You can familiarize yourself with other diseases starting with the letter “G”: Ganglioneuritis, Ganglioneuroblastoma, Ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine node, Soft tissue hematoma, Hematomyelia, Hemiballism, Hemorrhagic stroke, Ganglioneuroma, Hemangioblastoma, Hemifacial spasm, Generalized epilepsy, Germinoma of the brain, Hydrocephalus, Hyperventilation syndrome, Hyperkinesis, Hypersomnia, Hypertensive cerebral crisis, Hypertensive encephalopathy, Hypnic headache, Brain glioma
Hypertensive encephalopathy: how to maintain brain health
Chronic progressive damage to brain tissue caused by pathology of cerebral hemodynamics, which is provoked by prolonged hypertension, is called hypertensive encephalopathy. It develops in patients with poorly controlled, sudden increases in blood pressure. Characteristic symptoms of HE are signs of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. To make a diagnosis, not only an examination by a neurologist is required, but also a consultation with a psychiatrist and cardiologist, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and a study of brain dynamics. Therapy requires taking antihypertensive drugs to stabilize blood pressure and adding nootropic, neuroprotective and symptomatic drugs.
Causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
Pathology develops mainly in older people against the background of the following conditions:
- Deposition of blood clots inside a vein, artery;
- Angiospasm with a significant increase in blood pressure;
- Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries;
- Cholesterol plaques inside the vessel wall;
- Damage to the vascular wall by bacterial toxins (botulism, streptococci);
- Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the cervical spine;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD);
- Inflammatory processes of the arterial wall (vasculitis).
To predict clinical symptoms, it is rational to divide etiological factors into five categories:
- Venous;
- Hypertensive;
- Atherosclerotic;
- Neurological (VSD, rheumatism);
- Mixed.
The most common causes of nosology in older people are hypertension, atherosclerosis, and varicose veins.
General information about the disease
Discirculatory encephalopathy is most often caused by atherosclerosis. The second place among the causes of pathology is hypertension. GE is included in a separate category in ICD-10. It occurs in patients against the background of chronic symptomatic hypertension or hypertension. The term appeared in 1985. It was introduced into use by neurophysiologists N.V. Lebedev and I.V. Ganushkina. Hypertensive encephalopathy occurs with damage to small vessels. This distinguishes it from the atherosclerotic form. But the difference is conditional, since atherosclerotic changes rapidly progress against the background of GE.
The reasons that provoke it
The disease develops against a background of high blood pressure, regardless of whether hypertension is primary or secondary, forming against the background of endocrine disorders, kidney damage or atherosclerosis of the aorta. Hypertension can be provoked by pathologies such as chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hypercortisolism, pheochromocytoma, hyperaldosteronism. The development of hypertensive encephalopathy is caused by factors such as:
Hypertensive crises, since a rapid rise in blood pressure thins and increases the permeability of the vascular wall. Because of this, hemorrhagic impregnation of the cerebral tissue occurs at the site of thinning;- Uncontrolled high blood pressure leads to more rapid changes in blood vessels than in patients who regularly receive antihypertensive therapy. It is worth noting that even with the use of medications, in some cases it is not possible to correct hypertension;
- High pulse pressure aggravates the course of the pathology, since it causes additional stress on the muscular system and vascular walls. According to studies, the difference between diastolic and systolic pressure is 40 mm Hg. st;
- Nocturnal hypertension is dangerous because it occurs hidden. Because of this, it is not corrected in a timely manner and leads to prolonged spastic states of cerebral vessels with the development of ischemia in the tissues of the central nervous system.
Drug therapy for hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy is a progressive damage to the brain substance caused by a lack of blood circulation in the cerebral vessels due to a poorly controlled increase in blood pressure (BP). Pathomorphological changes in the cerebral vessels in arterial hypertension (AH), such as plasmatic and hemorrhagic impregnation, necrosis of the vascular wall with its subsequent thinning and adaptive thickening of the walls of extracerebral vessels, are defined by the term “hypertensive angioencephalopathy”.
Early damage to the predominantly white matter of the brain in hypertension, which is the destruction of the myelin of the central conductors, small cavities, dilated perivascular spaces (creblures) due to edema, spongiosis, is caused by damage to the cortico-medullary arteries and has a typical picture on CT (decreased signal intensity) and MRI (increasing signal intensity). This phenomenon, usually detected in areas of the so-called terminal blood supply (periventricular areas of the brain), which are especially sensitive to fluctuations in blood pressure, is called hypertensive leukoencephalopathy, or leukorrheosis. ICD-10 mentions only hypertensive encephalopathy, the terms “hypertensive leukoencephalopathy” and “hypertensive angioencephalopathy” are not used, and the term “progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy” in the classification implies that hypertension is not the only cause of this process. From this point of view, subcortical atherosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger disease) is of interest, which is considered by some authors as a variant of hypertensive encephalopathy, and by others as an independent nosological unit, since hypertension is not detected in all patients with brain damage, and in addition, it is not always possible to carry out parallel between the values of systolic and diastolic blood pressure and disease progression. A significant difference between hypertensive encephalopathy and atherosclerotic encephalopathy can be considered the predominant damage in hypertension to small branches of brain vessels, rather than large extracranial and intracranial arteries. However, the division of hypertensive and atherosclerotic encephalopathy is quite arbitrary. Hypertension quite quickly leads to the development of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the brain. It is not always possible to detect atherosclerotic changes in extracerebral and cerebral vessels with ultrasound and MRI angiography in patients with hypertension, however, given the low sensitivity of these methods, in such cases it is impossible to completely exclude the presence of atherosclerosis and confidently make a diagnosis of “hypertensive encephalopathy”. Apparently, in most cases we are talking about “mixed” encephalopathy. It is hardly possible to separate these types of encephalopathy based on clinical manifestations. Many works have been devoted to the clinical manifestations of encephalopathy and its course, but there is no exact idea about the pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Many researchers artificially expand the concept of “encephalopathy”, using this term to designate the initial signs of cerebrovascular insufficiency, which is not progressive in nature in all cases. Others believe that hypertensive encephalopathy is always a consequence of a malignant variant of hypertension, which is also characterized by kidney damage.
With hypertensive encephalopathy, as with all other forms of discirculatory encephalopathies, three stages of the disease can be distinguished. At stage I
the clinical picture is dominated by subjective disturbances in the form of general weakness and fatigue, emotional lability, sleep disturbances, decreased memory and attention, and headaches.
Neurological disorders are represented by anisoreflexia, incoordination, and symptoms of oral automatism. There are no distinct neurological syndromes at this stage. Violations of memory, praxis and gnosis can be identified, as a rule, only when conducting special batteries of tests. At stage II
, subjective sensations worsen, and distinct neurological syndromes (pyramidal, discoordination, amyostatic, dysmnestic) are formed, usually with dominance of one of them.
Professional and social adaptation of patients decreases. Stage III
, along with an increase in neurological symptoms, is characterized by the appearance of pseudobulbar syndrome, paroxysmal conditions (including epileptic seizures), severe cognitive impairment, which causes social and everyday maladjustment and loss of performance. Thus, hypertensive encephalopathy ultimately leads to the formation of vascular dementia (usually subcortical).
In stages II and III of hypertensive encephalopathy, diffuse changes in the brain substance are usually combined with focal lesions in the form of lacunar infarcts - small cavities ranging in size from 0.1 to 1.0 cm, formed in areas of cerebral ischemia. Either asymptomatic development of a lacunar infarction or the formation of a transient ischemic attack or stroke is possible, which depends on the location and volume of the ischemic focus. The formation of multiple small-focal brain lesions - the so-called lacunar state - significantly worsens the prognosis of hypertensive encephalopathy and reduces the possibility of drug correction of the patient’s condition, even when good control of hypertension is achieved. Treatment of hypertensive encephalopathy includes several areas:
- treatment of arterial hypertension;
- impact on factors that aggravate the course of hypertensive encephalopathy - hypercholesterolemia, increased platelet aggregation and blood viscosity, diabetes mellitus, atrial fibrillation, smoking, alcohol abuse, etc.;
- improving blood supply to the brain;
- improving the metabolism of nerve cells under conditions of ischemia and hypoxia.
There is no doubt that effective therapy for hypertension at the earliest stages of the disease can prevent the development of encephalopathy, but the problem is that many patients do not experience elevated blood pressure for a long time. The basis for the prevention of hypertensive encephalopathy in patients with hypertension is to achieve control over hypertension, namely the target level of blood pressure, at which the threat of the risk of developing cerebrovascular complications is minimal. Tactically, this can be solved by prescribing antihypertensive drugs and correcting existing risk factors. The target blood pressure level can vary significantly depending on the presence of risk factors for the development of cerebrovascular complications (diabetes mellitus, renal failure, etc.). Thus, the target level of systolic blood pressure in the general population of patients with hypertension is less than 140 mm Hg. Art., diastolic - less than 90 mm Hg. Art., while for patients with chronic renal failure - less than 120 mm Hg. Art. and 75 mm Hg. Art. respectively. Achieving the target blood pressure level, especially with initially high blood pressure values in patients with cerebrovascular pathology, should not occur in a short time, as this is fraught with the development of ischemic stroke. Depending on the initial level of blood pressure, duration of the disease, and the severity of cerebral disorders, this period should be from 6 to 12 weeks.
The question of the advisability of prescribing additional pharmacological drugs to patients with hypertension without cerebral symptoms that affect the rheological qualities of the blood, stimulate endothelium-dependent reactions of the vascular wall, improve metabolic processes in brain tissue, and reduce the content of free radicals has not been fully studied. In elderly people with lipohyalinosis of the walls of small vessels, courses of treatment with drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and have neuroprotective properties are advisable even with good blood pressure control. The use of these drugs in courses lasting 2–3 months with breaks of 6–8 months can slow down the development of vascular pathology and prevent damage to the brain substance. Prevention of damage to brain structures in hypertension should include not only effective control of hypertension, but also additional treatment aimed at improving cerebral blood flow and metabolic processes in the brain.
At stage I of hypertensive encephalopathy, it is necessary to add to the main therapy drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and metabolism of nervous tissue, as well as drugs that act on internal factors that can affect the progression of encephalopathy. In stages II and III of hypertensive encephalopathy, the general principles of therapy remain the same, but, first of all, the dosages of drugs acting on cerebral blood flow and metabolic support of brain structures change. To prevent the progression of atherosclerotic processes, normalization of fat metabolism is necessary, which implies a decrease in body mass index (following a low-fat diet) and taking statins. With good and satisfactory blood pressure control, it is possible to prescribe antiplatelet agents to improve the rheological properties of the blood. The use of drugs with a vascular protective effect, which improve the metabolism of brain tissue and have neuroprotective properties, is mandatory at all stages of hypertensive encephalopathy. One of the highly effective drugs of combined action is Mexidol.
Mexidol (2‑ethyl-6‑methyl-3‑hydroxypyridine succinate) belongs to the group of antihypoxants with antioxidant, nootropic and anxiolytic properties. The drug improves cerebral metabolism and blood supply to the brain, microcirculation, rheological properties of blood, reduces platelet aggregation, has a hypolipidemic effect, and reduces the level of total cholesterol and LDL. Mexidol improves cell energy metabolism, synaptic transmission, activates the energy-synthesizing functions of mitochondria, affects the content of biogenic amines, inhibits free radical oxidation of lipids and the synthesis of thromboxane A, enhances the synthesis of prostacyclin, increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes, SOD. The lipid-lowering effect of this drug is to reduce the amount of total cholesterol and LDL, reducing the cholesterol/phospholipid ratio. Mexidol also modulates the receptor benzodiazepine, GABAergic, acetylcholine complexes of brain membranes, enhances their ability to bind, stabilizes biological membranes, membranes of erythrocytes and platelets.
The nootropic effect of the drug is carried out by stimulating the transmission of excitation in central neurons, improving cerebral blood flow, metabolic processes and information exchange between the hemispheres, which helps improve memory, learning, preserving a memory trace and counteracts the process of extinction of acquired skills and reflexes. The drug eliminates the symptoms of hypomnesia, increased absent-mindedness, improves the ability to concentrate and count, short-term and long-term memory. Mexidol accelerates the recovery of motor functions in patients who have suffered a stroke. The drug increases the degree of control of the cerebral cortex over subcortical structures, provides a psychoanalgesic, anxiolytic effect, and reduces extrapyramidal dysfunction. The pronounced antihypoxic and anti-ischemic effect is due to a direct effect on the endogenous respiration of mitochondria with activation of their energy-synthesizing function. The antihypoxic effect of the drug is due to the presence of succinate in its composition, which, entering the intracellular space, under hypoxic conditions is capable of being oxidized by components of the respiratory chain. Mexidol has a pronounced geroprotective effect, helps restore emotional and vegetative status, and smoothes out the manifestations of neurological deficits. For the treatment of hypertensive encephalopathy, Mexidol is recommended to be administered either 100 mg (2 ml) per 10.0 ml of physiological NaCl solution intravenously daily for 10 days; or 200 mg (4 ml) intramuscularly daily for 10 days. After a parenteral course of treatment with Mexidol, it is advisable to take a tablet form of 0.125 g three times a day for 2–6 weeks. You can also start treatment by taking the tablet form of 0.125 g three times a day for a course of at least 4-6 weeks.
A number of studies provide evidence of the high effectiveness and safety of Mexidol. At the Krasnoyarsk State Medical Academy, the effectiveness and safety of Mexidol was studied in patients with various forms of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency [5]. After three weeks of use of the drug, a subjective improvement in the patients’ condition was noted (complaints of noise in the head, weakness and anxiety decreased). Mexidol had a positive effect on memory, improved concentration and emotional state of patients. At the Department of Nervous Diseases of the Military Medical Academy of St. Petersburg, the dynamics of changes in neurological symptoms and syndromes in patients with chronic cerebrovascular accidents during complex therapy using the drug Mexidol was studied [6]. During therapy with Mexidol, early normalization of coordination functions and overcoming asthenic syndrome were revealed, and the dependence of the severity of cranialgic syndrome on the degree of dyscirculatory disorders in the veins of the brain and the elimination of its manifestations was shown. At the Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, a comprehensive clinical and biochemical study of the effectiveness of Mexidol in patients with chronic cerebrovascular diseases was carried out with a detailed analysis of the relationship between the clinical effectiveness of the drug and the quantitative characteristics of oxidative stress. Analysis of the study results demonstrated the promise of using Mexidol as a neuroprotector for vascular diseases of the brain. It was concluded that the use of Mexidol in patients with chronic cerebrovascular diseases leads to an improvement in the condition of patients and a decrease in the severity of the most common clinical manifestations of this pathology - asthenic syndrome, psychoemotional disorders and cochleovestibular disorders. The maximum therapeutic effect of Mexidol is observed in patients with an initially increased content of lipid peroxidation products and depletion of the body's antioxidant systems, which indicates the importance of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of chronic cerebrovascular diseases. The biochemical basis of the therapeutic effect of Mexidol is its antioxidant activity: the drug significantly reduces damage to lipoprotein structures, restoring the activity of the endogenous antioxidant system [7].
Hypertensive encephalopathy is a progressive disease characterized by a variety of neurological syndromes, a high risk of stroke and leading to vascular dementia. Timely and correctly selected therapy makes it possible to maintain the patient’s professional, social and everyday adaptation for many years, and improves the prognosis for the patient’s life expectancy. The effectiveness of treatment of hypertensive encephalopathy increases when antihypertensive drugs are combined with drugs that improve cerebral blood flow, metabolism of nervous tissue and have a neuroprotective effect.
Development mechanism
When blood pressure rises, a compensatory mechanism appears, causing the small vessels of the arterioles to narrow to prevent their rupture. The pathogenesis is due to the fact that a regular increase in blood pressure leads to hypertrophy of the muscular layer of the walls of arterioles, which leads to thickening of the walls of blood vessels and a narrowing of their lumen. The process occurs in all tissues, but the most quickly affected are the brain, heart, and kidneys. As the lumen of the cerebral arterioles decreases, cerebral perfusion begins to fall and chronic ischemia of the central nervous system develops. Brain tissue suffers from a constant lack of oxygen and nutrients, which leads to degenerative processes. Atherosclerotic changes further aggravate cerebrovascular insufficiency and intensify its symptoms.
This leads to early damage to the white matter, expansion of the perivascular spaces, and demyelination of nerve fibers. Degenerative processes are accompanied by individual local foci - lacunar infarctions. But basically the changes are diffuse in nature and symmetrical in both hemispheres. They begin from the lateral ventricles and spread periventricularly.
Classification of encephalopathy
GE progresses gradually. Symptoms worsen and the condition of cerebral tissue deteriorates. To prescribe effective therapy, a classification has been developed that allows us to determine at what stage the pathology is. Neurologists distinguish three stages of hypertensive encephalopathy:
At the first stage, one can note the presence of subjective sensations of the patient, including complaints of fatigue, memory loss, and headaches. Objective symptoms are not expressed. Cognitive disorders are only detected through rigorous testing;- At the second stage, pronounced neurological symptoms appear: atactic, pyramidal, vestibular, subcortical, dysmnestic syndrome. Most often, one of the symptoms is dominant. Cognitive impairment remains moderate, but social adaptation is reduced. There are objective difficulties in pre-professional activity;
- At the third stage, the symptomatic picture increases and other syndromes join. The debut of parkinsonism, pseudobulbar syndrome, and epileptic seizures is possible. There are severe cognitive impairments, including dementia. Household and professional adaptation is disrupted.
Symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
Let us describe the main symptoms of all forms of DEP:
- Disorders of the functioning of the cerebellum - fluency of speech, walking disorders, instability during movements;
- Affective disorders;
- Vascular dementia;
- Pyramidal spasticity;
- Pseudobulbar problems;
- Slow speech;
- Autonomic vestibular disorders;
- Instability of blood pressure;
- Smoothness and slowness of speech.
It is difficult to unambiguously determine the symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, since the manifestations are based on functional disorders of cerebral circulation.
The main signs of alcoholic encephalopathy:
- Decreased memory for short-term events;
- Mental and emotional disorders;
- Apathy, lack of interest in favorite activities;
- Severe headaches;
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Vomiting reflex;
- Dizziness;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Neurological focal symptoms.
Discirculatory encephalopathy is characterized by the appearance of symptoms closer to the night. In the first degree, initial symptoms occur after heavy physical activity:
- Unsteady walking;
- Decreased memory;
- Pathology of attention;
- Fall of self-criticism;
- Depressive syndrome;
- Dementia;
- Muscle tremors;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Pseudobulbar syndrome;
- Irritability;
- Ataxia.
The appearance of any sign requires MRI or CT angiography to verify changes in cerebral circulation.
Clinical manifestations
At the initial stage, slowly progressive nonspecific symptoms are observed. It includes:
Cephalgia;- Chronic fatigue;
- Memory impairment;
- Decreased concentration.
As the pathology develops, certain neurological syndromes appear. Dysmnestic syndrome is manifested by memory impairment. With a subcortical disorder, tremor, secondary parkinsonism, and hyperkinesis dominate. Vestibular is characterized by unsteadiness of gait, pyramidal - muscle weakness such as mild hemiparesis.
Also observed:
- Narrowing the range of interests;
- Deterioration in the speed and productivity of thinking;
- Apraxia, that is, difficulties with organizing activities;
- Motivation problems;
- Increased emotional lability;
- Problems in the cognitive sphere arise due to a lack of a critical attitude towards one’s own state;
- Behavioral and affective disorders.
The clinical picture is characterized by a transient improvement of the condition and flickering of the symptomatic picture.
The third stage of the disease is accompanied by severe cognitive and organic disorders:
Agnosia;- Apraxia;
- Dysarthria;
- Decay of intellectual abilities;
- Personality change;
- Mental disorders;
- Loss of professional skills;
- Pseudobulbar palsy;
- Vascular dementia with personality disorder;
- Violent crying;
- Swallowing disorder;
- Epileptic paroxysms caused by lacunar infarctions;
- Syncope;
- Increases in ataxic, pyramidal and parkinsonian syndrome, which limit the possibility of household services and independent movement.
Degrees of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
The stages of DEP determine the clinical picture of the disease:
- First (I) degree – memory loss appears;
- Second (II) degree – personality changes occur, self-criticism decreases;
- Third (III) degree – several syndromes exist simultaneously, the ability to self-care is lost.
Stage 1 DEP is common among the population. Medical sources claim that every second resident has a nosology. Cerebral circulation disorders (dyscirculation) develop due to constant stress and air pollution.
Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree occurs in old age. The development of nosology provokes cerebral infarctions and strokes. Depending on the symptoms, several clinical variants of the nosology are formed:
- Social maladjustment;
- Movement disorders;
- Polyneuropathy.
One of the common types of the disease is atherosclerotic dyscirculation. An imbalance of fat metabolism causes disturbances in the patency of cerebral arteries due to the presence of atherosclerotic plaques inside the lumen.
Venous discirculatory encephalopathy occurs due to stagnation of venous blood in the body. Congestion of the veins ensures the formation of blood clots. Migration of blood clots from the primary focus into the cerebral vessels provokes a stroke.
Possible complications
Hypertensive encephalopathy in its chronic form is often accompanied by acute episodes that occur against the background of a rapid rise in blood pressure. They are caused by hypotonic dilatation of intracerebral vessels and disruption of vascular regulation. This condition is caused by sweating of blood plasma with the formation of perivascular edema. In the absence of adequate timely treatment, the acute form of HE can lead to hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, lacunar infarction. Pseudobulbar syndrome arising against the background of pathology leads to dysphagia, which leads to possible food getting stuck in the larynx and asphyxia, as well as the reflux of food particles into the respiratory tract, threatening the development of aspiration pneumonia.
Diagnostic methods
If a characteristic symptomatic picture develops against the background of hypertension, the specialist suggests hypertensive encephalopathy. Diagnostics is required to exclude other cerebral pathologies, as well as to assess the degree of changes in the central nervous system and blood vessels. The main diagnostic stages include:
Consultation with a neurologist to assess the patient’s neurological status. In the initial stages of the disease, it remains unchanged. Anisoreflexia may develop. Cognitive testing is also carried out to determine minor mnemonic, gnostic and praxic changes;- Cardiac examination can confirm the presence of hypertension. The specialist may prescribe echocardiography, ECG, daily blood pressure monitoring;
- A mental examination is carried out by a neuropsychologist, a psychiatrist, if there are suspicions of mental abnormalities. During the consultation, anamnesis collection, conversation, testing and observations are carried out;
- Study of cerebral hemodynamics using duplex scanning of cerebral vessels, magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral vessels, transcranial ultrasound. Diagnostics makes it possible to identify narrowing of the lumen of arterioles, determine where the most pronounced changes are localized, and also clarify the degree;
- Laboratory tests to determine the level of lipid spectrum and cholesterol in the blood. In addition, a Rehberg test, a biochemical blood test and a urine test are required to assess kidney function;
- MRI of the brain is the most informative method, allowing maximum visualization of the state of brain tissue and detection of disorders at the earliest stages. Reveals diffuse degenerative changes, foci of previous lacunar infarctions in stage II-III hypertensive encephalopathy and excludes organic pathologies of the central nervous system.
Consultation with an epileptologist and electroencephalography can reveal paroxysmal activity. If renal dysfunction is detected using urine tests, consultation with a nephrologist and ultrasound of the kidneys is necessary.
During diagnosis, it is very important to distinguish hypertensive encephalopathy from Parkinson's disease, slow CNS infections, encephalitis, brain tumors, Alzheimer's, demyelinating diseases and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. The vascular nature of the lesion is revealed by traces of lacunar infarctions, noticeable during MRI.
What is encephalopathy and why is it dangerous?
Every person experiences headaches from time to time. Many people do not take into account the reasons for feeling unwell and prefer to take painkillers. However, recurrent headaches can be caused not only by fatigue or changes in blood pressure. Is this often how encephalopathy manifests itself? a common brain disease caused by oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. We will talk further about whether this pathology can be cured and prevented.
What is encephalopathy?
This is a non-inflammatory disease in which the brain tissue receives insufficient blood and, therefore, oxygen. As a result, nerve cells die, stagnant processes appear, and swelling of the meninges forms in local areas.
Encephalopathy? this is a general concept that unites degenerative processes in the brain. Very often, pathology is not defined as an independent disease, but is detected against the background of other diseases. There are no age restrictions for encephalopathy.
| ! | The optimal rate of blood supply to the brain is 45-50 ml of blood every minute per 100 g of brain matter. Reducing this figure to 18 ml per minute is considered critical. |
Causes of the disease
Encephalopathy can be congenital or acquired. In each case, the causes of the disease are different factors, but they are united by a persistent violation of cerebral circulation.
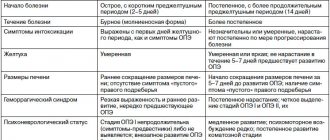
| Congenital | Acquired |
|
|
In the case of newborn children, the presence of the disease is not always obvious. As a rule, the diagnosis is made closer to a year in the presence of specific symptoms. In adults, pathologies caused by vascular disorders are widespread. For example, with atherosclerosis, the lumen of blood vessels decreases as a result of the deposition of lipids on their walls. Blood flow to the brain decreases, ischemia develops. In difficult cases, the lumen of the vessel is blocked by a blood clot or cholesterol plaque, a stroke occurs, as a result of which brain cells die.
Types of encephalopathy
Two main forms of the disease? perinatal (congenital) and acquired. The first includes a decrease in blood supply to the brain that occurred between 28 weeks of intrauterine development of the fetus and the 7th day of the child’s life. All other types of encephalopathy? acquired.
Each type of disease has its own specific symptoms and treatment methods. For this reason, it is important to see a doctor in time to undergo diagnosis and treatment. The manifestations of the disorders depend on which area of the brain is affected.
- Vascular encephalopathy.
It occurs as a result of impaired blood supply to the brain and oxygen starvation of cells. The pathology may be atherosclerotic or hypertensive in nature. In the first case, atherosclerotic plaques are present in the blood vessels, and in the second, high blood pressure is observed with a complication in the form of cerebral edema.
- Traumatic.
In this case, encephalopathy develops as a result of a traumatic brain injury. The disease may cause degenerative, dystrophic, and scarring changes in brain tissue. Most often, the pathology is observed in athletes, drivers and passengers of vehicles, as well as newborn children.
- Radial.
The disease can result from exposure of the brain to ionizing radiation. This type of encephalopathy can be observed among specialists involved in eliminating the consequences of radiation accidents, as well as among those who work with related equipment.
- Metabolic (toxic).
Brain damage can be caused by intoxication of the body due to liver failure, diabetes, carbon monoxide poisoning, heavy metal salts, etc. Toxic poisoning also leads to severe neurological disorders.
- Alcoholic.
The breakdown products of ethyl alcohol, entering the brain through the bloodstream, cause irreversible metabolic disorders. Does Wernicke's encephalopathy also belong to this group? damage to the midbrain and hypothalamus due to alcohol abuse, as well as vitamin deficiency and other reasons.
- Inflammatory.
Most often we are talking about inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels. The severity and specificity of manifestations depend on the affected area.
- Vaccine.
This is a rare type of neurological disorder that occurs in response to the vaccine. The most common reaction is to whooping cough medications.
- Discirculatory.
Brain dysfunction occurs due to gradually increasing insufficiency of blood supply. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy directly affects cognitive abilities and neurological disorders.
- Residual encephalopathy (residual).
Structural changes in tissue occur in the brain due to previous injuries, ischemic disease, and infections.
- Spongy.
This type of encephalopathy combines severe diseases in which the brain turns into a spongy body. Among them are Getsmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, etc.
Symptoms of encephalopathy
The disease is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, which depend on the causes of brain dysfunction. Encephalopathy can have an acute and chronic course.
In the first case, symptoms appear suddenly and very quickly lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition. The main cause of acute encephalopathy is toxic damage to the body.
In the second case, signs of brain dysfunction appear gradually in the form of headaches, forgetfulness, and emotional instability.
The disease goes through several stages in its development, which are characterized by the following manifestations:
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 |
|
|
|
| ! | The main manifestations of encephalopathy at the initial stage? headaches, dizziness, tinnitus. Symptoms may occur when the weather changes, physical fatigue, or stress. When they appear, it is necessary to undergo examination. |
Diagnosis of the disease
Modern examination methods make it possible to establish the localization, nature of the pathology, and the mechanism of its occurrence. Diagnostics may include:
Blood tests to determine the levels of hormones, lipids, cholesterol, sugar and other elements that may indicate the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Rheoencephalography (REG) to measure blood flow in the brain, determine the elasticity and tension of the walls of blood vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging
to analyze morphological changes in brain tissue. MRI allows you to differentiate encephalography from other diseases of the nervous system: Alzheimer's disease, stroke, tumors, etc.
Doppler ultrasound
to determine the speed of blood flow in an individual blood vessel and clarify the location of the atherosclerotic plaque. Provides information about the state of cerebral circulation.
Ultrasound scanning
to clarify the cause of vessel obstruction? the presence of a spasm, plaque, blood clot, etc. The method has no contraindications and allows you to quickly obtain a reliable result.
Ultrasound monitoring
to determine the cause of blood clot formation? thrombi and emboli. The method also allows you to assess the risk of stroke.
Can encephalopathy be cured?
The disease requires long-term course therapy and observation by a neurologist. For successful treatment and elimination of the symptoms of the disease, diagnosing the causes of its occurrence is of paramount importance.
Acute encephalopathy is an indication for urgent hospitalization and detoxification therapy in a hospital setting. The chronic form of the pathology requires following a certain diet and taking medications as prescribed by a doctor 2–3 times a year.
For hypertension (high blood pressure), the doctor may prescribe Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril, Fosinopril and other drugs.
Medicines for hypertension require strict adherence to the dosage schedule, usually 2–3 times a day. Many patients require lifelong use of medications to normalize blood pressure. The dosage and type of medication should be prescribed by the attending physician, since each of them acts with different intensity and is excreted from the body differently.
Modern antihypertensive drugs are divided into the following groups:
- ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme);
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- calcium antagonists;
- direct renin inhibitors;
- combination and other drugs.
To improve brain metabolism, Cavinton, Vasobral, Corinfar, Tseliprol, Nikoshpan, Picamilon and other drugs of various groups are prescribed.
Medicines help restore cerebral circulation and thereby eliminate symptoms such as:
- headache and dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- memory problems;
- insomnia;
- mood swings, etc.
The main groups of drugs to improve cerebral circulation:
- vasodilators;
- blood thinners;
- nootropic;
- vascular strengthening;
- blood microcirculation correctors, etc.
Do free radicals accumulate in the human body during life? reactive oxygen species that destroy cells and lead to diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. To protect tissues from their effects, are antioxidants prescribed? “Actovegin”, “Tiogamma”, “Emoxipin”, “Quertin”, “Riboxin”, “Mexidol”, “Cerakson”, etc. The drugs improve capillary blood flow, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, prevent or slow down atherosclerotic changes, reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack.
| For encephalopathy, the treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient, taking into account data from laboratory and instrumental studies. Almost all drugs for the treatment of chronic forms of the disease are available in pharmacies with a doctor’s prescription. In addition to the listed groups of drugs, the patient may be prescribed anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antiplatelet agents and other drugs. |
Consequences and complications of encephalopathy
Delaying treatment for a long time leads to extensive brain damage. As the disease worsens, the patient may experience:
- constant headaches;
- disorder of consciousness;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- facial expression disorders;
- movement coordination disorders;
- tremor of limbs, tic, convulsions;
- sexual function disorder;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia and much more, depending on the area of brain damage.
Prevention of encephalopathy
For successful treatment, elimination of symptoms of the disease and prevention of degenerative processes in the brain, the patient is recommended:
- adjust your diet? give up foods high in cholesterol and fast carbohydrates in favor of vegetables, fruits, and herbs;
- to refuse from bad habits ? smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Exercise regularly to keep your body in good shape.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and detect encephalopathy in the early stages, the prognosis is positive. The effectiveness of treatment will largely depend on the causes of the pathology. Severe cardiovascular (ischemia, stroke, heart attack) and neurological (osteochondrosis, traumatic brain injury) diseases may require lifelong course therapy. In each case, the treatment and prevention program should be drawn up by the attending physician.
Methods of therapy
How effective the treatment will be primarily depends on whether the blood pressure can be stabilized. Neurological therapy is carried out while taking antihypertensive drugs and treating the primary disease that provokes hypertension. Treatment of hypertensive encephalopathy is aimed at improving cerebral perfusion, restoring the functions of the central nervous system, and maintaining the metabolism of brain tissue. For this purpose the following are assigned:
Preparations to improve blood microcirculation. The course takes anticoagulants, for example dipyridamole, acetylsalicylic acid. Taking pentoxifylline can also improve microcirculation;- Vasodilators help relieve spasm of arterioles, that is, the main pathogenetic link in the development of GE. The choice of drugs should take into account the presence of side steal syndrome. It is necessary to focus on such medications as: calcium channel blockers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, a2-adrenergic receptor antagonists;
- Symptomatic drugs that are prescribed depending on the clinical picture accompanying encephalopathy. For hyperlipidemia, the prescription of statin drugs is indicated. If there is a decrease in cognitive abilities, taking nootropics is necessary. When mental abnormalities occur, mood stabilizers, sedative pharmaceuticals, and tranquilizers are needed. For epileptic paroxysms - anticonvulsants;
- Neuroprotectors can increase the resistance of nerve cells to a reduced supply of nutrients and chronic hypoxia. This group of drugs includes antioxidants: lipoic acid, ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate and amino acid drugs: glycine, aminobutyric acid.
Arterial hypertension and dyscirculatory encephalopathy: treatment algorithm
ABOUT
The main objective of this article is to consider the issue of treatment of patients with cerebrovascular pathology who have elevated blood pressure. Much attention is paid to the issues of blood pressure correction in patients with cerebral strokes, which is understandable, since these conditions directly threaten the lives of patients [1,2,3]. At the same time, arterial hypertension (AH) can form not only local, but also diffuse or multifocal lesions of the brain with progressive impairment of its function, as a result of cerebral circulatory failure - hypertensive discirculatory encephalopathy [4]. The term discirculatory encephalopathy implies a wide range of etiological factors leading to pathology of cerebral blood flow, not only related to the condition of the wall of cerebral vessels (atherosclerotic), but also hemodynamic (with heart pathology), rheological (blood diseases) or associated with pathology of the venous sinuses and vessels . Discirculatory encephalopathy, caused primarily by hypertension, is one of the most common variants of this cerebrovascular pathology.
The main sign of the presence of hypertension is an increase in blood pressure to 140/90 mm Hg.
, recorded repeatedly and without connection with any situation (physical activity, emotional experience, etc.).
The prevalence of hypertension in Russia is very high and occurs in almost 40% of the population, equally common in men and women. In 95% of cases, we are talking about hypertension, while symptomatic hypertension is detected only in 5% of patients. The importance of polymorphism of not one, but several genes in the development of predisposition to high blood pressure has been shown, and environmental (smoking, alcoholism, stress) or internal factors (the development of insulin resistance), the action of which leads to the development of genetically determined hypertension, are no less important.
Considering the external and internal factors responsible for the development of hypertension, with the subsequent formation of hypertensive encephalopathy (Table 1), we can understand the ways of preventive and therapeutic effects. Impact on external factors is possible only if the patient is motivated to fight hypertension. In Russia, the ability of patients, especially men, to change their lifestyle, achieving the elimination of the main external factors influencing hypertension, is extremely low. Most of them do not even take the necessary pharmacological medications, what can we say about following a low-salt diet, giving up smoking and alcohol, a rational work and rest schedule, exercising, the need to lose weight, and sometimes taking antidepressants or anxiolytics. The most radical thing for the prevention of hypertensive encephalopathy is the creation of schools for patients with hypertension with the development of motivation in them to constantly monitor blood pressure, and as a priority task - training patients to independently change antihypertensive therapy depending on the level of blood pressure. This does not look like a utopia at all if we remember that the main task for schools for patients with diabetes is to teach them to independently change their glucose-lowering therapy, including insulin therapy. Another thing is that this will require huge human (medical) and material costs, but this is the future.
Hypertensive encephalopathy can develop in two scenarios
.
The first - quite rare at present - acute hypertensive encephalopathy
.
It occurs against the background of severe long-term hypertension or as a result of a rapid rise in blood pressure to very high numbers. In some cases, this occurs as a result of unjustified withdrawal of antihypertensive drugs or when patients with hypertension take drugs that increase blood pressure, and sometimes with diseases that can lead to unexpected increases in blood pressure to high numbers (pheochromocytoma, toxicosis of pregnancy, aortic dissection). The disease develops rapidly within several hours against a background of diastolic blood pressure of 120 mm Hg. and higher, manifested by diffuse headache, nausea, vomiting, visual phenomena in the form of flickering, hallucinations, and sometimes blurred vision. Possible disturbance of consciousness, up to coma, psychomotor agitation, development of epileptic seizures. There may not be focal neurological symptoms, and their appearance after some time most often indicates the development of hemorrhage or cerebral infarction. General hemodynamic disturbances can manifest as left ventricular failure, pulmonary edema, and, less commonly, anuria. Diagnosis should be based on the detection of objective signs of cerebral tissue edema: swelling of the optic nerves during ophthalmoscopy, cerebral edema according to CT or MRI. Overdiagnosis of this disease should be avoided in cases where there are only headaches, nausea and vomiting, but no signs of cerebral edema. In addition, hemorrhagic or ischemic strokes can, at the beginning of their development, imitate acute hypertensive encephalopathy, as they often occur against the background of high blood pressure. The primary mechanism of acute hypertensive encephalopathy is
thought , which leads to cerebral arterial dilatation, hyperperfusion, and cerebral edema, with secondary capillary compression and slowing of cerebral blood flow. From here follow the basic principles of therapy - lowering blood pressure and combating cerebral edema. To quickly reduce blood pressure, sodium nitroprusside (0.3 mcg/kg per minute) or labetalol (2 mg/min) is administered intravenously. The main goal is to reduce blood pressure by 20–30% within an hour (not lower than 90 mm Hg diastolic blood pressure), then within 24 hours the blood pressure can be brought up to the patient’s usual numbers. In the future, oral medications are selected, achieving stable blood pressure values that are adequate for a particular patient. To reduce cerebral edema, use furosemide (40–80 mg intravenously every 4–12 hours), mannitol (20% solution at a dose of 1 g/kg) or glycerol (10% solution in isotonic saline at a rate of 1–2 mg/kg over 2 hours) . The dynamics of blood pressure, the condition of the fundus, CT, MRI pictures, the patient’s well-being and neurological symptoms allow us to assess the success of treatment. The prognosis is not always favorable even with timely hospitalization and adequate effective therapy. Fortunately, modern pharmacotherapy for hypertension has reduced such cases to a minimum.
Another option for the development of damage to brain structures in hypertension is a steadily progressive damage to the brain substance, associated with a poorly controlled increase in blood pressure, causing circulatory deficiency in the cerebral vessels - hypertensive chronic encephalopathy.
. Consideration of pathomorphological changes in the vessels of the brain in hypertension in the form of plasmatic and hemorrhagic impregnation, as well as necrosis of the vascular wall with its subsequent thinning, adaptive thickening of the walls of extracerebral vessels made it possible to propose the term “hypertensive angioencephalopathy” [5]. Early damage to the predominantly white matter of the brain in hypertension and representing the destruction of the myelin of the central conductors, small cavities, dilated due to the presence of edema, perivascular spaces (creblures), spongiosis, is caused by damage to the cortico-medullary arteries and has a typical picture on CT (decreased signal intensity ) and MRI tomography (increased signal intensity). This phenomenon, usually detected in areas of the so-called “terminal” blood supply, is especially sensitive to blood pressure fluctuations, i.e. in the periventricular areas of the brain, is called “hypertensive leukoencephalopathy” or “leukorrheosis.” ICD-10 mentions only “hypertensive encephalopathy”, the term “hypertensive leukoencephalopathy” is not used, as is “hypertensive angioencephalopathy”, and the term “progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy” available in the classification implies that hypertension is not the exclusive cause of this process. Of interest from this point of view is “subcortical atherosclerotic encephalopathy” (Binswanger’s disease), which is considered by some authors as a variant of “hypertensive encephalopathy”, and by others as an independent nosological unit, since hypertension is present in the vast majority, but not in all patients, but in addition, it is not always possible to draw a parallel between the values of systolic and diastolic blood pressure and the progression of the disease.
A significant difference between “hypertensive encephalopathy” and “atherosclerotic encephalopathy” can be considered the predominant damage in hypertension not to large extracranial and intracranial vessels, but to massive damage mainly to small branches of cerebral vessels. At the same time, the division of “hypertensive” and “atherosclerotic” encephalopathy is always quite arbitrary. Hypertension quite quickly stimulates the development of atherosclerotic changes in cerebral vessels. It is not always possible to detect atherosclerotic changes in extracerebral and cerebral vessels with ultrasound and MRI angiography in patients with hypertension, but the sensitivity of these methods is not so great as to completely exclude the presence of atherosclerosis and confidently make a diagnosis of “hypertensive encephalopathy.” Apparently, in most cases we are talking about “mixed encephalopathy”. The possibility of clinical separation of these conditions is also very doubtful.
With hypertensive encephalopathy, as with all other forms of discirculatory encephalopathies, three stages of the disease can be distinguished. At stage I
the clinic is dominated by subjective disorders in the form of general weakness and fatigue, emotional lability, sleep disturbances, decreased memory and attention, and headaches.
Neurological symptoms do not form distinct neurological syndromes, but are represented by anisoreflexia, discoordination, and symptoms of oral automatism. Violations of memory, praxis and gnosis can be identified, as a rule, only when conducting special batteries of tests. At stage II
, subjective complaints worsen, and neurological symptoms can already be divided into distinct syndromes (pyramidal, discoordination, amyostatic, dysmnestic), with one neurological syndrome usually dominating.
Professional and social adaptation of patients decreases. At stage III
, along with an increase in neurological symptoms, the appearance of a distinct pseudobulbar syndrome, paroxysmal conditions (including epileptic seizures), severe cognitive impairment leads to disruption of social and everyday adaptation, and loss of performance. Thus, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, including hypertensive encephalopathy, ultimately leads to the formation of vascular dementia. With hypertensive encephalopathy, subcortical dementia usually develops.
In stages II and III of hypertensive encephalopathy, diffuse changes in the brain substance are usually combined with focal lesions in the form of lacunar infarcts - small cavities ranging in size from 0.1 to 1.0 cm, formed in areas of cerebral ischemia. Either asymptomatic development of a lacunar infarction or the formation of a transient ischemic attack or stroke is possible, which is determined by the localization and volume of the ischemic focus. The formation of multiple small-focal brain lesions - lacunar state - significantly worsens the prognosis of hypertensive encephalopathy and reduces the possibility of drug improvement of the patients' condition, even when good control of arterial hypertension is achieved.
There is no doubt that effective treatment of arterial hypertension at the earliest stages of the disease can prevent the development of encephalopathy, but the complexity of the situation lies in the fact that many patients do not feel elevated blood pressure for a long time. An already developed vascular catastrophe (heart attack, TIA, stroke) forces them to see a doctor. The basis of prophylactic treatment of patients with hypertension to prevent the development of hypertensive encephalopathy is to achieve good control of hypertension. The question of the advisability of prescribing additional pharmacological drugs to patients with hypertension who do not have cerebral symptoms, affecting the rheological quality of blood, improving endothelium-dependent reactions of the vascular wall and metabolic support of brain tissue, reducing the content of free radicals, has not been studied. Although there is a clear connection between the control of hypertension and the development of hypertensive encephalopathy, in elderly people with lipohyalinosis of the walls of small vessels, it is advisable to carry out courses of treatment with drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and have neuroprotective properties, even with good blood pressure control. Preference should be given to tablet drugs that have a combined effect on the condition of the endothelium and the walls of brain vessels, cerebral blood flow and metabolism of nervous tissue. These may be drugs such as Vinpocetine and Actovegin. Prescribing these drugs in courses of 2–3 months with breaks of 6–8 months can slow down the development of pathology of blood vessels and brain matter. No studies have yet been conducted on the prevention of the development of hypertensive encephalopathy, although there is an urgent need to answer the question of whether good blood pressure control alone is sufficient to prevent brain damage in hypertension. The main data on the prevention of cerebral vascular disorders are related to the study of the risk of stroke. A meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled trials (47,653 patients) showed that regular use of antihypertensive drugs for several years leads to a reduction in the incidence of stroke by 35–40% [6]. In connection with the issue of prevention of hypertensive encephalopathy, it is interesting to consider the results of the multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study “Progress”
, published in 2001 [7]. Combination therapy with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) (perindopril) and a diuretic (indapamide) has been shown to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke by 28%. However, other facts obtained in this study and published in 2003 are extremely important [8]. There was a decrease in the likelihood of developing cognitive impairment and dementia with perindopril monotherapy or with combination therapy, and the effect did not depend on the initial presence or absence of hypertension. It follows that this fact should be associated not only with good control of hypertension, but also with other effects of the therapy, for example, repair of the structure of the walls of the cerebral arteries, improvement of endothelium-dependent reactions (vasodilation and vasoconstriction), and a decrease in the thickness of the intima/media complex. Thus, the question is again raised that preventive treatment of damage to brain structures in hypertension should be associated not only with good control of hypertension, but also with additional treatment aimed at improving cerebral blood flow and metabolic support of the brain substance.
The main risk factors for the development of hypertensive encephalopathy, directly related to the severity and course of hypertension, are poorly controlled hypertension, hypertensive crises, high blood pressure variability, disturbed circadian blood pressure rhythm with high nocturnal arterial hypertension, spontaneous or iatrogenic drops in blood pressure.
The strategy of antihypertensive therapy is to achieve a level of blood pressure - a target level at which the threat of the risk of developing cerebrovascular complications is minimized. Tactically, this can be solved by prescribing antihypertensive drugs and correcting existing risk factors. The target blood pressure level can vary significantly depending on the presence of risk factors for the development of cerebrovascular complications (diabetes mellitus, renal failure, etc.). Thus, the target level in the general population of patients with hypertension is <140 mm Hg for systolic blood pressure, and <90 mm Hg for diastolic blood pressure, while for patients with chronic renal failure – <120 mm Hg. and <75 mmHg, respectively. Achieving the target blood pressure level, especially with initially high blood pressure values in patients with cerebrovascular pathology, should not occur in a short time, as this is fraught with the development of ischemic stroke. Depending on the level of initial blood pressure and its duration, the severity of cerebral disorders, this period should vary from 6 to 12 weeks. The modern approach to antihypertensive therapy involves the use of combination therapy with several drugs taken in lower doses than monotherapy - low-dose combination antihypertensive therapy.
All antihypertensive pharmacological agents can be divided into drugs of the main and reserve series. Main line drugs include:
- diuretics (thiazide and thiazide-like - xipamide, hypothiazide; loop - furosemide; potassium-sparing - spironolactone, triamterene)
- ACE inhibitors – lisinopril, fosinopril, etc.
- Blockers of slow calcium channels - nifedipine, verapamil, etc.
- b-adrenoblockers – without vasodilating properties (bisoprolol, atenolol, sotalol) and with vasodilating properties (pindolol, Dilatrend)
- a-blockers
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (AT1 receptors)
Reserve-line drugs include central α2-adrenergic receptor agonists (clonidine), I1-imidazoline receptor agonists (cynt), peripheral adrenergic inhibitors (octadin), direct vasodilators (apressin, minoxidil), antiseronergic (ketanserin)
Such a wide variety of pharmacological drugs used for the treatment of hypertension makes it difficult to choose the optimal drug or their combination, and the selection of adequate therapy sometimes requires considerable time. The general principles are: at the beginning of treatment with monotherapy and minimal doses of the drug; switching to drugs with a different mechanism of action if treatment is ineffective; preference for long-acting medications; When using combination therapy, drugs must have different mechanisms of action and not be antagonistic to each other. To obtain an idea of the optimality of treatment in modern conditions, one-time, although frequent, blood pressure measurements are not enough. For the most complete picture of blood pressure variability, the presence of “mountains” (rises in blood pressure to high numbers) and “gags” (excessive decreases in blood pressure) during the day and night, which can disrupt the mechanisms of autoregulation of cerebral blood flow, it is necessary to conduct a study of the daily blood pressure profile in order to selection of optimal antihypertensive therapy [9].
The choice of antihypertensive therapy in a particular patient depends not only on the severity of hypertension, but also on his age (Table 2).
In a situation where there is stage I hypertensive encephalopathy, it is necessary to add to treatment drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and metabolism of nervous tissue, as well as drugs that act on internal factors that can affect the progression of encephalopathy.
In order to prevent the increase in atherosclerotic processes, it is necessary to normalize fat metabolism: reducing body mass index, low-fat diet, prescribing statins (simvastatin, pravastatin). With good and satisfactory blood pressure control, it is possible to prescribe antiplatelet agents to improve the rheological properties of the blood (acetylsalicylic acid, ticlopedine, clopidogrel, dipyridamole). In any case, the CAPRIE
and
ESPS-2
showed that the use of acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel and dipyridamole reduces the risk of developing cerebral ischemia [10]. At this stage of hypertensive encephalopathy, the use of drugs that act on the vascular wall, improve the metabolism of brain tissue and have neuroprotective properties is mandatory. These drugs include Actovegin and Tanakan. Actovegin, a deproteinized extract of the blood of young calves, containing amino acids, electrolytes and trace elements, oligosaccharides, glycolipids and superoxide dismutase, improves the transport of glucose and oxygen in the brain tissue, resulting in an increase in the energy cellular potential, also has an antioxidant effect and is used in the form of tablets (200 mg of active substance) at a dose of 6–9 tablets per day (2–3 tablets 3 times a day for 3–4 months [11]. Cerebrolysin, a peptidergic drug that contains neurotrophic factors, is administered intravenously at a dose of 10– 15 ml in courses of 10 infusions 1-2 times a year.It is also possible to use vinpocetine, instenon, pentoxifylline.
In stages II and III of hypertensive encephalopathy, the general principles of therapy remain the same, but primarily the dosages of drugs acting on cerebral blood flow and metabolic support of brain structures change. Treatment with Actovegin begins with intravenous administration of 250 ml of a 20% solution for 2–3 weeks, and then proceeds to taking 9 tablets per day for 3–4 months.
Hypertensive encephalopathy, a variant of discirculatory encephalopathy, is a severe progressive disease that forms a variety of neurological syndromes, threatens the development of strokes and leads to vascular dementia.
Timely treatment can preserve the patient’s professional, social and everyday adaptation for many years, and improves the prognosis for the patient’s life expectancy. The principle of treatment of hypertensive encephalopathy is to eliminate external factors that influence the increase in blood pressure, constant antihypertensive therapy and the use of drugs that improve cerebral blood flow, metabolism of nervous tissue and have a neuroprotective effect. Literature:
1. Shevchenko O.P., Praskurnichy E.A., Yakhno N.N., Damulin I.V. Arterial hypertension and cerebral stroke. M., "Reafarm", 2001, 191 pp.
2. Vibers D.O., Feigin V.L., Brown R.D. Guide to Cerebrovascular Diseases. Per. from English M., 1999, 672 pp.
3. Vilensky B.S. Stroke: prevention, diagnosis and treatment. St. Petersburg, 1999, 336 pp.
4. Diseases of the nervous system. Ed. Yakhno N.N., Shtulmana D.R. M., Medicine, 2001, pp. 231–302.
5. Vereshchagin N.V., Morgunov V.A., Gulevskaya T.S. Pathology of the brain in atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. M., Medicine, 1977, 228 pp.
6. Chalmers J., MacMahon S., Anderson C. et al. Clinician's manual on blood pressure and stroke prevention. Second ed., London, 2000, 129 P.
7. PROGRESS Collaboratory Group. Randomized trial of a perindopril –based blood pressure lowering regimen among 6,105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischemic attack. Lancet, Vol. 358, pp.1033–1041.
8. The PROGRESS Collaboratory Group. Effects of blood preassure lowering with perindopril and indapamide therapy on dementia and cognitive decline in patients with cerebrovascular disease. Arch Intern Med, 2003, Vol.163, P.1069–1075.
9. Kalashnikova L.A., Kulov B.B. Risk factors for subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy. J. neurol. and a psychiatrist. named after S.S. Korsakov, Stroke (supplement), 2002, No. 7, pp. 3–8.
10. Antithrombotic Trialists Collaboration. Collaborative meta–analysis of randomized trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. British Med J., 2002, Vol.324, P.71–86.
11. Shmyrev V.I., Ostroumova O.D., Bobrova T.A. Possibilities of the drug Actovegin in the prevention and treatment of dementia. Russian medical journal, 2003, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 216–220.
Forecast
A prognosis can only be made taking into account the stage of hypertensive encephalopathy, the possibility of complete pressure correction, the presence of an underlying disease or concomitant pathologies such as endocrine system disorders and atherosclerosis. In the first stage of GE, complex neurological treatment and stabilization of pressure can ensure the patient’s ability to work and long-term intellectual safety. And in stage III, therapy only slows down the progression of the disease and alleviates its manifestations.