An ulcer is painful, disgusting and dangerous. In the recent past, doctors could not find the root cause of this pathology. They blamed it on stress, poor nutrition and treated it almost blindly experimentally.
At the end of the 19th century, German scientists discovered a spiral-shaped bacterium that lived in the stomach and duodenum. It was given the name Helicobacter pylori. In 1981, the connection between this microorganism and the appearance of ulcers in the stomach and intestines was scientifically proven, for which in 2005 the discoverers of the medical significance of the bacterium, Robin Warren and Barry Marshall, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
What kind of bacteria is this? How to destroy a pathogenic microorganism and cure erosion of the gastric mucosa once and for all? How to treat Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pylori: general information about the microorganism and route of infection
Helicobacter colonizes areas of the mucous membrane.
Helicobacter is a spiral-shaped gram-negative microorganism. Its dimensions are only 3 microns. This is the only microorganism capable of surviving and multiplying in the acidic environment of gastric juice.
Under favorable conditions, Helicobacter colonizes areas of the mucous membrane. The negative effect on the stomach occurs due to the complex properties of this microorganism:
- The presence of flagella allows for rapid movement in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Adhesion to stomach cells. This creates inflammation and the body's immune response.
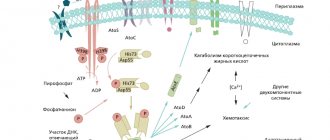
- Produces enzymes that break down urea into ammonia. This neutralizes the hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, and the bacterium receives an environment favorable for development. Ammonia additionally burns the mucous membranes. This causes an inflammatory process.
- The microorganism produces and releases exotoxins that destroy mucosal cells.
Scientists have proven that Helicobacter strains in patients with ulcers are more aggressive than in patients with gastritis and other inflammatory processes in the stomach or intestines.
Infection with this microorganism occurs asymptomatically in 70% of cases. Doctors call possible routes of infection oral-fecal or oral-oral - through kissing, sharing utensils, in canteens and cafes, during medical procedures.
How dangerous is the bacterium?
There are two mechanisms of the pathogenic effect of Helicobacter pylori on the human body.
How dangerous is the bacterium?
- Helicobacter pylori endotoxins have a negative effect on tissue, damaging the endothelium lining the inside of blood vessels, affecting smooth muscle muscles;
- when exposed to it, immune-inflammatory reactions are activated and associated pathologies arise.
With the influence of bacteria, the digestive system becomes functionally imperfect, since the protective function of the gastric mucosa is disrupted and substances that previously did not enter it are absorbed into the blood. When Helicobacter pylori persists in the stomach for a long time, gastrointestinal motility is disrupted and the synthesis of hormones that stimulate gastric and intestinal peristalsis is disrupted.
Colonies of bacteria displace beneficial microorganisms of the digestive system, provoking the development of dysbiosis. The long course of chronic gastritis caused by it leads to atrophy of the mucosa and the formation of foci of metaplasia on it, when the typical covering of the wall of the stomach and intestines is transformed into atypical cells. In addition to these changes, the secretion of gastric juice, which performs a protective function that prevents the development of tumors, decreases. All these factors stimulate the development of stomach cancer, and less commonly, intestinal cancer.
The danger of this condition is that the patient may not feel significant pain, especially if cancer occurs against the background of atrophic gastritis. Much more often he experiences an aversion to protein foods, weakness, irritability, depression, and loses interest in his surroundings.
Helicobacter: diagnostic measures
To diagnose Helicobacter, you need to undergo tests.
Diagnostic procedures begin with interviewing and examining the patient. Then special studies are carried out to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis. Tests for Helicobacter pylori:
- Non-invasive procedures - blood for specific antibodies, breath test, stool and saliva analysis
- Invasive techniques - endoscopy with collection of material for histological examination
- To determine the microorganism in biological media, PCR analysis is carried out.
- For breath tests, the patient takes a solution of urea with labeled carbon atoms. The microorganism breaks down urea, and the labeled atoms are found in the air exhaled by a person. Additionally, an analysis is carried out to determine the concentration of ammonia in exhaled air.
The most accurate results are provided only by invasive examination methods.
Long courses of treatment with NSAID drugs
There are 2 methods of treating Helicobacter pylori infection.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively. According to the WHO methodology, any drug regimen must meet the following criteria:
- Efficiency and speed
- Safety for the patient
- Convenience – use long-acting drugs, short course of treatment
- Interchangeability - any drug must be interchangeable with a complete analogue or generic
Currently, 2 methods have been adopted for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. It is not recommended to use them simultaneously. If 1 scheme does not give a positive result, then the second one is used and vice versa. This prevents Helicobacter from developing immunity to drugs. Treatment regimens:
- Three-component method - 2 antibacterial drugs and 1 agent to reduce the acidity of gastric juice
- Four-component method - 2 antibacterial drugs, 1 - to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid, 1 - bismuth compounds
There is a 3rd treatment regimen for combating the microorganism. It is used when the first 2 did not have the desired effect. In this case, they speak of a resistant Helicobacter strain.
In this case, a preliminary endoscopic examination is carried out with the collection of material for a biopsy. In the laboratory, drugs for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori are individually selected. And only after that the doctor develops an individual course.
Antibacterial drugs
Macmiror destroys the parasite's genetic material.
The choice of antibacterial drugs that can cope with Helicobacter is small. This is "Trichopol" or "Metronidazole", or "Makmiror".
Trichopolum and Metronidazole are complete analogues. The main active ingredient of the drug, metronidazole, penetrates the microorganism and breaks down, releasing toxic substances.
They destroy the parasite's genetic material. The main active ingredient of Macmiror is nifuratel. It simultaneously inhibits the growth of bacteria and prevents the proliferation of microorganisms.
The peculiarity of this drug is that nifuratel does not reduce the patient’s overall immunity, but, on the contrary, improves the body’s defenses. Macmiror is a second-line drug. It is prescribed if treatment with metronidazole does not give the expected result. This medicine is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers in children.
Symptoms of infection
Helicobacter pylori infection can be recognized by the following specific signs:
- Heaviness and discomfort in the epigastric region.
- Belching sour.
- Heartburn.
- Stool disorders in the form of alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- Decreased appetite.
- Loss of body weight.
- Bad breath.
As a rule, the listed symptoms begin to bother a person at the stage of active development of gastritis or gastric ulcer. At the initial stage of infection, this condition occurs in an asymptomatic form.
Bismuth preparations and proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of Helicobacter
De-nol is a bismuth-based medicine.
A bismuth-based drug, De-nol, was used even before the discovery of the pathogenic microorganism. It has an enveloping effect, forming a film on the gastric mucosa.
It protects the walls from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid. After the discovery of Helicobacter, it turned out that bismuth subcitrate has an inhibitory effect on the bacterium. It is able to penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membrane, where the pathogen likes to settle.
Proton pump inhibitors - Omez, Omeprazole, Pariet - block areas of the mucosa responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. This promotes the healing of erosions, reduces the acidity of gastric juice and allows the antibiotic molecules to be preserved in an acidic environment.
Why can Helicobacter cause gastrointestinal diseases?
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that is associated with the occurrence of certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: peptic ulcers, stomach cancer, chronic gastritis and duodenitis.1
This bacterium is found in 70-80% of Russian residents.1 However, not everyone who is a carrier of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori develops symptoms of disease. This is due to genetic characteristics on which the protective properties of the mucous membranes depend. There are research results that show that the presence of several strains of Helicobacter pylori can cause more severe inflammation of the mucous membranes and other unfavorable changes compared to the situation when a patient has only one strain of this bacterium.2
The main route of transmission of Helicobacteriosis is intrafamilial. Infection with Helicobacter pylori occurs through contact, as well as through food and drinks.1
Why does Helicobacter cause inflammation?
Normally, the surface of the gastric mucosa is protected by the action of hydrochloric acid. This is a strong chemical agent that destroys pathogenic microbes. Helicobacter pylori secretes a special substance - the enzyme urease. It breaks down the gastric contents, producing ammonia, which protects this bacterium from the action of hydrochloric acid. The bacterium destroys the protective layer of the gastric mucosa and penetrates the surface of cells, starting the process of their damage and death. Helicobacter pylori can exist in the stomach and duodenum for a long time, maintaining inflammation and unpleasant symptoms.2
Symptoms.
Manifestations depend on the disease, which is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. All symptoms associated with this bacterium are nonspecific and require consultation with a doctor and further examination.
Possible manifestations:
- Pain. The intensity and location of pain depend on the disease. With gastritis, pain may be associated with eating irritating foods or alcohol. With a peptic ulcer, “hungry” pain may occur, including night pain.3
- Dyspepsia. This is a complex of varied symptoms that includes belching, heartburn, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, excessive gas formation and bowel movements.
- Other symptoms. Sometimes other manifestations may occur: general weakness, irritability, sleep disturbances.4
There is also a variant of asymptomatic carriage of Helicobacter pylori infection.8 In one study involving residents of Moscow, Helicobacter pylori was found on average in 88% of working-age residents: in 78% of young people and in 97% of people over the age of 61.8
How to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body
An endoscopic examination allows you to obtain a biopsy sample - a piece of mucous membrane, which is then examined under a microscope.2 Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is also prescribed to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, to detect inflammation, ulcers and other defects.
However, there are also non-invasive tests - tests for Helicobacter pylori, which are carried out quickly and do not require medical intervention:
- urease breath test,
- test to determine H. pylori in stool,
- determination of antibodies to H. pylori in the blood.2
Treatment.
A treatment regimen to help eliminate the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is called eradication therapy.6 This may include:
An example of a drug with the active ingredient bismuth tripotassium dicitrate is Ulcavis®. Its pharmaceutical substance has targeted bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori and forms a protective film on the surface of erosions and ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane.6, 7 Ulcavis® prevents the fixation of bacteria on the surface of the mucosa and promotes the restoration of its damaged areas.6
Bibliography:
1. Loranskaya I.D., Rakitskaya L.G., Mamedova L.D. Problems of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection // RMZh. 2013. No. 31. P. 1638 2. Lazebnik L. B., Vasilyev Yu. V., Shcherbakov P. L., Khomeriki S. G., Masharova A. A., Bordin D. S., Kasyanenko V. I., Dubtsova E. A. Helicobacter pylori: prevalence, diagnosis, treatment // EiKG. 2010. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/helicobacter-pylori-rasprostranennost-diagnostika-lechenie (date of access: 09/10/2017). 3. Dasaeva L.A., Lopatina V.V. Diagnosis of gastric and duodenal ulcers and selection of effective treatment regimens for patients of different ages // RMZh. 2013. No. 20. P. 1014 4. Zryachkin N.I., Chebotareva G.I., Buchkova T.N. Chronic gastritis and gastroduodenitis in children of preschool and school age (parts 1 and 2) // Questions of children's dietology. 2015. T. 13. No. 4. P.46-51. No. 5. From 55-61. 5. P.L. Shcherbakov, T.N. Kalachnyuk. The use of bismuth subcitrate in eradication schemes. 6. Kazyulin A.N., Partsvania-Vinogradova E.V., Dicheva D.T. and others. Optimization of anti-Helicobacter therapy in modern clinical practice. Consilium Medicum. 2016; 18 (8): 32. 7. Instructions for medical use of the drug Ulcavis® 8. S.V. German, I.E. Zykova, A.V. Modestova, N.V. Ermakov. Prevalence of H. pylori infection among the Moscow population. RZHGGK 2010; 2: 25–30.
Created by experts commissioned by KRKA PHARMA LLC
Take the testHow to calculate body mass index (BMI)?
RecipesSalad with diet turkey and rice “Spring drops”
RecipesChou-fleur soup (cauliflower)
Good to knowThe truth about fast food. Why is fast food dangerous?
Helicobacter pylori. How to do without antibiotics?
There is no effective treatment regimen for diseases associated with Helicobacter without the use of antibiotics. Only in some cases, without symptoms of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract and with a low contamination of bacteria, is it possible to remove Helicobacter pylori from the body.
All treatment regimens place a serious strain on the body. If carriage is detected without signs of inflammation, it is recommended to use more gentle methods.
How to get infected?
Infection with this microorganism is becoming a real problem for modern medicine, because almost every second adult is a carrier of the bacterium
Both adults and children can become infected with Helicobacter pylori. The main route of transmission is fecal-oral, oral-oral. Thus, you can become infected by kissing, sharing utensils, cups, bottles, toothbrushes or lipsticks of other people, through dirty hands, etc.
That is why this bacterium is often called a family problem.
- if it appears in one person, with a high probability expect it to appear in his loved ones.
Traditional medicine and Helicobacter
Traditional medicine recipes should not be used without consulting a doctor.
What does traditional medicine offer for the treatment of Helicobacter? Recipes are often contradictory:
- Raw chicken eggs. It is recommended to drink 1 raw egg before breakfast. This should normalize the normal microflora of the stomach.
- St. John's wort, calendula and yarrow are mixed in equal proportions. Make a decoction - 250 ml of water per 5 g of mixture. Take the infusion 0.5 cups 3 times a day for a month.
- It is recommended to consume 1 teaspoon of rosehip syrup per month.
- Flaxseed decoction. For 1 tablespoon of seed you will need 1 glass of water. Simmer over low heat for 20 minutes. Strain the broth and take 1 tablespoon before each meal.
The use of traditional medicine recipes should only be started after consulting a gastroenterologist. Otherwise, within a month of treatment you risk getting a perforated ulcer with all the ensuing consequences.
Diet for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection
Modern techniques allow you to be cured in a matter of weeks.
There is no specialized nutrition to combat Helicobacter. During treatment, you should adhere to the diet recommended for patients with gastritis, ulcers and other diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Food should be light, pureed and not irritate the mucous membranes. Heavy, spicy, fried and fatty foods are prohibited.
An ulcer is a dangerous disease. The cause of this pathology has now been identified. Helicobacter pylori should be treated under the guidance of a gastroenterologist. Modern techniques make it possible to get rid of this microorganism in a matter of weeks.