Symptoms and treatment of allergic bronchitis in adults
Allergic bronchitis in adults and children develops as a result of contact with an allergen, which, once in the body, provokes an inadequate immune response of the defense system. Under the influence of an irritating factor, nerve endings are excited, blood tissues expand, muscles contract, which is accompanied by a strong, dry cough, profuse lacrimation, and a disturbance in general well-being.
In order for the treatment of allergic bronchitis in children and adults to be effective and the disease not to recur, it is first necessary to determine the source of the irritation. To do this, you need to consult an allergist who, based on the results of a comprehensive diagnostic examination, will identify the allergen, prescribe treatment and a special diet. It will not be possible to completely get rid of the disease, therefore, in the presence of predisposing factors, bronchitis of an allergic nature will worsen.
Causes
The cause is various allergens:
- Household dust. It contains microscopic mites and their metabolic products, particles of the chitinous shell, which have a pronounced allergenic effect.
- Pollen. In adults, plant pollen is the leading allergen.
- Epidermis and animal fur.
- Cigarette smoke.
- Animal poison.
- Food. Food allergies in childhood increase the risk of allergic cough.
- Perfumes and cosmetics.
- Household chemicals.
- Smoke.
- Latex.
- Inhalation medications.
Provoking factors may be:
- Smoking.
- Stress.
- Unfavorable production conditions.
- Unfavorable environment.
- Hormonal changes.
- Poor nutrition.
- Genetic predisposition.
Predisposing factors
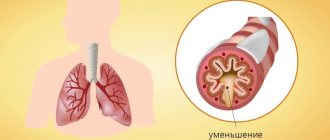
Allergic bronchitis, the symptoms of which in adults and children are almost identical, usually proceeds according to a certain pattern. Penetration of a foreign allergen protein into the body provokes an inadequate immune response, which is manifested by profuse lacrimation, sneezing, and coughing. If the irritant is not promptly eliminated and the symptoms progress, reserve protection is activated, accompanied by hyperspasm of the bronchial tree and swelling of the ciliated mucosa that lines the internal respiratory organs.
As a result of constant irritation, the lung tissue begins to produce thick mucus, which gradually accumulates in the alveoli and becomes a source of bacterial infection. Stagnation and infection of mucus in the bronchi is the main cause of allergic bronchitis.
If a person has a strong immune system and good health, infection of bronchial tissues rarely occurs. The defense system quickly destroys the infection, preventing it from actively multiplying and spreading to healthy structures. But if the immune system is weakened and a person is prone to allergies, then under the influence of predisposing factors the risk of developing allergic bronchitis increases significantly.
Reasons that provoke the development of bronchitis of an allergic nature:
- abuse of bad habits;
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- unbalanced diet;
- passive smoking;
- living in an unfavorable environmental environment;
- uncontrolled use of drugs;
- lack of competent treatment for allergic diseases;
- inactive lifestyle;
- use of bedding with natural fillings: down, feathers;
- work with industrial hazards, involving constant contact with chemical or organic substances.
For a long time, the immune system can suppress a foreign irritant that regularly penetrates the body, so a person will not suspect a tendency to allergies. But at a certain point, all the predisposing factors converge at one point, as a result of which a serious disease begins to progress sharply, the consequences of which sometimes have to be fought throughout life.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Allergic bronchitis causes acute symptoms in adults, so it is better not to self-medicate and visit a doctor as soon as possible. After contact with an allergenic irritant, the following clinical picture develops:
- Dry, unproductive cough. As a result of irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane, a person suffers from a barking, scratchy, unproductive cough. Sputum does not come out well, sometimes there is none at all. The patient cannot cough well and feels discomfort in the chest. A dry cough can get worse at night, preventing a person from getting a good night's sleep and rest.
- Expiratory dyspnea. In the initial stages of development of bronchitis of an allergic nature, shortness of breath does not bother you. However, as mucus accumulates in the bronchi, breathing problems appear. The patient cannot take a full breath and complains of pain in the chest.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane. An allergen, having entered the body through the respiratory system, first of all causes irritation of the mucous membrane. Therefore, in addition to a dry cough, a person may be bothered by excessive lacrimation, runny nose, swelling of the nasopharynx, and allergic conjunctivitis.
Prolonged coughing attacks and breathing problems cause the development of non-specific symptoms:
- weakness, lethargy;
- headaches, dizziness;
- sore throat, hoarse voice.
On average, the exacerbation period lasts 3–4 days. After this, acute symptoms gradually disappear, and the disease goes into remission. Allergic bronchitis, which is not treated or treated incorrectly, can lead to the development of severe complications, such as:
- pneumonia;
- bronchial asthma;
- damage to the walls of the bronchi;
- pulmonary emphysema;
- respiratory, heart failure;
- embolism;
- pneumosclerosis.
Diet
Hypoallergenic diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21-40 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1300-1400 rubles. in Week
With food allergies, patients must strictly adhere to a hypoallergenic diet . However, for other allergic diseases, highly allergenic foods must be excluded from the diet. The diet should be complete in terms of protein (110-120 g), fat (120 g) and carbohydrates (200 g). The diet should be rich in vitamins, so it is important to diversify the diet with permitted fruits, berries, vegetables and their juices. You should limit salt, salty foods (marinades, pickles, sausage, dried fish, cheese) and smoked foods, which increase allergic manifestations.
Products that often cause allergies are excluded:
- citrus;
- nuts;
- Fish and seafood;
- eggs;
- smoked meats;
- mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard;
- tomatoes;
- mushrooms;
- eggplant;
- Strawberry wild-strawberry;
- pineapple, melon;
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- honey.
Limit the consumption of confectionery and sugar.
Patients' diets may include:
- rabbit, veal, beef;
- cereal and vegetable soups, cabbage soup, beetroot soup;
- vegetable oil and butter;
- plums, prunes, cherries, pears, watermelon, gooseberries, cranberries, blueberries, green apples;
- potatoes, all types of cabbage, zucchini, beets, dill, parsley, onions, pumpkin, seasonal cucumbers;
- dairy products;
- buckwheat, rice and oatmeal porridge;
- black and white bread, lean dry bread, homemade pies without eggs.
At President-Med clinics you can
- undergo examination and treatment in more than 30 medical specialties, rehabilitation after strokes, surgeries, injuries,
- pass various types of tests (more than 5,000 types of tests and laboratory tests),
- undergo functional diagnostics (ultrasound, endoscopy: gastroscopy), ECG, installation and interpretation of ABPM and Holter ECG and others,
- pass a medical examination in one day, undergo a medical examination (for both organizations and individuals), undergo a medical examination (for both organizations and individuals),
- obtain all kinds of certificates - certificates from the traffic police and for admission to sports, to purchase weapons, to a sanatorium,
- if there is evidence, issue a certificate of temporary incapacity for work,
- draw up and receive other types of medical documentation,
- make any injections,
- use the services of one-day surgery or day hospital.
Treatment of allergic bronchitis
Allergic bronchitis symptoms and treatment in adults is carried out after a comprehensive diagnostic examination. The diagnosis is made on the basis of an initial examination of the patient, a detailed study of the medical history, and laboratory and instrumental diagnostic examinations.
To identify the inflammatory process in the bronchi, the doctor gives directions for the following procedures:
- general blood analysis;
- bacteriological culture of sputum;
- chest x-ray;
- spirometry.
It is also important to identify the allergen, because without eliminating it, drug treatment will not bring the desired results and upon subsequent contact with the irritant, the disease will recur.
To identify the pathogen, the following procedures are prescribed:
- allergy tests;
- blood test for immunoglobulins;
- immunoblotting.
A person prone to allergic reactions must exclude from life all factors that provoke an acute immune response:
- dust;
- animals;
- clothes made from natural wool;
- bedding with fillings such as down and feathers;
- some products, for example, honey, citrus fruits, chocolate, etc.;
- aggressive hygiene and washing products;
- some medicines.
If the allergen is no longer present in a person's life, the risk of recurrence of allergic bronchitis will be minimized. To prevent exacerbations, it is important to follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- give up bad habits such as alcohol, cigarettes;
- improve nutrition;
- give preference to active pastime to a sedentary lifestyle;
- undergo sanatorium-resort treatment once a year;
- eliminate the stress factor.
To relieve the pathological symptoms of bronchitis of an allergic nature, certain groups of medications are prescribed:
- Antihistamines. They block the histamine receptor, stopping the acute immune response to a foreign protein.
- Expectorants, mucolytics. The drugs dilute the secretion and accelerate its removal from the bronchi. Mucoltics are used to thin the cough, and after the cough becomes productive, the doctor prescribes expectorants. There are new generation medications that combine the effects of mucolytics and expectorants.
- Glucocorticoids. They are prescribed only in exceptional situations when attacks of allergic bronchitis cannot be controlled with the above medications. Drugs in this group have anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects, help relieve swelling, and reduce vascular permeability. The course of therapy and dose are determined by the doctor individually. Including glucocorticosteroids into your treatment regimen on your own is fraught with negative consequences and complications.
- Sedatives. Some patients who have experienced attacks of allergic bronchitis are terrified of their recurrence. They are worried about the fear of death from suffocation, panic attacks at the slightest breathing problems. To make you feel better and reduce psycho-emotional stress, the doctor will prescribe sedatives.
In order for drug therapy to give the most positive effect, it is recommended to additionally follow simple measures to prevent the disease:
- change bed linen daily and do wet cleaning of the room;
- try to completely eliminate contact with allergens, including aggressive hygiene products, powders, and detergents;
- ventilate the room several times a day;
- remove objects that collect dust from the room: carpets, upholstered furniture and toys, books, curtains;
- try not to contact pets.
A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and eliminating irritating factors will help avoid exacerbation of allergies, the development of allergic bronchitis and its complications.
Make an appointment with a doctor
Pathogenesis
An allergic cough develops when an allergen enters the respiratory tract, and in response to this, class E immunoglobulins are produced. Basophils, eosinophils and mast cells are of great importance in the development of respiratory allergosis. They are the components of the inflammatory reaction in the bronchi. During allergic reactions, histamine is produced in high concentrations. This powerful mediator causes a wide range of effects: increased vascular permeability, contraction of smooth muscles, itching. The biochemical interaction of histamine with immunoglobulin E proceeds as an avalanche-like chain reaction, so an allergic reaction quickly appears and develops with great speed.
The mucous membrane of the bronchial tree is characterized by pronounced edema, while mucus secretion is disrupted and sputum transport worsens.
There are three phases in the pathogenesis of immune inflammation.
- Immunological . It is associated with the interaction of the allergen with macrophages - this produces specific antibodies. B lymphocytes synthesize IgE, which circulates in the blood and is deposited on mast cells and smooth muscles.
- Pathochemical reaction . At this stage, the leading role is given to mast cells (basophils). histamine and tryptase are released 20 minutes after interaction with the allergen during degranulation . After 2-5 hours, second-order mediators ( thromboxanes , leukotrienes , prostaglandins ) are released.
- Pathophysiological phase . During this phase, under the influence of inflammatory mediators, the bronchi are damaged - capillary permeability increases, cellular infiltrates are formed and edema develops. At this stage there are already clinical manifestations, which is associated with increased bronchial reactivity and narrowness of the airways (the obstructive component increases).
Cost of treatment for allergic bronchitis
The cost of treatment for allergic bronchitis for each patient is calculated individually, taking into account factors such as:
- degree of neglect of the pathology;
- presence of associated complications
- duration of therapy, etc.
It's cheaper with us
- Beneficial programs for annual placement, pregnancy management, medical examination and “check-up” with discounts from the price list to 25%
- Discounts for disabled people, veterans, pensioners 10%
- Discount on deposit program up to 25%
- Discounts on promotions and seasonal offers up to 50%