A pharmaceutical preparation for topical use restores the natural tear film of the conjunctiva of the eyes, prevents them from drying out, eliminates pain, fatigue and physical discomfort. Thealosis should be on hand for everyone who uses a computer, wears ophthalmic contact lenses, or experiences periodic vision difficulties.
Composition and dosage form
The artificial tear preparation is a transparent liquid gel without color or odor. Packaged in plastic bottles with 10 ml drip dispensers. Thealose contains the disaccharide trehalose as its main component. Its share in the pharmaceutical solution is 3%. This substance has a moisturizing effect, protects the cornea from damage by dust particles, reduces increased sensitivity to light, prevents redness of the whites, and the development of dry eye syndrome.
Thealoz Duo drops also contain hyaluronic acid, a natural humectant that retains water molecules and maintains its concentration in tissues.
Additional components of the drug: distilled water, sodium salts, stabilizers. The drug bottle dispenser of the AVAC system has an antibacterial filter that prevents harmful microorganisms from entering the solution even when in contact with contaminated surfaces.
Mechanism of action
Thealoz is an isotonic solution with a neutral acid-base level, close in structure and composition to natural tear fluid. Upon contact with the mucous membrane of the eye, the drops are distributed over its surface and cornea, replenishing moisture deficiency and eliminating its main symptoms:
- itching;
- feeling of sand in the eyes when blinking;
- dryness, burning;
- redness;
- fatigue;
- visual disturbances: blurred contours of surrounding objects.
Thealoz Duo has more pronounced protective properties, since the hyaluronic acid in its composition retains moisture longer and has an anti-inflammatory effect. The drug provides long-lasting comfort during visual stress, eliminates the effects of adverse factors: wind, dust, smoke, sun. Protects against irritation from contact lenses, helps restore normal microcirculation and tissue nutrition.
It has been proven that Thealose protects the eyes from ultraviolet solar radiation, prevents the loss of water from deep layers of tissue, and has some antioxidant properties, as it prevents lipid peroxidation. The drug also protects the cornea from mechanical damage and burns.
After administration, the effect of the drug lasts for 6–8 hours. The components of the drops are not absorbed into the general bloodstream, descending through the lacrimal canals into the nasal cavity.
Material and methods
All patients were informed about an open study of the effectiveness and tolerability of the medical device Thealoz for the treatment of dry eye syndrome after laser keratorefractive surgery. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (WMA Declaration of Helsinki - Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects, 2013).
Patients were selected based on inclusion criteria, which were planned keratorefractive laser surgery for moderate myopia, astigmatism, or a combination of these conditions; constant wearing of contact lenses over the past 2 years; age from 20 to 35 years; corneal thickness equal to or greater than 480 µm; the patient's ability to understand the study and sign informed consent.
Exclusion criteria from the study were the presence of conjunctivitis, keratitis, glaucoma, cataracts, blepharitis, eyelid anomalies, severe DES, keratoconus, or any other pathology that is a contraindication for refractive surgery; individual drug intolerance to drugs planned for use in the study; history of use of any other ophthalmic agents 1 month before the planned examination and surgical interventions on the eyeball, including laser; any clinical condition that will not allow the study protocol to be safely completed without risk to the patient's health will either affect the results of the study or complicate participation in this study; the only seeing eye; for women - pregnancy, breastfeeding; lack of reliable methods of contraception for women of childbearing age; alcohol and drug abuse; simultaneous participation in other clinical trials using drugs or participation in such trials within the last 30 days.
We observed 20 patients (40 eyes) aged 21 to 35 years who underwent laser vision correction for moderate myopia (10 women, 10 men). The patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the type of surgical intervention:
Group 1 consisted of 10 people (20 eyes) who underwent refractive surgery ReLEx SMILE; Group 2 included 10 people (20 eyes) who underwent refractive surgery FEMTO LASIK.
In the postoperative period, in addition to the instillation of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs (ofloxacin 4 times a day, dexamethasone 4 times a day for 10 days), the drug Thealoz was used as a tear substitute in the form of instillations 4 times a day for 3 months.
All patients before and after surgery underwent a standard ophthalmological examination, which included autorefractometry, visometry, pneumometry, biomicroscopy, ophthalmoscopy, keratotoprography, and pachymetry.
To diagnose dry eye syndrome and assess its course, we examined the stability of the tear film (Norn test), measured the height and depth of the tear meniscus (OCT meniscometry), and determined the osmolarity of the tear fluid.
Instrumental monitoring of the condition of the ocular surface was carried out 1 and 3 months after surgery.
To evaluate the Norn test, ophthalmic strips with sodium fluorescein USP, Ophtolic-test (India) were used, the standard method was used.
The osmolarity of tear fluid was determined using the TearLab Osmolarity System device (TearLab Corp., San Diego, USA), which implements an innovative approach to the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome in vivo
- “lab on a chip.” This method of measuring tear osmolarity is safe, least invasive, and does not affect the volume of tear fluid and the time of tear film rupture; For the analysis, disposable consumables were used to collect 50 nl of tear fluid from the lower meniscus. Normally, tear osmolarity ranges from 275 to 316 mOsm/L [20].
Lacrimal meniscometry was performed using an RT-Vue-100−2 optical coherence tomograph (Optovue, USA). The study conditions were standardized; on the resulting image of the lower tear meniscus at the lowest point, 2 conventional values were determined: the height of the tear meniscus - the largest segment drawn from the point of contact of the tear fluid with the cornea to the point of contact of the tear fluid with the edge of the eyelid; depth - a segment drawn from the point of contact of the cornea and the edge of the eyelid to the middle of the tear-air interface (D. Park et al., 2011) [21].
The indicators of the Norn test, osmolarity and OCT meniscometry in the studied groups of patients before refractive surgery are presented in Table. 1.
Table 1. Instrumental indicators of the condition of the ocular surface before refractive surgery (M±σ)
All patients underwent excimer laser correction using a Visumax laser unit (Carl Zeiss, Germany). Surgical interventions were performed by 2 surgeons of the highest qualification category with extensive experience in the field of refractive surgery using standard technology.
The operations and postoperative period in all patients proceeded without complications.
The indicators obtained during the clinical study were entered into a Microsoft Excel database. Statistical processing of the results was performed using nonparametric statistical tests (Wilcoxon test was used to analyze the data obtained within each study group) of the Statistica 10.0 program, version 10.0 (StatSoft, Inc., USA). Results with a significance level equal to or less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant differences.
During a biomicroscopic examination the day after surgery, in all patients the cornea was transparent, the edges of the flap (FEMTO LASIK) and incision (ReLEx SMILE) were adapted, and a slight injection of conjunctival vessels was noted.
All patients experienced a decrease in symptoms of discomfort while using the drug Thealoz.
The dynamics of the Norn test data of the studied groups are presented in Table. 2.
Table 2. Dynamics of Norn test parameters in patients of the study groups after treatment (M±σ) Note. Here and in the table. 3, 4: * — p≤0.05 compared with preoperative values.
Analysis of the dynamics of the Norn test indices in the postoperative period indicates that when using both methods of laser exposure, the tear film rupture time significantly increases from 11.16 ± 0.38 s to 12.95 ± 0.24 ( p
≤0.05) and 13.85±0.03 (
p
≤0.05) s by the 1st and 3rd months of treatment, respectively.
Moreover, in the group of patients who used the drug Thealoz after ReLEx SMILE surgery, the average value of the Norn test significantly increased and amounted to 13.12±1.14 s after 1 month and 13.87±0.88 s after 3 months. In the group of patients operated on using the FEMTO LASIK method, these indicators also significantly increased compared to the initial values and amounted to 12.78±1.59 and 13.83±0.85, respectively ( p
≤0.05). The increase in tear film stability time with this tear film is likely due to its positive effect on conjunctival goblet cells and, consequently, on the mucin layer of the tear film.
Our results are confirmed in a number of clinical studies by other authors, who have shown that the use of the drug Thealoz contributes to a statistically significant increase in the stability of the tear film after keratorefractive operations: photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), trans-PRK and laser keratomileusis [22-24].
We did not establish statistically significant differences in Norn test performance between groups.
OCT meniscometry for diagnosing and assessing the course of dry eye syndrome is often used in clinical practice. According to O.S. Lobanova, A.V. Zolotareva, A.N. Volobueva (2010), the sensitivity and specificity of this method are estimated at 97.5 and 66.6%; the use of this method for dry eye syndrome of various origins is reflected in individual domestic and foreign studies [25-27].
The results of monitoring the condition of the inferior tear meniscus according to optical coherence tomography (OCT), obtained in the study, are presented in table. 3, out
Table 3. Dynamics of OCT meniscometry indices in patients of the study groups after treatment (M±σ), which shows that with the use of the drug Thealoz, the height of the tear meniscus statistically significantly increased from 310.89±9.66 to 322.66±5.18 µm and its depth from 217.72±1.65 to 227.63±0.28 µm.
Similar changes in the direction of increasing the depth and height of the tear meniscus in comparison with the initial data were also observed within the study groups ( p
≤0.05).
The results obtained clearly demonstrate both the possibility of using OCT in assessing the parameters of the lower tear meniscus (height and depth) in patients after excimer laser vision correction, and the effectiveness of using trehalose in the correction of dry eye syndrome in the postoperative period.
According to Dry Eye Workshop II, dry eye syndrome is a symptomatic disease characterized by a vicious cycle of tear film instability and hyperosmolarity, which leads to increased ocular surface inflammation, damage, and neurosensory changes [28].
According to a number of authors, changes in osmolarity parameters have been confirmed during keratorefractive interventions - FEMTO LASIK and ReLEx SMILE [26, 29].
The results of the tear fluid osmolarity test after refractive surgery are shown in Table. 4.
Table 4. Dynamics of tear osmolarity in patients of the study groups after treatment (M±σ)
As can be seen from table. 4, osmolarity values progressively decreased 1 and 3 months after treatment in comparison with the initial values of 317.29 ± 1.39 and amounted to 308.00 ± 0.79 and 301.75 ± 0.27 mOsm/l, respectively ( p
≤0.05). Similar significant changes in osmolarity parameters occurred within both groups (positive shifts towards a decrease in the osmolarity of tear fluid), which indicates the osmoprotective effect of the drug Thealoz. This effect of trehalose is based on the interaction of its components with membrane lipids, which provides significant protection against injury during surgery, increased osmolarity and leads to a lower incidence of inflammation and cell death.
According to experimental studies, the presence of trehalose provides resistance to desiccation of bacterial cells and human cell cultures due to the stabilization of lipids and proteins of the cell membrane [14, 18, 30, 31]. Positive changes towards a decrease in osmolarity with the use of the drug Thealoz after excimer laser interventions (FEMTO LASIK) were also obtained in the works of A. Mateo et al. [24].
As a clinical example demonstrating the effectiveness of the use of the drug Thealoz in correcting the manifestations of dry eye syndrome after keratorefractive surgery, we present the following observation.
Clinical case
Patient N.
A 27-year-old woman complained of poor distance vision. He has a history of moderate myopia in both eyes since the age of 15, and constantly uses contact lenses.
Visual acuity at the time of treatment was OD 0.2 sph –4.5 diopters = 1.0 and OS 0.15 sph –4.0 diopters = 1.0.
Biomicroscopy of both corneas revealed no pathological changes, the anterior chamber is of medium depth, the moisture is transparent, the iris is unchanged in structure and color, the pupil is round, 3 mm in diameter, in the center, reactions to light are preserved. The lens and vitreous body are transparent. The fundus showed no gross visible pathology.
Assessment of the condition of the ocular surface: the Norn test was 11 and 10 s, the osmolarity of the tear fluid was 316 and 314 mOsm/l; OCT meniscometry: height - 304 and 300 µm, depth - 216 and 212 µm in the right and left eyes, respectively.
Diagnosis: Moderate myopia in both eyes. Mild dry eye syndrome.
The patient underwent excimer laser vision correction in both eyes using the ReLEx SMILE method. No intra- or postoperative complications were observed.
The examination was carried out within the established observation period in accordance with the study protocol.
In the postoperative period, the cornea is transparent, shiny, sensitivity is preserved, and the incision edges are adapted.
Visual acuity on the 2nd day after surgery: OD 1.0 and OS 1.0.
In table 5 presented
Table 5. Dynamics of indicators of the Norn test, tear osmolarity and OCT meniscometry in the patient after treatment, instrumental indicators of the condition of the ocular surface after keratorefractive intervention while using the drug Thealoz.
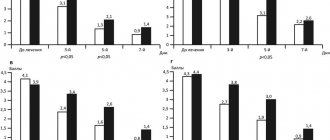
On the image
Dynamics of changes in OCT meniscometry indicators before surgery (a), after 1 (b) and 3 (c) months.
The depth of the tear meniscus is 216 µm, the height is 304 µm, after treatment after 1 month - 221 and 313, after 3 months - 227 and 319 µm, respectively. The results of lacrimal meniscometry of patient N.
before and after treatment.
This clinical example clearly demonstrates the increase in tear film breakup time, the positive dynamics of tear osmolarity in the form of their decrease and the increase in OCT meniscometry indicators: depth and height with the use of the drug Thealoz after keratorefractive surgery of the Smile type.
How to use Thealoz
Both versions of the drug: Thealoz and Thealoz Duo have general recommendations for use:
- Before contacting the bottle, you must wash your hands;
- instill the solution 1-2 times into each eye, behind the lower eyelid, slightly lifting the head up;
- Do not touch the tip of the bottle to your eyes when administering the solution;
- after administering the drug, it is advisable to avoid tilting your head down for a few seconds so that the artificial tear is evenly distributed;
- The bottle must be screwed on tightly after use.
The procedure must be repeated 2–6 times a day. When wearing lenses, you should moisturize your eyes after putting them on and after taking them off. If other pharmaceuticals are required to be instilled, Thealoz should be administered last, 20–30 minutes after the drug. After opening, the drops should be stored in the refrigerator.
Indications for use
Thealosis is used for the following conditions:
- the appearance of discomfort in the eyes: dryness, itching, burning, feeling of sand;
- with increased fatigue when working at a computer, watching TV and other visual stress;
- when wearing contact lenses to prevent dry eye syndrome;
- when the organs of vision are exposed to smoke, wind, sunlight;
- in complex therapy of conjunctivitis, keratitis and other diseases of the mucous membranes of the eyes, including: damage by viruses, fungi and pathogenic bacteria.
Drops are also necessary to prevent drying of the eyes during various ophthalmological procedures, after using a laser for diagnostic and corrective purposes. When wearing lenses and after laser vision correction, it is optimal to choose the drug Thealoz Duo with hyaluronic acid; it has a long-lasting moisturizing and protective effect.