SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Emergency contraception (“emergency” or “fire”, English “emergency contraception”) are drugs and methods that allow a woman to avoid pregnancy within 48 - 72 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse.
Girls may urgently need such contraceptive “pills after intercourse” or other means in different situations: after interrupted intercourse, in cases where the condom breaks, or you forget to take birth control pills, as well as after rape, sloppy petting or careless anal sex. Next, we will consider two conceptual questions that will help to better and more fully reveal the topic of the article, namely:
1) is it possible to get pregnant (after or during menstruation, a virgin from lubrication or without sex or penetration at all) and 2) how can a girl avoid becoming pregnant when this is not part of her plans; what means and methods of emergency contraception will help her in the next two to three days.
So, everything is in order.
Emergency contraception is a one-time contraception that cannot be used continuously.
1) Antigestagenic drugs Ginepriston or Agest are a modern hormonal postcoital drug. Compared to Postinor, it is almost harmless. Used within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse.
2) Progestin drugs Escapelle are a new means for emergency contraception. Recommended for use within 96 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse. The earlier the pill is taken, the more effective its effect.
How to avoid pregnancy
A brief overview of the scientific facts about emergency contraception:
- You need to take the emergency pill within 3 days/72 hours (Postinor, Escapelle) or 5 days/120 hours (Zhenale, Gynepriston) after unprotected sex for them to be effective. The sooner you take them, the better the result will be (maximum - up to 95.7%).
- The IUD can be inserted up to 5 days after unprotected intercourse or up to 5 days after the earliest period of ovulation.
- When taking 72-hour birth control pills, be aware that they may give you a headache or stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting.
- The emergency contraceptive pill may make your next menstrual period earlier, later, or significantly more painful than usual.
- In case of vomiting within 2 hours after taking Postinor, Escapel or within 3 hours after taking Zhenale, Ginepristone, consult a doctor, as you will need to take a new dose of the drug or install a spiral.
- If these methods do not work and an unplanned conception does occur, it is possible to solve the problem in the early stages through a medical abortion in a clinic.
The main methods of protection in emergency cases in reproductive medicine are: copper-containing intrauterine devices (IUDs) and pills (ECP, “72 hours after”). Gynecologists consider “copper” IUDs to be the most effective form of emergency contraception. It prevents fertilization by causing a chemical change in the structure of sperm and eggs before they meet, as well as shifts in the structure of the endometrium, preventing the implantation of a fertilized egg. Of the “after-act” pills, the best are those that contain mifepristone (Zhenale, etc.).
⚠ We recommend that you consult with a gynecologist-endocrinologist at our clinic or anyone else at your request about the possibility of using these funds and what would be better specifically in your case.
Emergency contraceptive pills
Drugs for “fire” cases save from pregnancy by preventing or delaying ovulation, but do not cause abortion. At the same time, even the best emergency contraception cannot terminate an existing pregnancy or harm a developing embryo.
Of the tablets taken within 72 hours after the act, the leading role belongs to 3 groups:
- Postinor and Escapel (contain levonorgestrel);
- Zhenale and Ginepristone (containing mifepristone);
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) consisting of ethinyl estradiol plus levonorgestrel.
How often and how much can you take emergency contraception?
Some women use pregnancy pills repeatedly after intercourse for any of the above reasons or as a primary method of contraception. In such situations, further counseling of the patient is necessary regarding which options for regular contraception may be suitable for her.
Repeated use of the 72 hour pill may be harmful to women. When used frequently, they can lead to increased side effects such as menstrual irregularities, although their repeated use poses no known health risks for many. Even the best emergency contraceptive pills have been found to be less effective in obese women, but there are no safety concerns. Obese women cannot be denied this method when they really need it.
Considering the rather significant impact of such drugs (especially Postinor and Escapella) on hormonal levels and the functioning of the uterus and ovaries, it would be useful to carry out some preventive measures aimed at normalizing and stabilizing the activity of these organs. We suggest paying attention to a procedure such as massage of the appendages and uterus, which has a number of advantages and allows you to achieve the desired effect without taking hormones and other medications. This will make it possible in the future to avoid ectopic and frozen pregnancies, other early and late complications when carrying a child (preeclampsia, ICI, threat of miscarriage and fetal hypoxia).
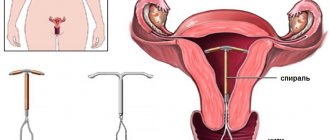
IUD for pregnancy
The second effective means of emergency contraception is the IUD. How does the IUD work as protection against pregnancy after intercourse?
An intrauterine device is a small T-shaped plastic and copper medical device that a gynecologist inserts into the uterus (womb). It releases copper to stop the egg from implanting in the uterus or fertilization.
For emergency protection, an IUD can be inserted up to 5 days after unprotected sex or up to 120 hours after the earliest time you could ovulate (release an egg) to prevent an unwanted pregnancy. You can also keep it as a permanent method of contraception. A copper IUD should not be inserted after sexual assault because the woman may be at high risk of sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea.
How effective is an IUD in preventing pregnancy? Inserting the IUD into the uterus within the recommended time frame is a highly effective method of emergency contraception—less than 1% of women using it become pregnant. This product is more effective at preventing unwanted pregnancy after unprotected sex than the “after-coital birth control pill.”
Who can use an IUD? Most women can use this technique if desired and there are no contraindications. However, the method may not work if you have:
- untreated sexually transmitted infection (STI) or pelvic infection,
- problems with the uterus or cervix,
- unexplained bleeding between periods or after sex,
- you are pregnant,
- There is a risk that you may already be pregnant.
The product is safe during breastfeeding - its use in emergency cases will not affect milk supply and lactation.
Postinor
Postinor is a hormonal drug for emergency contraception from the “last century”. The earlier the pill was taken, the more pronounced the contraceptive effect. Postinor contains a very high dose of the hormone levonorgestrel, which has a very noticeable impact on the ovaries. Therefore, after using the drug, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted. This drug should not be used more than 2 times a year and should not be considered as one of the possible contraceptives. This especially applies to young women under 18 years of age, whose hormonal balance has not yet been established.
After emergency contraception
- the next menstruation may begin earlier or later than usual; — menstrual flow may be more abundant, in which case you should consult a doctor; - be sure to contact a gynecologist before the start of your next menstruation to be examined for sexually transmitted infections; at the appointment, tell them that you used emergency contraception; - if three weeks after taking emergency contraception you have not started menstruation or have signs of pregnancy, immediately visit a gynecologist; — until the next menstruation, it is necessary to use barrier methods (condom).
Contraindications for the use of emergency contraception
- thromboembolism and uterine bleeding in the past; - severe liver diseases; - severe attack of headache (migraine); — age over 35 years; - long history of smoking.
What you need to buy in different countries
In most countries, birth control and abortion pills are sold strictly by prescription. Therefore, in such a situation you will have to come to the doctor for a prescription. For example, in Italy, in October 2022, AIFA (Italian Medicines Agency) gave the green light to the sale of a 5-day tablet even to those under 18 years of age, eliminating the requirement to present a prescription.
In this country, the “five day pill” can be purchased directly from the pharmacy, since the drug ulipristal acetate is available without a prescription. But the purchase of the drug is accompanied by a booklet and instructions from the pharmacist in order to prevent the inappropriate use of emergency contraception. At the same time, a package of ellaOne® containing a 30 milligram tablet of ulipristal acetate is not cheap - approximately 26 - 30 euros.
But a drug based on levonorgestrel (the active ingredient of the morning-after pill), even in Italy, can only be purchased with a prescription from a gynecologist. It will not be sold without a doctor's prescription for any money.
Gynecologist's prescription for emergency contraception
Previously, it was possible to purchase such contraceptives only upon presentation of a valid document proving identity and age, and only after a mandatory pregnancy test with a negative result for beta-hCG.
If you have an emergency or difficulty purchasing an emergency contraceptive pill, in most countries you can also go to a public health centre, health service or emergency department.
Note. Emergency contraception offers women an additional choice. The pharmacist or health care worker is required to provide all the information so that the patient can receive the medicine and take it on time, but the entire responsibility for taking the pills lies with the patient herself.
WHO recommendations for the provision of emergency contraception
All women and girls at risk of unwanted pregnancy have the right to access emergency contraception methods, and these methods should be routinely included in all national family planning programmes. In addition, emergency contraception should be included in health services for populations most at risk of unprotected sex, including services and care for women and girls who have survived sexual violence and living in humanitarian emergencies.
- Ensuring human rights in contraception programs: analyzing existing quantitative indicators from a human rights perspective - in English
WHO reaffirms its commitment to carefully review emerging evidence through its Continuous Evidence Identification (CIRE) System and to regularly update its recommendations accordingly.
- (1) Can we identify women at risk of pregnancy despite using emergency contraception? Data from randomized trials of ulipristal acetate and levonorgestrel. Glasier A, Cameron ST, Blithe D, Scherrer B, Mathe H, Levy D, et al. Contraception. 2011 Oct;84(4):363-7. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.02.009. Epub 2011 Apr 2.
- (2) Effect of BMI and body weight on pregnancy rates with LNG as emergency contraception: analysis of four WHO HRP studies. Festin MP, Peregoudov A, Seuc A, Kiarie J, Temmerman M. Contraception. 2022 Jan;95(1):50-54. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 12.
- (3) Family planning: a comprehensive guide for service providers Institute of Public Health. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg/Center for Information Programs and World Health Organization
Transition to permanent contraception
After using ECPs, a woman or girl can return to or start using a permanent method of contraception. If a copper-containing IUD is used for emergency contraception, then additional contraceptive protection is not required.
After taking levonorgestrel-containing ECPs (LNG) or combined oral contraceptive pills (COCs), women or girls can resume their current method of contraception or start using a method, including a copper-containing IUD.
After using ECPs with ulipristal acetate (UPA), women or girls can continue or start using any progestogen-containing product (combined hormonal contraception or progestogen-only contraceptives) on the sixth day after taking UPA. They can immediately receive an IUD with LNG if it can be established that they are not pregnant. They can immediately receive a copper-containing IUD.
When not to drink?
You should not take the pill the next day if:
- You know or suspect that you are pregnant. If there is a delay in menstruation or other symptoms. You must take a pregnancy test.
- History of allergy or hypersensitivity to its ingredients.
- There is a recent history of abnormal or vaginal bleeding for which the cause has not yet been identified.
- Some of the medications listed in the instructions for use have been used and may reduce the effectiveness of emergency contraception.
Many women use this form of emergency contraception without experiencing any serious side effects.
Possible side effects:
- nausea;
- pain and discomfort in the abdomen;
- fatigue;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- back or muscle pain;
- menstrual changes;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- mood swings;
- vomit.
If you start vomiting within three hours of taking the medicine, take another tablet immediately.
In addition, it is possible that before the expected menstruation there is rare bleeding with an average duration of two to four days. In this case, the effects of the pill make it more or less painful than usual.
Most women experience their period seven days earlier or later than expected.
If there is a significant delay in menstruation, it is necessary to take a pregnancy test.
Side effects and risks after taking the “5 days later pill”?
As with all hormonal medications, after taking the “after 5 day pill” there is a possibility that side effects such as spotting, headache, nausea may occur relatively frequently. Patients experience vomiting, mood swings, lower abdominal pain and a feeling of exhaustion. These effects usually subside within 48 hours of taking the tablet and are almost always minor.
Headache
In addition, during the month of use, disturbances in the next menstrual cycle may occur - delays or delays, painful or prolonged periods, irritation or discharge from the vagina, decreased or increased libido, heavier discharge, etc.
Other side effects for this type of medication are less common (1/100) and include chest tenderness, muscle pain, dizziness, diarrhea, and hot flashes.
During clinical trials conducted before marketing the drug, no side effects were found that could stop the trial. Thus, overall, the 5-day pill is well tolerated and effective, but remains an emergency intervention that cannot be used routinely.
In what cases should you not use 72 hour tablets?
The main indication for using 72-hour birth control pills is to prevent pregnancy. They are not suitable for abortion; contraceptives cannot cause an abortion after implantation of the embryo. Contraceptives with levonorgestrel are contraindicated for:
- pregnancy;
- allergies to any component of the drug;
- severe liver failure;
- some hereditary diseases associated with lactase deficiency;
- malabsorption syndrome.
Mifepristone should not be used in the following conditions:
- early ectopic pregnancy;
- long-term treatment with corticosteroids;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- anemia and blood clotting pathology.
Can be used with caution for bronchial asthma, hypertension and heart failure.
Important!
The “pill after 5 days” should be used exclusively as a method of emergency contraception and only in emergency cases. This drug should not be an alternative to classical contraceptives, especially since there are cheap and safe ways to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
[contact-form-7 id=”296" title=”Untitled”]
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 3,300 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
Review of emergency contraceptives 72 hours
The pills, which are used to prevent conception after sexual intercourse, can be purchased without a doctor's prescription. They can be used by women of fertile age over 18 years of age. Such hormonal drugs are not recommended for adolescents.
№1 Postinor
A progestogen drug for immediate protection, which includes a single dose of 0.75 mg levonorgestrel. The Postinor blister contains 2 tablets, which are divided into 2 doses . You can take the entire dose at one time if the woman is in the middle of her menstrual cycle and there is no high probability of ovulation within a few hours after sex. The cost of a pack is 310-342 rubles.
No. 2 Escapelle
The drug Escapel contains the active ingredient levonogrestrel, but in an increased dose of 1.5 mg. For contraception, one tablet is taken, which cannot be divided or crushed. Repeated administration of the medicine is required only in case of vomiting in the next 2-3 hours. Price 382-406 rub.
Attention! A large dosage of the hormone increases the likelihood of adverse reactions. Levonorgestrel in such quantities may exhibit weak androgenic properties.
No. 3 Genale
Zhenale birth control pills are based on mifepristone. A single dose is 10 mg. It is enough to increase myometrial contractility and prevent implantation of the fertilized egg. But as the dose increases, the risk of adverse reactions increases. To terminate pregnancy, analogues of Zhenale are used, but with a concentration of the active substance 60 times higher. The average price of emergency contraception is 450 rubles.
No. 4 Eskinor-F
The package contains 2 tablets based on levonogrestrel. It is recommended to use them no more than once during the cycle. But emergency contraception does not replace the subsequent use of condoms.
Eskinor-F, like other drugs in its group, can cause intermenstrual bleeding and cycle disruption. Therefore, it is better to resort to this method of protection against pregnancy as a last resort. The cost of tablets is on average 350 rubles.
No. 5 Gynepriston
Tablets with mifepristone in a dosage of 0.01 g. Prevent implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall.
It is recommended to take them 2 hours before meals or 2 hours before meals to increase the contraceptive effect. The package can contain 1 or 2 tablets. Women who have had more than 24 hours after unprotected sex, or who are in the middle of their menstrual cycle, should take a double dose.
No. 6 Modell 911
Levonorgestrel tablet at a dose of 1.5 mg, the package contains 1 piece. Research shows that this drug is highly effective and helps prevent pregnancy in 84% of cases. If you use 2 tablets of 0.75 mg with an interval of 12 hours, the chances of not getting pregnant are reduced to 79%. The cost of packaging is about 400 rubles.