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects (for example, raspberries are rich in them). It is also a common ingredient in many skin care products.
Salicylic acid, lat. Acidum salicylicum (genus Acidi salicylici ) , (from the Latin salix “willow”, from the bark of which it was first isolated) - 2-hydroxybenzoic or phenolic acid, C6H4(OH)COOH; colorless crystals, highly soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether and other polar organic solvents, poorly soluble in water (1.8 g/l at 20 °C).
Isolated from willow bark by the Italian chemist Rafael Piria and then synthesized by him.
Found naturally in plants as derivatives, usually as a methyl ester glycoside, salicylic acid in particular was first isolated from willow bark, hence its name. Free salicylic acid, along with salicylic aldehyde, is found in small quantities in the essential oil isolated from the flowers of some species of spirea (Spiraea ulmaria, Spiraea digitata).
Salicylic acid is easily soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether, and slightly soluble in carbon disulfide. Solubility in water (g/l): 1.2 (0 °C), 1.8 (20 °C), 8.2 (60 °C), 20.5 (80 °C).
Pharmacological action - wound healing, antiseptic, local irritant.
Promotes cleansing of the wound from purulent discharge and its healing, eliminates perifocal inflammation. It has a distracting, keratolytic (in high concentration) and keratoplastic (in low concentration) effect. Suppresses the secretion of sebaceous and sweat glands.
It is used as monotherapy and as part of combination drugs for inflammatory, infectious and other skin lesions, incl. burns, psoriasis, eczema, dyskeratosis, ichthyosis, acne vulgaris, warts, hyperkeratosis, calluses, calluses, oily seborrhea, pityriasis versicolor; hair loss; sweaty feet.
Due to its antiseptic effect, salicylic acid is used in food preservation;
Production of azo dyes, fragrances (salicylic acid esters);
Colorimetric determination of Fe and Cu to separate thorium from other elements.
Salicylic acid is a product that is used externally. It is quite cheap, but at the same time it has several methods of use and really helps with various problems.
Principles of action on the skin:
- Deep penetration at the site of application.
- Suppression of the activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Elimination of the inflammatory process.
- Softening of the outer layer of the skin and its gradual discoloration, which leads to easy separation from the surface of the skin.
- Cleansing wounds from purulent discharge and stopping the spread of pathogenic bacteria.
- Accelerating the healing process by increasing blood flow to this area of the skin.
Properties: antimicrobial and irritant.
There are several methods of use; salicylic acid is available in different forms with different concentrations of the active substance:
- solution (aqueous and alcoholic) - 1% and 2%;
- ointment – 1%, 2%, 5%, 10%;
- powder (powder);
- paste;
- patch.
In medicine, the use of salicylic acid is effective for the treatment of skin diseases of various origins:
- pyoderma;
- mycosis of the feet;
- versicolor and pityriasis versicolor;
- psoriasis;
- seborrhea;
- hair loss;
- dermatitis.
- keratoses;
- eczema.
- healing of weeping wounds, for example, after a burn.
In these cases, it is better to use ointments with the required concentration of the active substance, and when treating lichen, the use of salicylic acid should be combined with sulfuric ointment. They will enhance each other's antimicrobial properties.
Salicylic acid is also used to reduce pain with:
- rheumatism;
- gout;
- arthrosis and arthritis.
The use of salicylic acid in cosmetology.
Indications:
- hyperhidrosis and hyperkeratosis;
- skin burns;
- acne and post-acne;
- warts;
- corns and calluses;
- black dots;
- eczema;
- infectious skin diseases;
- inflammation of the skin;
To get rid of these problems, it is recommended to use a solution of salicylic acid.
Contraindications for use:
- hypersensitivity;
- very dry skin;
- renal failure;
- pregnant women and during lactation;
- prohibited for use by children under 3 years of age.
Products containing salicylic acid and BHA are generally safe for adults when used as directed, but are not always safe for children. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that children under 18 years of age not use this ingredient.
Children may have unexpected reactions to topical salicylic acid because younger skin may absorb the substance more quickly and experience more irritation.
It is always necessary to be careful with the dosage and use of salicylic acid to avoid consequences, such as burns.
Salicylic acid in cosmetology belongs to the class of BHA acids. It is a fat-soluble acid, which means it can penetrate deep into cells through the pores, and also has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Therefore, it is perfect for problematic, rash-prone and oily skin, and helps fight open and closed comedones.
BHA acids can dry out the skin due to interaction with sebum. To prevent this from happening, use products with a salicylic acid concentration of 0.5–2% and do not forget about moisturizer and sunscreen.
Salicylic acid is widely used in dermatology and cosmetology, as a weak antiseptic, plus an irritant and keratolytic agent. Also, it is an excellent additional agent for synergy with other peeling components due to the phenolic group, denatures proteins and facilitates passage through the stratum corneum. During the chemical peeling procedure using salicylic acid, the stratum corneum and epidermis are damaged, recovery takes place within 1-2 days, and during this time pronounced peeling is observed. Clinical indications for their use: hypermigmentation, melasma, moderate photoaging, acne and post-acne. The minimal effect is visible after the first procedure, but a significant improvement in the appearance of the dermis occurs after several procedures; the appointment and implementation of the procedure is carried out by a specialist.
Alternatives to salicylic acid.
Alpha Hydroxy Acid (AHA): Like BHAs, AHAs work to exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells. AHAs (such as glycolic acid) are also effective against acne, and these substances can help your skin appear smoother and more even-toned.
Benzoyl peroxide: This product is effective as an acne treatment, but instead of exfoliating, benzoyl peroxide kills bacteria that cause inflammation and dries out the affected skin.
Scrubs: When you really want to exfoliate your skin, using a brightening scrub can be your best friend. Look for ingredients such as vitamin C and citric acid.
Difference between salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide.
Salicylic acid is a legendary exfoliant and benzoyl peroxide is an organic aromatic compound and a very worthy antibacterial analogue of “salicylic acid” that kills acne-causing bacteria right inside the pores. Dermatologists believe that benzoyl peroxide is better suited for sensitive skin, since salicylic acid is still an acid that can lead to peeling, irritation and allergic reactions if not handled carefully.
What percentage is best to use?
For facial care, the optimal concentration of salicylic acid is 0.5-2%.
For use on the body in almost all cases, you can use a more active salicylic acid in a concentration of about 3%. It is important to consider: if you are not sure how your skin will react to the use of a product containing salicylic acid, first consult with a specialist who will give you all the necessary care recommendations.
Possible side effects:
If you overuse salicylic acid or use too much over a long period of time, side effects may occur. Most often these problems are associated with skin reactions.
Below are some of the most common side effects:
Sun and Chemical Burns – Excessive amounts of salicylic acid can cause chemical burns because it makes the skin overly sensitive to the sun. Sunburn is a common side effect for people who use any product containing BHA, so be sure to apply sunscreen along with any salicylic acid-based product.
If your skin is dry or feels oily, a salicylic acid treatment can have a drying effect as it helps exfoliate and renew the skin. Sometimes, however, these products have the opposite effect as the skin overreacts to dryness by producing more sebum than usual. Since both of these problems can lead to acne and other skin problems, reduce your salicylic acid intake to reduce irritation.
Salicylic acid is naturally occurring, but that doesn't mean this exfoliant and anti-inflammatory is for everyone. Whether you've been using a salicylic acid product for years or are considering adding it to your routine, be sure to understand its uses, applications, and potential side effects.
Sources: https://cosmar.com.ua/, https://www.letoile.ru/, https://iledebeaute.ru/, https://med.vesti.ru/, https://www. kiz.ru/.
Educational phone numbers : 8-812-248-99-34, 8-812-248-99-38, 8-812-243-91-63, 8-929-105-68-44
Application for ordering products here
Seminar schedule here
What to do in case of overdose
A person who has been poisoned by aspirin must take the following measures on his own.
- If no more than 2 hours have passed since administration, induce vomiting.
- Take activated carbon. The cold mixture of 150 mg/ml is effective even without gastric emptying. Adults: 50 g of activated carbon, children: 100-150 ml (15-20 g of activated carbon).
After implementing emergency measures at home and stabilizing the condition, medical attention is required. As with all poisonings, therapy consists of rapid assessment and stabilization of the airway and circulation.
How to treat acne with salicylic acid
The antiseptic drug effectively fights pimples, acne and other pathologies that are accompanied by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands.
Lotions are made for this. The skin is pre-cleansed and dried. Soak a cotton swab in a salicylic acid solution and wipe your face. For small and rare rashes, they are burned with the drug locally using a cotton swab.
After the procedure, the face must be washed and lubricated with moisturizer.
It is recommended to carry out treatment no more than 2 times a week. Duration of the course until acne disappears.
Treatment principle
If you use aspirin in excessive doses, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will assess the health risk and provide first aid.
Treatment goals:
· Provide vital functions.
· Minimize poisoning and harmful effects of the drug. Activated carbon will help reduce acid absorption.
· Relieve stomach pain. It often occurs soon after eating.
· Increase excretion by alkalinizing urine output.
· Perform dialysis if necessary.
Plasma acetylsalicylic acid and acid-base measurements should be taken every two hours until they stabilize and the values begin to decrease.
Salicylic acid: for ingrown hairs
Salicylic acid is good for ingrown hairs, which often appear after hair removal and depilation. Ingrown hairs can cause serious discomfort and often lead to inflammation. Conventional measures such as scrub or massage with a hard washcloth are not always effective, and they are irritating to the skin.
Peeling with salicylic acid is much gentler. Gradually thinning the upper layer of the epidermis, salicylic acid allows you to painlessly release ingrown hair and relieve inflammation of the hair follicles.
Poisoning therapy
Therapy consists of the following processes.
1. Alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate. At a normal pH of 7.40, most salicylic acid is in the ionic form, which does not cross the blood-brain barrier as well as the uncleaved form (H++ Sal->HSal). If the pH increases, even more HSal will be broken down into ions, which helps clear HSal from the brain. Initially, bicarbonate delivery will increase plasma salicylate due to salicylate release from tissue. Alkalosis is not a contraindication for bicarbonate infusion; plasma pH is <7.60. Urine pH should be between 7.5 and 8.
2. Alkalinization of urine. It is effective because it increases salicylate secretion.
By increasing urine pH from 6.5 to 8.1 by adding bicarbonate, the total excretion of salicylate increases fivefold or more.
3. Intubation if necessary. Great care is advised as intubation may worsen the condition.
4. Oxygen. Oxygen supplements should be given as needed. In case of lung injury, there is a high need for it.
5. Restoring water balance. The patient may be hypotensive, in part due to inappropriate systemic vasodilation. Aggressive fluid delivery is acceptable unless there is cerebral or pulmonary edema.
6. Glucose. ASA poisoning reduces glucose levels in the central nervous system, despite normal peripheral blood sugar levels. Supplementation with 100 mL 50% dextrose (adults) is considered in patients with altered mental status regardless of blood sugar.
7. Vitamin K supplements.
Symptomatic treatment of complications in the second stage of poisoning requires hemodialysis.
Interaction
Salicylic acid can increase the permeability of the skin to other topical medications and, accordingly, enhance their absorption.
Absorbed salicylic acid may potentiate the side effects of sulfonylureas , oral hypoglycemic agents and methotrexate .
The solution is pharmaceutically incompatible with zinc oxide (forms insoluble zinc salicylate) and with resorcinol (forms melting mixtures).
When is hemodialysis indicated?
Indications for its implementation are:
· Altered mental status.
· Edema of the lungs or brain.
· Kidney failure, which prevents the secretion of salicylate.
· Fluid overload preventing bicarbonate flow.
· Plasma ASA more than 7.2 mmol/l.
· Clinical deterioration despite aggressive and appropriate treatment.
To prescribe the procedure, the patient must consult a nephrologist.








![Table 1. Bioavailability (absorption) of various organic forms of calcium within 2 hours after oral administration in the experiment [22]](https://laram-halal.ru/wp-content/uploads/tablica-1-biousvoyaemost-absorbciya-razlichnyh-organicheskih-form-kalciya-v-techenie-330x140.jpg)