There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Causes General symptoms Types of hemorrhoids Symptoms Stages Diagnosis Treatment Prevention
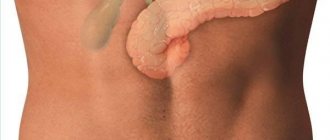
Hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids) are varicose, deformed and inflamed blood vessels (hemorrhoidal plexuses) located in the smooth muscles of the walls of the rectum and anus. They are a normal part of the rectum and are located at the junction of small arteries that become veins. Hemorrhoidal plexuses contain smooth muscle and connective tissue and are classified by where they are located in relation to the pectineal line, the point dividing the upper 2/3 and lower 1/3 of the anus. The anatomical difference is formed due to the type of cells lining the hemorrhoidal veins and the nerves that provide sensation. It is damage to these vessels that forms the signs of hemorrhoids.
Often people go to the doctor, noting the first signs of hemorrhoids in women or men - enlarged nodes, causing itching, pain or bleeding.
In our clinics you can treat hemorrhoids in the following ways:
- Hemorrhoid ligation surgery with latex rings
- Laser removal of hemorrhoids
- Non-surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
- Desarterization of hemorrhoids (new technique)
Hemorrhoids: causes of occurrence
Although the presence of hemorrhoidal plexuses is part of the normal anatomy of the rectum, if the nodes become inflamed, increase in size, and blood stagnates in them, a disease develops - hemorrhoids. Changes occur gradually, starting from barely noticeable and reaching severe and pronounced. Symptoms of hemorrhoids occur when pressure increases in the small vessels supplying the rectum and anus, causing the veins and plexuses to swell and fill with blood. This leads to an increase in the size of the nodes, which contributes to the appearance of symptoms of external or internal hemorrhoids. Increased pressure in the veins and the development of pathology can be caused by many factors, and the causes of hemorrhoids in women or men may vary. Common risk factors include:
- Lack of fiber-rich foods in the diet, which causes hardening of the stool. Difficulty during bowel movements causes a person to strain and strain, which increases the pressure in the blood vessels of the anus.
- Prolonged sitting on the toilet, which can increase the pressure in the blood vessels of hemorrhoids.
- Obesity;
- Diarrhea – both acute and chronic.
- Colon cancer or previous rectal surgery.
For women, an additional cause of hemorrhoids that affects treatment is pregnancy. Carrying a baby is associated with swelling and enlargement of hemorrhoids, which most likely occurs due to the increased pressure of the enlarged uterus on the rectum and anus. In addition, hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken the muscles that support the rectum and anus, which form the tone of the veins.
Features of therapy
Treatment of the pathological process requires a thorough approach:
- begin at the first appearance of symptoms;
- be comprehensive;
- include both medications and changes in the patient’s usual lifestyle.
Only fulfilling all the conditions will help you recover and forget about the problem.
Diet food
Hemorrhoids are caused by poor circulation and weakening of blood vessels. The disease requires exclusion from the daily menu:
- acute;
- smoked;
- fried food;
- alcoholic drinks.
The patient should reduce the amount of salt consumed. The menu should contain coarse fibers and plant fiber supplied from vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
Pills
Complex therapy involves the use of drugs that strengthen the vascular walls, helping to stabilize local blood circulation and facilitate lymph outflow. Popular means include:
- Detralex - reduces the distensibility of venous vessels, increases their tone, strengthens the walls, prevents fragility, use 2 tablets. per day, in the acute phase - up to 6 units per day;
- Glivenol is an angioprotector and microcirculation corrector;
- Rutoside - affects capillaries, suppresses swelling, strengthens blood vessels.
The attending physician is responsible for selecting the appropriate medication.
Candles
They are used for local effects on pathology, treatment is carried out with Relief, Ultra-Proct, Aurobin, etc. The active components of the drugs stop the inflammatory process, relieve obsessive itching and tissue swelling. Due to the drugs, damaged tissues are restored, they have a local hemostatic spectrum of action.
During pregnancy and the development of hemorrhoids, taking any medications should be justified. Medicines must meet safety criteria; preference is given to options with a natural base:
- with sea buckthorn - the element effectively reduces inflammation, relieves redness, swelling, pain, has an antibacterial spectrum of action, and at the same time increases immunity;
- with propolis - the ingredient helps improve local blood circulation, suppresses itching, soreness, and affects areas of inflammation.
Both products are considered harmless, but require prior consultation with a proctologist and permission to use them. During pregnancy, the most harmless medications can cause unusual reactions.
What are internal and external hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are located above the pectineal line and are covered with the same cells as those lining the rest of the intestine. External hemorrhoids occur below the line and are covered with skin-like cells.
Outer
Externally it manifests itself as hemorrhoids outside the anus. They are located near the sphincter. The nodes become inflamed and enlarge due to stagnation of blood in the pelvic area. If a blood clot appears in the external node, swelling forms, causing pain to the person. The patient feels a voluminous lump on sensitive thin skin. This development of the disease is typical with an incorrect diet, stagnation of blood in the rectum, low physical activity, and heavy physical exertion. When the skin that covers the node becomes thinner, a blood clot comes out, followed by bleeding.
Interior
With this form, hemorrhoids are almost invisible. They are located inside the anal canal, in the place where it passes into the rectum, under the mucous membrane. The nodes appear due to the protrusion of blood vessels and are usually painless. However, even in this case, hemorrhoidal thrombosis may occur. At an early stage, the disease can be recognized by a small amount of blood discharge after bowel movements.
Moderate physical activity
- When working sedentarily, you should get up every hour and take breaks for at least five to ten minutes. It is advisable to move during your lunch break.
- Introduce moderate physical activity: exercise, swimming, running and walking. This is especially true for those who drive.
- Do simple exercises at home. These are pelvic lifts, lying on your back, abdominal exercises, bending.
- In the office, sit on a hard chair, it is safer than a soft chair. Even while working at the computer, you can quietly squeeze and relax your buttocks.
How to determine external and internal hemorrhoids
Normal hemorrhoidal tissue is not visible because it must first swell and become inflamed or form a clot to cause symptoms. Swollen external hemorrhoids or internal prolapsed hemorrhoids outside the anus may be seen, but internal hemorrhoids are not visible because the nodes remain inside the anus. A thrombosed hemorrhoid will appear as a lump on the edge of the anus protruding from the anus and will be dark bluish in color due to the clot contained within the swollen blood vessel. A nonthrombosed hemorrhoid will appear as a lump of skin. Often several swollen hemorrhoids appear at the same time.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids in men and women
Acute hemorrhoids or exacerbation of a chronic process are the most common cause of complaints from the rectum and anus. Most common symptoms:
- painless bleeding from the anal area, blood stains on linen, toilet paper;
- anal itching;
- pain, discomfort in the anal area;
- swelling and the sensation of a lump or foreign body in the anus are associated with inflammation and exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids.
Inflammation of internal hemorrhoids has special symptoms, for example, it can cause swelling. This in itself does not cause pain because there are no pain fibers attached to the veins above the pectineal line. Hard stool can damage the thinned mucous membrane of the node, causing painless bleeding. However, swollen hemorrhoids can also cause the muscles surrounding the rectum and anus to spasm, causing pain, especially if they prolapse through the anus. You can feel a lump along the edge of the anus. Internal hemorrhoids can also thrombose (clot), causing severe pain.
Inflamed hemorrhoids can produce mucus, which can cause inflammation of the skin around the anus, causing burning and anal itching. However, there may be other causes of itching, including yeast and other skin infections.
External hemorrhoids behave differently because the nodes are covered with “regular skin”, which contains pain receptors. Thrombosis of external hemorrhoids occurs when the underlying vein inside the hemorrhoid becomes blocked, causing severe pain due to the rapid stretching of the skin covering the hemorrhoid. You may feel a hard, painful lump in your anus. External hemorrhoids can also result in excess skin tags that can be felt at the edge of the anus and can cause difficulty cleaning the skin after bowel movements, leading to secondary skin infections.
Stages of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be acute (when the disease develops rapidly and is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort) and chronic. In the second case, a mild pain syndrome is observed, the disease develops over a long period of time with periods of exacerbation (bleeding, prolapse and pinched nodes occur).
First stage
Mild discomfort is felt, and short-term bleeding is typical, which occurs after any overexertion - hard work, defecation. Inflammation is detected only during examination. At this stage, conservative treatment, sclerotherapy, and photocoagulation are recommended.
Second stage
It is characterized by periodic prolapse of inflamed hemorrhoids, while bleeding may be absent. The dropped nodes are set on their own without much effort. Conservative treatment, sclerotherapy, photocoagulation, ligation, or a combination of these techniques is recommended.
Third stage
Dystrophic changes occur in the sphincter, it weakens, as a result of which prolapsed hemorrhoids can only be set manually. The course of the disease is accompanied by severe itching, frequent and heavy bleeding. Ligation, surgical treatment, and a combination of techniques are recommended.
Fourth stage
Hemorrhoids are in a constantly prolapsed state along with the rectal mucosa. It is impossible to set them. It may be accompanied by bleeding or occur without it. Inflammation can affect nearby tissues. Surgery to remove hemorrhoids is indicated.
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids: determining the cause and symptoms in men and women
Common symptoms of hemorrhoids include itching, pain, rectal fullness or hardness, and bleeding. Diagnosis is made based on a history and physical examination. The history may indicate associated symptoms, including constipation, problems with bowel movements, and straining to go to the toilet. Your doctor will ask more questions to look for other causes of rectal bleeding, including tumors, inflammatory bowel disease, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
To confirm the diagnosis, determine the cause of hemorrhoids and select treatment, an examination is performed. It involves a rectal examination, in which a finger is used to feel for abnormal lumps or masses. A rectal examination may be delayed if pain or swelling is severe. Additionally, hemorrhoids and constipation may be associated with anal fissures in the skin surrounding the anus. The associated pain and spasm makes rectal examination very painful. If the doctor is concerned that symptoms, especially rectal bleeding, cannot be explained by hemorrhoids, an anoscopy may be considered. This is a procedure in which a lighted tube is inserted to view the anus. If there is concern that bleeding is coming from other areas of the colon, a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be performed. These procedures are usually performed by a gastroenterologist or surgeon.
Depending on the situation, blood tests may be ordered. If there was heavy bleeding, you need to check your hemoglobin or red blood cell levels. If the patient is taking blood thinners, a coagulation test is necessary.
Benefits of Duphalac®
- Duphalac® has a favorable safety profile6,7.
- The drug can be used for as long as necessary5,7, which is suitable for people with hemorrhoids, since in most cases it is a chronic problem.
- Duphalac® is approved for use by pregnant women, who may also experience this problem. You can read more about this in the material “Hemorrhoids during pregnancy.”
The material was developed with the support of Abbott to improve patient health awareness. The information in the material does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. See your doctor.
RUS2120920 from 03/25/2020 Your browser does not support the video tag.
Co-author of articles, editor - Shimbaretsky Georgy Alekseevich.
Methods for treating internal and external hemorrhoids
When hemorrhoids occur or worsen, it is important to choose the right treatment methods. It can be conservative, minimally invasive and surgical.
“SM-Clinic” provides services for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment of hemorrhoids in clinics in St. Petersburg. Both non-surgical and surgical treatment are used, including laser surgery for hemorrhoid removal. The disease can have several stages, which determines the type of treatment.
Non-surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
Conservative therapy
Allows you to reduce the frequency, duration and severity of exacerbations. It involves taking general medications (normalize blood flow, increase venous tone, etc.) and using local remedies (suppositories, ointments, gels to eliminate inflammation, pain, itching, prevent thrombosis, etc.).
Ligation with latex rings
One of the most modern and popular low-traumatic methods of treating internal hemorrhoids. Through an anoscope, a latex ring is applied to the stem of the hemorrhoidal node, which leads to compression of the tissues and disruption of blood circulation in them. After 1-2 weeks, the node is rejected.
Sclerotherapy
During the procedure, with the help of special drugs (sclerosants) that are introduced into the node, the inner lining of the venous wall is affected, which leads to its damage and subsequent gluing. As a result, the pathologically deformed vein no longer participates in the blood circulation process and dies. The technique is effective only for small hemorrhoids; the risk of relapse cannot be excluded.
Infrared photocoagulation
This technique involves temperature exposure to the node. The coagulator is applied to the node at 3-5 points. As a result, a burn of 2-3 mm appears. The morbidity of this method is extremely low, and patients become able to work on the same day or within 24 hours. The damaged node disappears after some time.
Surgical techniques
Surgical removal (hemorrhoidectomy)
Surgery is resorted to in the third and fourth stages of the disease. The surgical method involves excision of the hemorrhoidal node along with part of the mucous membrane and is indicated for chronic hemorrhoids of stages 3 and 4, severe bleeding, frequent relapses and thrombosis of the nodes. Surgery takes little time, and patients recover quickly. The method is considered one of the most effective, where the number of relapses is reduced to an absolute minimum.
Laser removal of hemorrhoids
The idea is to cauterize the vessels with a laser beam. This is a modern, painless, low-traumatic and effective way to treat hemorrhoids at any stage. The operation itself takes only 15 minutes, is performed under local anesthesia and does not require the patient to stay in the hospital for a long time.
Dearterization of hemorrhoids (HAL-RAR method)
This is a minimally invasive operation aimed at ligating the vessels, so that blood stops flowing to them. As a result, the nodes stop bleeding, are deprived of nutrition and disappear. The technique is highly effective (up to 95%), painless and does not require long recovery.
Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the disease, the severity of clinical manifestations and diagnostic results. At the first and second stages of hemorrhoids, conservative treatment and minimally invasive methods are recommended - sclerotherapy, photocoagulation, ligation or a combination of these methods. In the third and fourth stages, surgery is required in most cases.
Is it possible to cure hemorrhoids using traditional methods?
Herbal baths, decoctions and compresses are appropriate only as part of combined conservative therapy for uncomplicated hemorrhoids. We are not aware of cases in which these isolated measures would be truly effective. Traditional methods of treating hemorrhoids should be treated especially carefully and from a critical point of view. Still, we are talking about a serious pathology of the rectum, often with cracks, prolapse of nodes and even thrombosis. Self-medication can be dangerous.
A separate group of proctologist patients are those whom doctors treat for complications after treatment with traditional methods.
They will definitely not help with hemorrhoids:
- ice candles
- fresh potato paste
- aloe leaf
- cucumbers from the garden
- steam baths
- leeches
How to get rid of hemorrhoids at different stages
Hemorrhoids will recur after conservative treatment in approximately 50% of cases, while the recurrence rate after surgery is only 5%. The goal is to control hemorrhoid inflammation through diet and hydration so that surgery is not required. In this regard, hemorrhoids are a lifelong condition that needs to be managed.
Hemorrhoids of 2 and 3 degrees are initially treated conservatively or using minimally invasive methods. These include injections into the hemorrhoidal vein to sclerosize or harden it, using rubber bands to cut off the blood supply and cause the hemorrhoidal tissue to shrink, or other procedures that cause the lining to shrink and die.
Treatment of hemorrhoids without surgery: what therapy does the doctor prescribe?
Hemorrhoids are a collective name for diseases of the rectum with a corresponding set of symptoms. The classification of hemorrhoids is extensive, so adequate treatment is prescribed after examination, and recommendations for a treatment regimen are strictly individual.
Generally speaking, treatment for hemorrhoids without surgery includes:
- Correction of diet and diet to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Herbal medicines;
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Minimally invasive non-surgical treatment methods: sclerotherapy, coagulation or ligation of hemorrhoids.
Why are hemorrhoids dangerous?
The most common complications of hemorrhoids are inflammation, thrombosis or bleeding. It is important to remember that rectal bleeding or blood in the stool is always abnormal, and although it can be caused by a relatively benign cause (such as hemorrhoids), other, more serious causes can be life-threatening. These include bleeding from ulcers, diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease and tumors. This is especially important if a person is taking blood thinners.
What foods are good for preventing intestinal diseases?
In order not to risk your health and not be a victim of hemorrhoids, it is recommended to include more vegetables, fruits and fiber in your daily diet.
For the prevention of hemorrhoids it is useful:
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables (apples, avocado, pumpkin, broccoli)
- Beetroot and beet salad
- Freshly squeezed juice, especially pumpkin juice
- Prunes
- Chew food thoroughly
Harmful:
- Hot, spicy, fried, smoked
- Marinades
- Eat dry
- Soda
- Whole milk
- Baking and flour
- Lots of sweets
- Pasta, white rice and bread
- Canned food
If microflora disorders are detected, it is better to cure them. Sometimes it is necessary to prescribe probiotics that restore the intestinal microbiome, and enzymes that help digest food.
*For patients with diagnosed intestinal disease, the diet is individually prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention of hemorrhoids
Prevention is the most effective treatment. Diet and adequate fluid intake are very important to maintain normal bowel movements. Symptoms of hemorrhoids can occur with the passage of hard stools and constipation, as well as with diarrhea and frequent bowel movements. People with constipation may need a high-fiber diet, adequate fluids, and stool softeners. Those who have excessively frequent bowel movements may need antidiarrheal medications and dietary adjustments. These preventive measures reduce the strain required to have a bowel movement, thereby reducing the pressure in the blood vessels to prevent swelling.
The SM-Clinic Surgery Center provides services for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment of hemorrhoids using non-surgical methods and surgical techniques. Our patients recover within 24 hours in a comfortable hospital setting and quickly return to their normal lifestyle. Other treatment methods are also used, depending on the stage and type of disease. Advanced equipment is used for diagnostics, ensuring accuracy and speed of obtaining results.
Balanced diet
Diets, colon cleanses and enemas are the main provocateurs of anal problems. But a diet balanced in carbohydrates, proteins and fiber, and adherence to a drinking regime will improve regular bowel movements and relieve constipation.
Consume fermented milk products, which improves intestinal microflora. Eat fruits, vegetables, cereals and bran bread - all these foods improve intestinal motility.
Avoid alcohol and spicy foods. Reduce your consumption of flour, especially baked goods.
Prices
Price (rub.)In installments* (rub.)Consultation with a surgeon on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Online doctor’s opinion on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Hemorrhoidectomy Cat. I. complexity from 35000—Non-surgical removal of hemorrhoids, category I. complexity from 3550—Coagulation of a hemorrhoid using radio wave surgery from 6400—Thrombosis of hemorrhoids (1 ligation) from 300—Thrombectomy from an external hemorrhoid from 4800—Removal of a thrombosed hemorrhoid I cat. complexityfrom 7800—Removal of a thrombosed hemorrhoid, category II. complexity from 9600—Removal of a thrombosed hemorrhoid, category III. complexityfrom 13750—See full list
Hide
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments
The cost is preliminary. The exact cost of the operation can only be determined by a surgeon during a free consultation.