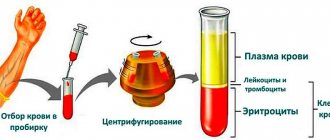
- Formerly called clinical (CBC) now - a general blood test - the fastest and most informative testing; a quick and informative screening that reflects the state of health;
- The analysis examines the number of blood components, their ratio and the general specificity of the elements - hemoglobin, red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets;
- The abbreviation for leukocytes in the results is WBC (White Blood Cells, white blood cells - translation from English);
- The role of leukocytes is immunity, resistance to pathogens, disposal of tissue destruction residues (phagocytosis).
WBC blood test – immunity and leukocytes
A general blood test may contain up to 25 parameters for assessing its quality and composition. It is white blood cells (cells) that receive more attention, and to obtain a detailed informative picture of leukocytes, about 20 blood test indices are used: these are the relative and absolute content of subpopulations of white blood cells. These include basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes and macrophages of the mononuclear system.
Leukocytes are the main markers of any inflammatory process, the body’s immune response to internal and external interference: tumor, allergen, infection. The task of white blood cells is to neutralize pathogens, foreign components and their own cells that have exhausted their resources.
To diagnose acute systemic diseases and inflammation, a detailed study is prescribed: leukocytogram, leukocyte formula. The need for such blood tests arises, for example, in case of anemia (anemia), tumors, poisoning, during the diagnosis and treatment of pathological processes of a bacterial or viral nature, etc.
To monitor health status, among other indicators in the list of UAC tests, a shortened study is sufficient: the content of individual formed elements in the blood and their morphology. Basic information about the absence of an increased load on the immune system is provided by calculating the mass of white blood cells, this is determined by the calculation of WBC - White Blood Cells.
Regardless of whether the WBC value is decreased or increased in the general analysis, any deviation indicates a reaction of the immune system, and it occurs against the background of any disease or pathological process.
Low and high white blood cell count
White blood cells are the first line of defense in the body. An increase in the level of WBC in the blood indicates atypical activity of the immune system and the need to look for the cause that caused the mobilization of protective forces. A low WBC threshold is evidence that the body’s immune capabilities are running out.
The weight and ratio of WBC varieties in the blood fluctuates not only due to diseases or injuries of a different nature. Any changes in the total volume of white blood cells, an increase or decrease in the indicator, are also influenced by temporary conditions:
- Bleeding – including during the monthly cycle in women;
- Poisoning – food, medicine, alcohol, toxic substances;
- Injuries – burns, cuts, dislocations, fractures, etc.;
- Various procedures - therapeutic, surgical, hardware cosmetology;
- High physical activity or a sharp increase in its level;
- Stress – an imbalance in the mental and/or emotional state, including destructive long-term experiences (distress);
- Lack of vitamins, especially B12 (cobalamins) and B9 (folic acid), micronutrient deficiency.
Eosinophilia and basophilia
An increase in the number of eosinophilic leukocytes, which are designated EOS in the WBC analysis, is when the resulting figure exceeds 5%. This is possible when:
- Allergic reactions;
- Skin diseases (atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema);
- Worm infestation;
- Autoimmune processes;
- Some infections (scarlet fever);
- Eosinophilic type of leukemia.
The norm for basophil content is no more than 1%. These cells are usually not detected by WBC analysis. Their appearance may occur in some forms of myeloblastic leukemia.
Additional blood tests for leukocytes
If we talk about the choice of additional cellular nutrition programs - micronutrients - the data in the WBC analysis is only enough to understand whether an inflammatory process or disease is currently developing in the body. The WBC data does not influence what exactly the vitamin complex should be. However, it is the CBC that shows the level of white blood cells and helps determine the further path to study the composition and quality of blood.
The results for white blood cells can be clarified by deciphering the leukocyte formula in the composition of the UBC, also called a leukogram shift and studying the percentage of all types of WBC:
- To the left – a regenerative shift, the release of young, immature WBC into the blood. A sign of inflammation, excessive physical activity, poisoning, bleeding;
- To the left with rejuvenation - indicates the undesirable presence of cells in the blood that normally should only be found in the bone marrow. It is necessary to examine for chronic and acute diseases: leukemia, spread of metastases, myelofibrosis, etc.;
- To the right - degenerative shift, lack of production of new WBC. It is at this point in the leukocytogram that one can suspect a lack of vitamins B9 (folate deficiency anemia) B12 (anemia with a lack of red blood cells, polyneuropathy). Also – kidney disease, liver disease, reaction to blood transfusion.
Analysis for vitamins and microelements
Against the background of a low WBC level, it is recommended to add to the blood test a comprehensive study of the concentration of key micronutrients - important participants in the formation, development, and regulation of the immune system. The reason for the decrease in the level of white blood cells can most likely be vitamin deficiency or the intake of an unbalanced complex of additional cellular nutrition, especially if inflammatory processes and diseases are excluded.
This blood test is called “Basic micronutrients of immunity”, also can be referred to as Vitamins and trace elements, Immune response. It is a fairly informative addition to the OAC, clarifies the reasons for the deterioration of well-being when there are no diseases, injuries or other obvious reasons for reducing the level of leukocytes.
Changes in leukocyte formula
Its main components are considered to be neutrophilic band and segmented cells. The former characterize the number of immature forms of leukocytes in the blood being tested, the latter - mature, full-fledged cells. The explanation of these components of the leucoformula is given in the table.
| Type of neutrophils | Normal in WBC analysis | Level up | Downgrade |
| Rod | 1-6% | This is called shifting the formula to the left. Happens when:
| A decrease in the level of any form of neutrophil leukocytes indicates leukopenia. |
| Segmented | 46-72% | This is called shifting the formula to the right. Happens when:
| |
| Blast cells, myelocytes, metamyelocytes | Must not be detected | These types of leukocytes are among the most immature and are not able to perform immune function. Their appearance is possible only with leukemia, severe infections and destruction of body tissues. | |
What vitamins and microelements are necessary for immunity?
A complex multi-stage system protects our health at different levels: from skin integrity to humoral and cellular reactions involving lymphocytes - one of the subtypes of leukocytes. The action of micronutrients is also aimed at supporting various functions in the body. For example, vitamin A is responsible for skin condition, phagocytosis and stimulation of immunoglobulin production; group B compounds provide and maintain the activity of red (erythrocytes) and white blood cells. Each element not only has its own function, but also has a close relationship with many others.
Priority participants in the regulation of the immune system
Vitamins
-fat-soluble (accumulate) – A, E, D3, K2;
- water-soluble (do not accumulate, systematic intake is required) – C, B9, B12, B5, B6;
Micro- and macroelements
-Iron (Fe) – is part of the WBC activators, increases the saturation of tissues with macrophages (antibacterial protection);
-Zn (zinc) – stimulates phagocytosis, antimicrobial defense (including viruses);
-Cu (copper) – macrophage activator;
-Mn (manganese) – protection of the cell membrane;
-Se (selenium) – potentiates both cellular and humoral responses;
Change in lymphocyte level
Lymphocyte cells, like neutrophil leukocytes, provide immune surveillance in the body. But in contrast to them, lymphocytes are responsible for both cellular and immunoglobulin immunity. Their norm is 18-40%. Explanation of possible results of WBC analysis is given in the table.
| Lymphocytosis (increased blood lymphocytes) | Lymphopenia (decreased blood lymphocytes) |
|
|
Video about the functions of different types of leukocytes, their norms in the blood:
WBC blood test is an excellent alternative to the classic study of its leukocyte composition. The main thing is to know the subtleties of correct interpretation of the results obtained.
How often should you take a leukocyte blood test?
It is recommended to monitor WBC parameters as part of a general laboratory blood test at least once a year if the state of health is satisfactory and the tests themselves do not have diagnostic value.
If we are talking about somatic diseases or in cases where caring for one’s own health is based on the principles of expediency, within the framework of evidence-based medicine, the frequency of blood tests and laboratory tests is determined by a doctor or a certified nutritionist or dietitian. It is on the study of the individual characteristics of blood and further on its composition, the body’s response to micronutrients that the bioniq system for assembling personalized vitamin complexes is built.
Monocytosis
Monocytosis is a condition in which the number of blood monocytes exceeds the standard. The norm is from 2 to 9%. This may indicate:
- Specific infections with a long course (tuberculosis, chlamydia, viral and bacterial diseases);
- Parasitic infestations;
- Monocytic type of leukemia;
- Lymphogranulomatosis and other types of lymphomas;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- Condition after removal of the spleen.
A decrease in the level of monocytes practically does not occur.
Where to get tested for leukocytes
It is the CBC, abbreviated or with a leukocytogram, that can be done by any laboratory; the quality of such blood tests will not differ. The issue is a little more complicated with studies of vitamin levels, since there is no single form for such a task. In each case, the doctor prescribes a list of microelements and vitamins that are priority for study.
For example, you can donate blood specifically for the group of fat-soluble vitamins or group B. Microelements are most often studied according to the following list: iron, magnesium, manganese, calcium, zinc, copper.
The choice of tests is made on the basis of personal complaints about health or regarding a specific purpose for collecting information.
For this purpose, bioniq has developed comfortable programs for assembling personalized bioniq LIFE and bioniq BALANCE micronutrient complexes, with the ability to collect material at home or in a place convenient for you.
Tables of norms by age
Among women
| Age | Indicator in units *109 per liter of blood |
| 16-25 | 4-10.5 |
| 25-50 | 4-12.1 |
| After 50 years | 3.6-12.4 |
The wbc norm in women is 3.6-12-4 U *109 per liter of blood and changes over the years and reaches its peak after 50 years and during pregnancy.
In men
| Age (years) | Norm of leukocytes Units * 109 / per liter |
| 16-25 | 3.3-8 |
| 25-50 | 4-9 |
| 50 and older | 3-7 |
In children
| Age (years) | Norm in units * 109 / per liter |
| Up to 1 | 6-17.5 |
| 1-5 | 5.7-17.5 |
| 5-10 | 4.4-15.5 |
| 10-16 | 4.6-13.2 |
The wbc rate also depends on gender: in men it is initially slightly lower and ranges from 3 to 9 U * 109 / per liter, in children - more than in adults (4.6-17.5 U * 109 / l) due to active formation immunity.
What indicators are included in the UAC?
The general blood test includes the following indicators: red blood cells, hemoglobin, leukocytes, color index, hematocrit, reticulocytes, platelets, ESR.
The leukocyte formula in some laboratories is signed by default, in some a doctor’s note is required. It includes the following indicators: eosinophils, basophils, band and segmented neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes.
Below is a table of norms for a general blood test:
| Index | Laboratory designation | Norma (women) | Norma (men) | Unit |
| Red blood cells | R.B.C. | 3,8-4,5 | 4,4-5,0 | 1012/l |
| Hemoglobin | HGB | 120-140 | 130-160 | g/l |
| Leukocytes | WBC | 4,0-9,0 | 4,0-9,0 | 109/l |
| Color index | CPU | 0,8-1,0 | 0,8-1,0 | |
| Hematocrit | HCT | 35-45 | 39-49 | % |
| Reticulocytes | RET | 0,2-1,2 | 0,2-1,2 | % |
| Platelets | PLT | 170,0-320,0 | 180,0-320,0 | 109/l |
| ESR | ESR | 2-15 | 1-10 | mm/hour |
| Leukocyte formula: | ||||
| Basophils | BAS | 0-1 | 0-1 | % |
| Eosinophils | EO | 0,5-5 | 0,5-5 | % |
| Myelocytes | 0 | 0 | % | |
| Metamyelocytes | 0 | 0 | % | |
| Band neutrophils | NEUT | 1-6 | 1-6 | % |
| Segmented neutrophils | NEUT | 47-67 | 47-67 | % |
| Lymphocytes | LYM | 18-40 | 18-40 | % |
| Monocytes | MON | 3-11 | 3-11 | % |
At some points, the standard blood test for adults differs from that for children.
For example, the norm of hemoglobin in a child is 110-145 g/l, leukocytes 5.0-12.0 109/l, the content of lymphocytes can be in the range of 26-60%. The remaining blood test parameters correspond to the reference values for adults.
By order of the Ministry of Health, in the first year of life, a child’s blood is taken for general analysis 4 times, then at 1 year 6 months, and then annually, starting from two years. Such measures are necessary for the early detection of blood diseases, anemia, and infections.
Elevated red blood cells
Red blood cells can be elevated due to many reasons, ranging from banal dehydration to erythremia - chronic leukemia.
Therefore, if there are any deviations in test results, you should consult a specialist to determine the cause. An increase in the number of red blood cells is called erythrocytosis, which can be: 1. Primary. A rare hereditary disease characterized by loss of energy, dizziness and darker color of the mucous membranes. 2. Secondary. Caused by other diseases or conditions (for example, smoking or staying in high mountains) and is associated with oxygen starvation of cells.
Thus, the following reasons for the increase in red blood cells can be identified:
- Dehydration. When the volume of fluid in the body is reduced, the percentage of red blood cells (and other blood cells) artificially increases.
- A lack of oxygen, which the body tries to compensate by producing more red blood cells.
- Congenital heart defect. If the heart cannot pump blood effectively, the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues is reduced. The body creates more red blood cells to compensate for oxygen deprivation.
- Genetic causes (changes in sensitivity to oxygen, impaired release of oxygen by hemoglobin).
- Polycythemia vera is a rare disease in which the body produces too many red blood cells.
Increased production of red blood cells can cause blood to thicken, slow blood flow, and related problems (eg, headaches, dizziness, vision problems, excessive blood clotting).
Often, elevated red blood cell levels are due to dehydration, hot weather, extreme stress, or excessive exercise. A pathological increase in red blood cells is a fairly rare pathology. Much more often, patients encounter reduced levels.
Definition and Purposes of Purpose
CBC (complete blood count) is a laboratory diagnostic method for assessing the condition of the body and searching for the source of pathology. This test can be prescribed by a doctor of any specialty. In what cases is OAC prescribed:
- For prevention during medical examinations. The composition of the blood is relatively constant and rarely goes beyond the normal range in a healthy person. And some diseases may not affect your well-being for a long time, and then a preventive test will become a reason for subsequent examination.
- When the first symptoms of illness appear. Analysis in this case can make it possible to determine the nature of the disease, the degree of intensity of inflammation or an allergic reaction.
- OAC may be re-prescribed to monitor the course of the disease over time. Also to assess the effectiveness of the therapy.