Composition and release form
The drug is sold in pharmacies in the form of small tablets for oral administration. Externally, they are white in color with a soluble thin shell. Packaged in blisters of 14 pieces and secondary cardboard packaging. One pack contains 1-2 cells of 14-28 tablets and includes instructions for use.
The active component of the drug is moxonidine. Its amount in 1 tablet is 200 mcg.
Additional substances: castor oil, cellulose, magnesium stearate, Tween 80, Klucel and Aerosil.
Moxonidine analogs
Pharmacies offer a large selection of Moxonidine analogues Canon and North Star (SZ). The drugs differ in their basic composition, packaging and manufacturers. The selection of funds is carried out exclusively by a cardiologist.
SPTs of Moxonidine analogues with prices
| Drug name | price, rub. | Manufacturer country |
| Moxonidine | 180-440 | Russia |
| Moxonidine Canon | 110-180 | |
| Popular substitutes | ||
| Captopril | 40-160 | Germany, Russia |
| Moxonitex | 170-400 | Germany |
| Moxarel | 260-430 | Russia |
| Physiotens | 280-900 | |
| Kapoten | 170-320 | |
| Other analogues | ||
| Amlodipine | 110-170 | Serbia |
| Cordaflex | 90-240 | Hungary |
| Tenzotran | 690-720 | Israel |
| Corinfar | 70-160 | Croatia |
| Lerkamen | 440-1200 | Germany |
| Indapamide | 90-130 | Russia |
| Nifedipine | 40-55 | |
| Losartan | 50-170 | |
| Lisinopril | 30-250 | |
| Enalapril | 20-220 | |
| Prestarium | 380-600 | |
| Lorista | 150-970 | |
| Perindopril | 230-500 | |
| Lozap | 280-770 | Slovenia |
| Valsacor | 38-1200 | |
pharmachologic effect
The drug belongs to the group of antihypertensive drugs. It is a direct agonist of imidazoline receptors. When used once, it helps to simultaneously restore the level of diastolic and systolic pressure. At the same time, it does not change the activity of the heart and does not affect the heart rate.
The drug is highly digestible, regardless of the time of meal. The biological availability of the drug is at least 88%. The highest concentration of the drug in the red channel is observed after 30 minutes or a maximum of 3 hours.
Moxonidine or Physiotens - which is better and more effective, what is the difference
Manufacturer: Abbott Laboratories EPD, Russia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: moxonidine
Physiotens is a domestic analogue of Moxonidine, which is an antihypertensive agent. The mechanism of action depends on the main component. With regular use of the drug, a gradual decrease in blood pressure is observed.
After consumption, it is quickly and almost completely absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract. A distinctive feature of the Russian analogue is its inflated cost.
Reviews from doctors about these drugs for arterial hypertension are positive, as they help cope with the problem, stabilize the condition and have the same active ingredient.
Contraindications
It is prohibited to take the medicine for the following conditions:
- Individual intolerance to the active or auxiliary components.
- Acute form of bradycardia.
- Severe arrhythmia.
- Glaucoma.
- Mental disorders.
- Cardiac failure.
- Previous Quincke's edema.
- The period of bearing a child and breastfeeding.
- Children under 18 years of age.
- Disturbance of the liver and kidneys.
- Angina pectoris.
- Lactose deficiency or intolerance.
- Various pathologies of the circulatory system.
Moxonidine or Capoten - which is better during a crisis
Manufacturer: AKRIKHIN, Russia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: captopril
Kapoten is a domestically produced substitute for Moxonidine. This is a prescription drug that is an ACE inhibitor. The positive effect of administration and stabilization of the patient’s condition is observed 60–90 minutes after ingestion.
The drug is prescribed to patients of the older age category. Moxonidine analogue SZ Kapoten has an extensive list of indications, which include:
- High blood pressure.
- Chronic heart failure (CHF).
- Coronary heart disease (CHD).
- Diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
In case of hypertensive crisis, it is allowed to use both Moxonidine and its analogue Capoten.
Side effects
As a result of treatment with Moxonidine, patients may experience the following adverse reactions:
- High fatigue, malaise.
- Migraine.
- Sleep disorder - insomnia or drowsiness.
- Dizziness, headache.
- Dyspeptic manifestations - dry mouth, discomfort in the epigastrium, nausea, vomiting, abnormal stool.
- Increased nervousness and irritability.
- Swelling of peripheral tissues.
- A sharp decrease in pulse and blood pressure.
- Allergic signs are skin rash and severe itching.
Moxonidine or Moxarel – which is better?
Manufacturer: VETEKS, Russia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: moxonidine
Moxarel is an analogue of the active substance. It has antihypertensive properties with a central mechanism of action. Does not develop a sedative effect. After oral administration, dryness of the oral mucosa is not observed. The drug reduces systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure.
Prescribed to patients of the older age group with hypertension. The duration of the course and dosage are adjusted by the cardiologist depending on the general condition.
Self-therapy should be completely excluded, as this will lead to negative consequences.
Drug overdose
If medical recommendations are not followed and the maximum volume of the drug is exceeded, an overdose may develop. The condition is determined by severe symptoms:
- Intense headache and dizziness.
- Nausea followed by vomiting.
- Painful sensations in the stomach area.
- Weakness and severe malaise.
- Extensive reduction in pressure.
- Dryness in the mouth.
If the above symptoms occur, you should definitely consult a doctor. Treatment involves relief of symptoms. Prescribed medication, gastric lavage, parenteral administration of saline. To suppress the symptoms of bradycardia, the use of Atropine is indicated.
Moxonidine or Captopril - which is better during a crisis
Manufacturer: SANDOS, Germany
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: captopril
If you don’t know how to replace Moxonidine for hypertension, then use the ACE inhibitor – Captopril. It is an antihypertensive agent that has a vasodilator effect. If you take the tablets for a long time, the severity of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy decreases. The drug has a vasodilating effect mainly on the arteries and improves blood supply to the ischemic myocardium.
Indications for the use of this cheap analogue of Moxonidine are related to the pharmacology of this drug:
- High blood pressure.
- CHF (chronic heart failure).
- Impaired left ventricular functionality after myocardial infarction.
- Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
In case of hypertensive crisis, experts recommend taking an imported analogue of the drug Moxonidine - Captopril. This is explained by the fact that the drug has extensive indications and effective pharmacological action, as well as positive reviews.
special instructions
The use of an antihypertensive drug for therapeutic purposes requires constant monitoring of blood pressure, heart function and heart rate.
During the course of treatment, you should completely avoid alcoholic beverages. It is recommended not to drive vehicles or engage in activities that require concentration, memory and high mental activity.
You need to stop taking the drug gradually, gradually reducing the dose until complete withdrawal.
If the use of Moxonidine was combined with beta-blockers and it is necessary to discontinue both drugs, the latter are removed first. After some time, the antihypertensive drug is discontinued.
Moxonidine canon 0.4 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets
pharmachologic effect
Centrally acting antihypertensive agent.
Composition and release form Moxonidine canon 0.4 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets
Tablets - 1 tablet:
- active substance - moxonidine 0.4 mg;
- excipients: hyprolose (hydroxypropylcellulose) 4.2 mg, mannitol 95 mg, croscarmellose sodium 4.7 mg, magnesium stearate 0.7 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 35 mg;
- composition of the film shell: Opadry II pink 4 mg, including polyvinyl alcohol 1.6 mg, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 0.808 mg, talc 0.592 mg, titanium dioxide 0.9608 mg, sunset yellow dye 0.0004 mg, indigo carmine dye 0.0060 mg, crimson dye [Ponceau 4R] 0.0328 mg.
Film-coated tablets 0.4 mg.
7, 10, 28 or 30 tablets in a blister pack in polyvinyl chloride film and printed varnished aluminum foil.
2, 4, 6, 8 blister packs of 7 tablets each, or 1,2, 3, 4, 6 blister packs of 10 tablets each, or 1,2 blister packs of 28 tablets each, or 1, 2, 3, 4 blister packs of 30 tablets, together with instructions for use, are placed in a cardboard pack.
Description of the dosage form
The tablets are round, biconvex, pink film-coated. Almost white in cross section. Minor roughness is allowed.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, regardless of food intake, with a sufficient amount of liquid.
In most cases, the initial dose of Moxonidine Canon is 0.2 mg per day, in one dose, preferably in the morning. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, the dose can be increased after 3 weeks of therapy to 0.4 mg per day, which should be divided into 2 doses (morning and evening) or once.
The maximum daily dose, which should be divided into 2 doses (morning and evening), is 0.6 mg.
The maximum single dose is 0.4 mg.
In elderly patients with normal renal function, dosage recommendations are the same as for adult patients.
In patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min) and patients on hemodialysis, a single dose should not exceed 0.2 mg, the maximum daily dose is 0.4 mg.
Pharmacodynamics
Selective agonist of imidazoline receptors responsible for tonic and reflex control of the sympathetic nervous system (localized in the venterolateral medulla oblongata). Reduces the pressor effect of the sympathetic system on peripheral vessels, reduces peripheral vascular resistance, reduces systolic and diastolic pressure both with single and long-term administration, while cardiac output and heart rate (HR) do not change significantly. With long-term use, it reduces left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy, eliminates signs of myocardial fibrosis, microarteriopathy, and normalizes capillary blood supply to the myocardium. During treatment, the activity of norepinephrine and epinephrine, renin, angiotensin II at rest and during exercise, atrial natriuretic peptide (with exercise) and plasma aldosterone decreases.
It has a lower affinity for alpha2-adrenergic receptors, which explains the lower likelihood of developing sedation and dry mouth.
Reduces tissue resistance to insulin. Does not affect the metabolism of glucose and lipids.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption after oral administration is 90%. Food intake does not affect the amount of absorption. Bioavailability - 88%.
Communication with blood plasma proteins - 7.2%. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in plasma is determined 30-180 minutes after oral administration and is 1-3 ng/ml. Volume of distribution - 1.4-3 l/kg.
The main metabolite is dihydrogenated moxonidine. The pharmacodynamic activity of dehydrogenated moxonidine is about 10% compared to moxonidine. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. Does not accumulate with prolonged use.
The half-life of moxonidine and metabolites is 2.5 and 5 hours, respectively. Within 24 hours, more than 90% of moxonidine is excreted by the kidneys (78% unchanged, 13% as dihydrogenated moxonidine, 8% as other metabolites). Less than 1% of the dose is excreted through the intestines. Moxonidine is excreted to a small extent during hemodialysis.
Pharmacokinetics in patients with arterial hypertension
In patients with arterial hypertension, no changes in the pharmacokinetics of moxonidine are observed.
Pharmacokinetics in elderly patients
Clinically insignificant changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of moxonidine were noted in elderly patients, probably due to a decrease in the intensity of its metabolism and/or slightly higher bioavailability.
Pharmacokinetics in renal failure
Moxonidine excretion is significantly correlated with creatinine clearance (CC).
In patients with moderate renal failure (creatinine clearance in the range of 30-60 ml/min), steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life are approximately 2 and 1.5 times higher than in patients with normal renal function (creatinine clearance more than 90 ml/min ).
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life are 3 times higher than in patients with normal renal function.
In patients with end-stage renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min) on hemodialysis, steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life are, respectively, 6 and 4 times higher than in patients with normal renal function.
In patients with impaired renal function, the dosage should be adjusted individually.
Indications for use Moxonidine canon 0.4 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets
Arterial hypertension.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- severe heart rhythm disturbances;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- sinoatrial and atrioventricular blockade of II and III degrees;
- severe bradycardia (heart rate less than 50 beats/min);
- acute and chronic heart failure of functional class III and IV according to the NYHA classification;
- history of angioedema;
- severe liver failure (more than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale);
- chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min, creatinine more than 60 µmol/l);
- hemodialysis;
- simultaneous use of tricyclic antidepressants;
- age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established);
- age over 75 years;
- lactation period.
Carefully -
- Parkinson's disease (severe form);
- epilepsy;
- glaucoma;
- depression;
- "intermittent" claudication;
- Raynaud's disease;
- atrioventricular block of the first degree;
- chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance more than 30 ml/min, but less than 60 ml/min);
- severe cerebrovascular disorders;
- after myocardial infarction;
- severe diseases of the coronary vessels;
- severe coronary heart disease or unstable angina (insufficient experience);
- chronic heart failure of functional class I and II according to the NYHA classification;
- liver dysfunction;
- pregnancy.
Application Moxonidine canon 0.4 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There is no clinical evidence of a negative effect on pregnancy. However, Moxonidine Canon should be prescribed to pregnant women only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Moxonidine passes into breast milk, so if taking Moxonidine Canon is necessary during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
special instructions
If it is necessary to cancel simultaneously taken beta-blockers and the drug Moxonidine Canon, first cancel the beta-blockers and only after a few days the drug Moxonidine Canon.
It is not recommended to prescribe tricyclic antidepressants simultaneously with Moxonidine Canon.
During treatment, regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and ECG is necessary.
The drug Moxonidine Canon can be prescribed with thiazide diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and blockers of “slow” calcium channels.
You should stop taking Moxonidine Canon gradually.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Taking into account the possible occurrence of drowsiness and dizziness during treatment with Moxonidine Canon, patients should be careful when engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention, such as driving a vehicle or operating equipment that requires increased concentration.
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, sedation, drowsiness, marked decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, general weakness, bradycardia, increased fatigue, dry oral mucosa, vomiting and stomach pain. Paradoxical increases in blood pressure, tachycardia, and hyperglycemia are also potentially possible.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote. Gastric lavage (immediately after administration), taking activated charcoal and laxatives, symptomatic therapy.
In the case of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, it is recommended to restore circulating blood volume by administering fluids and administering dopamine. Bradycardia can be relieved with atropine.
Alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists can reduce or eliminate transient arterial hypertension following an overdose of Moxonidine Canon.
Side effects Moxonidine canon 0.4 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets
WHO classification of the incidence of side effects - very often - ≥1/10 prescriptions (>10%); often - from ≥1/100 to 1% and 0.1% and 0.01% and
Mental disorders: Often - decreased concentration; Uncommon: depression, anxiety, nervousness.
Disorders of the central nervous system: Often - increased fatigue, drowsiness, headache, dizziness; Uncommon: paresthesia, insomnia, fainting.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Often - dry oral mucosa, constipation, dyspeptic disorders; Uncommon: nausea, anorexia; Very rarely - hepatitis, cholestasis.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: Uncommon - skin rash, itching, swelling of various locations; Very rarely - angioedema.
Disorders of the genitourinary system: Uncommon - urinary retention or incontinence, impotence, decreased libido.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: Rarely - hepatitis, bile stagnation.
Eye disorders: Uncommon: dry eyes, causing itching or burning sensation in the eyes.
Hearing and labyrinthine disorders: Uncommon: tinnitus.
Vascular disorders: Often - symptoms of vasodilation; Uncommon: decreased blood pressure (BP), orthostatic hypotension, Raynaud's syndrome, peripheral circulation disorders.
Endocrine system disorders: Uncommon: gynecomastia.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Often - back pain; Uncommon: neck pain.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: Often - asthenia; Uncommon: weakness in the legs, fainting, pain in the parotid glands.
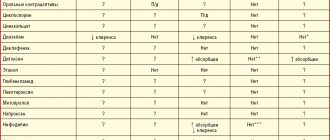
Drug interactions
Moxonidine Canon can be prescribed with thiazide diuretics and slow calcium channel blockers. The combined use of the drug Moxonidine Canon with these and other antihypertensive drugs leads to an additive effect and increased hypotensive effect.
When prescribing Moxonidine Canon with hydrochlorothiazide, glibenclamide (glyburide) or digoxin, there is no pharmacokinetic interaction.
Tricyclic antidepressants may reduce the effectiveness of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, so their simultaneous use is not recommended.
The drug Moxonidine Canon moderately enhances reduced cognitive ability in patients taking lorazepam.
Prescribing the drug Moxonidine Canon together with benzodiazepine derivatives may be accompanied by an increase in the sedative effect of the latter.
The drug Moxonidine Canon enhances the inhibitory effect on the central nervous system of anxiolytics, barbiturates and ethanol.
Beta-blockers, when used together with moxonidine, increase bradycardia and the severity of negative ino- and dromotropic effects.
When prescribing Moxonidine Canon together with moclobemide, there is no pharmacodynamic interaction.