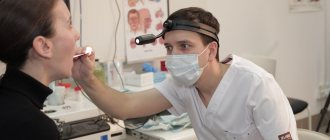
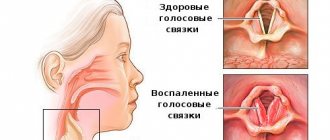
Pneumonia can be suspected by its characteristic symptoms - high body temperature combined with a severe cough. However, this is not always the case. In some cases, the temperature does not rise, but the person continues to cough. This can confuse the patient and he puts off visiting the doctor. As a result, valuable time is lost. When contacting the Yusupov Hospital, the patient is immediately prescribed an examination, thanks to which it is possible to accurately diagnose and begin treatment on time.
Causes of pneumonia
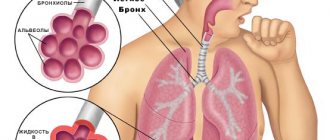
Almost always, an inflammatory reaction in the lung tissue is caused by an infection. Pneumonia can be caused by many microorganisms - bacteria (most often), viruses, fungi and even some types of protozoa. In the vast majority of cases, the cause of pneumonia is:
- streptococcus pneumoniae - pneumococcus;
- chlamydia;
- haemophilus influenzae - hemophilus influenzae;
- respiratory syncytial virus is the most common cause of viral pneumonia
- other types of streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- mycoplasma.
Sometimes pneumonia can also be non-infectious and be caused by:
- toxic lesions of lung tissue;
- allergic reactions;
- autoimmune diseases;
- exposure to extreme temperatures;
- penetrating radiation (cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy to the lungs).
Risk factors
Predisposing factors for the occurrence of inflammation in the lung tissue are:
- chronic diseases of the endocrine, cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- bad habits (primarily smoking);
- malformations of the respiratory system;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Severe cases of the disease occur especially often in older people over the age of 65. Pneumonia is also extremely dangerous in newborns and children of primary school age. It is these categories of patients that account for the vast majority of deaths.
Prevention
Vaccination against influenza and flu helps reduce the risk of infection. Preventive measures are strongly recommended for people at risk:
- Anyone should receive further treatment. The choice of drugs, especially potent ones, is determined by the doctor.
- Avoiding contact with people with acute respiratory infections will help reduce the risk of infection.
- Nutrition should be complete. During periods of exacerbation of colds, it is strongly recommended to include more fruits and vegetables in the diet and start taking multivitamins.
- To protect yourself from hypothermia and getting wet, and to reduce the body’s reaction to temperature changes, hardening and using a contrast shower will help.
- Exercise and breathing exercises promote healthy lung function.
- A living or work space in which a lot of time is spent requires regular wet cleaning and ventilation.
Failure to comply with the work and rest regime greatly depletes the body physically and mentally. The appearance of colds cannot be ignored, much less endured on your feet; in case of complications, treating the consequences will be much more difficult.
Types of pneumonia
According to the prevalence of the process, pneumonia can be:
- focal, affecting only a small area;
- segmental, spreading to one or more segments of the lung;
- lobar, occupying the entire lobe of the lung;
- total, with damage to the entire lung.
The disease is classified according to its causes:
- bacterial pneumonia;
- viral pneumonia;
- mycopneumonia;
- mixed types, in which massive infection with various microorganisms leads to inflammation of the lung tissue.
In addition, there are unilateral (affecting one lung) and bilateral pneumonia (affecting both lungs). Based on the duration of the course, there are acute forms, lasting up to 3 weeks, and subacute forms, lasting from 3 to 6 weeks. Finally, depending on the severity of symptoms, pneumonia can be mild, moderate, or severe, and may or may not have complications (primarily heart and/or respiratory failure).
Symptoms in children
Diagnosis of pneumonia without fever in children is complicated by the fact that the child cannot independently understand what is happening to his body. Therefore, parents should be on guard of children's health.
Symptoms to look out for:
- Decreased usual activity.
- Increased drowsiness, unexplained lethargy.
- He begins to study worse.
- Refusal of outdoor games.
- Increased thirst, decreased appetite.
- Fatigue.
Parents who suspect their child has pneumonia should pay attention to the breathing rate during sleep and listen for wheezing or whistling.
Signs of pneumonia
The standard clinical picture of pneumonia is characterized by symptoms:
- Sudden onset.
- A sharp rise in body temperature above 38 0C.
- Rapid onset of cough with sputum production.
This is how almost all bacterial and viral pneumonias begin, including the most common variants caused by pneumococcus. As the disease progresses, the symptoms include shortness of breath and painful, often stabbing, sensations in the chest. Such symptoms can persist in the patient for up to 2 weeks.
The modern clinical picture of community-acquired pneumonia can vary widely and be “erased” due to the uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs. Has symptoms of respiratory infections:
- your health will deteriorate over several days;
- dry cough with virtually no phlegm;
- headache;
- increased weakness and fatigue;
- muscle soreness;
- pain and sore throat.
Symptoms in bedridden patients
Bedridden patients are at increased risk because their immunity is reduced and sputum discharge is difficult. Very often, it is these patients who develop a latent form of the disease, in which not only hyperthermia, but also a cough is absent.
Impaired lung function, stagnation of sputum, limited mobility, stasis of blood in the vessels - all this is fertile ground for the proliferation of microbial flora.
To identify the disease in time, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- The appearance of an unusual blush on the cheeks.
- Increased sweating, which leads to the need to change clothes more often.
- Refusal to eat, but increased need for fluid.
- Indifference to the surrounding world.
If you notice such symptoms, you must inform your doctor.
Expert opinion
More than 1 million cases of pneumonia are diagnosed annually on our planet.
Moreover, almost 8.5% of them are fatal. Of course, the vast majority of such adverse outcomes occur in groups at risk for pneumonia: children under 5 years of age and elderly people over 65 years of age. However, even if you are young and healthy, neglecting pneumonia is extremely dangerous. At the first manifestations of this disease, you should immediately consult a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate. Pulmonologists at SM-Clinic will make a diagnosis as quickly as possible, determine what exactly caused pneumonia and prescribe the necessary therapy. It will include modern highly effective drugs and techniques, and will be built in accordance with the clinical recommendations of the Russian Respiratory Society and the Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and WHO recommendations.
Savina Maria Yuryevna, pulmonologist at SM-Clinic in Ryazan
Diagnostics
If you suspect latent pneumonia, you should undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. The disease can be identified by studying the gas composition of the blood, analyzing lavage water from the bronchi, or examining mucus obtained during bronchoscopy.
Tests that are widely used but do not allow for a correct diagnosis:
- Donating blood to count the number of leukocytes. The analysis is not informative due to the reduced immune status.
- Sputum analysis. The patient is simply unable to cough it up.
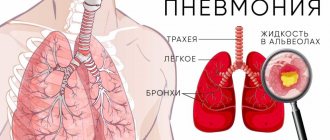
- X-rays of light. The source of inflammation is simply not visible during the study.
Bronchoscopy is one of the priority examination methods to detect pneumonia without fever. The patient is seated on a chair with a straight back. The airways should be as relaxed as possible. A device equipped with a camera and a light source is inserted through the mouth or nose. With its help, the doctor examines the condition of the respiratory organs from the inside, and also collects material for further study. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Treatment of pneumonia
The basis of treatment for pneumonia are drugs that act directly on the cause of the disease:
- antibiotics for bacterial infections;
- antiviral drugs for viral infection;
- antifungal agents for fungal invasion, etc.
The total duration of treatment of bacterial pneumonia with antibiotics averages from 7 to 10 days. For infection with mycoplasma or chlamydia, the course of treatment lasts at least 14 days. If pneumonia was caused by rarer pathogens (enterobacteria, legionella, etc.), then therapy can last 21 days or more. The criteria for stopping antibacterial treatment of pneumonia in adults are maintaining normal body temperature for 2-3 days, the absence of inflammatory symptoms and normalization of blood counts.
Also, for pneumonia, therapy is prescribed to alleviate the symptoms of the disease:
- drugs that dilate the bronchi and thin the sputum to clear the airways;
- corticosteroids;
- saline solutions to maintain water-salt balance;
- oxygen inhalation for respiratory failure;
- physiotherapy at the final stages of the disease (UV irradiation, vibration massage, physical therapy, etc.).
Breathing exercises
To prevent pneumonia
Today, the prevention of pneumonia is one of the most important in the complex of health practices and care for the condition of the human body. It has become obvious that lung damage is a real threat, much more widespread and urgent than it seemed to many of us just recently. The coronavirus pandemic has made adjustments not only to our way of life, but has also made it extremely important to take care of our respiratory system and its healthy and complete state.
One of the most effective ways to prevent pneumonia is regular breathing training with the Samozdrav simulator. And there are justified reasons for this and many years of indisputable evidence.
Breathing exercises strengthen the respiratory muscles, which increases the mobility of the chest and diaphragm. Effective movements of the respiratory muscles increase the volume of the chest and lungs. This ensures maximum pulmonary ventilation and air circulation in the alveoli and increases the utilization rate of oxygen in the lungs and its delivery to the tissues.
Maintaining normal lung volumes and regular training of the respiratory muscles forms the correct respiratory rhythm. As a result of this, the respiratory rate, its minute volume and other indicators that are disturbed due to stress, physical inactivity, and chronic diseases are normalized. Physiologically correct breathing is maintained for a long time.
Breathing exercises maintain the elasticity of the lung tissue. This increases the vital capacity of the lungs and prevents the development of fibrosis and other changes in the lung tissue. CO2 eliminates bronchospasm, which also increases breathing efficiency.
Breathing training increases the efficiency of the pulmonary circulation. This is especially important for older people, because one of the common causes of pneumonia in the elderly is stagnation of blood in the small circle.
As a result of restoration of the functions of the respiratory system and blood circulation, the inflammatory process is reduced, congestion in the bronchi and lungs is prevented, and mucus and exudate are reabsorbed.
In addition, Samozdrav compensates for the lack of physical activity, and breathing training, like physical exercise, promotes the production of a natural antioxidant (superoxide dismutase), which prevents the development of pneumonia.
All these arguments are the result of numerous in-depth studies related to the study of the effect of breathing training with Samozdrav on human lungs and the prevention of pneumonia, as well as the experience of people of different ages and different levels of health.
Today, millions of people from around the world train with Samozdrav to prevent the development of pneumonia - one of the main dangers to the body during a pandemic.
If you want to get one of the most effective ways to take care of your respiratory system, an indispensable assistant for the prevention of pneumonia, purchase the Samozdrav breathing simulator. Years of experience have proven its effectiveness, accessibility and the highest results in maintaining lung health.
For rehabilitation after pneumonia
During a difficult period of threats of a high viral load on the body, it is important to know how to quickly get back into shape after pneumonia and allow your lungs to work at full strength again. Firstly, it is important to follow the general rules of caring for yourself and your health. Sleep at least 8 hours at night and a couple of hours during the day, eat well, not forgetting vitamins A, B, C and calcium, ventilate the room every three hours.
Particular attention should be paid to your lungs, devoting time to breathing exercises to improve pulmonary circulation and strengthen the pulmonary muscles. Through breathing training with the Samozdrav simulator, exudate will be absorbed, sputum separation will be facilitated, the airways will be cleared, lung tissue will remain healthy and elastic, tissue metabolism will be normalized and intoxication that accompanies the acute stage of the disease will be eliminated. Healthy breathing and normal inspiratory volume will be restored, shortness of breath will go away due to the normalization of oxygen levels in the body,
In the process of breathing training with the Samozdrav simulator, rehabilitation after pneumonia will be successful, it will be quick and comfortable, and you will be able to regain your vital energy in a natural way - by training through correct and healthy breathing.
Vaccination against pneumococcus
The most common cause of pneumonia is streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). A vaccine has already been developed against it and is widely used, which protects a person against 23 of the most common strains of pneumococcus. According to WHO, vaccination reduces the risk of developing pneumonia caused by this microorganism by more than 90%. In 2014, the PCV vaccine (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) became part of the national vaccination calendar of the Russian Federation. Its effectiveness does not depend on age, so this vaccination is recommended for all those born before 2014.
Diagnostic tests
When visiting a medical facility, an adult patient is referred to a therapist. During the examination, the doctor observes the symmetry of breathing, conducts auscultation, and evaluates complaints. The presumptive diagnosis is confirmed by separate laboratory diagnostic procedures:
- clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examination of sputum;
- X-ray.
The images clearly show areas of the inflammatory process, and sampling of saliva makes it possible to identify the pathogen that has entered the body. Additional methods of diagnostic examination are prescribed by the therapist at his own discretion. The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the competence of the doctor and the availability of the necessary equipment in the clinic.
List of scientific literature used:
- Lai CC, Shih TP, Ko WC, Tang HJ, Hsueh PR Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. March, 2020, 55 (3): 105924.
- Marchello CS, Ebell MH, Dale AP, Harvill ET, Shen Y., Whalen CC Signs and Symptoms That Rule out Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Outpatient Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. April, 2022, 32 (2): 234–247.
- Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, Anzueto A, Brozek J, Crothers K, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults with Community-acquired Pneumonia. An Official Clinical Practice Guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. October, 2022, 200(7): e45–e67.
- Pneumonia. Mayo Clinic Staff. Patient Care & Health Information. Mayo Clinic. Last reviewed: August, 2, 2022.
- Who Is at Risk for Pneumonia? US Department of Health & Human Services. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Last reviewed: March 3, 2016.
- Pneumonia. News bulletin. World Health Organization. July 25, 2022.
- Chuchalin A.G., Sinopalnikov A.I., Kozlov R.S., Avdeev S.N., Tyurin I.E., Rudnov V.A., Rachina S.A., Fesenko O.V. Russian Respiratory Society (RRO). Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC). Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of severe community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Pulmonology. 2014, (4): 13-48.