Compound
The injection solution contains sodium heparin at a concentration of 5 thousand units/ml.
The auxiliary components of the drug include sodium chloride, benzyl alcohol, and water. 1 gram of gel contains 1 thousand units of sodium heparin , as well as auxiliary components: 96% ethanol, carbomer , dimethyl sulfoxide, propylene glycol, dietanolamine, methyl and propylparaben (additives E 218, E 216), lavender oil and purified water.
Literature:
- Drugs: properties, action, pharmacokinetics, metabolism: textbook / N. V. Veselovskaya [etc.]. — 3rd ed., revised, corrected. and additional - Moscow: Narkonet, 2008. - 262 p.
- Psychotropic drugs: reference book. practicing doctor / [F. Bochner et al.] ; scientific ed. rus. ed. Yu. A. Alexandrovsky; lane English A. N. Redkin. - Moscow: Litterra Publishing House, 2006. - 292 p.
- Guide to addictionology / Axelrod B. A. et al.; edited by V. D. Mendelevich. - St. Petersburg: Rech, 2007. - 766 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group: anticoagulants .
Group of the drug Heparin, produced in the form of a gel: drugs for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Group of the drug Heparin, produced in injection form: agents affecting blood and hematopoiesis.
Heparin sodium contained in the drug has an antithrombotic effect , slows down the aggregation and adhesion of leukocytes , platelets and erythrocytes ; reduces wall spasm and the degree of vascular permeability; helps improve collateral circulation.
What can be replaced
An analogue of Heparin is also a solution of a drug, but from a different production.
The following solution analogues exist:
- Sodium Brown.
- Richter.
- Frayn.
The use of these funds should be carried out after consultation with a specialist.
Thus, Heparin is a good drug for thinning the blood and preventing the development of blood clots inside blood vessels. However, during its use it is necessary to carefully monitor blood clotting parameters and follow the chosen therapeutic course.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
What is Heparin?
Heparin (INN: Heparin) is an acidic mucopolysaccharide with Mr about 16 kDa. A direct anticoagulant that helps slow down the formation of fibrin .
The gross formula of heparin is C12H19NO20S3.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of heparin is based primarily on its binding to AT III (its plasma cofactor). Being a physiological anticoagulant , it potentiates the ability of AT III to suppress activated coagulation factors (in particular, IXa, Xa, XIa, XIIa).
When used in high concentrations, heparin also inhibits thrombin activity .
Suppresses activated factor X, which is involved in the internal and external blood coagulation system.
The effect occurs when significantly lower doses of heparin are used than are required to inhibit the activity of coagulation factor II ( thrombin ), which promotes the formation of fibrin from the plasma protein fibrinogen .
This justifies the possibility of using small doses of heparin (subcutaneously) for prophylactic purposes, and large doses for treatment.
Heparin is not a fibrinolytic (i.e., it is capable of dissolving blood clots), but it can reduce the size of the blood clot and stop its expansion. Thus, the blood clot is partially dissolved under the action of fibrinolytic enzymes of natural origin.
Suppresses the activity of the enzyme hyaluronidase, helps reduce the activity of surfactant in the lungs.
Reduces the risk of developing MI, acute thrombosis of myocardial arteries and sudden death. In small doses it is effective for the prevention of VTE, in high doses it is effective against venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism .
Deficiency of AT III at the site of thrombosis or plasma may reduce the antithrombotic effect of the drug
When applied externally, the product has a local antiexudative , antithrombotic and moderate anti-inflammatory effect .
Promotes the activation of fibrinolytic properties of blood, inhibits the activity of hyaluronidase, and blocks the formation of thrombin. Gradually released from the gel and passing through the skin, heparin helps reduce inflammation and has an antithrombotic effect .
At the same time, the patient’s microcirculation improves and tissue metabolism is activated and, as a result, the processes of resorption of blood clots and hematomas are accelerated, and tissue swelling is reduced.
Pharmacokinetics
When used externally, absorption is negligible.
After injection under the skin, TCmax is 4-5 hours. Up to 95% of the substance is in a state bound to plasma proteins, Vp - 0.06 l/kg (the substance does not leave the vascular bed due to strong binding to plasma proteins).
It does not penetrate the placental barrier or into breast milk.
Metabolized in the liver. The substance is characterized by rapid biological inactivation and short duration of action, which is explained by the participation of the antiheparin factor in its biotransformation and the binding of heparin to the macrophage system.
T1/2 - 30-60 minutes. Excreted by the kidneys. Up to 50% of the substance can be excreted unchanged only if high doses are used. It is not excreted by hemodialysis.
First aid
What to do in case of a heroin overdose before the ambulance arrives? Depends on the condition of the victim.
Procedure for detecting a person with signs of drug poisoning:
- Check the pulse
- it is best to do this in the area of the radial artery on the hand, or on the neck, next to the trachea, where the carotid artery is located. - Track breathing
- lean towards the patient’s face, try to hear how he breathes. Look closely at the movement of the chest. - Check pulse and breathing every 10-15 seconds,
as the patient’s condition can change at any time. - To explore consciousness
- call a person by name loudly. If there is no reaction, press on the tip of the nose with a sharp object or press the trapezius muscle on the back. - A person is conscious
- do not let him fall asleep. - Does not react to what is happening, is completely turned off
- turn it on its side, thereby eliminating the possibility of tongue retraction. Check the airways for foreign objects and vomit. If necessary, peel with a spoon or fingers wrapped in cloth. - Unbutton your clothes
to make breathing easier. - If a person is unconscious, try to revive him
- rub his earlobes, hold a cotton swab soaked in ammonia to his nose for a couple of seconds, and lightly pat his cheeks.
The patient continues to remain unconscious, the pupils are dilated, breathing and pulse are not detected - begin resuscitation measures (artificial respiration, chest compressions).
Indications for use
Indications for use of the gel
Heparin gel is used for the treatment and prevention of thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins , phlebitis (post-injection and post-infusion), lymphangitis , superficial periphlebitis, elephantiasis, localized infiltrates, bruises, swelling and injuries (including muscles, joints, tendons), superficial mastitis , subcutaneous hematomas .
Indications for use of the solution
Heparin injections are prescribed for thrombosis of deep veins , myocardial arteries , renal veins , pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis , atrial fibrillation (including if cardiac arrhythmia is accompanied by embolization), unstable angina , disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome , acute myocardial infarction, mitral heart disease (prevention of blood clots ), bacterial endocarditis , hemolyticouremic syndrome , lupus nephritis , glomerulonephritis , for the prevention and treatment of microthrombosis and microcirculation disorders.
For preventive purposes, the drug is used during surgical interventions that use extracorporeal blood circulation methods, during cytapheresis, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, forced diuresis, hemosorption, and when washing venous catheters.
When Heparin is administered intravenously, blood clotting slows down almost immediately, when administered into a muscle - after 15-30 minutes, when administered subcutaneously - after 20-60 minutes, when administered by inhalation, the effect is most pronounced after 24 hours.
Contraindications
Heparin containing ointments (Heparin, Heparin-Acrigel 1000, etc.) are contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to the components they contain, as well as in diseases accompanied by ulcerative-necrotic processes, and injuries that are accompanied by violations of the integrity of the skin.
Heparin gel (ointment) should be used with caution in case of thrombocytopenia and increased tendency to bleeding.
Contraindications to the use of the injection form of the drug:
- hypersensitivity;
- diseases accompanied by increased bleeding ( vasculitis, hemophilia , etc.);
- bleeding;
- aortic dissection , intracranial aneurysm;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- traumatic brain injury;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- uncontrolled hypertension;
- liver cirrhosis , accompanied by pathological changes in the veins of the esophagus;
- threatened miscarriage;
- menstrual period;
- pregnancy;
- childbirth (including recent);
- lactation period;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestinal tract;
- recent surgical interventions on the prostate gland, brain, eyes, bile ducts and liver, as well as the condition after lumbar puncture .
Heparin injections should be prescribed with caution to patients with polyvalent allergies (including bronchial asthma ), diabetes mellitus , arterial hypertension , active tuberculosis , endo- and pericarditis , chronic renal failure, liver failure ; patients undergoing dental procedures or radiation therapy; persons over 60 years of age (especially women); women using an IUD.
Signs of use
It is possible to recognize a heroin addict and prevent the negative consequences of addiction by encouraging treatment. The first thing that catches your eye are the injection marks.
. They are usually located on the bends of the elbows or in the groin.
Strong cravings for sweets, thirst quenched by small sips, saliva dried in the corners of the mouth, sudden changes in lifestyle, frequent colds and other infectious diseases. The above signs should make the patient’s relatives and friends wary.
Drug addicts rarely realize the severity of their situation on their own
. Most of them need confidential, frank conversations, which will result in consent to treatment. After all, the longer a person uses, the greater the chance that sooner or later he will have an overdose.
Side effects
When used externally, Heparin sodium can cause skin hyperemia and hypersensitivity reactions.
When administering the solution, the following are possible:
- Hypersensitivity reactions ( drug fever , skin hyperemia, rhinitis , feeling of heat in the soles, urticaria , skin itching, collapse, bronchospasm , anaphylactic shock ).
- Headaches, dizziness, diarrhea, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- Thrombocytopenia (in approximately 6% of patients), sometimes (rarely) with death. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is accompanied by: arterial thrombosis , skin necrosis and gangrene , stroke , myocardial infarction . In case of severe HIT (when the platelet is reduced to half the original number or below 100 thousand/μl), heparin should be stopped immediately.
- Local reactions ( hematoma , hyperemia , pain, ulceration, irritation at the injection site, bleeding).
- Bleeding. Typical ones are considered to be from the urinary tract and gastrointestinal tract, in areas that are subject to pressure, at the site of drug administration, from surgical wounds. Hemorrhages are also possible in various internal organs: in the retroperitoneal space, corpus luteum, adrenal glands, etc.
With long-term use of Heparin, intermittent alopecia , osteoporosis , hypoaldosteronism , soft tissues become calcified, spontaneous bone fractures occur, and the activity of liver transaminases increases.
Instructions for use of Heparin (Method and dosage)
Heparin injections, instructions for use, administration features
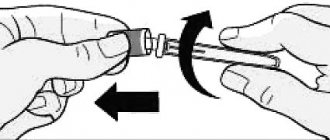
Heparin in ampoules is prescribed in the form of:
- regular injections into a vein;
- continuous infusion;
- subcutaneously (injections in the stomach).
For preventive purposes, sodium heparin is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 5 thousand IU/day, leaving 8-12 hours between injections (to prevent thrombosis, the patient is injected with 1 ml of solution under the skin of the abdomen 2 times/day).
For medicinal purposes, the solution is infused intravenously (the method of administration is drip infusion). Dose - 15 IU/kg/h (that is, an adult with average body weight is prescribed 1 thousand IU/h).
To achieve a rapid anticoagulant effect, 1 ml of solution is injected intravenously into the patient immediately before infusion. If administration into a vein is impossible for some reason, then the medicine is injected under the skin 4 times a day. 2 ml.
The highest daily dose is 60-80 thousand IU. The use of Heparin at the indicated dose for more than 10 days is permitted only in exceptional cases.
For children, the solution is injected into a vein by drip. The dose is selected depending on age: at the age of 1 to 3 months the daily dose is 800 IU/kg, from 4 months to a year - 700 IU/kg, children over 6 years of age are prescribed (under APTT monitoring) 500 IU/kg/ days
Technique for administering Heparin, preparation for manipulation and administration of solution
Subcutaneous injections are usually given into the anterolateral wall of the abdomen (if this is not possible, the medicine can be injected into the upper thigh/shoulder area).
A thin needle is used for injection.
The first injection is given 1-2 hours before the start of the operation; in the postoperative period, the drug continues to be administered for 7-10 days (if necessary, longer).
Treatment begins with a jet injection of 5 thousand IU of heparin into a vein, after which the solution is continued to be administered using an intravenous infusion (a 0.9% NaCl solution is used to dilute the drug).
Maintenance doses are calculated depending on the route of administration.
The algorithm for administering Heparin is as follows:
- 15-20 minutes before administering the drug, apply cold to the injection site in the abdominal area (this will reduce the likelihood of bruising).
- The procedure is performed in compliance with the rules of asepsis.
- The needle is inserted into the base of the fold (the fold is held between the thumb and forefinger until the end of drug administration) at an angle of 90°.
- Do not move the tip of the needle after insertion or retract the piston. Otherwise, tissue damage and hematoma formation may occur.
- The solution should be injected slowly (to reduce pain and avoid tissue damage).
- The needle is removed easily, at the same angle at which it was inserted.
- There is no need to wipe the skin; the injection site is lightly pressed with a sterile dry swab (the swab is held for 30-60 seconds).
- It is recommended to alternate anatomical sites for injection. The areas in which injections are given during the week should be 2.5 cm apart from each other.
Heparin ointment, instructions for use
The gel is used as an external agent. It should be applied to the affected area from 1 to 3 times a day. A single dose is a column 3 to 10 cm long.
For thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins, the drug is used rectally.
Gel-impregnated cotton pads are applied to the inflamed nodes and secured with a bandage. Gel-soaked tampons are inserted into the anus. Treatment usually lasts 3-4 days.
For leg ulcers, the ointment is carefully applied to the inflamed skin around the ulcer.
Frequency of applications - 2-3 rubles/day. Treatment is continued until the inflammation disappears. Usually the course lasts from 3 to 7 days. The doctor decides whether a longer course is necessary.
Other heparin-containing ointments are used in a similar way (for example, the instructions for Heparin-Acrigel 1000 are practically no different from the instructions for Heparin gel or Lyoton 1000 ).
For the treatment of hemorrhoids (external and internal), anal fissures , thrombophlebitis of the anal veins , as well as to relieve itching and eliminate eczema suppositories for hemorrhoids (for example, Hepatrombin G can be used as an alternative to Heparin ointment .
Additional Information
Heparin is available only in the form of a solution, ointment or gel (gel, unlike ointment, contains a larger amount of the active substance and is better absorbed into the skin).
Heparin tablets are not available because heparin is practically not absorbed from the digestive tract.
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose with parenteral use are bleeding of varying severity.
Treatment: for minor bleeding caused by an overdose of the drug, it is enough to stop using it. If bleeding is extensive, protamine sulfate (1 mg per 100 IU of heparin) is used to neutralize excess heparin.
Please note that heparin is eliminated quickly. Thus, if protamine sulfate is administered 30 minutes after the previous dose of heparin, it should be administered at half the dose; The highest dose of protamine sulfate is 50 mg.
It is not excreted by hemodialysis.
Cases of overdose with external use of the drug have not been described. Due to the low systemic absorption of the drug, an overdose is considered unlikely. With prolonged use on large surfaces, hemorrhagic complications .
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, if necessary, use of a one percent solution of protamine sulfate (heparin antagonist).
Interaction
Drugs that block tubular secretion, indirect anticoagulants that reduce the formation of vitamin K by intestinal microflora, antibiotics, NSAIDs, dipyridamole , ASA and other drugs that reduce platelet aggregation enhance the effect of heparin.
The weakening of the effect is facilitated by: cardiac glycosides , ergot alkaloids , phenothiazines , antihistamines, nicotine , ethacrynic and nicotinic acids , nitroglycerin (iv administration), ACTH, tetracyclines , alkaline amino acids and polypeptides, thyroxine , protamine .
Do not mix the solution in the same syringe with other medications.
When applied topically, the anticoagulant effect of the drug is enhanced when the gel is used in combination with antiplatelet agents, NSAIDs, and anticoagulants. Tetracycline , thyroxines , nicotine and antihistamines reduce the effect of heparin.
Special Recommendations
Heparin therapy is carried out under strict control of hemocoagulation parameters. A coagulogram is carried out in the first week of treatment with the drug and immediately after surgery, the optimal number of studies is 1 time every 2-3 days. With fractional administration of the solution, a blood test is done immediately before the injection.
It is not recommended to abruptly interrupt the course of treatment with Heparin, as this may lead to the initiation of thrombus formation. Therefore, it is necessary to gradually reduce the dosage of the drug with the parallel use of indirect anticoagulants. The only exceptions are cases of individual intolerance to some components of the solution.
Despite the possibility of intramuscular injection of the solution, experts do not recommend it due to the fact that bruises form at the injection site.
special instructions
Due to the risk of hematoma formation at the injection site, the solution should not be injected into the muscle.
The solution may acquire a yellowish tint, which does not affect its activity or tolerability.
When prescribing the drug for therapeutic purposes, the dosage should be selected taking into account the aPTT value.
During treatment with the drug, organ biopsies and other medications should not be administered intramuscularly.
To dilute the solution, only 0.9% NaCl solution can be used.
The gel should not be applied to mucous membranes or open wounds. In addition, it is not used in the presence of purulent processes. The use of ointment is not recommended for DVT.
Unfractionated Heparin
Heparin with an average molecular weight of 12-16 thousand daltons, which is isolated from bovine lung or the mucous membrane of the intestinal tract of pigs, is called unfractionated. It is used in the production of drugs that have local and systemic effects (heparin containing ointments and solutions for parenteral administration).
The drug, through interaction with AT III (indirectly), inhibits the main enzyme of the blood coagulation system, as well as other coagulation factors, and this in turn leads to antithrombotic and anticoagulation effects.
Endogenous heparin in the human body can be found in muscles, intestinal mucosa, and lungs. In structure, it is a mixture of glycosaminoglycan fractions, which consist of sulfatide residues of D-glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid with a molecular weight of 2 to 50 thousand daltons.
Fractionated Heparin
Fractionated (low molecular weight) heparins are obtained by enzymatic or chemical depolymerization of unfractionated heparins. This Heparin consists of polysaccharides with an average molecular weight of 4-7 thousand daltons.
LMWHs are characterized as weak anticoagulants and highly effective direct-acting antithrombotics. The action of such drugs is aimed at compensating hypercoagulation processes.
LMWH begins to act immediately after administration, while its antithrombotic effect is pronounced and prolonged (the drug is administered only 1 time per day).
Classification of low molecular weight Heparins:
- drugs used to prevent thrombosis/thromboembolism ( Klivarin , Troparin , etc.);
- drugs used to treat unstable angina and MI without a pathological Q wave, thrombosis and thromboembolism , acute DVT, PE ( Fragmin , Clexane , Fraxiparine );
- drugs used to treat severe vein thrombosis ( Fraxiparine Forte );
- drugs used to prevent thrombus formation and coagulation during hemofiltration and hemodialysis ( Fraxiparine , Fragmin , Clexane ).
What then
It is important to socialize the patient
. To do this, you need to redirect a person’s thoughts in a positive direction. Form a new circle of values. Instill the habit of a healthy lifestyle. In this work, doctors and workers at rehabilitation centers must be in constant contact and interaction with the patient’s relatives and friends. At the same time, it is important to understand that addiction can be overcome only if the person himself strives for this. Forced treatment never produces positive results in the long term.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Girudoproct
Heparoid Zentiva
Heparin ointment
Gepatrombin G
Lyoton
Trombless
Venolife
Hepatrombin
Gel analogues: Heparin-Acrigel 1000 , Lyoton 1000 , Lavenum , Trombless .
Generic injection forms: Heparin J , Heparin-Ferein , Heparin-Sandoz .
Drugs with a similar mechanism of action: tablets - Piyavit , Angioflux , Wessel Due F ; solution - Angioflux , Hemapaxan , Antithrombin III human , Wessel Due F , Fluxum , Anfibra , Fraxiparine , Enixum .
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Heparin solution is not contraindicated for pregnant women. However, despite the fact that the active substance of the drug does not penetrate into milk, its use in nursing mothers in some cases led to the rapid (within 2-4 weeks) development of osteoporosis and spinal damage.
The feasibility of use should be decided individually, taking into account the risk to the fetus/benefit to the mother ratio.
There are no data on the use of the gel during pregnancy and lactation.
Reviews
Heparin is an effective and well-studied antithrombotic agent , the mechanism of action of which is to suppress the activity of thrombin , which catalyzes the biotransformation of fibrinogen into fibrin and a number of other reactions in the hemostatic system.
Most often, the external use of gel and ointment forms of the drug is discussed on the Internet. Reviews of heparin-containing ointments and gels (in particular, reviews of Heparin Acrigel 1000 ) are overwhelmingly positive: such drugs really help with bruises, thrombophlebitis and hemorrhoids , and also remove localized infiltrates well.
Content
- 1 Heparin 1.1 Chemical properties and mechanism of action 1.1.1 Related glycosaminoglycans
- 1.1.2 Sources
- 1.3.1 Other properties of heparin
- 2.1 Pharmacokinetics
- 2.3.1 Bleeding
Heparin price
The average price of Heparin injections in Ukrainian pharmacies is from 180 to 226 UAH (5 ml ampoules, No. 5). You can buy Heparin ointment for an average of 35 UAH. The price of Heparin Acrigel 1000 in Ukraine is about 250 UAH.
In Russian pharmacies, sodium heparin in ampoules can be purchased for 360-550 rubles. The price of Heparin gel is 260-300 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Heparin-Akrikhin 1000 gel 1 thousand.
IU/1g 30gAO Akrikhin RUR 340 order - Heparin-Akrikhin 1000 gel for external use. approx. 1000 IU/g tube 50g JSC AKRIKHIN
RUB 532 order
- Heparin ointment 25g RUP Belmedpreparaty
70 rub. order
- Heparin ointment for external use 25gPAO Biosintez
72 RUR order
- Heparin ointment 25 gAO "Nizhpharm"
86 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Heparin ointment (tube 25g) Nizhpharm JSC
90 rub. order
- Heparin (solution IV, SC 5tIU/ml 5ml amp. No. 5) Belmedpreparaty
RUB 1,540 order
- Heparin-Akrikhin gel (gel 1000EM/g 30g) Akrikhin JSC
RUB 357 order
- Heparin (vial IV and SC injection 5tIU/ml 5ml No. 5) Ozon LLC
RUB 1,700 order
- Heparin (vial IV and SC injection 5tIU/ml 5ml No. 5) Moscow Endocrine Plant
RUB 1,611 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Heparin-Darnitsa 600 units 30 g gel PrAT" Pharmaceutical company "Darnitsa", Ukraine
62 UAH. order - Heparin ointment 25 g TOV DKP Pharm.Fabrika, Ukraine
46 UAH order
- Heparin-Indar 5000 MO/ml 5 ml (25000 MO) No. 1 solution PrAT “On the production of insulin” Indar”, m. Kiev, Ukraine
34 UAH order
- Heparin-Novopharm 5000 MO/ml 5 ml No. 5 solution Novofarm-Biosintez TOV, Novograd-Volinsky, Ukraine
256 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Heparin ointment Heparin ointment 25g tube Ukraine, Zhytomyr FF LLC
60 UAH.order
- Heparin gel Heparin gel 30g Ukraine, Darnitsa ChAO
68 UAH order
- Heparin bottle Heparin solution d/in. 5000U/ml 5ml vial. №5 Ukraine, Pharmstandard-Biolek
166 UAH order
- Heparin solution d/in. 25000U/ml 5ml No.1 Ukraine, INDAR
39 UAH order
- Heparin bottle Heparin-Novopharm solution d/in 5000 MO bottle. 5ml. No.5 Ukraine, Novofarm-Biosintez LLC
268 UAH order
show more