Who among us has not experienced a feeling of confusion and helplessness when, for some reason, we could not hear the words of our interlocutor? Hearing loss is a serious detriment to a full life, because we receive the vast majority of information about the world around us through our ears. A healthy person is able to recognize over 400,000 different sounds. Hearing loss significantly reduces a person’s quality of life and complicates his speech communication.
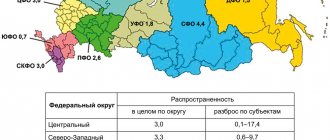
In Russia today there are about 13 million people with poor hearing. 14% of the world's inhabitants over the age of 30 begin to experience these problems. After the age of 60, 30% of the adult population of the planet suffers from hearing loss.
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Flushing the ear canals
3 Diagnosis of hearing loss in MedicCity
Degrees of hearing loss
Hearing loss refers to any weakening of hearing. There are 3 degrees of hearing loss:
- mild hearing loss (the hearing threshold rises to 40 decibels, speech differs at a distance of 4-6 meters);
- moderate hearing loss (hearing threshold from 41 to 50 decibels, a person perceives spoken language at a distance of 1 to 4 meters);
- severe hearing loss (hearing threshold up to 70 decibels, spoken speech can be heard from a distance of 1 meter).
How does the disease manifest itself?
Hearing problems can manifest themselves clearly or develop unnoticed by the patient. Acute sensorineural hearing loss is characterized by a sudden loss or progressive decrease in hearing in one or both ears, as well as one or a combination of the following symptoms:
- tinnitus of various types (high-frequency ringing or squeaking, low-frequency noise, etc.);
- vestibular dysfunctions (dizziness, nausea, vomiting, coordination problems, etc.);
- autonomic dysfunctions (sweating, rapid heartbeat, changes in blood pressure, etc.).
At the beginning of the development of chronic pathology, the clinical picture may be erased. The patient should be alert to the following situations:
- during a regular or telephone conversation you constantly have to ask again;
- there are difficulties communicating in an environment with background noise (on the street, in public places, etc.);
- understanding the interlocutor requires observing his lips;
- There are regular problems with identifying the source of noise.
The attention of loved ones should be attracted by oddities in a conversation (for example, a person hears words incorrectly or does not catch the meaning of what was said), watching TV at excessive volume, lack of reaction to events accompanied by noise (outside the patient’s field of view), and others.
Sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss
Sensorineural ( sensorineural ) hearing loss is characterized by damage to sound-receiving organs and the death of hair cells that transform sounds into neuroelectric impulses.
The main symptom of sensorineural hearing loss is hearing loss. Often occurs after an acute respiratory viral infection, psycho-emotional stress, or intoxication. It can affect either one ear or both at the same time. A very common symptom of this disease is noise in the ear: it can be either high-frequency (ringing, squeaking, “buzzer,” “hissing”) or low-frequency (hum). Such phenomena require immediate medical attention. A doctor who suspects sensorineural hearing loss needs to perform tuning fork tests. To verify the diagnosis and accurately determine the degree of hearing loss, a hardware test is performed - pure tone threshold audiometry. Without treatment and prevention, the disease progresses and leads to complete deafness.
Clinical forms of sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss
Sudden hearing loss
Sudden hearing loss can produce symptoms of conductive, sensorineural and mixed hearing loss, depending on the cause. If hearing has been impaired as a result of exposure to noise, the person first loses the ability to hear sounds of certain frequencies (about 4000 Hz), and then becomes less and less able to distinguish sounds of all frequencies.
A person can lose their hearing suddenly over a period of hours or even minutes. As a rule, infection is to blame for hearing loss. Patients with this disorder compare their sensations to a broken telephone wire: a sudden onset of silence. As a rule, the disease of this form is unilateral. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. When assistance is provided in the first days of the disease, hearing can be restored in more than 90% of cases.
Acute hearing loss
A week has passed since the man lost his hearing. The probability of hearing returning at this stage is 70-90%. If the clinical picture persists for 1-3 months, then we can talk about subacute hearing loss.
With subacute hearing loss, a person feels fullness in the ears, which becomes permanent. Against the background of tinnitus, the patient begins to feel that he is beginning to hear worse and worse. Of course, the time to restore hearing has already been lost a little, but you still need to see a doctor. Otherwise, hearing loss may develop into a chronic form.
Chronic hearing loss
The duration of the disease is more than 3 months. It is characterized by the fact that even with existing hearing loss, a further decrease in hearing occurs, accompanied by tinnitus. Periods of hearing deterioration may alternate with periods of slight remission. The likelihood of complete hearing recovery at this stage is extremely low. However, courses of maintenance vascular therapy can prevent further hearing loss.
There is also senile hearing loss (presbycusis). related hearing loss is characterized by ringing in the ears and an inability to understand speech (ie, speech intelligibility).
1 Diagnosis of hearing loss in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of hearing loss in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of hearing loss in MedicCity
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
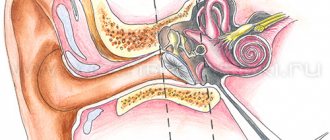
With sensorineural hearing loss, one of the parts of our auditory system is affected: hair cells, structures of the inner or middle ear, areas of the brain that are responsible for hearing. A distinctive feature of this type of hearing loss is the development of pathology of the nerve cells of the inner ear, auditory nerve or central nervous system.
If you miss the moment and do not deal with the disease in time, it can develop to complete deafness. This can happen within seven years or seven hours. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that hearing loss due to sensorineural causes is irreversible, but such hearing loss can be treated with prosthetics. To find out if you have a hearing loss, you need to get tested.
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive when the middle ear or eardrum is damaged as a result of mechanical trauma or infection.
Conductive hearing loss is a hearing impairment associated with poor perception of sounds, caused by dysfunction of sound conduction from the outer ear and eardrum to the middle ear and from it to the inner ear. That is why this type of hearing loss is called conductive – from the Latin word “to conduct”.
With conductive hearing loss, sound vibrations do not reach the main human receiving organ - the hairs of the epithelium of the organ of Corti located in the inner ear, which transmit signals to the auditory nerve.
Conductive hearing loss is characterized by reduced sensitivity in the perception of sounds, but there is no change in their clarity. It is enough to increase the volume and a patient with this form of hearing loss will hear normally. Typically, a person with conductive hearing loss speaks in a low voice and has normal ability to distinguish sounds, but has difficulty hearing when chewing.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
The causes of conductive hearing loss can be very diverse.
For example, it is often caused by wax plugs in the outer ear. Unfortunately, patients often try to get rid of such a traffic jam on their own, and often such amateur activity leads to serious injuries and inflammations, fraught with irreversible hearing loss.
Meanwhile, an experienced otolaryngologist at the MedicCity clinic can relieve you of cerumen impaction and the hearing loss it causes within a few minutes and without any discomfort.
Another common cause of conductive hearing loss is otitis externa, an inflammation in the outer ear, often accompanied by suppuration.
At the same time, attempts to treat otitis independently with the help of lotions and randomly selected medications can seriously aggravate the situation and dramatically complicate auditory perception, for a long time or even forever.
In addition, conductive hearing loss can be caused by the following eardrum-related causes:
- perforation or damage to the eardrum (may be accompanied by stabbing pain and bleeding);
- tympanosclerosis or sclerosis of the tympanic membrane is a pathological process of inflammation and degradation of the membrane tissue, accompanied by the formation of a purulent mass;
- anatomical anomalies of eardrum deformation.
These membrane conditions can be caused by injuries, thermal effects, infectious viral diseases, etc.
Sudden conductive hearing loss can also be caused by sudden changes in pressure on the eardrum, for example, when going underwater or into a mine, or when taking off on an airplane. In the middle ear, the consequences of acute and chronic otitis media - inflammation of the middle ear, as well as exudative otitis - can act as sound vibration blockers.
Finally, at the level of the inner ear, the causes of conductive hearing loss can be severe forms of otosclerosis and anatomical obstruction.
Forms of sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs in two forms: acute and chronic. The diagnosis of acute form is made if symptoms appear and develop within 30 days. If hearing problems bother a person longer, then we are dealing with a chronic form of hearing loss. It should be noted that the acute form of sensorineural hearing loss quickly turns into chronic, which is why at the first signs of a decrease in hearing acuity you should immediately seek help from specialists.
What is bilateral sensorineural hearing loss?
Also, sensorineural hearing loss is divided into unilateral and bilateral. Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss is a case where the pathology affects only one ear, and bilateral hearing loss affects both ears.
Diagnosis and treatment of hearing loss
In the department of otorhinolaryngology of the multidisciplinary clinic "MedicCity" you will quickly and accurately be diagnosed using special diagnostic procedures and first-class equipment from the world's leading manufacturers.
A special study - audiometry - is aimed at determining the degree of hearing loss. This study also evaluates the effectiveness of treatment for hearing loss. Tuning fork tests and impedance measurements are also carried out .
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Audiometry in MedicCity
3 Audiometry in MedicCity
Depending on the identified factors, one or another type of treatment is prescribed: conservative (taking anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy - electrophoresis, phonophoresis, etc.), surgical (for example, removal of sclerotized tissue or correction of an anatomical defect).
Special procedures are used to clean the ear in case of suppuration, plugs, etc. A very common procedure for cleaning the auditory tube is by blowing it according to Politzer, using a special balloon.
We have also developed comprehensive treatment programs for sensorineural hearing loss.
Why is treatment at Nearmedic convenient, reliable and effective?
Doctors at our center:
- They apply an individual approach to each patient, therefore they prescribe the diagnostic and treatment methods indicated only for him, and not everything in a row, as if according to a template;
- They work in a team, so if necessary, they immediately consult patients with related specialists in order to establish a true diagnosis;
- They constantly improve their qualifications at international symposia and congresses, which means they are aware of the latest medical advances in the field of hearing loss.
Nearmedic is a reasonable combination of quality medical services and affordable prices.
What does the diagnosis of Hearing Loss mean?
The term “hearing loss” refers to various hearing and speech perception disorders. It can be caused by damage to both the internal and external parts of the auditory organ. The disease can be congenital or acquired. Hearing loss often develops against the background of infectious diseases, for example, as complications after acute otitis media. It can also be caused by injury or taking medications with ototoxic side effects.
Hearing loss in most cases is considered a potentially reversible disease, in contrast to deafness, which is caused by irreversible pathological processes in the hearing organ. However, for successful therapy it is necessary to correctly classify it.
Auditory (auditory neuropathy)
With auditory neuropathy, the endings of the auditory nerve most often remain intact and can perceive surrounding sounds in full. However, as nerve impulses travel along the auditory nerve to the brain, sound information is decoded and distorted. This is why detecting and correcting this type of hearing loss is so difficult.
More information about the development of auditory neuropathy in children can be found here.
Causes of acute hearing loss
Neurosensory decline in hearing function can be provoked by:
- past infectious diseases (measles, rubella, mumps, etc.);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- exposure to toxins on the body (alcohol, household or industrial toxic substances, drug treatment with certain drugs, such as antibiotics);
- Acute trauma, barotrauma;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- heredity (hearing loss is a hereditary disease);
- blood diseases;
- aging.
What are the dangers of not seeking help in a timely manner?
The presence of sensorineural hearing loss indicates that a person has serious problems with intra-ear hair cells. They have a height of within a few thousandths of a millimeter. It is with their help that incoming mechanical vibrations are converted into electrical impulses and transmitted to the brain.
You can't get your hearing back. But you can stop the process of destruction of hair cells with the help of a properly selected hearing aid.
Dependence of quality of life on hearing
Hearing problems affect not only the usual way of life, but also everyday communication with others. Closedness and phobias appear, and the desire to be alone arises more and more often.
Indeed, despite the importance of vision in the aspect of obtaining new information, it is hearing that has an inextricable connection with the formation of emotions.
A simple example can be given. Try turning off the sound at the most dynamic moment while watching an action-packed film. Emotions will immediately become completely different. The Indonesian tsunami did not seem scary to people in the absence of sound. They saw him, but continued to go about their business. Therefore, the importance of hearing should not be underestimated.
Often, hearing disorders cannot be treated. And their irreversibility requires special attention to prevention. And it should start with hygiene.