Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
Delivery on Sundays and holidays does not work!
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2022 Pharmacy 84.
Papaverine
Papaverine (lat. Papaverinum) is a drug from the group of myotropic antispasmodics. Currently, it is used only in the form of hydrochloric acid salt (papaverine hydrochloride).
Reduces the tone and contractile activity of smooth muscles of blood vessels and internal organs.
Prescribed for spastic conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, bronchi, cerebral and peripheral circulatory disorders.
Thanks to long experience in use, it is one of the most studied drugs. Produced by various pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Story
It was discovered by chemistry student Heinrich Merck in 1848. The German isolated the new substance from opium - the milky juice of the soporific poppy (lat. Papaver Somniferum).
Based on its chemical structure, it was classified as an alkaloid. In 1910, A. Pictet was the first to synthesize papaverine artificially from veratraldehyde and hypuric acid. Around the same time, the alkaloid was discovered to have antispasmodic and vasodilating properties.
In 1913, the German physician J. Pahl introduced the drug into clinical practice, beginning to use it in patients with angina pectoris and bronchial asthma. Later it was used for spasms of the intestines, ureters and as an antihypertensive agent.
In 1930, the Hungarian corporation Chinon was the first in the world to begin producing the drug on an industrial scale. By the middle of the 20th century. the total number of papaverine manufacturing companies has grown to several dozen. In the 50s he now has a competitor - drotaverine (No-Shpa). In terms of antispasmodic properties, it turned out to be several times more active than its predecessor, so it has found wider use. However, in many countries it still remains a fairly popular medicine, both due to established traditions and due to its low cost.
We also recommend reading the article What drugs reduce blood pressure?
Properties
International nonproprietary name : papaverine. IUPAC chemical name : 1-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-6,7-dimethoxyisoquinoline hydrochloride. Gross formula : C20H21NO4 *HCl Molar mass : 375.85.
Papaverine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste and odorless. Melting point - 225ºС. It dissolves well in water, poorly in ethyl alcohol, chloroform, and diethyl ether. It is isolated from opium or obtained synthetically.
Research results
The first studies devoted to the study of its pharmacological activity were carried out by J. Pal in the 1910s. The scientist found that the drug has a toxic effect on lower organisms (amoebas, trypanosomes) comparable to morphine.
In higher animals, on the contrary, it exhibits significantly lower toxicity than morphine. For example, in rabbits, mild symptoms of poisoning occur only when the drug is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.25-0.30 mg per 1 kg of weight.
When treating patients with angina, Pahl noted that it had virtually no narcotic properties. In rare cases, the medication caused drowsiness, usually on the second day after use. Overdose phenomena occurred only after oral administration of the alkaloid in an amount of more than 400 mg.
In placebo-controlled clinical studies conducted in the second half of the 20th century, papaverine showed good effectiveness in the treatment of three groups of diseases:
- renal colic,
- gastrointestinal spasms,
- pathologies of the biliary tract.
According to tests, pronounced antispasmodic properties were noted on average by about 60% of patients. 23% described its effect as moderate or weak. In 17% no improvement was observed.
In separate clinical trials, the rationality of its use in patients with gastrointestinal ulcers was studied. It was found that taking a dose of 80 mg 3 times a day leads to a noticeable reduction in pain in 78% of patients.
Double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in the 1990s. confirmed the effectiveness of its use in intestinal disorders.
One Russian study involved 62 patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Volunteers in the experimental group took the drug 80 mg 3 times a day for 2 months.
The control group received a placebo. At the end of therapy, all subjects from the first population noted a decrease in the strength and frequency of pain. Whereas in the control group, patients complained of increased pain.
According to the results of the entire volume of clinical studies, it showed the greatest antispasmodic activity in the treatment of renal colic, gastrointestinal pain, cholelithiasis, and dysmenorrhea. Its use was least effective in patients with cerebrovascular disorders.
In all trials, the drug was well tolerated. Side effects occurred in no more than 0.5-3% of patients.
Application in different countries
It is approved for use in more than 50 countries, including Russia, Germany, France, Great Britain, USA and Japan. Various factories produce it under the trade names “Papaverine”, “Papaverine hydrochloride” or under their own brand names (for example, Paparin is produced in Taiwan, Atroveran in Venezuela, Mesotin in Argentina).
In most countries the alkaloid is recommended:
- to eliminate spasms of the digestive tract, biliary and urinary tracts,
- in complex therapy of cerebral and coronary circulatory disorders.
It was also approved in the US and Canada in 1986 as a treatment for erectile dysfunction in men*. However, after the invention of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis, etc.) it is practically not used for this purpose.
In Russia, it is included in the List of vital and essential drugs, approved by Order of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 2135-r dated December 30, 2009.
*In case of erectile dysfunction, the solution is injected intracavernosally (into the cavernous body of the penis). The positive effect is associated with relaxation of the trabeculae of the cavernous bodies and increased blood flow.
Composition and release forms
In Russia it is produced in the form:
- 2% (20 mg/ml) injection solution in ampoules of 2 ml,
- suppositories containing papaverine hydrochloride 20 mg,
- tablets containing papaverine hydrochloride 40 mg (for adults) and 10 mg (for children).
In some European countries (Switzerland, Great Britain) in pharmacies you can also find powders with it, packaged in 150 mg sachets, and 3% injection solutions.
Mechanism of action
It acts directly on the smooth muscles of internal organs and blood vessels, causing it to relax. Vasodilation leads to improved blood flow, including cerebral blood flow, and a decrease in blood pressure.
According to modern concepts, its antispasmodic effects are due to the blockade of the phosphodiesterase enzyme in the muscles, due to which cyclic 3,5-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) begins to accumulate in the cells. This leads to the release of calcium ions from the cells and a decrease in muscle contractile activity.
The relaxing properties of papaverine in relation to different organs are expressed differently. The colon undergoes the greatest relaxation, then in order of decreasing effect:
- duodenum,
- stomach, uterus,
- biliary and urinary tract, sphincter of Oddi,
- bronchi,
- vessels.
In high doses, it reduces myocardial excitability and slows intracardiac conduction.
It has virtually no effect on the central nervous system. The sedative effect appears only when consumed in doses above average therapeutic ones.
Its effectiveness decreases due to tobacco smoking.
Metabolism and excretion
When administered orally and rectally, it is quickly absorbed from the digestive tract. On average, up to 54% of the dose taken enters the bloodstream. In plasma, the drug is 90% protein bound.
The product is well distributed throughout the body. Passes through the blood-brain barrier. Biotransformed in the liver to inactive metabolites, which are excreted by renal filtration. The half-life is 0.5-2 hours (with kidney pathologies, this time can increase to 24 hours).
Indications for use
The reasons for its appointment are:
- spastic conditions of the abdominal organs (spastic colitis, cholecystitis, pylorospasm),
- renal colic,
- bronchospasm,
- spasm of peripheral (endarteritis) or cerebral vessels.
As an auxiliary medication, it is used to prepare patients for surgical interventions.
Previously, it was widely used to prevent angina attacks, but today more modern antianginal drugs are recommended for this purpose.
Contraindications
It is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- atrioventricular conduction disorders,
- comatose states,
- depression of respiratory functions,
- glaucoma,
- age up to 6 months. (for injection forms - up to 1 year),
- bronchial obstruction,
- severe liver dysfunction,
- inflammatory processes of the rectum (the limitation applies only to suppositories).
Due to the high risk of developing hyperthermia, it is not recommended for use in old age.
Pregnancy and lactation
No special studies have been conducted to prove its safety during pregnancy or lactation.
In Australia, it was assigned safety category A (safe for pregnant women), in the USA - category C (risks of exposure to the fetus cannot be excluded).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate complex machinery
After parenteral (especially intravenous) administration, you should avoid driving and engaging in hazardous activities for 1 hour.
Directions for use and doses
It is prescribed orally, rectally, subcutaneously, intramuscularly and intravenously.
Pills.
Adults are recommended to take 40-60 mg of papaverine 3-4 times a day. Single doses for children depend on age:
- children from 6 months. up to 2 years of age, 5 mg per dose is prescribed,
- from 3 to 4 years - 5-10 mg,
- from 5 to 6 years - 10 mg,
- from 7 to 9 years - 10-15 mg,
- from 10 to 14 years - 15-20 mg.
Dosage regimen: 1 dose 3-4 times a day.
Maximum permissible daily doses:
- for adults - 600 mg,
- for children from 6 months. up to one year - 10 mg, from 3 to 4 years - 20 mg, from 5 to 6 years - 40 mg, from 7 to 9 years - 60 mg, from 10 to 14 years - 200 mg.
Suppositories.
Adults: administer 1-2 soups. 2-3 times a day after spontaneous bowel movement or enema.
Injections.
Adults are administered subcutaneously and intramuscularly with 1-2 ml of ampoule solution (in terms of the active substance - 20-40 mg of papaverine hydrochloride).
Adults are administered intravenously 1 ml of the drug (or 20 mg of papaverine hydrochloride), which is pre-diluted with 10-20 ml of saline. The introduction is carried out slowly and under the supervision of a physician.
For elderly patients, the initial dose should not exceed 10 mg.
For children aged 1 to 12 years, the amount of medication is calculated based on body weight: 0.3 mg of papaverine per 1 kg of weight.
The maximum daily dose for adults when administered parenterally should not exceed 300 mg.
Side effects
With therapy they are possible:
- lowering blood pressure,
- dizziness,
- headache,
- weakness,
- drowsiness,
- atrioventricular block or ventricular extrasystole (risks increase with rapid intravenous administration of the drug),
- dyspeptic disorders (constipation, nausea),
- increased sweating,
- allergic reactions,
- eosinophilia,
- increased levels of liver transaminases.
When using suppositories, local negative reactions may be observed: a burning sensation or itching in the anal passage.
special instructions
During treatment you must stop drinking alcohol.
It should be used with caution in the elderly, in patients with hyperthyroidism, renal or hepatic failure, prostate adenoma, supraventricular tachycardia, severe heart disease, shock and traumatic brain injury.
Overdose
Poisoning is manifested by:
- general malaise,
- diplopia (double vision),
- increased sweating,
- headache,
- arrhythmia.
The condition is treated by gastric lavage and taking enterosorbents. If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy (adjust blood pressure).
Interaction with other drugs
It inhibits the effects of levodopa and dopegit.
Combination with barbiturates leads to a weakening of antispasmodic properties.
The effect of the alkaloid can be enhanced by:
- narcotic drugs,
- tranquilizers,
- analgesics,
- sedatives.
The hypotensive effect is potentiated by various antihypertensive drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, reserpine, quinidine, procainamide.
Due to the increased risk of arrhythmias, it is not recommended to combine it with adrenergic drugs.
Its activity is suppressed by nicotine.
Vacation conditions
Injections are available by prescription. Tablets and suppositories - without a prescription.
Storage
In a dry place, protected from light. Away from children. Tablets are stored at a temperature of 8 to 25ºС, solution for injection - at a temperature of 17-25ºС, suppositories - at a temperature of 8-15ºС.
In pharmacies and medical institutions, ampoules are stored according to the conditions of List B.
Best before date
Pills. 4 years.
Injection. 2 years.
Suppositories. 2-3 years (depending on the manufacturer).
Review of manufacturers
Products based on it are produced by a number of Russian and foreign enterprises.
Each company uses its own production technologies, so even identical dosage forms manufactured at different factories may differ from each other in the amount of impurities, composition of auxiliary components and physicochemical characteristics.
These differences may account for slight differences in the clinical effectiveness of the products.
In Russia, the following companies are registered and approved for sale of medicines containing it:
- JSC Pharmstandard,
- JSC Veropharm,
- OJSC Irbit Chemical and Pharmaceutical Plant,
- JSC Biokhimik,
- RUE Borisov Pharmaceutical Plant (Republic of Belarus),
- OJSC Novosibkhimpharm,
- JSC Biosintez,
- OJSC Nizhpharm,
- OJSC PFK Renewal,
- NPO FSUE Microgen,
- JSC Dalkhimfarm,
- JSC Moskhimfarmpreparaty im. Semashko,
- FSUE Armavir Biofactory,
- CJSC Medisorb.
The main production is concentrated in the Central, Siberian and Volga districts. Russian medicines are marketed under the trade names “Papaverine” and “Papaverine hydrochloride”.
Some foreign manufacturers:
| Trade name | Manufacturer | Countries in which it is registered |
| Papaverine Spofa | Spofa (Slovakia) | Slovakia, Czech Republic |
| Papaverine | Galen (Türkiye) | Türkiye, Taiwan |
| Papaverine hydrochloride Biosano | Biosano (Chile) | Chile |
| Papaverol | Cifsa (Ecuador) | Ecuador, Colombia |
| Para-Time | Time-Cap (USA) | USA, Canada |
| Papaverine Sopharma | Sofarma (Bulgaria) | Bulgaria |
| Papaverine hydrochloride | American Regent (USA) Bedford (USA) Eon (USA) United Research (USA) Hospira (New Zealand) Teva (Israel), etc. | Different countries |
Analogs
Other synthetic drugs and alkaloids have a similar antispasmodic effect:
- drotaverine,
- mebeverine,
- dibazole,
- hyoscine butyl bromide,
- bencyclane,
- theophylline.
Drotaverine and mebeverine are closest to it in chemical structure and mechanism of action. They similarly change the calcium content inside muscle cells, which leads to relaxation of internal organs.
However, in comparison with their predecessor, drotaverine and mebeverine exhibit stronger pharmacological activity. In addition, they differ in the range of side effects and contraindications.
Comparative characteristics of papaverine, drotaverine and mebeverine:
| Active substance | Some trade names and manufacturers | Release forms | Main indications for use | Adverse reactions | Contraindications |
| Papaverine hydrochloride | Papaverine hydrochloride and Papaverine (more than 100 different manufacturers | Tablets 10 and 40 mgSuppositories 20 mg2% solution for injection | Spastic conditions of the digestive tract, renal colic, vascular spasms, bronchospasms. | Rarely: hypotension, drowsiness, constipation, allergic reactions, heart rhythm disturbances. | Liver failure, glaucoma, age up to 6 months, atrioventricular block, allergic reaction to the components of the drug. |
| Drotaverine hydrochloride | No-Shpa (Chinoin Pharmaceutical and Chemical Works Co., Hungary) Vero-Drotaverin (Veropharm, ) Drotaverin-Teva (Teva, Israel) Drotaverin (Alsi Pharma, Biokhimik, Moskhimfarmpreparaty, etc., ) | Tablets and capsules of 40 and 80 mg 2% solution for injection | Spasms of smooth muscles of the urinary and biliary tract. As an auxiliary therapy - for gastrointestinal spasms and gynecological diseases. | Rarely or very rarely: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, allergic reactions. | Hypersensitivity, renal, hepatic or heart failure. |
| Mebeverine hydrochloride | Duspatalin (Solvay Pharmaceuticals, Netherlands), Niaspam (SUN Pharmaceutikal Industries Ltd, India), Sparex (Canonpharma, ) | Capsules 200 mg | Spasms of the digestive tract, including those associated with organic diseases. | Very rare: allergic reactions. | Age under 18 years, pregnancy, allergy to the components of the drug. |
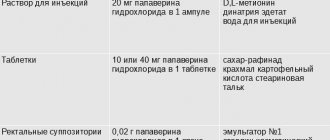
Compound
Injection:
- papaverine hydrochloride - 20 mg per 1 ml of medicinal liquid;
- D,L-methionine;
- disodium edetate;
- water for injections.
Pills:
- papaverine hydrochloride - 10 mg in 1 tablet;
- rafinated sugar;
- potato starch;
- stearic acid;
- talc.
Rectal suppositories:
- papaverine hydrochloride - 0.02 g in 1 suppository weighing 1.25 g;
- emulsifier No. 1;
- cosmetic stearin;
- hard fat.
Side effects
- From the cardiovascular system and blood: atrioventricular block , ventricular tachycardia , decreased blood pressure .
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea , constipation ( constipation ), bloating , impaired passage through the digestive tube, increased activity of liver transaminases.
- Others: drowsiness , allergic reactions , eosinophilia .