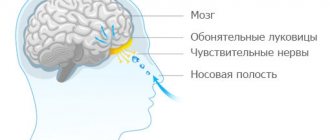
"Lindinet 20" is a combination drug produced in the form of tablets. It has a contraceptive effect and is used for planned, regular contraception. The composition includes gestodene and ethinyl estradiol, which in combination provide reliable contraceptive action. The drug inhibits the pituitary secretion of gonadotropins due to the action of estrogen-gestagens. The components of the drug prevent the maturation of the egg and prevent it from being fertilized. What else is included in Lindinet 20? Reviews will be presented below.
Ethinyl estradiol
Ethinyl estradiol is a highly effective component belonging to the group of estrogens. It is produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries and has an estrogenic effect. In combination with progesterone, ethinyl estradiol regulates the menstrual cycle, provokes the reproduction and division of endometrial cells and has a stimulating effect on the development of secondary sexual characteristics and the uterus in case of their insufficiency. In addition, this type of hormone can mitigate or completely eliminate complications due to dysfunction of the gonads and lower cholesterol levels in the blood. This is confirmed by the instructions for use for Lindinet 20 and 30. Many people are interested in analogues.
Gestoden
The second active component of the drug is gestodene. This is a synthetic progestin that is similar in structure to levonorgestrel, but is superior in selectivity and potency. It inhibits the pituitary synthesis of luteotropin and follitropin, thereby blocking ovulation.
In addition to effects such as blocking egg fertilization, the contraceptive effect is due to a decrease in the sensitivity of the uterine endometrium to the blastocyst and an increase in the viscous properties of the mucus in the cervix, which creates an obstacle to the passage of sperm through it. Regular use of Lindinet 20 over a certain period of time, according to reviews from gynecologists, helps regulate the menstrual cycle and reduces the risk of pathologies of the woman’s reproductive organs, including neoplasms.
The drug should be prescribed by a doctor based on the collected medical history and taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated for use in patients with the following manifestations:
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug or hormones in a certain combination.
- Tendency or presence of factors that can lead to venous thrombosis.
- Ischemia as a precursor to thrombosis.
- Irregular hypertension.
- Damage to arteries and veins by thrombosis and thromboembolism.
- Frequent migraines associated with neurotic disorders.
- Surgery and, as a consequence, prolonged lack of physical activity.
- Blockage of veins in close relatives (thromboembolism).
- Dyslipidemic syndrome.
- Diabetic angiopathy (as a consequence of diabetes mellitus).
- Severe liver damage.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Neoplasms in the liver.
- Pigmentary hepatosis (only some forms).
- Yellowness of the skin as a result of taking steroid drugs.
- Otospongiosis, severe itching.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Pathological inflammatory processes in the pancreas with increased triglycerides in the blood.
- Smoking, especially over the age of 35.
- Tumors of the mammary glands and organs of the female reproductive system.
- Lactation.
- Pregnancy.
How to take Lindinet 20? Reviews confirm that this should be done only after consultation with a specialist.
Lindynette 20
If any of the conditions, diseases or risk factors listed below currently exist, the potential risks and expected benefits of using COCs, including the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol, should be carefully weighed in each individual case and discussed with the woman before starting taking the drug. If any of these conditions, diseases or risk factors worsen, intensify or appear for the first time, a woman should consult her doctor to decide whether to stop taking the drug.
Risk of developing VTE and ATE
The results of epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between the use of COCs and an increased incidence of venous and arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism (such as DVT, PE, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorders). These diseases are rare.
The increased risk of developing VTE associated with the use of COCs is due to the presence of estrogen in its composition. COCs containing levonorgestrel, norgestimate or norethisterone as a progestogen component are associated with the lowest risk of VTE. When using other COCs, such as the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol, the risk of developing VTE is twice as high.
The choice of a COC with a higher risk of VTE should only be made after consultation with the woman to ensure that she fully understands the risk of VTE associated with the contraceptive, the effect of the drug on her existing risk factors and that the risk of developing VTE maximum in the first year of taking such drugs.
An increased risk is also observed when the use of COCs is resumed (after a break between doses of the drug of 4 weeks or more). The increased risk of developing VTE is present primarily during the first 3 months.
VTE can be life-threatening or lead to death (in 1-2% of cases). VTE, manifested as DVT and/or PE, can occur with all COCs.
It is extremely rare when using COCs that thrombosis of other blood vessels occurs, for example, hepatic, mesenteric, renal, cerebral veins and arteries or retinal vessels.
Symptoms of DVT:
unilateral swelling of the lower limb or along the vein, pain or discomfort only in an upright position or when walking, local increase in temperature, redness or discoloration of the skin in the affected lower limb.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
: difficulty or rapid breathing; sudden cough, including with hemoptysis; sharp pain in the chest, which may intensify with deep inspiration; sense of anxiety; severe dizziness; fast or irregular heartbeat. Some of these symptoms (eg, shortness of breath, cough) are nonspecific and may be misinterpreted as signs of other more common and less severe complications (eg, respiratory tract infection).
ATE can lead to stroke, vascular occlusion, or myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of a stroke
: sudden weakness or loss of sensation in the face, limbs, especially on one side of the body, sudden confusion, severe or prolonged headache for no apparent reason, one- or two-sided loss of vision; problems with speech and understanding; sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination; sudden loss of consciousness or fainting with or without a seizure.
Other signs of vascular occlusion:
sudden pain, swelling and slight cyanosis of the extremities, “acute” abdomen.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction:
pain, discomfort, pressure, heaviness, a feeling of compression or fullness in the chest or behind the sternum, radiating to the back, jaw, upper limb, epigastric region; cold sweat, nausea, vomiting or dizziness, severe weakness, anxiety or shortness of breath; fast or irregular heartbeat. ATE can be life-threatening and lead to death.
In women with a combination of several risk factors or high severity of one of the factors, the possibility of their mutual reinforcement should be considered. In such cases, the degree of increase in risk may be higher than with a simple summation of factors. In this case, taking the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol is contraindicated.
The risk of developing thrombosis (venous and/or arterial) and thromboembolism or cerebrovascular disorders increases:
-with age;
- in women who smoke (with an increase in the number of cigarettes or an increase in age, the risk increases, especially over the age of 35);
- if there is a family history (for example, VTE or ATE in close relatives or parents aged less than 50 years). In the case of a hereditary or acquired predisposition, the woman should be examined by an appropriate specialist to decide on the possibility of taking COCs;
- for obesity (with a BMI more than 30 kg/m2);
- with dyslipoproteinemia;
- for arterial hypertension;
- for migraine;
- for diseases of the heart valves;
- with atrial fibrillation;
- in case of prolonged immobilization, serious surgery, any operation on the lower extremities, in the pelvic area or extensive trauma. In these cases, the use of COCs should be stopped (in the case of planned surgery, at least four weeks before it) and not resumed for two weeks after the woman has fully regained mobility.
Temporary immobilization (eg, air travel lasting more than 4 hours) may also be a risk factor for the development of VTE, especially in the presence of other risk factors.
The possible role of varicose veins and superficial thrombophlebitis in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The increased risk of thromboembolism in the postpartum period should be taken into account. Peripheral circulatory disorders may also occur in diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemolytic uremic syndrome, chronic inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis) and sickle cell anemia.
An increase in the frequency and severity of migraine (which may precede cerebrovascular events) during the use of COCs is grounds for immediate discontinuation of these drugs.
Biochemical indicators indicating a hereditary or acquired predisposition to the development of venous or arterial thrombosis include: resistance to activated protein C, hyperhomocysteinemia, antithrombin III deficiency, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies (anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant).
When assessing the risk-benefit ratio, it should be borne in mind that adequate treatment of the relevant condition/disease can reduce the associated risk of thrombosis.
Tumors
The most significant risk factor for the development of cervical cancer (CC) is persistent human papillomavirus infection. There are reports of a slight increase in the risk of developing CC with long-term use of COCs. However, the connection with taking COCs has not been proven. Controversy remains regarding the extent to which these findings are related to screening for cervical pathology or to sexual behavior patterns (less use of barrier methods of contraception, greater number of sexual partners).
A meta-analysis of 54 epidemiological studies showed that there is a slightly increased relative risk of developing breast cancer diagnosed in women currently taking COCs (relative risk 1.24). The increased risk gradually disappears within 10 years of stopping these drugs. Due to the fact that breast cancer is rare in women under 40 years of age, the increase in the incidence of breast cancer in women who are currently or recently taking COCs is insignificant in relation to the overall risk of this disease. Its connection with COC use has not been proven. The observed increase in risk may also be a consequence of earlier diagnosis of breast cancer in women using COCs (they are diagnosed with earlier clinical forms of breast cancer than women not taking COCs), the biological effects of COCs, or a combination of both of these factors.
In rare cases, during the use of COCs, the development of benign, and in extremely rare cases, malignant liver tumors, which in some cases led to life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding, was observed. In case of severe abdominal pain, liver enlargement or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, this should be taken into account when making a differential diagnosis.
Other states
Depressed mood and depression are known adverse reactions when using hormonal contraceptives. Depression can be a serious disorder and is a known risk factor for suicidal behavior and suicide. Women should be advised to contact their doctor if mood changes or depressive symptoms occur, including soon after starting treatment.
In women with hypertriglyceridemia (or a family history of this condition), the risk of developing pancreatitis may increase while taking COCs.
Although slight increases in blood pressure have been described in many women taking COCs, clinically significant increases have rarely been reported. However, if a persistent clinically significant increase in blood pressure develops while taking a COC, the COC should be discontinued and treatment of arterial hypertension should be initiated. COC use can be continued if normal blood pressure values are achieved with antihypertensive therapy.
The following conditions have been reported to develop or worsen both during pregnancy and while taking COCs, but their relationship with COC use has not been proven: cholestatic jaundice and/or pruritus associated with cholestasis; formation of gallstones; porphyria; systemic lupus erythematosus; hemolytic-uremic syndrome; chorea; herpes during pregnancy; hearing loss associated with otosclerosis. Cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have also been described with the use of COCs.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Acute or chronic liver dysfunction may require discontinuation of COCs until liver function tests return to normal. Recurrence of cholestatic jaundice, which developed for the first time during a previous pregnancy or previous use of sex hormones, requires discontinuation of COC use.
Although COCs may have an effect on insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, in patients with diabetes mellitus using low-dose COCs, as a rule, no dose adjustment of hypoglycemic drugs is required. However, women with diabetes mellitus should be carefully monitored while taking COCs.
Chloasma can sometimes develop, especially in women with a history of pregnancy chloasma. Women with a tendency to chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and exposure to ultraviolet radiation while taking COCs.
Effect on liver function tests
In clinical studies involving patients receiving hepatitis C viral therapy (a combination of drugs containing ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, dasabuvir, with or without ribavirin), increases in ALT activity more than 5 times the upper limit of normal were recorded more often in patients using COCs containing ethinyl estradiol.
If a course of therapy with this combination of drugs is necessary, a patient using the contraceptive drug gestodene + ethinyl estradiol should be switched to alternative methods of contraception (non-hormonal or contraceptives containing only gestagen) before starting the course of treatment. You can resume taking the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol no earlier than 2 weeks after the end of the course of therapy with antiviral drugs.
Laboratory tests
The use of drugs such as gestodene + ethinyl estradiol may affect the results of some laboratory tests, including biochemical indicators of liver, thyroid, kidney and adrenal function, the concentration of transport proteins in plasma (for example, transcortin, lipid / lipoprotein fractions, parameters of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis). These changes usually remain within normal physiological values.
Reduced efficiency
The effectiveness of COCs may be reduced in the following cases: in case of missed pills, gastrointestinal disorders or as a result of drug interactions.
Effect on bleeding pattern
While taking COCs, irregular bleeding may occur (“spotting” and/or “breakthrough” bleeding), especially during the first months of use. Therefore, any irregular bleeding should be assessed only after an adaptation period of approximately 3 cycles of dosing.
If irregular bleeding recurs or develops after previous regular cycles, careful evaluation should be performed to rule out malignancy or pregnancy.
Some women may not develop bleeding during a break in taking pills. “ooContraindications” and “With caution.”
-Local compaction in the mammary gland.
-Concomitant use of other medications.
-If prolonged immobilization is expected (for example, a cast is applied to the lower extremity), hospitalization or surgery is planned (at least four weeks before the proposed operation).
-Unusually heavy bleeding from the vagina;
-Missed a pill in the first week of taking the drug and had sexual intercourse seven days or less before.
- Absence of regular menstrual-like bleeding two times in a row or suspicion of pregnancy (you should not start taking pills from the next package before consulting your doctor).
You should stop taking the tablets and consult your doctor immediately if there are possible signs of thrombosis, myocardial infarction or stroke: unusual cough; unusually severe pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm; unexpected shortness of breath, unusual, severe and prolonged headache or migraine attack; partial or complete loss of vision or double vision; slurred speech; sudden changes in hearing, smell, or taste; dizziness or fainting; weakness or loss of sensation in any part of the body; severe abdominal pain; severe pain in the lower limb or sudden swelling of any of the lower limbs.
This medicine contains lactose (in the form of lactose monohydrate) and sucrose. Patients with rare hereditary diseases such as galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, as well as rare congenital forms of fructose intolerance or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency should not take this drug.
Careful reception
You should take the drug with caution in the following situations:
- Development of azotemia, thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia (hemolytic uremic syndrome).
- Liver diseases.
- Quincke's edema caused by a genetic factor.
- Conditions that increase the risk of thromboembolic or thrombotic damage to the arteries and veins, such as age over 35, family history, or smoking.
- Diseases that appeared during pregnancy, as well as while taking other hormonal drugs: chloasma, herpes, porphyria, rheumatic chorea.
- Obesity.
- Hypertension.
- Migraines of a regular nature.
- Dislipoproteinemic syndrome.
- Cramps.
- Heart valve dysfunction.
- A state of prolonged immobility.
- Severe injuries.
- Extensive operations.
- Atrial fibrillation.
What other restrictions do the instructions for use indicate for Lindinet 20?
- Superficial vein thrombophlebitis and varicose veins.
- Postpartum period.
- Depression.
- Biochemical changes in blood composition.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (Libman-Sachs disease).
- Diabetes mellitus that does not affect blood vessels.
- Granulomatous enteritis.
- Liver diseases in acute and chronic form.
- Anemia (sickle cell).
- Inflammatory processes in the colon against the background of ulcers.
- Elevated levels of triglycerides (glycerol-based lipids) in the blood.
Lindinet 20 No. 21 tab.
LINDYNETTE 20
ATX code: G03AA10 (Gestodene and estrogen)
Active substances
ethinylestradiol (ethinylestradiol) Rec.INN registered by WHO gestodene (gestodene) Rec.INN registered by WHO
Dosage form
The drug is dispensed with a prescription LINDINET 20 tablets, coated. coated, 20 mcg+75 mcg: 21 or 63 pcs. reg. No.: P N015122/01 dated 10.31.08 - Indefinitely
Release form, composition and packaging
Light yellow film-coated tablets, round, biconvex, unprinted on both sides; on the fracture it is white or almost white with a light yellow edging.
1 tab. ethinylestradiol 20 mcg gestodene 75 mcg
Excipients: sodium calcium edetate - 0.065 mg, magnesium stearate - 0.2 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 0.275 mg, povidone - 1.7 mg, corn starch - 15.5 mg, lactose monohydrate - 37.165 mg.
Shell composition: quinoline yellow dye (D+S yellow No. 10) (E104) - 0.00135 mg, povidone - 0.171 mg, titanium dioxide - 0.46465 mg, macrogol 6000 - 2.23 mg, talc - 4.242 mg, calcium carbonate - 8.231 mg, sucrose - 19.66 mg.
21 pcs. - blisters (1) - cardboard packs. 21 pcs. - blisters (3) - cardboard packs.
Clinical and pharmacological group: Monophasic oral contraceptive.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Contraceptive (estrogen + progestogen).
pharmachologic effect
Monophasic oral contraceptive. Inhibits the secretion of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland. The contraceptive effect of the drug is associated with several mechanisms. The estrogenic component of the drug is ethinyl estradiol, a synthetic analogue of the follicular hormone estradiol, which participates together with the corpus luteum hormone in the regulation of the menstrual cycle. The gestagenic component is gestodene, a derivative of 19-nortestosterone, which is superior in strength and selectivity to not only the natural corpus luteum hormone progesterone, but also other synthetic gestagens (for example, levonorgestrel). Due to its high activity, gestodene is used in low dosages, in which it does not exhibit androgenic properties and has virtually no effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Along with the indicated central and peripheral mechanisms that prevent the maturation of an egg capable of fertilization, the contraceptive effect is due to a decrease in the susceptibility of the endometrium to the blastocyst, as well as an increase in the viscosity of the mucus located in the cervix, which makes it relatively impenetrable for sperm. In addition to the contraceptive effect, the drug, when taken regularly, also has a therapeutic effect, normalizing the menstrual cycle and helping to prevent the development of a number of gynecological diseases, incl. tumor nature.
Pharmacokinetics
Gestoden
Suction
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After a single dose, Cmax is observed after 1 hour and is 2-4 ng/ml. Bioavailability is about 99%.
Distribution
Gestodene binds to albumin and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). 1-2% is found in plasma in free form, 50-75% specifically binds to SHBG. An increase in the level of SHBG in the blood caused by ethinyl estradiol affects the level of gestodene: the fraction associated with SHBG increases and the fraction associated with albumin decreases. Average Vd - 0.7-1.4 l/kg. The pharmacokinetics of gestodene depends on the level of SHBG. The concentration of SHBG in blood plasma under the influence of estradiol increases 3 times. When taken daily, the concentration of gestodene in the blood plasma increases 3-4 times and in the second half of the cycle reaches a state of saturation.
Metabolism and excretion
Gestodene is biotransformed in the liver. The average plasma clearance is 0.8-1 ml/min/kg. The level of gestodene in the blood serum decreases in two phases. T1/2 in the ?-phase is 12-20 hours. Gestodene is excreted only in the form of metabolites, 60% in urine, 40% in feces. T1/2 of metabolites - about 1 day.
Ethinyl estradiol
Suction
After oral administration, ethinyl estradiol is absorbed quickly and almost completely. The average Cmax in the blood serum is reached 1-2 hours after administration and is 30-80 pg/ml. Absolute bioavailability due to presystemic conjugation and primary metabolism is about 60%.
Distribution
Completely (about 98.5%), but nonspecifically binds to albumin and induces an increase in the level of SHBG in the blood serum. Average Vd - 5-18 l/kg.
Css is established by the 3-4th day of taking the drug, and it is 20% higher than after a single dose.
Metabolism
It undergoes aromatic hydroxylation to form hydroxylated and methylated metabolites, which are present in the form of free metabolites or in the form of conjugates (glucuronides and sulfates). Metabolic clearance from blood plasma is about 5-13 ml.
Removal
Serum concentration decreases in two phases. T1/2 in the ?-phase is about 16-24 hours. Ethinyl estradiol is excreted only in the form of metabolites, in a 2:3 ratio with urine and bile. T1/2 of metabolites - about 1 day.
Indications for use
- contraception.
ICD-10 codes
Dosage regimen
Prescribe 1 tablet/day for 21 days, if possible at the same time of day. After taking the last tablet from the package, take a 7-day break, during which withdrawal bleeding occurs. The next day after a 7-day break (i.e., 4 weeks after taking the first tablet, on the same day of the week), the drug is resumed.
The first tablet of Lindinet 20 should be taken from the 1st to the 5th day of the menstrual cycle.
When switching to Lindinet 20 from another combined oral contraceptive, the first Lindinet 20 tablet should be taken after taking the last tablet from the package of another oral hormonal contraceptive, on the first day of withdrawal bleeding.
When switching to taking Lindinet 20 from drugs containing only gestagen (“mini-pill”, injections, implant), when taking a “mini-pill”, taking Lindinet 20 can be started on any day of the cycle, switching from using the implant to taking Lindinet 20 is possible the day after removal of the implant, when using injections - on the eve of the last injection. In these cases, additional methods of contraception should be used in the first 7 days.
After an abortion in the first trimester of pregnancy, you can start taking Lindinet 20 immediately after surgery. In this case, there is no need to use additional methods of contraception.
After childbirth or after an abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy, taking the drug can be started on days 21-28. In these cases, additional methods of contraception must be used in the first 7 days. If you start taking the drug later, an additional barrier method of contraception should be used in the first 7 days. If sexual intercourse took place before starting contraception, pregnancy should be ruled out before starting the drug or the start of use should be delayed until the first menstruation.
If you miss a pill, take the missed pill as quickly as possible. If the interval in taking the pills is less than 12 hours, then the contraceptive effect of the drug is not reduced, and in this case there is no need to use an additional method of contraception. The remaining tablets should be taken at the usual time. If the interval is more than 12 hours, the contraceptive effect of the drug may be reduced. In such cases, you should not make up for the missed dose, continue taking the drug as usual, but in the next 7 days you must use an additional method of contraception. If at the same time there are less than 7 tablets left in the package, taking the drug from the next package should be started without interruption. In this case, withdrawal bleeding does not occur until the end of taking the drug from the second package, but spotting or breakthrough bleeding may occur.
If withdrawal bleeding does not occur after completing the drug from the second package, then pregnancy should be excluded before continuing to take the drug.
If vomiting and/or diarrhea begins within 3-4 hours after taking the drug, the contraceptive effect may be reduced. In such cases, you should follow the instructions for skipping pills. If the patient does not want to deviate from her usual contraceptive regimen, the missed pills should be taken from another package.
To speed up the onset of menstruation, you should reduce the break in taking the drug. The shorter the break, the more likely it is that breakthrough or spotting bleeding will occur while taking tablets from the next package (similar to cases with delayed menstruation).
To delay the onset of menstruation, the drug must be continued from a new package without a 7-day break. Menstruation can be delayed as long as necessary until the end of taking the last tablet from the second pack. When menstruation is delayed, breakthrough or spotting bleeding may occur. Regular use of Lindinet 20 can be resumed after the usual 7-day break.
Side effects
Side effects requiring discontinuation of the drug
From the cardiovascular system: arterial hypertension; rarely - arterial and venous thromboembolism (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism); very rarely - arterial or venous thromboembolism of the hepatic, mesenteric, renal, retinal arteries and veins.
From the senses: hearing loss caused by otosclerosis.
Other: hemolytic-uremic syndrome, porphyria; rarely - exacerbation of reactive systemic lupus erythematosus; very rarely - Sydenham's chorea (which goes away after discontinuation of the drug).
Other side effects are more common but less severe. The advisability of continuing to use the drug is decided individually after consultation with a doctor, based on the benefit/risk ratio.
From the reproductive system: acyclic bleeding/bloody discharge from the vagina, amenorrhea after discontinuation of the drug, changes in the state of vaginal mucus, the development of inflammatory processes in the vagina, candidiasis, tension, pain, enlarged mammary glands, galactorrhea.
From the digestive system: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, the occurrence or exacerbation of jaundice and/or itching associated with cholestasis, cholelithiasis, hepatitis, liver adenoma.
Dermatological reactions: erythema nodosum, exudative erythema, rash, chloasma, increased hair loss.
From the central nervous system: headache, migraine, mood lability, depression.
From the senses: hearing loss, increased sensitivity of the cornea (when wearing contact lenses).
From the metabolic side: fluid retention in the body, change (increase) in body weight, decreased tolerance to carbohydrates, hyperglycemia, increased TG levels.
Other: allergic reactions.
Contraindications for use
- the presence of severe and/or multiple risk factors for venous or arterial thrombosis (including complicated lesions of the heart valve apparatus, atrial fibrillation, diseases of the cerebral vessels or coronary arteries, severe or moderate arterial hypertension with blood pressure 160/100 mm Hg. Art.);
- presence or indication in history of precursors of thrombosis (including transient ischemic attack, angina pectoris);
- migraine with focal neurological symptoms, incl. in the anamnesis;
- venous or arterial thrombosis/thromboembolism (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the leg, pulmonary embolism) currently or in history;
- a history of venous thromboembolism in relatives;
- surgery with prolonged immobilization;
- diabetes mellitus (with angiopathy);
- pancreatitis (including a history), accompanied by severe hypertriglyceridemia;
- dyslipidemia;
- severe liver diseases, cholestatic jaundice (including during pregnancy), hepatitis, incl. history (before normalization of functional and laboratory parameters and within 3 months after their normalization);
- jaundice when taking GCS;
- gallstone disease currently or in history;
- Gilbert's syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome;
- liver tumors (including history);
- severe itching, otosclerosis or its progression during a previous pregnancy or taking corticosteroids;
- hormone-dependent malignant neoplasms of the genital organs and mammary glands (including if they are suspected);
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- smoking over the age of 35 (more than 15 cigarettes per day);
- pregnancy or suspicion of it;
- lactation period;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in conditions that increase the risk of developing venous or arterial thrombosis/thromboembolism: age over 35 years, smoking, hereditary predisposition to thrombosis (thrombosis, myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident at a young age in one of the immediate family), hemolytic-uremic syndrome, hereditary angioedema, liver diseases, diseases that first appeared or worsened during pregnancy or against the background of previous use of sex hormones (including porphyria, herpes of pregnant women, minor chorea / Sydenham disease /, Sydenham chorea, chloasma) , obesity (BMI more than 30 kg/m2), dyslipoproteinemia, arterial hypertension, migraine, epilepsy, valvular heart disease, atrial fibrillation, prolonged immobilization, major surgery, surgery on the lower extremities, severe trauma, varicose veins and superficial thrombophlebitis, postpartum period (non-lactating women /21 days after childbirth/; lactating women after the end of the lactation period), the presence of severe depression (including a history), changes in biochemical parameters (activated protein C resistance, hyperhomocysteinemia, antithrombin III deficiency, protein C or S deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies, including . antibodies to cardiolipin, lupus anticoagulant), diabetes mellitus not complicated by vascular disorders, SLE, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, sickle cell anemia, hypertriglyceridemia (including family history), acute and chronic liver diseases.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation. The components of the drug are excreted in breast milk in small quantities. When used during lactation, milk production may decrease.
Use for liver dysfunction
Contraindicated in case of liver dysfunction.
Use for renal impairment
The drug is not recommended for use in patients with kidney disease.
special instructions
Before starting to use the drug, it is necessary to conduct a general medical examination (detailed family and personal history, blood pressure measurement, laboratory tests) and gynecological examination (including examination of the mammary glands, pelvic organs, cytological analysis of a cervical smear). Such examinations during the period of taking the drug are carried out regularly, every 6 months.
The drug is a reliable contraceptive: the Pearl index (an indicator of the number of pregnancies occurring during the use of a contraceptive method in 100 women over 1 year) when used correctly is about 0.05. Due to the fact that the contraceptive effect of the drug from the start of administration is fully manifested by the 14th day, it is recommended to additionally use non-hormonal methods of contraception in the first 2 weeks of taking the drug.
In each case, before prescribing hormonal contraceptives, the benefits or possible negative effects of their use are individually assessed. This issue must be discussed with the patient, who, after receiving the necessary information, will make the final decision on the preference for hormonal or any other method of contraception.
The woman's health condition must be carefully monitored. If any of the following conditions/diseases appear or worsen while taking the drug, you must stop taking the drug and switch to another, non-hormonal method of contraception:
- diseases of the hemostatic system;
- conditions/diseases predisposing to the development of cardiovascular and renal failure;
- epilepsy;
- migraine;
- the risk of developing an estrogen-dependent tumor or estrogen-dependent gynecological diseases;
- diabetes mellitus not complicated by vascular disorders;
- severe depression (if depression is associated with impaired tryptophan metabolism, then vitamin B6 can be used for correction);
- sickle cell anemia, because in some cases (for example, infections, hypoxia), estrogen-containing drugs for this pathology can provoke thromboembolism;
- the appearance of abnormalities in laboratory tests assessing liver function.
Thromboembolic diseases
Epidemiological studies have shown that there is a connection between taking oral hormonal contraceptives and an increased risk of developing arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism). An increased risk of venous thromboembolic diseases has been proven, but it is significantly less than during pregnancy (60 cases per 100 thousand pregnancies). When using oral contraceptives, arterial or venous thromboembolism of the hepatic, mesenteric, renal or retinal vessels is very rarely observed.
The risk of arterial or venous thromboembolic disease increases:
- with age;
- when smoking (heavy smoking and age over 35 years are risk factors);
- if there is a family history of thromboembolic diseases (for example, parents, brother or sister). If a genetic predisposition is suspected, it is necessary to consult a specialist before using the drug;
- for obesity (BMI more than 30 kg/m2);
- with dislipoproteinemia;
- with arterial hypertension;
- for diseases of the heart valves complicated by hemodynamic disorders;
- with atrial fibrillation;
- with diabetes mellitus complicated by vascular lesions;
- with prolonged immobilization, after major surgery, after surgery on the lower extremities, after severe trauma.
In these cases, it is assumed that the use of the drug should be temporarily discontinued (no later than 4 weeks before surgery, and resumed no earlier than 2 weeks after remobilization).
Women after childbirth have an increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease.
It should be taken into account that diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, sickle cell anemia increase the risk of developing venous thromboembolic diseases.
It should be taken into account that resistance to activated protein C, hyperhomocysteinemia, protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies increase the risk of developing arterial or venous thromboembolic diseases.
When assessing the benefit/risk ratio of taking the drug, it should be taken into account that targeted treatment of this condition reduces the risk of thromboembolism. Symptoms of thromboembolism are:
- sudden chest pain that radiates to the left arm;
- sudden shortness of breath;
- any unusually severe headache that continues for a long time or appears for the first time, especially when combined with sudden complete or partial loss of vision or diplopia, aphasia, dizziness, collapse, focal epilepsy, weakness or severe numbness of half the body, movement disorders, severe unilateral pain in the calf muscle, symptom complex “acute abdomen”.
Tumor diseases
Some studies have reported an increased incidence of cervical cancer in women who took hormonal contraceptives for a long time, but the results of the studies are inconsistent. Sexual behavior, infection with the human papillomavirus and other factors play a significant role in the development of cervical cancer.
A meta-analysis of 54 epidemiological studies found that there is a relative increase in the risk of breast cancer among women taking oral hormonal contraceptives, but the higher detection rate of breast cancer may have been associated with more regular medical screening. Breast cancer is rare among women under 40, whether they take hormonal birth control or not, and increases with age. Taking pills can be considered one of many risk factors. However, the woman should be made aware of the possible risk of developing breast cancer based on an assessment of the benefit-risk ratio (protection against ovarian and endometrial cancer).
There are few reports of the development of benign or malignant liver tumors in women taking hormonal contraceptives for a long time. This should be kept in mind when differentially assessing abdominal pain, which may be associated with an increase in liver size or intraperitoneal bleeding.
Chloasma
Chloasma can develop in women with a history of this disease during pregnancy. Those women who are at risk of developing chloasma should avoid contact with sunlight or ultraviolet radiation while taking Lindinet 20.
Efficiency
The effectiveness of the drug may be reduced in the following cases: missed pills, vomiting and diarrhea, simultaneous use of other drugs that reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills.
If the patient is concomitantly taking another drug that may reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills, additional methods of contraception should be used.
The effectiveness of the drug may decrease if, after several months of their use, irregular, spotting or breakthrough bleeding appears, in such cases it is advisable to continue taking the tablets until they run out in the next package. If at the end of the second cycle menstrual-like bleeding does not begin or acyclic bleeding does not stop, stop taking the pills and resume it only after pregnancy has been ruled out.
Changes in laboratory parameters
Under the influence of oral contraceptive pills, due to the estrogen component, the level of some laboratory parameters (functional indicators of the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hemostasis indicators, levels of lipoproteins and transport proteins) may change.
Additional Information
After acute viral hepatitis, the drug should be taken after normalization of liver function (no earlier than 6 months).
With diarrhea or intestinal disorders, vomiting, the contraceptive effect may be reduced. While continuing to take the drug, it is necessary to use additional non-hormonal methods of contraception.
Women who smoke have an increased risk of developing vascular diseases with serious consequences (myocardial infarction, stroke). The risk depends on age (especially in women over 35 years of age) and on the number of cigarettes smoked.
The woman should be warned that the drug does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
No studies have been conducted to study the effect of Lindinet 20 on the abilities necessary to drive a car and operate machinery.
Overdose
No severe symptoms have been described after taking the drug in high doses.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, and in girls, bleeding from the vagina.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy is prescribed; there is no specific antidote.
Drug interactions
The contraceptive activity of Lindinet 20 is reduced when taken simultaneously with ampicillin, tetracycline, rifampicin, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, griseofulvin, topiramate, felbamate, oxcarbazepine. The contraceptive effect of oral contraceptives is reduced when these combinations are used, breakthrough bleeding and menstrual irregularities become more frequent. While taking Lindinet 20 with the above drugs, as well as for 7 days after completing the course of taking them, it is necessary to use additional non-hormonal (condom, spermicidal gels) methods of contraception. When using rifampicin, additional methods of contraception should be used for 4 weeks after completion of the course of taking it.
When used simultaneously with Lindinet 20, any drug that increases gastrointestinal motility reduces the absorption of active substances and their level in the blood plasma.
Sulfation of ethinyl estradiol occurs in the intestinal wall. Drugs that are also subject to sulfation in the intestinal wall (including ascorbic acid) competitively inhibit the sulfation of ethinyl estradiol and thereby increase the bioavailability of ethinyl estradiol.
Inducers of microsomal liver enzymes reduce the level of ethinyl estradiol in the blood plasma (rifampicin, barbiturates, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, griseofulvin, topiramate, hydantoin, felbamate, rifabutin, oscarbazepine).
Liver enzyme inhibitors (itraconazole, fluconazole) increase the level of ethinyl estradiol in the blood plasma.
Some antibiotics (ampicillin, tetracycline), by interfering with the intrahepatic circulation of estrogens, reduce the level of ethinyl estradiol in plasma.
Ethinyl estradiol, by inhibiting liver enzymes or accelerating conjugation (primarily glucuronidation), can affect the metabolism of other drugs (including cyclosporine, theophylline); The concentration of these drugs in the blood plasma may increase or decrease.
When Lindinet 20 is used simultaneously with St. John's wort preparations (including infusion), the concentration of active substances in the blood decreases, which can lead to breakthrough bleeding and pregnancy. The reason for this is the inducing effect of St. John's wort on liver enzymes, which continues for another 2 weeks after completing the course of taking St. John's wort. It is not recommended to prescribe this combination of drugs.
Ritonavir reduces the AUC of ethinyl estradiol by 41%. In this regard, during the use of ritonavir, a hormonal contraceptive with a higher ethinyl estradiol content should be used or additional non-hormonal methods of contraception should be used.
It may be necessary to adjust the dosage regimen when using hypoglycemic agents, because oral contraceptives may decrease carbohydrate tolerance and increase the need for insulin or oral antidiabetic agents.
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 3 years.
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is available with a prescription.
Side effects
Contraceptive pills "Lindinet 20", according to reviews, are usually well tolerated. But there are still side effects.
The drug is completely discontinued for the following symptoms: porphyria, hypertension, hearing loss as a result of otospongiosis and hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
The following pathologies are rare: thromboembolism of the arteries and veins of the circulatory system, lower extremities, brain, lungs, as well as aggravation of lupus erythematosus (Libman-Sachs disease).
The most rare are thromboembolism of the arteries and veins of the liver, mesentery of the retina, kidneys and chorea. This is confirmed by the instructions for use and reviews for Lindinet 20.
Frequent manifestations
Common side effects include:
- From the reproductive system: absence of menstrual bleeding after discontinuation of the drug, irregular vaginal hemorrhages and discharge, decreased libido, vaginal inflammation, changes in the state of mucus.
- Discomfort, increase in size, soreness and galactorrhea of the mammary glands.
- On the part of the digestive system: diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, granulomatous enteritis, pain in the epigastric region, ulcerative inflammation in the colon, vdenomatous liver damage, hepatitis, liver dysfunction, bile stagnation and cholelithiasis.
- Allergic reactions: rashes, erythema, alopecia, increased pigmentation.
- From the central nervous system: migraines, depression, headaches and emotional lability.
- Weight gain and fluid retention, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, decreased tolerance and absorption of carbohydrate compounds by the body as a result of changes in metabolism.
- Decreased hearing function, feeling of discomfort when wearing contact lenses.
- Hypersensitivity.
There are a lot of reviews from gynecologists about Lindinet 20.
special instructions
When deciding to take an oral contraceptive, you need to take into account the following features:
1. Lactation and pregnancy are absolute contraindications for use.
2. Before prescribing medication, the doctor needs to collect comprehensive information about the health of the patient and immediate family. Twice a year you need to undergo a gynecological and medical examination to eliminate the risk of contraindications and complications.
3. Research has clearly proven the high contraceptive effectiveness of Lindinet 20, since over the course of a year of use, pregnancy occurred in 0.05 percent of cases out of 100 women.
4. The maximum contraceptive effect is achieved two weeks after starting to take the pills, so during this period there is a need to use additional non-hormonal contraceptives.
5. The drug is prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. The specialist assesses the feasibility and necessity of prescribing Lindinet 20, informing the patient about possible side effects. While taking hormonal medications, regular gynecological monitoring is necessary. This is what the instructions for Lindinet 20 describe. Reviews from gynecologists are given below.
6. There are situations when it is necessary to completely stop using hormonal contraceptives and switch to other contraceptives. Such complications include: convulsions, impaired hemostasis and, as a result, the development of problems in the circulatory system and kidneys, migraines, diabetes, depression, poor blood tests for biochemistry, anemia and a high risk of neoplasms caused by taking hormones.
7. A scientifically proven fact is the relationship between taking hormonal drugs and the development of blood clots and thromboembolism in various systems and organs.
8. The risk of thrombosis and thromboembolism is especially high with the following factors: the patient’s age over 35 years, genetic predisposition, smoking, obesity, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, heart valve pathologies, etc.
9. During the postpartum period, the risk of thromboembolism increases significantly.
10. Deviations of biochemical blood parameters from the norm increase the risk of developing thromboembolism of veins and arteries. Bringing indicators back to normal reduces the likelihood of disease. The most common symptoms of thromboembolism are: shortness of breath, pain in the chest region, radiating to the left arm, headaches, causing blurred vision, dizziness, speech disorder, epilepsy, heart failure, numbness and weakness of the body, acute abdomen, pain in the calf muscle.
11. Studies have shown that taking hormonal contraceptives increases the risk of developing cervical cancer. The same applies to the development of breast cancer.
12. Oral hormonal contraceptives do not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
13. The appearance of pain in the abdominal area during long-term use of Lindinet 20 may indicate the development of a neoplasm (benign or malignant), which may be a sign of hepatomegaly or bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
14. The effect of taking the drug may decrease due to a missed pill, diarrhea, vomiting, or improper combination with other medications.
15. When taking a contraceptive simultaneously with drugs that reduce the contraceptive effect, it is necessary to use additional methods of contraception. There are reviews of gynecologists about this. Lindinet 20 may not be able to do its job.
16. A common complication during pregnancy is chloasma. It can also occur while taking oral contraceptives. If this possibility cannot be excluded, it is necessary to exclude exposure to ultraviolet radiation and sunlight during administration.
17. Estrogens can affect the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland and adrenal glands, causing changes in test parameters.
18. After treatment of a liver affected by a virus, taking Lindinet 20 is possible only after six months.
19. The effect of the contraceptive may be reduced as a result of severe intestinal disorders and vomiting.
20. Smoking while taking the drug can cause problems with blood vessels, especially after 35 years.
Lindinet 20
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation.
The components of the drug are excreted in breast milk in small quantities.
When used during lactation, milk production may decrease.
Use for liver dysfunction
Contraindicated in case of liver dysfunction.
Use for renal impairment
The drug is not recommended for use in patients with kidney disease.
special instructions
Before starting to use the drug, it is necessary to conduct a general medical examination (detailed family and personal history, blood pressure measurement, laboratory tests) and gynecological examination (including examination of the mammary glands, pelvic organs, cytological analysis of a cervical smear). Such examinations during the period of taking the drug are carried out regularly, every 6 months.
The drug is a reliable contraceptive: the Pearl index (an indicator of the number of pregnancies occurring during the use of a contraceptive method in 100 women over 1 year) when used correctly is about 0.05. Due to the fact that the contraceptive effect of the drug from the start of administration is fully manifested by the 14th day, it is recommended to additionally use non-hormonal methods of contraception in the first 2 weeks of taking the drug.
In each case, before prescribing hormonal contraceptives, the benefits or possible negative effects of their use are individually assessed. This issue must be discussed with the patient, who, after receiving the necessary information, will make the final decision on the preference for hormonal or any other method of contraception.
The woman's health condition must be carefully monitored. If any of the following conditions/diseases appear or worsen while taking the drug, you must stop taking the drug and switch to another, non-hormonal method of contraception:
- diseases of the hemostatic system;
- conditions/diseases predisposing to the development of cardiovascular and renal failure;
- epilepsy;
- migraine;
- the risk of developing an estrogen-dependent tumor or estrogen-dependent gynecological diseases;
- diabetes mellitus not complicated by vascular disorders;
- severe depression (if depression is associated with impaired tryptophan metabolism, then vitamin B6 can be used for correction);
- sickle cell anemia, because in some cases (for example, infections, hypoxia), estrogen-containing drugs for this pathology can provoke thromboembolism;
- the appearance of abnormalities in laboratory tests assessing liver function.
Thromboembolic diseases
Epidemiological studies have shown that there is a connection between taking oral hormonal contraceptives and an increased risk of developing arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism). An increased risk of venous thromboembolic diseases has been proven, but it is significantly less than during pregnancy (60 cases per 100 thousand pregnancies). When using oral contraceptives, arterial or venous thromboembolism of the hepatic, mesenteric, renal or retinal vessels is very rarely observed.
The risk of arterial or venous thromboembolic disease increases:
- with age;
- when smoking (heavy smoking and age over 35 years are risk factors);
- if there is a family history of thromboembolic diseases (for example, parents, brother or sister). If a genetic predisposition is suspected, it is necessary to consult a specialist before using the drug;
- for obesity (BMI more than 30 kg/m2);
- with dislipoproteinemia;
- with arterial hypertension;
- for diseases of the heart valves complicated by hemodynamic disorders;
- with atrial fibrillation;
- with diabetes mellitus complicated by vascular lesions;
- with prolonged immobilization, after major surgery, after surgery on the lower extremities, after severe trauma.
In these cases, it is assumed that the use of the drug should be temporarily discontinued (no later than 4 weeks before surgery, and resumed no earlier than 2 weeks after remobilization).
Women after childbirth have an increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease.
It should be taken into account that diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, sickle cell anemia increase the risk of developing venous thromboembolic diseases.
It should be taken into account that resistance to activated protein C, hyperhomocysteinemia, protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies increase the risk of developing arterial or venous thromboembolic diseases.
When assessing the benefit/risk ratio of taking the drug, it should be taken into account that targeted treatment of this condition reduces the risk of thromboembolism. Symptoms of thromboembolism are:
- sudden chest pain that radiates to the left arm;
- sudden shortness of breath;
- any unusually severe headache that continues for a long time or appears for the first time, especially when combined with sudden complete or partial loss of vision or diplopia, aphasia, dizziness, collapse, focal epilepsy, weakness or severe numbness of half the body, movement disorders, severe unilateral pain in the calf muscle, symptom complex “acute abdomen”.
Tumor diseases
Some studies have reported an increased incidence of cervical cancer in women who took hormonal contraceptives for a long time, but the results of the studies are inconsistent. Sexual behavior, infection with the human papillomavirus and other factors play a significant role in the development of cervical cancer.
A meta-analysis of 54 epidemiological studies found that there is a relative increase in the risk of breast cancer among women taking oral hormonal contraceptives, but the higher detection rate of breast cancer may have been associated with more regular medical screening. Breast cancer is rare among women under 40, whether they take hormonal birth control or not, and increases with age. Taking pills can be considered one of many risk factors. However, the woman should be made aware of the possible risk of developing breast cancer based on an assessment of the benefit-risk ratio (protection against ovarian and endometrial cancer).
There are few reports of the development of benign or malignant liver tumors in women taking hormonal contraceptives for a long time. This should be kept in mind when differentially assessing abdominal pain, which may be associated with an increase in liver size or intraperitoneal bleeding.
Chloasma
Chloasma can develop in women with a history of this disease during pregnancy. Those women who are at risk of developing chloasma should avoid contact with sunlight or ultraviolet radiation while taking Lindinet 20.
Efficiency
The effectiveness of the drug may be reduced in the following cases: missed pills, vomiting and diarrhea, simultaneous use of other drugs that reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills.
If the patient is concomitantly taking another drug that may reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills, additional methods of contraception should be used.
The effectiveness of the drug may decrease if, after several months of their use, irregular, spotting or breakthrough bleeding appears, in such cases it is advisable to continue taking the tablets until they run out in the next package. If at the end of the second cycle menstrual-like bleeding does not begin or acyclic bleeding does not stop, stop taking the pills and resume it only after pregnancy has been ruled out.
Changes in laboratory parameters
Under the influence of oral contraceptive pills, due to the estrogen component, the level of some laboratory parameters (functional indicators of the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hemostasis indicators, levels of lipoproteins and transport proteins) may change.
Additional Information
After acute viral hepatitis, the drug should be taken after normalization of liver function (no earlier than 6 months).
With diarrhea or intestinal disorders, vomiting, the contraceptive effect may be reduced. While continuing to take the drug, it is necessary to use additional non-hormonal methods of contraception.
Women who smoke have an increased risk of developing vascular diseases with serious consequences (myocardial infarction, stroke). The risk depends on age (especially in women over 35 years of age) and on the number of cigarettes smoked.
The woman should be warned that the drug does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
No studies have been conducted to study the effect of Lindinet 20 on the abilities necessary to drive a car and operate machinery.
Directions for use and dosage of Lindineta 20
How to take Lindinet 20 (LS)? Reviews confirm that there is nothing complicated about this.
The drug is taken 1 tablet once a day; it is not advisable to change the time of administration. After three weeks of use, a week-long break is taken, after which a new package begins on the eighth day. During the break between doses of the drug, bleeding begins.
The first tablet should be taken from the first to the fifth day of menstruation. If you switch to Lindinet 20 from another hormonal contraceptive, then the first tablet is taken the day after the end of the previous drug. When switching from progestin medications, you can start taking them on any day of the cycle. After removal of the implant, you can start taking the drug the next day, after the injection before the last injection.
During the first week of use, you will need to use additional methods of contraception to avoid unwanted pregnancy.
The contraceptive effect continues even if you miss one pill. This is confirmed by reviews of gynecologists about Lindinet 20.
Lindineth
Contraceptive pill form. One package contains 21 tablets. The active ingredients are ethinyl estradiol (estrogen) and progestogen (gestodene). It interferes with the ovulation process and increases the viscosity of cervical mucus, thereby making it difficult for sperm to penetrate the uterus.
In addition to preventing unwanted pregnancy, Lindinet regulates the menstrual cycle, reduces pain and helps reduce the intensity of bleeding. For oily skin and acne - has a beneficial effect on oil levels, improves skin condition and intensity of rashes. The drug also inhibits the development of iron deficiency anemia, reduces the risk of cysts and tumors of the genital organs and mammary glands, the risk of ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory diseases and endometrial cancer.
Reception scheme
Lindinet is taken one tablet per day, preferably at the same time. The duration of continuous use is 21 days. This is followed by a week-long break, during which menstrual-like bleeding occurs. Then the reception continues - from the next package. It turns out that the menstrual cycle lasts four weeks, three of which the woman takes Lindinet, and one she does not take. Each new package starts on the same day of the week.
The first tablet is taken on the first day of the menstrual cycle. After an abortion, if it occurred in the first trimester of pregnancy, taking the drug can be started immediately after surgery. Additional barrier methods of contraception are not required. If it was not possible to start taking the drug immediately after the abortion, then you can do this after 21-28 days (in the first seven days you need to use barrier methods of contraception), or wait until the first menstrual cycle.
The same should be done after childbirth - start taking it after 21-28 days, using additional contraceptives during the first week. If you wait until your first menstruation, then follow the rule “the first day of the cycle - the first pill.” Please note: if you have had sexual intercourse after childbirth or abortion and menstruation has not yet begun, pregnancy must be ruled out.
If you forget to take your pill...
In such cases, you need to proceed according to the following schemes.
If the delay in taking is less than 12 hours, then you need to take the pill as soon as possible and continue to follow the usual regimen. No other contraceptive measures are required.
If the delay is more than 12 hours, the contraceptive effect is reduced. You should act in the same way, but additionally use barrier methods of protection for a week.
Separately, it is worth noting the situation when you forgot to take a tablet, and there are less than 7 tablets left in the package. In this case, you need to take the pill as soon as possible, then stick to your usual schedule, and start taking the drug from the next package without interruption. Menstrual-like bleeding does not occur in this cycle; it should occur only after completing all the tablets from the second package. However, spotting or breakthrough bleeding may occur while taking it. If bleeding does not occur in the second cycle, then a pregnancy test must be taken.
Vomiting and/or diarrhea that occurs within three to four hours after taking the drug may affect the effectiveness of the drug. If such symptoms bother you within an interval of up to 12 hours, you need to additionally take another tablet and then proceed according to your usual schedule. If symptoms continue for more than 12 hours, then the contraceptive effect is reduced and it is necessary to additionally use barrier methods of contraception over the next week.
Contraindications to taking Lindinet are:
- liver diseases, dysfunctions and tumors;
- thrombosis and thromboembolism - currently diagnosed or occurring previously;
- myocardial infarction, heart failure;
- cerebrovascular disorders;
- transient ischemic attacks, angina pectoris;
- sickle cell anemia;
- breast or endometrial tumors;
- diabetes mellitus complicated by microangiopathies;
- uterine bleeding of unknown etiology;
- idiopathic jaundice and itching during pregnancy;
- history of genital herpes.
[[see_also_3]]
Lindinet should not be taken during pregnancy and lactation.
Please pay special attention to the fact that taking other medications may reduce the effectiveness of Lindinet. Therefore, for any therapeutic appointments, inform your doctor that you are taking a contraceptive. It is recommended to use additional barrier methods of protection while you are taking the following drugs: ampicillin, tetracycline, rifampicin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, griseofulvin, topiramate, felbamate, oxcarbazepine, ritonavir. After completing the course of treatment, additional contraceptive measures should be used for the next week, or act in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
You should also know that a decrease in the contraceptive effect of Lindinet is caused by taking St. John's wort in any form (decoctions, infusions, etc.). The reason for this is the special effect that St. John's wort has on liver enzymes. This effect lasts during the course of taking St. John's wort, as well as for two weeks after its completion.
Side effects when taking Lindinet may be as follows:
- nausea, vomiting;
- emotional instability, irritability, depression, fatigue;
- headaches, dizziness;
- leg cramps;
- increased blood pressure;
- vaginal discharge of unknown origin;
- change in body weight, change in libido;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- chloasma;
- swelling;
- discomfort when wearing contact lenses;
- allergic reactions.
The drug should be taken with extreme caution in the following cases:
- family history of breast cancer;
- kidney diseases;
- chorea of pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- epilepsy;
- gallbladder diseases, especially cholelithiasis;
- liver failure;
- cholestatic jaundice;
- high blood pressure;
- prolonged immobility (for example, in case of serious injury);
- surgical intervention;
- migraine.
Lindinet is not recommended for women over 35 years of age who smoke, as it may increase the risk of developing cardiovascular complications.
The drug should be stopped if:
- while taking it, there is an increase in the frequency and intensity of headaches and migraines;
- epileptic seizures occur;
- signs of depression increase;
- surgical intervention is pending (appointment is stopped 4 weeks before the planned operation and can be resumed 1 week after the patient is mobilized).
Please note: intermenstrual bleeding may occur in the first three months of taking Lindinet. If they occur after regular cycles have formed, pregnancy and malignant neoplasms should be excluded.
If menstrual-like bleeding does not occur during the period without taking pills (the week between two packs) and the dosage regimen was violated in the previous cycle, it is necessary to take a pregnancy test.
Reviews
Gynecologists characterize Lindinet 20 as a modern and relatively safe contraceptive. In the absence of contraindications for use, the drug does not have a significant effect on the woman’s body; on the contrary, it has a beneficial effect on the menstrual cycle, improves the quality of skin and nails. Side effects from the Gedeon Richter Lindinet 20 contraceptives, according to reviews, are extremely rare, and the most common include headaches, nausea and decreased libido.
If the drug does not suit you, you should not completely abandon oral contraceptives. In this case, it is necessary to additionally consult with a gynecologist and select another drug.
Price for "Lindinet 20" Tbl. p/o No. 21 (one blister in a cardboard package) - 400–480 rubles. “Lindinet 20” No. 63 (three blisters in a cardboard package) can be found at a price of 850–1100 rubles.
Contraceptives Gedeon Richter Lindinet 20 - reviews
Katrina
https://citykey.net/review/nadezhnoe-sredstvo-kontratseptsii
My daughter takes birth control pills Lindinet 20. She was prescribed them by a gynecologist for the treatment of postpartum fibroids. I have not heard of this method of treating fibroids, but my daughter started taking this drug anyway, because for now one daughter is enough for them and they are not planning a second child in the near future since there is no one to help them.
Lindinet's daughter takes one tablet in the morning for 21 days, then takes a break for 7-9 days and resumes taking it on the second or third day of the cycle. In principle, she likes the drug, only once, when she felt unwell and had a headache and nausea for several days; due to a break in taking it, she had withdrawal bleeding. But it went away as soon as she took the next pills again within three days.
This drug is not suitable for everyone; it may increase the likelihood of blood clots and women with increased blood clotting should not take the drug. In general, there are quite a few contraindications to taking these contraceptives. I would rather take tests to select a hormonal contraceptive than take the drug like this. It is relatively inexpensive, which I’m afraid was the reason my daughter chose the drug. But I can’t convince her.
Nadia
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/contraception/1698690#comm_152201000
In general, I got pregnant on OK, missed 2 pills... I also heard a lot that, on the contrary, it’s very easy to get pregnant when you stop, especially for those who have problems with their cycles... I have problems without OK. I’ve been drinking OK for 10 years now, intermittently (the longest break was pregnancy), at first I was treated, then I started drinking for contraception. There are side effects, but you need to select the drug, some drugs have side effects, some don’t, if it doesn’t matter which ones are OK, you should choose the one with the lowest dosage, just read the instructions and find the dosage. I’m not getting fat or losing weight, my libido is fine, I have less acne, I don’t feel nauseous, my head doesn’t hurt... I take Logest, I feel the same way on Regulon, but the dose is higher. Jess has excellent skin, but it just gives me toxicosis... Lindinet-20 is the same as Logest, a different company - it didn’t work: my chest hurt + thrush. Yarina - the cycle went wrong, M was not there during the break, Janine: recovered. Jess, Yarina and Janine are from the same group, they have similar hormones, the dosage is different - I realized that this group is not suitable for me. I took Regulon for 2 years with breaks of 2 months/once a year, but I stopped using it, skipping the pills in the first cycle after the break, so it’s bullshit that you can’t stop after OK. I have been taking Logest for 3 years after giving birth, I take a break once a year, everything is fine.
Olga Kolmakova
https://xlebez.ru/kontraceptivy-gedeon-richter-lindinet-20/
After the terrible consequences from YARINA (which the doctor prescribed for me!) I didn’t think that I would still drink OK, but the circumstances were such that I had to take a risk. The fact is that my man is allergic to latex and had to forget about condoms. But with us everything is serious! I won’t leave him and I don’t want to give up frequent sex either. So I decided to try Lindinet 20. In general, I used them twice to delay my periods and everything was fine and most importantly it helped. I know it’s harmful, but I think every girl has something that happens at the wrong time :(
To delay, I drank like this (for those who don’t drink OK): My cycle is 28 +/- day. So I started three days in advance, that is, from the 25th day of the cycle and continued as long as I needed it until the 30th day. After stopping treatment, menstruation began on days 31-32. THERE WERE NO CONSEQUENCES, THE CYCLE DID NOT START.
Now I’m drinking the third pack (21 days, 7 days off, etc.) everything is fine. I noticed that in the first 7 days of each pack I feel sick, but only at night. I go to bed very late and after 12 at night for some reason I start to feel sick, but if I go to bed earlier everything is ok. Many people write that libido decreases from OK, but for me it’s the opposite; in the second and third weeks of taking it I turn into a nymphomaniac. For me this is a minus, I already have a big appetite, but now it’s going off scale. I even started making eyes at my boss, not seriously of course, but you never know what he’ll decide, he’s liked me for a long time :)
The biggest, but pleasant, side effect: BREASTS HAVE INCREASED VERY INCREASED! I had it before, but I was always unhappy with the size, about 1.5, it seemed to me, I bought busts 75B. And now everything is coming out of them, they have definitely grown one size and this in 2.5 months. Many girls talk about this, but I’ll prove it with photos and I’m not ashamed))), I did it on purpose in the same bra; as you can see in the photo, I didn’t raise the straps higher). Another plus is the price of 293 rubles. and say Yarina or Jess from 700 rubles. But Lindinet has no cosmetic effect, if this is important to someone, I personally don’t care.
THE PACKAGING WAS A HUGE MINUS FOR ME. The tablets there are numbered with numbers, and not with days of the week like Yarina’s. As a forgetful girl, this seems very inconvenient to me. I can forget to drink or, on the contrary, drink and forget, and in order to understand whether I drank or not, you need to know exactly the day of the cycle, you have to open the calendar and count. And when the tablet is marked with the day of the week, everything is simple.
I also think it’s better to drink them in the evening for convenience. I drank the first package in the morning before work at about 7 and on the weekend I had to set the alarm for this time, but I really wanted to sleep until at least 11….
PHOTO:
1) inconvenient packaging;
2) before photo, I didn’t take it on purpose and it wasn’t such a close-up, but it was very useful
3) photo after 2.5 months of use. I did it for clarity in the same bust, I didn’t raise the straps.
Olga Nikolaevna - doctor
https://puzkarapuz.ru/review/detail/lindinet_20_otzyvy_sovety_i_otzyvy_vrachej_ginekologov_o_lin
Lindinet 20 is a monophasic contraceptive for oral use.
Estrogen in the composition is represented by ethinyl estradiol, which physiologically, together with progesterone, regulates the menstrual cycle. The gestagenic component of the drug, gestodene, has a minimal effect on the lipid and carbohydrate profile, as a result of which it does not cause weight fluctuations.
The contraceptive effect is ensured by several processes, the main one is the inhibition of the production of pituitary hormones; the drug also affects the transformation of the endometrium, increases the viscosity of the cervical contents, this is an unfavorable factor for the movement of sperm to the uterine cavity.
Lindinet 20 ensures the reliability of the ovarian-menstrual cycle and prevents the development of a number of gynecological diseases, including those of oncogenic origin.
Lindinet 20 rarely causes side effects. There is a convenient form of release of the drug for 3 months, we compare the price/quality ratio. If a side effect occurs such as acyclic bleeding associated with insufficient dosage of ethinyl estradiol (which does not disappear when using the drug for more than 3 months), it is possible to switch to Lindinet 30, which is very convenient.
Anonymous
https://v_dguk.ukr/ru/contraceptives_gedeon_richter_lindinet_20-r119231.html
I took these pills about 2 years ago, I chose them because the gynecologist recommended them as a drug with the lowest hormone content. Well, in principle, I didn’t deceive, there were no side effects and the weight, in principle, neither decreased nor increased. I was satisfied, then they cost three hundred rubles a pack for a month, after I finished taking them I became pregnant without any problems, and when I wanted to take them again I began to hear bad reviews about them, that they were starting to make counterfeits, that of course you don’t get pregnant with them, but you get better(
natusik.
https://www.otzyvua.net/lindinet/review-167057
I had two surgeries. Resection of the left and right ovary. The cysts burst. The doctor prescribed Lendinet 30. I took it for about a year. I lose a lot of weight from them. I do not like it. Because breast shapes are correct and so small. I thought my breasts would be bigger, but apparently it doesn’t work on me. I quit and took a break. Then I decided to switch to railway, it would be better not to start all the side effects on my face. I finished my drink and switched back to Lindinet 30. I got tired and went to the doctor, the doctor didn’t even do any tests. She said that I’ve been drinking her rating on Lindenet20 for three days now. While there is a slight nausea, let's see what happens next.
seawave9
https://otzovik.com/review_3687833.html
Advantages:
No side effects, convenient packaging, regular painless cycle, confidence.
Flaws:
No.
I have been taking these pills for 5 years and have no desire to switch to others. During this time I did not find any side effects for myself. The doctor prescribed them to me after the next ovulation ended in the hospital. This drug is probably not suitable for everyone, everything is individual. But I only have positives. The cycle has become regular, passes quickly and painlessly (before they climbed the wall, I even took time off from work, it was so painful). The condition of the skin has noticeably improved, and the weight, which had always been unstable, has normalized. My hair has become thicker, there is no feeling that it is dry or burned, my bad nails have become much better. Well, the main plus is that they fulfill their function of protection, I am sure that nothing will happen unplanned.
Mashalex
https://otzovik.com/review_5238975.html
Advantages:
normalize the menstrual cycle, price, pain in the lower abdomen, contraception
Flaws:
side effects
Good day to all. I want to tell you about our experience in taking one drug for women, namely the Gedeon Richter hormonal contraceptive “Lindynet 20”. We have encountered similar drugs before, but for other purposes. I got acquainted with this remedy quite recently, when my wife was at a doctor’s appointment. It was his doctor who advised us to take it in our case. The reason for contacting a gynecologist was pain in the lower abdomen before menstruation and disruption of the menstrual cycle. I must say that similar situations have happened to my wife before, and this problem was also resolved in a similar way. The advantages of these tablets include their relatively inexpensive price compared to other similar drugs. The price for one record is approximately 130 hryvnia. In addition, these tablets are a good contraceptive. But we used it for slightly different purposes. It must be said that the effect was not long in coming. Firstly, after the second pill, the pain in the lower abdomen went away and a month before the next menstruation, no such unpleasant sensations were observed. Secondly, these pills really helped regulate the menstrual cycle - everything was done right on time. But do not forget about the many side effects, everything is individual. In general, in our case, these tablets really helped. Effective and inexpensive.
Lady_in_plaid
https://irecommend.ru/content/otzyv-o-protivozachatochnykh-tabletkakh-lindinet-20-dlya-vsekh-somnevayushchikhsya-vse-chto
Good day, my beloved readers. The review of Lindinet 20 has been brewing for me for a long time. I have something to say. I took these OK for about a year and a half. The review will be without photos, because... I've been taking pills for over a year
Jess Plus. In my review of Lindinet 20 I want to sort everything out for those who doubt it. 1. Contraceptive effect. This, in fact, is why we buy contraceptives. I have to give it my due, Lindinet 20 did not let me down. One of the shortcomings on this point is the absence of a scale with the days of the week on the plate. Yes, all the pills are numbered, but sometimes in order to remember whether I took a pill today, I had to count for a long time and tediously. Sometimes, for this reason, there were omissions; in this case, according to the instructions, you need to take additional protection, which is what I did. If you ignore this recommendation, you can easily get pregnant, even if you continue to take Lindinet 20 regularly. 2. Acne. Before taking Lindinet 20, I had acne. After I started taking the pills, they did not disappear immediately. I noticed a noticeable effect approximately on the third cycle of use. Yes, my skin has cleared up. I was happy. But nothing lasts forever under the sun. More on this later. 3. Cycle. This is the biggest plus. I am a happy owner of polycystic disease. Those who know will understand me. For those who are not in the know, I won’t bore you with long stories about this scourge, you don’t need it. Let me just say that before taking OK, I didn’t know what a regular cycle was. Even approximately. Lindineth 20 gave me regular periods. They began to come on the same day, almost at the same time. 4. Hair. With Lindinet 20, the hair on my head began to become oilier more slowly. In other places they began to grow more slowly. 5. Weight. Did not change. 6. Cellulite. This was a real disappointment. Lindinet 20 is a hormonal drug, and the hormones are female. And female hormones cause cellulite. I heard on TV that cellulite is something like another female gender characteristic. 7. Chest. But I wouldn’t refuse this gender characteristic. But no. She hasn't grown up. From the word “absolutely”. Neither in adolescence, nor after taking Lindinet 20. I'll go cry 8. Sex. OK suppress libido. Not really, of course. But, based on personal experience and the experience of my friends, I can say that any contraceptives affect sexuality. This is a side effect of hormones. Having read a whole bunch of reviews about Lindinet 20 at one time, I couldn’t understand why some young ladies complained that their libido had disappeared completely, while others seemed to not notice the difference at all. So, this is something similar to drinking coffee. It invigorates some, some feel no difference, and some feel ill. No one will deny the tonic effect of the drink. Everyone just has different body sensitivities. Same with hormones. All side effects from Lindinet 20 and any other hormonal drugs are purely individual. 9. The price of Lindinet 20 is very affordable, especially compared to the tablets that I
I'm drinking now. 10. Do I need to take a break from taking Lindinet 20? I did. Once. I don't see the point. The opinions of doctors were divided into two camps: to do and not to do. There are a whole bunch of arguments in favor of both opinions. There is an active debate going on. I'm in favor of not doing it. Why? Because this is additional stress for the body - once. When you stop taking OCs, the chance of getting pregnant increases significantly—two times. This is the famous rebound effect, so beloved by women's forums. 11. Cancellation. This is my favorite part. I felt the withdrawal effect on the third cycle. It was something. My face had never seen such acne even at 15 years old. The chest seems to have completely deflated. And my hair came out in clumps. The menstruations have completely confused the shores. For half a year I waited for everything to get better, that it was just a restructuring of the body, and I walked around like a folk beauty. I smeared myself with creams, treated my skin with “talkers”, and bought shampoos for hair loss. But no. The doctors announced the verdict: “Without pills, you can’t go anywhere.” Summarize. I am now dependent on birth control. All girls who think that Lindinet 20 can be taken for acne or for breasts, I ask you to think ten times whether they are ready for all the consequences. For some, even long-term use of OCs may pass without a trace, while others may become a contraceptive addict. Kisses, Lady_in_a_plaid
ElisWong
https://irecommend.ru/content/spaset-ne-tolko-ot-nezhelatelnoi-beremennosti-opisanie-pervykh-3-mesyatsev-privykaniya-i-che
Hi all. I’ll tell you about my experience of preventing unwanted pregnancy, in a way that many are so afraid of. Namely, about hormonal contraceptives.
A friend suggested this to me. She started taking them first, told me about her impressions and I made up my mind. I’ll say right away that I didn’t prescribe them for myself, because I take my health seriously and wasn’t too lazy to go to the doctor. She prescribed them exactly and warned about possible side effects, how to take them, etc. So girls, don’t be lazy to go to the doctor, you’ll feel better later.
So, the doctor warned that since I sometimes suffer from migraines , it is not advisable for me to take OK at all and that I will take them at my own peril and risk. She said that the pills would have a good effect on the menstrual cycle, on the condition of the skin and hair, and (which I didn’t really understand) that they should be taken for at least 9 months if they had already started. About the fact that during the first 3 months there may be some spotting in the middle of the cycle, that this is normal and not a cause for concern. She warned about possible nausea during the first 2 weeks, headaches, etc. She also said one interesting thing: that it cannot be that the pills are not suitable for someone. Any body will get used to them, just not everyone can tolerate it. Like, now all the pills are such that they simply cannot fail. After that, I went and bought my first blister pack. It cost 350 rubles.
The blister contains 21 tablets. I take it every evening at 11 pm. I set a reminder so I don’t forget.
Now I’ll tell you about my feelings and side effects.
First month
- After my first pill, I lay down and waited for nausea, like after a great drinking session. I just didn’t organize a basin for myself near the bed. But she still didn’t come.
- For the first month I didn’t have any headaches AT ALL, which is strange because I periodically, consistently get migraines once a week.
- The first month I did not notice any significant improvement in my skin. I've been having constant acne lately, I don't know why. The first month of taking the pills did not help me get rid of them. Well, there’s nothing to say about the hair at all; nothing was noticed there at all.
- Starting from about 9-10 tablets (days), my chest began to hurt wildly. Like with PMS.
- With 17 tablets in the first month of taking it I had a spot. I found information on the Internet that spotting when taking OCs at the beginning of the cycle means that the body does not have enough estrogen, and at the end - gestagen. There were no periods at all for the first month.
Second month
- The frequency of migraines has returned. They occurred to me regularly once a week.
- I was pleased with the skin. It really cleared up, not a single pimple, smooth, soft.
- The breasts were just as sensitive as with PMS.
- The mood is normal, no jumps.
- Libido, as usual, neither increased nor decreased
- This time the cravings started a little later, with 19 tablets, and my period came on the first day of the break. It's a bit early. They were scanty and lasted exactly 2 days, compared to my usual duration of 6-7 days. Fairy tale straight. No pain, discomfort or other “pleasures”
Third month
Everything finally returned to normal: the skin was clean, no unnecessary spotting, my period was right on time - on the second day of the break, my chest no longer hurt.
By the way, there are two issues that are of great concern to girls who start taking OK: breast enlargement and weight gain.
About the first one I can say that there is such a thing. Not much, of course, you won’t look like Pamela Anderson after your first size (or my minus first), but now at least it’s clear that I’m not a guy and I have some rudiments of breasts :) Literally half a size.
About the second I will say that I have gained weight. Not much, but it has increased. Considering that I am an extremely thin lady (I was), it is noticeable that I have “freshened up”. But I won’t say for sure that it’s because of the pills, because I also quit smoking about a year ago, so maybe it all had an effect. The beastly appetite wakes up on the 2-3rd day of taking the pills, and then returns to normal. For those who are prone to obesity, just restrain yourself during this period and everything will be fine.
What I want to say: hormonal contraceptives are not as scary as our mother told us :)) In their times, it was truly a terrible thing, from which it spread in all directions, godlessly and irrevocably. Now they have been made relatively safe. The main thing is to monitor your condition, your feelings, listen to your body and go to the doctor at the first “bell”.
And yes, if you decide to take OK, before you start, go to the doctor. It will take you no more than an hour and will save you from many unpleasant problems. I wish you health and only pleasant surprises :)