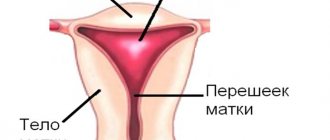
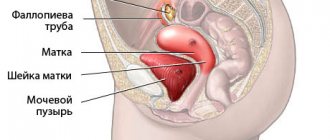
How are female reproductive organs formed?
Before we begin to consider the main topic, we want to explain how the female reproductive organs are formed.
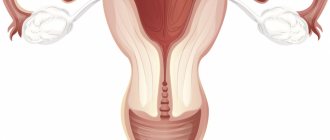
When a girl is in the womb, starting from the 6th week of development, her womb develops in two separate halves, which are called “Müllerian ducts”. Normally, the Müllerian ducts merge with each other into a single structure - the uterus with one cavity, and the septum between the ducts resolves even before the girl is born. Until the 12th week, the uterus acquires the mature morphological shape of a pear. This entire process is completed by the 22nd week of development and leads to the formation of 2 fallopian tubes, one uterus, cervix and vagina.
If the functioning of this system is disrupted, a wide variety of developmental defects can occur. They range from agenesis (absence) of the uterus to more subtle abnormalities, which are classified into specific categories:
- saddle uterus;
- bicornuate uterus;
- uterus with complete and incomplete septum;
- duplication of the uterus;
- unicornuate uterus.
Real reviews about conception, pregnancy and childbirth with a saddle-shaped uterine cavity
We present them in the form of screenshots. Quotes from women from a popular social network for moms.
Back to contents
This is also interesting
- New business: selling positive pregnancy tests
- 3 unusual ways to determine pregnancy
- Is it painful to examine your cervix before giving birth?
Reasons for the formation of abnormalities in the development of the uterus
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy , especially in the first trimester (measles, rubella, influenza, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection, syphilis);
- metabolic disorders and endocrine pathology (especially thyroid dysfunction, prolonged fasting, deficiency of vitamins and microelements);
- intoxication (long-term use by a woman before and during pregnancy of alcohol, narcotic substances, and some medications - the most negative effect is in the early stages, when the formation of all organs and systems is formed);
- hereditary factor (chromosomal and gene mutations);
- negative environmental influences (radiation, chemicals, psychological trauma).
Prevention
To prevent a saddle uterus from occurring, even before planning a pregnancy, a woman should observe the following preventive measures:
- timely treatment of infectious diseases and inflammatory processes of the reproductive system;
- prepare well for pregnancy, undergo the necessary examination and start taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- balance your diet so that it contains many plant components;
- visit a gynecologist regularly;
- register with a gynecologist during pregnancy up to three months.
This deviation is not a death sentence, so a woman can conceive, carry and give birth to a completely healthy baby. She just needs to be careful about her health.
When can you suspect an abnormal development of the uterus?
These anomalies manifest themselves in different ways - ranging from asymptomatic / random to a complex effect on conception on bearing a baby.
Specific complaints rarely arise, therefore, as a rule, an anomaly in the structure of the organ is discovered by chance. Possible symptoms of uterine development abnormalities include:
- painful, heavy or prolonged menstruation, spotting between two menstruation (but you yourself understand that such a symptom complex can be “attributed” to every second gynecological pathology);
- infertility
- miscarriage;
- There may be certain risks during a pregnancy that has already occurred: the threat of miscarriage or premature birth, abnormal position of the fetus, in which independent childbirth is impossible, premature placental abruption, improper attachment of the placenta, impaired contractility of the uterus during childbirth.
- combination with developmental anomalies of other organs, most often the urinary system.
Clinical manifestations during pregnancy
Before pregnancy, clinical symptoms do not appear in a woman with a saddle-shaped uterus. Often women learn about the presence of an anomaly only during examination at the planning stage of conception or during pregnancy.
In rare cases, pathology can cause the following features of the female body:
- painful and too heavy menstruation;
- the appearance of “spotting” in the last days of menstruation;
- acute pain during sexual intercourse;
- rejection of the intrauterine device by the body.
If young spouses have problems conceiving a baby, then it makes sense to undergo a full medical examination, including a thorough diagnosis of the uterus.
During pregnancy, ultrasound allows diagnosing an anomaly. Often the saddle shape does not “interfere” with the process of bearing a child. That is, the woman does not feel pathological symptoms, and the pregnancy proceeds normally.
But if an anomaly is detected, the expectant mother is advised to carefully monitor her condition. If signs of vaginal bleeding appear, you should call an ambulance.
What methods exist for diagnosing uterine anomalies (UDA)?
The detection of APM has increased significantly with the advent of 3D ultrasound, which clearly allows one to establish the diagnosis and is also non-invasive compared to X-ray and surgical diagnosis.
Therefore, 3D ultrasound is now considered the gold standard for assessing ARM. For a more accurate diagnosis, we recommend performing a 2D ultrasound in phase II of the menstrual cycle (18-20 days).
3D ultrasound helps: hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, MRI, metrosalpingography (x-ray diagnostics).
Possible complications
A saddle uterus can become a problem during conception, however, other abnormalities may appear against its background, for example:
- the development of pregnancy is difficult due to the fact that the fertilized egg is fixed in the lower part of the placenta;
- possible placental abruption or improper attachment;
- sometimes uncoordinated labor occurs, meaning the woman is unable to give birth on her own, so a caesarean section must be performed immediately.
From all of the above, it is clear that the saddle uterus mainly affects not conception, but the course of pregnancy. Therefore, doctors should pay more attention to such pregnant women, and, if necessary, take all measures to preserve the fetus.
Classification of uterine development anomalies
Saddle uterus
Saddle uterus
Saddle uterus is a mild form of developmental disorder. The shape resembles a saddle and is sometimes associated with a heart shape. It is characterized by a small intrauterine indentation, thinner than 1 cm and located in the fundus of the uterus. Formed as a result of almost complete resorption of the septum.
As a rule, a saddle uterus is a finding during a 3D ultrasound. The endometrium with a saddle uterus is completely healthy and suitable for embryo implantation. There may be certain risks during pregnancy, which requires additional vigilance of the obstetrician-gynecologist during pregnancy management.
The uterus, even saddle-shaped, is a muscular organ, stretches perfectly, and there is enough space in it for a comfortable position for your baby.
The saddle uterus does not require either surgical or hormonal treatment. If you have certain difficulties conceiving and you have a saddle uterus, contact a fertility specialist; another cause of infertility will probably be diagnosed.
Bicornuate uterus
A bicornuate uterus is a congenital malformation in which the uterus has an irregular shape, that is, it is divided into two, so-called “horns,” two separate cavities, which converge into one in the lower part. The size and location of the 2 cavities relative to each other may be different. In some cases, one of the uterine cavities may be underdeveloped and rudimentary.
A bicornuate uterus forms when the Müllerian ducts completely merge at the level of the fundus of the uterus.
The most important step is to distinguish a bicornuate uterus from a septate uterus. Doctors are challenged to make an accurate diagnosis as their treatment strategies and reproductive outcomes vary markedly.
Normal uterus
Bicornuate uterus
Is pregnancy possible with a bicornuate uterus?
With a bicornuate uterus, reproductive function is preserved. The embryo finds a suitable place for attachment in one of the horns of the uterus and begins to fully grow and develop. However, there is an increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage and premature birth, so the doctor must take this feature into account.
A bicornuate uterus rarely requires surgical reconstruction. In case of infertility, habitual pregnancy losses, or when one uterine cavity is rudimentary, and it is a site of accumulation of infection, poor outflow of menstrual blood, leading to severe pain during menstruation, and to prevent pregnancy in the rudimentary uterine horn, surgical correction methods are indicated.
Uterus with septum (intrauterine septum)
A uterus with a septum is the result of incomplete resorption of the middle septum after complete and correct fusion of the Müllerian ducts. Externally, the uterus looks normal, but inside there is an intrauterine septum, consisting of non-elastic tissue with poor blood supply.
There are numerous variations of the septum:
complete (completely divides the uterine cavity into two halves)
and partial (divided in the upper third of the uterine cavity)
Sometimes this deficiency can be combined with a septum in the vagina, which leads to discomfort and pain during sexual activity.
There is evidence that the endometrium, which covers the septum, is abnormal, cannot provide a reliable site for implantation, and has a reduced blood supply that is insufficient to support the development of the placenta and the growth of the baby.
Uterus with septum
Is pregnancy possible with a uterus with a septum?
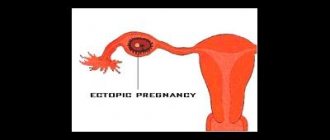
Fertility in patients with a uterine septum may be affected. Pregnancy is possible, but this feature is associated with a high risk of spontaneous miscarriage, premature birth, and ectopic pregnancy compared to other disorders of uterine development.
In order to increase the capacity of the uterus, hysteroscopic removal of the septum is performed. This approach is a safe and effective method of achieving normal or near-normal uterine architecture. Hormone therapy with drugs containing estrogen is also prescribed for 3 months to restore normal endometrium at the site of septum removal. After 3-6 months you can plan a pregnancy.
Duplication of the uterus
Complete duplication of the uterus and cervix
Duplication of the uterus is a disorder that results in the formation of two separate uteruses. Occurs when the two Müllerian ducts do not fuse to form one uterus, and as a result, two uteruses begin to develop from each duct. Such a defect is usually limited to two bodies of the uterus (one fallopian tube departs from each) and a duplication of the cervix. In addition, doubling of the vagina, bladder, urethra, anus and vulva sometimes occurs.
Is pregnancy possible with a double uterus?
In women with a double uterus, reproductive function is usually preserved. Endometrial disorders are diagnosed quite often. Pregnancy is possible. When this anomaly is combined with a vaginal membrane, pain may occur during sexual activity, then there is a need for surgical correction.
Complete duplication of the uterus
Unicornuate uterus
A unicornuate uterus, a rare developmental disorder of the uterus, is a uterus with a single angle from which one fallopian tube arises. For a better understanding, this is “half” of the uterus.
Forms when one Müllerian duct is completely absent while the other develops normally. The anomaly may be accompanied by the absence of an ovary and a kidney on the opposite side.
Unicornuate uterus
Women with a unicornuate uterus have an increased risk of endometriosis, infertility, premature birth, abnormal fetal position, and labor disturbances. Therefore, pregnancy management in such patients requires close attention from an obstetrician-gynecologist and monitoring of the cervix to prevent premature birth.
Each developmental anomaly in a particular woman requires an individual approach, based on clinical manifestations, the ability to conceive and bear a healthy baby. Each of us is unique and has every right to become a mother.
Our goal is to help you have healthy sexual relationships and achieve successful reproductive results.
4.Treatment
The decision on the need, plan and extent of surgical intervention (obviously, drug treatment in this case is absurd) is made on the basis of the clinical picture and a number of individual characteristics of a particular case. Of greatest importance is the volume of the single uterine cavity (excluding bifurcated “horns”), as well as the history of pregnancy, childbirth, artificial and spontaneous abortions. In some cases, surgical correction is indicated, in others it is recommended to resort to in vitro fertilization or surrogacy, in others the anomaly has virtually no effect on fertility and reproductive function, i.e. It is quite advisable to limit ourselves to observation tactics.
Sign up for a consultation
Symptoms
There are no symptoms of pathology. Typical symptoms appear during pregnancy. These include:
- increased tone;
- soreness;
- bleeding;
- spontaneous miscarriage/placental abruption;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- weak labor activity.
Important! A breech presentation of the fetus is often diagnosed, requiring a cesarean section.