Lung structure
The lungs are the organs that provide human breathing. These paired organs are located in the chest cavity, adjacent to the heart on the left and right. The lungs have the shape of semi-cones, the base adjacent to the diaphragm, the apex protruding 2-3 cm above the collarbone. The right lung has three lobes, the left - two. The skeleton of the lungs consists of tree-like branching bronchi. Each lung is covered on the outside by a serous membrane - the pulmonary pleura. The lungs lie in the pleural sac, formed by the pulmonary pleura (visceral) and the parietal pleura (parietal) lining the inside of the chest cavity. Each pleura contains glandular cells on the outside that produce fluid into the cavity between the layers of the pleura (pleural cavity). On the inner (cardial) surface of each lung there is a depression - the hilum of the lungs. The pulmonary artery and bronchi enter the gates of the lungs, and two pulmonary veins exit. The pulmonary arteries branch parallel to the bronchi.
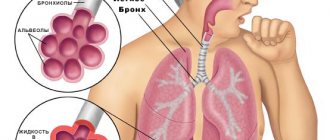
Lung tissue consists of pyramidal lobules, with their bases facing the surface. The apex of each lobule includes a bronchus, which sequentially divides to form terminal bronchioles (18-20). Each bronchiole ends with an acinus, a structural and functional element of the lungs. The acini consist of alveolar bronchioles, which are divided into alveolar ducts. Each alveolar duct ends in two alveolar sacs.
Alveoli are hemispherical protrusions consisting of connective tissue fibers. They are lined with a layer of epithelial cells and abundantly intertwined with blood capillaries. It is in the alveoli that the main function of the lungs is carried out - the processes of gas exchange between atmospheric air and blood. In this case, as a result of diffusion, oxygen and carbon dioxide, overcoming the diffusion barrier (alveolar epithelium, basement membrane, blood capillary wall), penetrate from the erythrocyte to the alveoli and vice versa.
Lung functions
The most important function of the lungs is gas exchange - supplying hemoglobin with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. The intake of oxygen-enriched air and the removal of carbon dioxide-saturated air is carried out thanks to the active movements of the chest and diaphragm, as well as the contractility of the lungs themselves. But there are other functions of the lungs. The lungs take an active part in maintaining the required concentration of ions in the body (acid-base balance), and are capable of removing many substances (aromatic substances, esters, and others). The lungs also regulate the body’s water balance: approximately 0.5 liters of water per day evaporates through the lungs. In extreme situations (for example, hyperthermia), this figure can reach up to 10 liters per day.
Ventilation of the lungs is carried out due to the pressure difference. During inhalation, pulmonary pressure is much lower than atmospheric pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs. When you exhale, the pressure in the lungs is higher than atmospheric pressure.
There are two types of breathing: costal (chest) and diaphragmatic (abdominal).
- Costal breathing
At the points where the ribs are attached to the spinal column, there are pairs of muscles that are attached at one end to the vertebra and at the other to the rib. There are external and internal intercostal muscles. The external intercostal muscles provide the process of inhalation. Exhalation is normally passive, but in case of pathology, the act of exhalation is assisted by the internal intercostal muscles.
- Diaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing is carried out with the participation of the diaphragm. When relaxed, the diaphragm has a dome shape. When its muscles contract, the dome flattens, the volume of the chest cavity increases, the pressure in the lungs decreases compared to atmospheric pressure, and inhalation occurs. When the diaphragmatic muscles relax as a result of the pressure difference, the diaphragm returns to its original position.
Pneumonia and bronchitis: what is the difference?
Both diseases affect the human respiratory system, which means they have similar symptoms. It is often difficult to distinguish the two pathologies from each other.
| Pneumonia | Bronchitis |
| In most cases, it is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39° and a feverish state. There is a slight increase in temperature. | Accompanied by a strong dry cough. In some cases, sputum may appear greenish or streaked with blood. Wet cough, sputum is light in color. |
| When listening to the chest, “wet” rales are heard. | When listening to the chest, “dry” wheezing is heard. |
Lungs of a smoker
In the process of smoking, the lungs are subjected to severe shock. Tobacco smoke that penetrates the lungs of a smoker contains tobacco tar (tar), hydrogen cyanide, and nicotine. All these substances settle in the lung tissue, as a result the epithelium of the lungs simply begins to die. The lungs of a smoker are a dirty gray or even just a black mass of dying cells. Naturally, the functionality of such lungs is significantly reduced. In the lungs of a smoker, ciliary dyskinesia develops, spasm of the bronchi occurs, as a result of which bronchial secretions accumulate, chronic pneumonia develops, and bronchiectasis is formed. All this leads to the development of COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Is pneumonia contagious?
The inflammatory process in the pulmonary system most often appears due to the multiplication of the virus and as a complication of influenza or acute respiratory viral infection. In such cases, it is impossible to get sick from pneumonia itself, but it is easy to catch the disease that became the root cause. That is, pneumonia itself is not contagious, and the development of inflammation in the lungs is an independent complication that arose against the background of a weakened immune system and improper self-medication.
Can pneumonia go away on its own without treatment?
Pneumonia or pneumonia is one of the most dangerous and common diseases of the respiratory system. The danger is that specialists do not always have time to make a diagnosis in time. People do not go to the doctor with a cough and fever, but prefer to stay at home for a couple of days until the disease spreads. The condition can worsen to bilateral pneumonia, which carries severe consequences, long-term treatment or chronic diseases.
A hundred years ago, before the discovery of penicillin, pneumonia took the lives of those who fell ill. Science and medicine do not stand still - our lives have changed dramatically in a hundred years. People have antibiotics in every medicine cabinet, and hospitals carry out operations using modern equipment. However, according to the Russian Academy of Sciences, pneumonia is still on the list of the deadliest infectious diseases and should not be underestimated.
Pneumonia will not go away on its own. This disease can lead to death, so seeing a doctor is vital. Treatment for pneumonia should be prescribed by a doctor. It is he who determines whether antibiotics are needed and which ones, and also decides on the severity of the disease.
With pneumonia there is always a high temperature and a strong cough, is this true?
This is a very big and dangerous misconception. Errors in diagnosing the disease are one of the main causes of mortality from pneumonia. According to doctors, up to 30% of cases of pneumonia are not diagnosed or detected too late, since people do not see the need to see a doctor before a high temperature appears. As a result, this leads to a deterioration in the person’s condition and the development of severe complications. Asymptomatic, hidden, but real pneumonia often develops in children and the elderly. The main and most dangerous problem in diagnosing pneumonia in elderly patients is that the disease successfully disguises itself as various chronic diseases. In this case, it passes without the most important marker of the disease for us - without fever. How then do you understand that pneumonia is going away in an adult? - Monitor your body, and promptly consult a doctor if your health worsens.
If you have what signs you should consult a doctor?
- increased sweating;
- weakness;
- dyspnea.
By the way, the myth that pneumonia is necessarily accompanied by a severe cough is just a myth. This problem is mostly characteristic not of the older generation, but of children. There are often cases when pneumonia progresses, but there is no cough. If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not make a diagnosis, the child may experience chronic consequences.
Pneumonia in children can be identified by the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and chest pain when moving;
- pain when turning the body
- inability to take a deep breath;
- tachycardia;
- exercise intolerance;
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- the person looks pale, but with a bright, unhealthy blush.
How is pneumonia transmitted?
The disease can be transmitted in different ways, including:
- Airborne method. During the disease, droplets form on the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose, which spread through the air during sneezing and coughing. You can become infected by airborne droplets in any public place: hospital, store, public transport. The pathogenic agent spreads through the air along with particles of mucus, sputum, and saliva.
- Contact. The infection is also transmitted through contact - shaking hands, hugging, kissing. People become infected when they touch contaminated objects or when they touch their mouth, eyes, or nose with dirty hands.
- Domestic. The infection can be transmitted through shared towels, dishes and bedding. Therefore, the patient needs to be provided with personal hygiene items, and, if possible, change and wash them more often.
- Fecal. The virus survives up to two days in fecal matter with normal bowel movements. You can easily acquire the disease from improper toilet cleaning or personal hygiene. To prevent infection, especially from young children, it is important to constantly wash your hands after cleaning the child's potty, change diapers frequently and thoroughly wash the area where bowel movements occur.
However, personal hygiene items must be handled very carefully. It has been proven that the viral microorganism can survive up to 4 hours on any surface. Morbid bacteria are not afraid of frost; even with bleach it can be destroyed only five minutes after direct treatment.
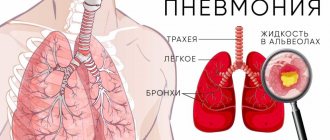
Pneumonia
One of the most common severe pulmonary diseases is pneumonia. The term “pneumonia” includes a group of diseases with different etiologies, pathogenesis, and clinical features. Classic bacterial pneumonia is characterized by hyperthermia, cough with purulent sputum, and in some cases (when the visceral pleura is involved in the process) – pleural pain. With the development of pneumonia, the lumen of the alveoli expands, exudative fluid accumulates in them, red blood cells penetrate into them, and the alveoli are filled with fibrin and leukocytes. To diagnose bacterial pneumonia, X-ray methods, microbiological examination of sputum, laboratory tests, and study of blood gas composition are used. The basis of treatment is antibacterial therapy.
Methods for treating pneumonia
If pneumonia is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are prescribed. Their effectiveness can be assessed after 48-72 hours. If the temperature subsides, the cough becomes less frequent, and the patient begins to feel better, the treatment continues. You cannot interrupt the course of medications, and it is important to take them correctly as prescribed by your doctor. If antibiotics do not help, another treatment is prescribed or changed to a drug from another group.
For viral pneumonia, antibiotics are not effective, so antiviral drugs are prescribed. Vitamins and immunomodulators can be prescribed as auxiliary substances.
Once the patient's body temperature has returned to normal, physical therapy can be prescribed. It allows you to remove phlegm from the lungs. For this purpose, herbal medicines are often taken, for example, licorice root or complex breast mixtures.
Along with drug treatment, patients need bed rest, meals containing protein and vitamins, and plenty of warm drinks. For the best effect, therapeutic methods are recommended - electrophoresis, inhalation, massage, magnetic therapy, etc.