12 April 2021
51372
0
3.1 out of 5
Numbness or hypoesthesia of the fingers is a rather unpleasant situation, which can be either a consequence of physiological reasons or a sign of various types of diseases. Therefore, if this symptom persists for an hour or more, and there is no improvement in rubbing your hands, clenching and unclenching your fists, you should consult a doctor. He will help you understand the reasons for its appearance and, if necessary, prescribe the necessary treatment. This will be the key to detecting pathology at an early stage of development and the success of therapy, and will also help to avoid aggravation of the situation and eliminate the risk of complications. After all, it is not so much the numbness of the fingers that is dangerous, although it can cause significant difficulties in performing everyday tasks, but the consequences of the lack of treatment for the diseases that provoked its occurrence.
What is hand numbness and its causes?
Many people are familiar with the unpleasant feeling of tingling, “crawling on the skin,” as well as pain, decreased sensitivity and deterioration of mobility in the limb. All of these manifestations characterize numbness, which can occur in the arms, legs and other areas of the body. It is associated with impaired blood circulation in the tissues or compression of the nerves.
Along with numbness in the hands, the following symptoms may also occur:
- burning sensation;
- muscle spasms;
- tingling sensation;
- pain in hands, fingers;
- feeling of itching;
- tingling and numbness that gets worse when you move your fingers;
- increased sensitivity to touch;
- pain in the cervical spine.
Treatment methods
In modern medicine, there are several effective methods for treating numbness in the fingers of the left hand.
- Drug therapy. This method involves the use of products selected by a specialist, in the form of ointments, preparations and creams. Which can relieve inflammation, swelling and pain.
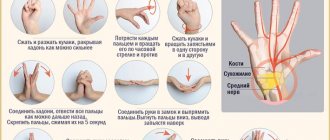
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy.
- Using ultrasound or laser. This will help restore damaged tissue and lost sensitivity.
- Special exercises and health-improving physical education. This will help improve blood circulation and the general condition of the body.
Causes of numbness in the left hand:
- Cardiac ischemia. In addition to numbness in the left arm, there is discomfort in the chest. If after taking nitroglycerin or stopping the physical activity that caused the symptoms, these manifestations disappear, then it is angina pectoris. In addition to numbness of the left arm, it is accompanied by chest pain in the heart area, panic, pale skin, nausea, shortness of breath, and cold sweat.
- Myocardial infarction. Sometimes hand numbness is the only sign of this acute cardiovascular disaster. During an attack, the patient experiences intense pain and a feeling of constriction in the chest, shortness of breath, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The skin becomes covered with cold sweat. Along with numbness in the hand, a person experiences pain radiating to the lower jaw, stomach, and the area between the shoulder blades.
- Atherosclerosis. Due to atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels, decreased strength and numbness in the arm may occur. Symptoms intensify when raising the limb upward.
- Stroke. Numbness in the left hand may indicate damage to the right hemisphere of the brain. In this case, the upper and lower limbs on the left side become numb, vision and speech are impaired. Along with numbness in the hand, a stroke can cause a complete loss of sensation in the hand. Other symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage include weakness in the limbs, loss of coordination, severe headache, blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, and irritation from bright lights and sounds.
- Vegetative-vascular, or neurocirculatory dystonia. This is a complex of autonomic disorders that is associated with disorders of nervous regulation. In addition to numbness of the left hand, it may be accompanied by headaches, insomnia, pressure fluctuations, arrhythmia, and panic attacks.
- Raynaud's disease. The pathology is accompanied by paroxysmal circulatory disorders in the arteries of the extremities. Along with the numbness of the hand, its rapid freezing is felt. In the cold and with excitement, a person’s fingers may turn blue. As Raynaud's disease progresses, not only the hands become numb, but also the legs, chin, nose, and ears.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency. This connection is extremely important for the normal functioning of nerve tissue. With its deficiency, a person not only experiences numbness in the hand, but also suffers from dry mouth and pale skin.
- Osteochondrosis (usually cervical and thoracic). First, the fingers go numb, then weakness develops in the upper limb, and the grip strength of the hand decreases. Sometimes pain is felt along the outside of the shoulder and forearm.
- Overstrain of muscles in the cervical-collar region. Pianists and PC operators suffer from hand numbness due to prolonged maintenance of the same position. The problem lies in the overstrain of the muscles, which compress the nerve fibers responsible for the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Insufficient blood circulation. The upper limb becomes numb due to impaired blood flow due to damage to the walls of blood vessels, for example, in diabetes mellitus.
- Stress and psycho-emotional overload can cause hand numbness.
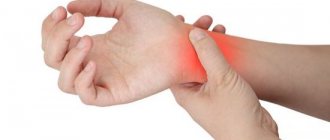
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. When the median nerve passing through the wrist is compressed, the left hand may become numb. This problem is familiar to people of certain professions (programmers, musicians). Nerve compression can also occur in women during pregnancy due to swelling, as well as in patients after surgery, in obese people.
My legs are going numb
If one lower limb or both goes numb, this may be a sign of cauda equina syndrome, herniated disc, or multiple sclerosis.
In cauda equina syndrome, all 18 nerves located in the lumbar spine are compressed. This may occur due to a hernia, inflammation, tumor, or stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal. The result is not only numbness in both legs, but also lower back pain, problems with urination, defecation, and erectile dysfunction.
Radiculitis associated with a hernia occurs due to the fact that the nucleus pulposus, which is located in the intervertebral disc, breaks out and compresses nearby nerve endings. With a hernia, not only numbness occurs, but also back pain and weakness in the limbs. Symptoms usually go away within 6–8 weeks. If this does not happen, the doctor may prescribe more aggressive treatment, including surgery.
With sciatica, most often only one leg goes numb. Sciatica, or lumbosacral radiculitis, is compression of the sciatic nerve, which also causes pain in the lower back. The cause of sciatica can be a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, piriformis syndrome (compression of the sciatic and gluteal nerves by the piriformis muscle), bone fractures and pelvic injuries, tumors. Usually, along with numbness, a person feels aching pain, tingling or burning. Treatment depends on the cause of sciatica.
Numbness in the right hand may have the following causes:
- impaired blood flow, pinched nerve due to incorrect position of the limb (for example, during sleep);
- staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time (may be due to the nature of the work, for example, carpal tunnel syndrome);
- frequent carrying of bags, suitcases and other heavy objects;
- long exposure to frost or in a cold room;
- long-term muscle tension of the upper limb.
When should you see a doctor?
In case of numbness, you should consult a doctor immediately if:
- numbness in the genital area and anus is accompanied by back pain and uncontrollable urination/defecation;
- the person’s consciousness is impaired to the point of loss of consciousness;
- numbness significantly complicates normal life;
- numbness appeared after a head, neck or back injury;
- numbness is accompanied by slow speech, vision problems, difficulty walking, or weakness;
- the entire limb became numb;
- numbness is accompanied by paralysis or weakness - it is impossible to move the limb;
- numbness is accompanied by a sudden and severe headache;
- significant numbness occurred suddenly.
If you have numbness, you should consult a doctor if:
- it is impossible to explain the cause of numbness;
- there is pain in the neck, forearm or fingers;
- the urge to urinate occurs more frequently;
- numbness in the legs increases when walking;
- a rash appeared;
- not only numbness occurred, but also dizziness, muscle spasms or other unusual symptoms;
- the numb area gradually increases in size;
- numbness is felt in the limbs on both sides.
How is the diagnosis made?
Usually, with numbness, a neurological examination and history taking will provide the doctor with a lot of information, and only then can a preliminary diagnosis be made. But for a final decision, it is often necessary to do an x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, electromyography or blood tests.
How to get rid of unpleasant feelings?
Of course, there is no universal way to get rid of numbness, regardless of the cause of this condition. You need to act based on what exactly triggered the numbness. For example, a set of exercises often helps with carpal tunnel syndrome. If numbness is associated with diabetes, then you can only more carefully monitor your blood sugar levels. Vitamin B12 deficiency is corrected with therapeutic doses of appropriate medications.
Why can't you ignore numbness? The fact is that a person can damage a numb part of the body and not notice it. Therefore, even if there are no additional serious symptoms indicating a stroke or other serious condition, it is still worth contacting a neurologist with numbness.
Why does hand numbness occur?
When a patient says that his upper limbs are numb, he may mean:
- a tingling feeling that causes discomfort;
- sensation of “goosebumps” under the skin;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin.
Numbness of the hands does not always indicate pathology. It may be the result of wearing too tight clothes and jewelry that compress blood vessels and nerves.
The most common causes of numbness in the hands:
- Uncomfortable body position, monotonous mechanical work, disrupting blood flow. After changing the position of the limb, the unpleasant sensations disappear.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (usually affects the working hand due to prolonged monotonous work).
- Atherosclerosis. Accompanied by tingling and numbness of the hands, in the future a decrease in their muscle strength is likely.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (numbness, usually symmetrical, may intensify after physical activity).
- Diabetic neuropathy (usually both hands go numb).
- Intervertebral hernia in the cervical region (numbness is associated with compression of the spinal nerve roots).
- Ischemic stroke of the brain (threatens numbness and paralysis of the arm).
- Multiple sclerosis (if part of the postcentral gyrus of the brain is affected, the limbs may go numb).
- Thoracic outlet syndrome (compression of nerve trunks and blood vessels in the area of the upper chest opening).
- Brachial plexitis (numbness of the arm occurs due to inflammation of the brachial plexus).
- Damage to peripheral nerves due to alcoholism (alcoholic polyneuropathy).
- Brain tumor (the formation can compress the motor and sensory neurons responsible for the innervation of the upper extremities).
- Raynaud's disease (a disorder of the innervation of small arterioles, more common in women, manifested by numbness and pain in the extremities).
- Rheumatoid arthritis (inflammation and deformation of joints leads to compression of nerve fibers) and others.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Why do my fingers go numb?
Numbness and decreased sensitivity in the fingers may be a consequence of the development of neurological disorders and changes in their blood supply, which is caused by vascular pathologies. However, this can also occur as a result of such harmless factors as prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, which compresses the blood vessels supplying the fingers. This is often observed in the morning when a person has just woken up, especially if during sleep he put his hand under his head or threw them behind it. In such situations, numbness is usually combined with tingling in the fingers of varying strength, as well as a feeling of loss of control over the hands. But all these symptoms go away on their own with the restoration of normal quality of blood circulation in the hands, which takes no more than 10-15 minutes.
Also, one of the physiological causes of numbness in the fingers is prolonged exposure to the cold. As a result of prolonged exposure to low temperatures, blood vessels reflexively contract. This leads to a decrease in the rate of blood circulation in the fingers and the occurrence of characteristic numbness, and sometimes aching pain. This is no longer as harmless as sleeping in an uncomfortable position, since this already indicates the possibility of frostbite on the fingers. Therefore, in such situations, it is necessary to take measures to warm your hands.
But, if your fingers often go numb and this feeling persists for a long time, you should look for the reason in:
- neurological disorders (tunnel syndrome, polyneuropathy, plexitis, etc.);
- traumatic injuries;
- vascular disorders, etc.
Sometimes fingers go numb while taking medications such as Isoniazid, Vincristine, Metronidazole.
Neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome and polyneuropathy
As for neurological disorders, a fairly large number of different diseases can manifest themselves in a similar way. First of all, these are neuropathies of various origins. This term refers to damage or compression of one or more nerves of the peripheral nervous system, one of the first symptoms of which is the occurrence of a crawling sensation and numbness. But if in the early stages of development this is observed only periodically, then as the pathology progresses, the fingers become numb more often and longer, pain occurs, changes in the condition of the skin are observed, and the muscles lose tone.
With inflammation of the nerve, bruise, prolonged compression of the arm, for example, with the habit of leaning on the elbows at work, or the action of other isolated factors, local neuropathies or tunnel syndromes may occur. In such cases, in addition to numbness, pain, weakness or awkwardness may be observed when moving or grasping objects with your fingers. The nature of their manifestation directly depends on which of the nerve trunks is damaged. So:
- numbness in the 1st, 2nd and partially in the 3rd fingers is characteristic of damage to the radial nerve;
- numbness of the little finger and ring finger up to half on the palm side and the 4th, 5th and part of the 3rd fingers on the back side is observed with damage to the ulnar nerve;
- numbness of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and half of the 4th finger on the side of the palm and nails of 2-5 fingers is caused by damage to the median nerve;
- Numbness of 1-3 fingers and weakness when abducting the thumb are characteristic of the most common syndrome of the carpal or carpal tunnel, in which the median nerve is pinched in the flexor muscles of the wrist joint.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in 1% of people and often occurs in those who have to work with a computer for long periods of time.
Fingers can also go numb as a result of the development of polyneuropathies, i.e., with simultaneous damage to a large number of nerves of the peripheral nervous system as a result of the development of certain systemic diseases. In such situations, numbness of the fingers on both hands is observed, and other symptoms characteristic of these pathologies may also appear.
This may be a consequence of diabetes mellitus, in which constantly high blood sugar levels lead to damage to nerve fibers, i.e. the development of diabetic neuropathy. But diabetes is more likely to affect the toes, although the hands can also suffer.
Fingers also become numb during development:
- chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy;
- Roussy-Lévy syndrome;
- alcoholism, which led to the emergence of so-called alcoholic polyneuropathy;
- Refsum's disease;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS);
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- poisoning with chemicals and heavy metals.
Other neurological disorders
Some diseases can indirectly cause numbness in the fingers, but they are also characterized by a number of other symptoms, which makes it possible to differentiate them from neuropathies. These include:
- Cervical plexitis is a disorder that occurs when the nerves entering the cervical plexus are compressed by enlarged lymph nodes, cervical ribs or spinal structures as a result of the development of spondylosis, osteochondrosis, protrusion or intervertebral disc herniation of the cervical spine. It may also be the result of a birth injury or other damage to the cervical spine.
- Brachial plexitis is a neurological disorder that develops when the nerves that form the brachial plexus are pinched. It can occur as a result of injury to the collarbone, shoulder joint, the formation of an aneurysm (protrusion of the wall of a blood vessel), or a tumor. Sometimes brachial plexitis is observed in people against the background of dysmetabolic or infectious pathologies.
- Horner's syndrome is a neurological disorder that develops in response to damage to the sympathetic nerve fibers of the brachial plexus as a result of tumor formation, aortic aneurysm, thyroid dysfunction, and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Spinal diseases, in particular spondylosis, osteochondrosis, and intervertebral hernias, are among the most common causes of numbness in the fingers.
Injuries
Any bruises, fractures or other injuries to the hands, accompanied by severe swelling, can lead to short-term numbness of the fingers. This is a consequence of compression of the blood vessels by edematous tissue, which temporarily disrupts the blood supply. This can also be observed in the first days after applying a plaster cast to immobilize the injured arm and requires its prompt loosening.
It is extremely rare to observe the occurrence of myofascial compartment syndrome, which is characterized by numbness of the fingers and hands, severe pain that cannot be relieved with traditional non-narcotic drugs. This is a dangerous complication that requires immediate qualified medical care.
Also, numbness in the fingers immediately occurs after open wounds, during which the nerve trunks were damaged. But this is usually combined with noticeable limitations in mobility.
Patients who have suffered traumatic brain or spinal cord injuries often complain that their fingers go numb. At the same time, they have numbness constantly.
Vascular disorders
One of the possible causes of numbness may be hypertension, especially if it occurs without treatment. In such situations, the fingers usually go numb due to the development of swelling of the hands, which is combined with:
- redness of the face;
- increased sweating;
- long-term pain in the heart area.
Another cause of hypoesthesia can be anemia, i.e. a condition in which the number of red blood cells in the blood sharply decreases, and therefore the level of hemoglobin drops. Since this compound is responsible for transporting oxygen to cells, when it is deficient, signs of oxygen starvation are observed:
- feeling of weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- headache;
- decreased appetite;
- increased heart rate;
- shortness of breath even with minor physical exertion;
- decreased concentration;
- dizziness up to loss of consciousness.
Also, numbness in the fingers can be a consequence of a stroke.
Numbness in the fingers is also characteristic of Raynaud's syndrome. This is the name for a disorder in which there is a violation of arterial circulation in the 2nd and 4th fingers under the influence of cold or stress. It is characterized by a paroxysmal course with the initial appearance of a feeling of numbness, coldness and blueness of the fingers, which indicates a decrease in the intensity of blood circulation in them. Then these sensations are replaced by distension, aching pain and burning. When blood circulation is restored and, accordingly, the attack ends, a strong feeling of heat appears in the fingers, and they turn sharply red.
Raynaud's syndrome may be a sign of the development of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- damage to the sympathetic ganglia or neurovascular bundles;
- some endocrine diseases;
- blood pathologies.
Less commonly, it occurs against the background of vibration disease and frequent hypothermia.
Diagnosis of the causes of hand numbness. How to identify?
At the appointment, the doctor examines and palpates the patient’s limb and asks the following questions:
- Where exactly is the numbness felt?
- When did the unpleasant tingling sensation and decreased sensitivity first appear?
- How long does numbness in a limb bother you?
- What actions and movements aggravate symptoms?
- Are there any other complaints, such as burning, itching, tingling, pain?
- How do your arms, hands, and fingers feel—cold or warm?
The main task of the doctor is to determine the causes of hand numbness. It is necessary to exclude systematic mechanical compression of blood vessels, as well as to determine household and industrial factors that could cause disturbances.
Numbness may be a harmless symptom, but it may also hide serious problems - myocardial ischemia, stroke, spinal problems, diabetes mellitus, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc. In this case, the doctor issues a referral to doctors of relevant specializations (cardiologist, endocrinologist, neuropathologist, etc.).
The main emphasis in identifying the causes of numbness is on detecting signs of osteochondrosis. For this, the patient is referred for magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography, and electromyography. The purpose of imaging studies for arm numbness is to determine the height of the intervertebral disc, detect osteophytes, and clarify the presence of protrusion or intervertebral herniation.
Self-help and self-diagnosis
To answer the question of what to do if your toes go numb, you need to understand the causes of this condition. Loss of sensitivity in the fingers, local increase in temperature, swelling and decreased mobility may indicate a disease of small joints: arthritis, arthrosis or gout. Arthrosis and arthritis are characterized by a slow and gradual increase in symptoms. With gout, the toes go numb and burn, swell greatly, while the discomfort is paroxysmal in nature and is accompanied by an increase in temperature. If these symptoms occur, you should consult an orthopedist or rheumatologist. What to do if your toes go numb due to uncomfortable shoes:
- perform a light foot massage;
- take a warm bath with sea salt.
These actions relieve discomfort, but it should be remembered that constantly wearing unsuitable shoes often leads to the development of degenerative diseases of the joints of the lower extremities. Osteochondrosis, spondylosis, arthrosis of the spine, protrusions and hernias, tumors in the spine and soft tissues can also cause numbness in the fingers. All of these diseases can cause circulatory problems, nerve compression, and spinal cord damage. The following symptoms are typical for numbness of the fingers caused by spinal pathologies:
- decreased mobility;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- crunching, clicking when moving;
- pain in the back and chest;
- headache;
- changes in hearing, vision;
- dizziness;
- periodic “disobedience” of the limbs;
- causeless weakness;
- pressure surges.
If such signs appear, it is important to consult a neurologist or orthopedist as soon as possible. Without treatment, dangerous complications such as paralysis, spinal cord damage and cerebral hemorrhage may develop. In case of foot injuries, numbness and pain, as well as changes in the shape of the finger and skin color, swelling may not appear immediately, but several hours or in the morning after sleep. If these symptoms are detected, urgent assistance from a traumatologist is required. In the case of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, paresthesia is usually combined with coldness of the legs, the appearance of hematomas without bruises, a pronounced vein pattern and the formation of spider veins. If such signs are detected, you should visit a therapist or phlebologist.
Principles of treating hand numbness
The primary task of the doctor is to identify the root cause of this symptom. For this purpose, radiography, myelography, MRI, blood tests, etc. can be performed.
Depending on the nature of the disease that caused numbness in the hands, treatment methods are selected. First of all, the underlying disease is treated. Drug treatment is supplemented by:
- physiotherapy;
- physical therapy;
- reflexology;
- massage;
- diet therapy;
- lifestyle correction.
Treatment
For each patient, treatment is developed individually based on diagnostic results and detected diseases. In most cases, they begin by prescribing conservative therapy appropriate to the situation. It may include medication, physical therapy and exercise therapy.
Drug treatment may include drugs from different groups. They are selected based on the causes of numbness in the fingers, but they must take into account concomitant diseases, age and other characteristics of the patient. Typically used:
- NSAIDs - prescribed during an exacerbation of neuropathy to reduce the intensity of pain and eliminate swelling of soft tissues;
- corticosteroids - indicated for severe inflammatory processes, as well as complex neuropathy;
- B vitamins - used to improve the transmission of bioelectric impulses along nerve trunks;
- antiplatelet agents - prescribed to reduce blood viscosity and improve blood circulation;
- calcium antagonists - used to increase the lumen of blood vessels, which is indicated for Raynaud's syndrome;
To increase the effectiveness of drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are often used. The most effective for neurological disorders are:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- UHF;
- electromyostimulation;
- applications with paraffin;
- ozocrete treatment;
- mud therapy.
To eliminate numbness, an individually developed complex of exercise therapy must be prescribed. It helps to develop the joints of the hands, activate blood circulation and relieve muscle tension. As a result, tissue trophism and innervation of the fingers improves. But exercise therapy should be done systematically, devoting the proper amount of time to gymnastics every day.
Preventing numbness in the hands
In order to prevent discomfort in the upper extremities, it is recommended:
- exercise regularly (discuss the type and nature of exercise with your doctor in advance);
- maintain the health of blood vessels, joints and the body as a whole (give up bad habits, eat rationally);
- dress according to the season, keep your hands warm;
- take breaks every 40 minutes if your profession involves working on a PC or performing monotonous hand movements.
What external factors cause paresthesia?
Numbness of the big toe, little finger, and other toes can be caused by external causes that are not related to the general condition of the body. Paresthesia may occur due to:
- uncomfortable pose. When sitting in a position where one leg is crossed over the other or placed under oneself, the nerve is sometimes pinched and blood flow is reduced. First, a tingling sensation is felt in the fingers, then numbness sets in. When changing posture, all symptoms gradually disappear;
- increased load on the legs. This may cause pain, numbness and fatigue;
- presence of corns. Dead cells deposited in one place on the skin of the fingers or the foot itself reduce their sensitivity. Pain occurs when walking;
- any trauma that causes nerve damage. This causes movement to become somewhat limited as it heals, which can cause pain. The consequences of such an injury may be periodic numbness of the fingers;
- tight shoes or too narrow socks. Regular squeezing of the leg leads to swelling, which impairs its blood circulation, which is accompanied by subsequent numbness;
- poisoning With the regular intake of nicotine or other toxic substances into the body, a gradual narrowing of blood vessels occurs, impeding blood flow. At the same time, the walls of the blood vessels become thinner, which can also have unpleasant consequences.
Treatment with folk remedies
The following recipes help with numb hands:
- as a compress or therapeutic bath, use a mixture of 2 liters of milk, 600 g of salt and 50 g of honey, heated to 60? C;
- apply an infusion of wild rosemary with apple cider vinegar (1:3) 3 times a day;
- infusion of garlic (several cloves) in vodka (400 ml) taken orally, 3-5 drops dissolved in water;
- for 1 liter of vegetable oil - 100 g of ground black pepper, cook for 30–40 minutes, rub the cooled product into the skin of the affected limb.
Treatment of hand numbness in specialized hospitals
Department of Neurosurgery, City Clinical Hospital named after. A.K. Yeramishantseva sees patients with complaints of numbness in their hands. Here, progressive methods of conservative and surgical treatment of diseases manifested by such symptoms are used. Advanced technical equipment and extensive professional experience of the medical staff guarantee good treatment results. Telephone.
Neurosurgeon Evgeniy Evgenievich Zavalishin treats diseases that cause numbness in the hands. Sign up for a consultation by calling 8 (499) 940-04-30.