Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
ATP-Long is a drug in a new category of substances that has a molecule containing ATP , and magnesium salts , as well as histidine amino acids . The drug exhibits a specific, unique pharmacological effect that is not typical for its other chemical ingredients.
It has a stimulating effect on energy metabolism , helps normalize the level of saturation with magnesium and potassium , activates ion transport systems of cell membranes, reduces uric acid , and develops the protective antioxidant function of the myocardium.
In patients with paroxysmal supraventricular and supraventricular tachycardia , flutter and atrial fibrillation, the use of the drug helps restore natural sinus rhythm , as well as reduce the intensity of ectopic foci (ventricular and atrial extrasystoles ).
During hypoxia and ischemia, ATP-Long has antiarrhythmic, membrane-stabilizing and anti-ischemic activity, due to its ability to establish metabolic processes in the myocardium . It has a beneficial effect on coronary circulation , peripheral and central hemodynamics , increases the contractility of the heart muscle, improves cardiac output and left ventricular functionality.
This range of effects has a positive effect on physical performance, and also leads to a decrease in the number of attacks of shortness of breath and angina pectoris during physical work, which is what ATP-Long is used for.
ATP is the main energy sponsor of the cell. Or where to get energy? Mitochondrial dysfunction.
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
October 1, 2018
Today we are introducing ourselves into scientific research. The article will be difficult to read. I simplified the material as much as possible, but it couldn’t be simpler. As always, I was “inspired” to write by everyone’s endless complaint - “weakness, nothing helps, your IVs and pills lasted for 2 weeks...”. Today we will consider the most difficult case of Energy deficiency - Mitochondrial dysfunction . This is still a little-studied and complex part of medical science. Mitochondrial dysfunction can be congenital and, in our case (the case under consideration), acquired.
Energy in our body is presented in the following form - the ATP molecule.
ATP-adenosine triphosphate is the main source of energy for cells in particular and the body as a whole. It is an adenosine ester (purine). In addition, it is a source of synthesis of nucleic acids for the formation of DNA structure! (our genetic code) and an intermediary of the transmission of a hormonal signal into the cell! Conclusion: lack of ATP is fraught with perversion/lack of hormonal response and more. ATP is formed in mitochondria (these are small structural components of any cell, the mitochondrion has its own DNA!, like the cell nucleus!!, it is a highly organized structure). That is why diseases with impaired ATP synthesis are called mitochondrial dysfunction.
The body produces 40 kg of ATP per day. Organs with maximum ATP production: brain 22%, liver 22%, muscles 22%, heart 9%, adipose tissue only 4%, note that the thyroid gland is not even included in this list... The brain and liver are leaders!
Now about the process of energy formation itself . Let's look at the picture.
The process of energy generation can be divided into 3 stages.
Stage 1 is the production of simpler molecules (in the energy production cycle) from carbohydrates (U), fats (F) and food proteins (B). Carbohydrates are broken down into monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), fats into fatty acids, proteins into amino acids. “Splitting” of B, F, U occurs both in an oxygen environment (aerobic) and in an oxygen-free (anaerobic) environment. This is extremely important! Since from anaerobic glycolysis of 1 molecule of glucose - 2 molecules of ATP are formed, from aerobic (oxygen) glycolysis of 1 molecule of glucose - 36 molecules of ATP are formed, from aerobic oxidation of 1 molecule of fatty acid - 146 molecules of ATP, (fats and proteins in an oxygen-free environment do not are broken down!, conclusion - for example, with untreated anemia (O2 deficiency), weight loss is almost impossible). So, the absorption of 1 molecule of glucose requires 6 molecules of O2, and 1 molecule of fatty acids requires 23 molecules of O2. Conclusion - fats are the main source of energy, and everyone needs O2!!!
Stage 2 - formed from all molecules U, F, B - AcetylCoA - intermediate metabolite . The essence of this stage is that the amount of AcetylCoA produced depends on the level of many vitamins and microelements (vitamin C, group B, zinc, copper, iron, etc.). Why is it so important for energy production to replenish the deficiency of these elements!
Stage 3 - this same AcetylCoA enters 2 main biochemical pathways for the production of ATP - this is the Krebs cycle (citric acid) and the oxidative phosphorylation cycle (electron transfer, “respiratory chain”;), NAD- and NADH+ are formed. The connection between these two waste cycles is “a bottleneck”, a “weak spot” in the formation of ATP. And it depends on the pH of the cell environment - with the development of cellular hypoxia = cellular acidosis and the process of ATP formation worsens - the body drowns in excess NADH, and NADH is associated with “oxygen leakage from the cell” (I will not decipher the mechanism) and the formation of active ( aggressive) forms of oxygen (free radicals) - and these are damaging agents for cells when formed in excess.
Metabolic acidosis is a consequence of primary O2 deficiency in the body (acidosis itself becomes the cause of secondary O2 deficiency - oxygen leakage). Acidosis is expressed by the accumulation of an intermediate metabolic product - lactate, an excess of H+ (hydrogen ion), mitochondria “begin to suffocate and grow old and die”! And with the aging of mitochondria, the body ages, which is why some diseases become so younger - atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes mellitus (yes, this is a mitochondrial disease), cancer, arterial hypertension, AIT, chronic fatigue syndrome, even UC and Crohn's disease (as one of the theories), etc.
How does the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), for example, relate to obesity? - active intake of fatty acids from food leads to depletion of carnitine transport (everyone knows for comparison Carnitine for sports nutrition) systems (fatty acid transporters, there are few of them anyway) and a decrease in the activity of the “respiratory chain”, tissue sensitivity to insulin decreases - The well-known insulin resistance develops! The outcome is metabolic sadness - metabolic syndrome.
Accordingly: the reasons for the decrease in ATP synthesis are, first of all, O2 deficiency ! (as happens in big cities, where there is little greenery!!, gas pollution - the product of gasoline combustion is not O2, but CO2!!!!, people do not leave the premises, move little - “small vessels are closed to access of O2”, the causes may be respiratory diseases and cardiovascular pathologies), acidosis = “acidification of the body” (accumulation of lactate, excess H+), polydeficiency of vitamins and microelements to improve the absorption of fat, vitamins, and uranium. To treat O2 deficiency, a device was even invented - based on interval hypoxic training. This is a new era in the treatment of many pathologies.
How to suspect mitochondrial problems? They are difficult both to understand and to diagnose.
Among the “simple tests” that can be collected by any laboratory - a decrease in blood pH, O2, an increase in: lactate, CRP, fibrinogen, cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, homocysteine, uric acid (clinically - increased blood pressure, increased heart rate at rest, shortness of breath at rest), decrease in ferritin, from rare cases - decrease in glutathione, blood vitamins, decrease in Q10, disturbance in the antioxidant system (in the blood).
Among the rarer, but still available tests (more specific) are organic acids in urine (thanks to this analysis, you can determine approximately at what level the disorder is occurring and how to correct it). If the pathology is so difficult to detect, “how to treat it?”, ask You
It is possible to treat.
First of all, we change our lifestyle - improve the delivery of O2!, quit smoking! we breathe more often in the park and not only.. We treat and put into remission chronic respiratory diseases, replenish the deficiency of vitamins and minerals!, add antioxidants, vascular drugs (!) it is very important to improve the cows (weakness is always accompanied by absent-mindedness, decreased memory and attention - that’s right , maximum vascular network in the brain!!), less often we add “energy drinks” - succinic acid, Q10, carnitine, NADH, etc. I’m not talking here about congenital mitochondrial dysfunctions - this is a consequence of a genetic breakdown, and we are now talking more about acquired causes . We will wait for new scientific materials on this topic...
Indications for use
The drug ATP-Long is indicated for use in complex treatment for:
- unstable angina;
- coronary heart disease;
- angina pectoris of exertion and rest;
- heart failure;
- myocardial and post-infarction cardiosclerosis ;
- supraventricular tachycardia ;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- myocarditis of infectious-allergic nature;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- hyperuricemia of various origins;
- chronic fatigue syndrome ;
- surgical interventions in the pre- and postoperative periods;
- coronary syndromes , especially with nitrate intolerance, in order to enhance antiarrhythmic effectiveness and reduce the side effects of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Contraindications
- cardiogenic , as well as other types of shock ;
- hyperkalemia;
- lactation;
- hypersensitivity to ingredients;
- myocardial infarction in the acute period;
- pregnancy;
- hypermagnesemia;
- childhood;
- obstructive pathologies of the bronchi and lungs;
- AV block and sinoatrial block (2-3 degree);
- severe bronchial asthma
- hemorrhagic stroke.
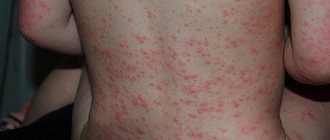
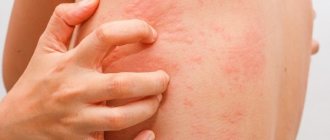
Side effects
- feeling of discomfort in the chest and epigastric region;
- itchy skin;
- nausea;
- rashes on the skin;
- decreased blood pressure;
- bronchospasm;
- hyperemia ;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- increased diuresis;
- feeling of heat;
- dizziness;
- increased gastrointestinal motility;
- Quincke's edema;
- hypermagnesemia or hyperkalemia (in case of uncontrolled and prolonged use).
ATP: role in the body and benefits of supplements
Our body produces ATP to provide energy for movement, but often this energy is not enough. Is it worth taking ATP in supplement form in this case?
Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP,
is the main source of energy that supports all processes in the body. In fact, if your body stops producing ATP, it means you're...well, you're dead.
ATP has long been considered a chemical that the body can synthesize from other nutrients but cannot obtain from a supplement on its own. However, taking ATP tablets or powders can provide significant benefits to your workouts.
What is ATP
Each ATP molecule has three phosphate groups (triphosphate). When phosphate groups are released from a molecule, a huge amount of energy is released. The body uses this energy to carry out essential life processes. These include the transport of proteins and lipids (fats) into and out of cells, communication between cells, DNA and RNA synthesis, and finally muscle contractions that make movement possible.
How does ATP provide energy?
During physical activity, the body constantly produces new ATP molecules to satisfy the energy needs of cells. The reserves of ready-made ATP in muscle tissue last only a couple of seconds. During intense muscle activity, energy is consumed very quickly, so the body requires sufficient amounts of phosphocreatine, glucose and oxygen to replenish ATP reserves.
Some people take creatine supplements to give them more energy to perform short-term, high-intensity exercise. Creatine provides an energy boost by increasing the supply of phosphocreatine, which the body can use to further form more ATP. Consuming carbohydrates before exercise works in a similar way. Eating carbohydrates increases your blood glucose levels. Glucose, in turn, can also be used to produce ATP through a process called glycolysis.
Benefits of ATP Supplements
Doesn't it make sense in this case to eliminate the intermediate and just take ATP supplements? Yes and no. Some studies indicate positive results, but mostly these were the results of experiments conducted on laboratory rats. Subsequent studies in humans were not as promising. However, this does not mean that ATP supplements do not have beneficial properties. While they may not directly increase ATP stores in muscle tissue, they do help improve blood flow to active tissue, improve physical performance, and speed up recovery.
Increased strength and endurance
A 2004 study published in the Journal
of Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise
found that two weeks of ATP supplementation had no effect on increasing ATP stores in muscle tissue. However, subjects taking ATP performed more bench press repetitions at 70% of their one-rep max than subjects taking placebo.
Another study, published in the Journal
of the International Society of Sports Nutrition
, demonstrated that taking 400 mg of ATP for 15 consecutive days reduced muscle fatigue and helped subjects use energy more efficiently during intense exercise compared to a control group.
Researchers at the University of Tampa found that during a 12-week strength training program, subjects taking 400 mg of ATP daily had significantly improved 1RM performance in the squat and deadlift compared to subjects taking a placebo substance. The study also found that athletes who took the supplements saw their quadriceps muscle thickness increase twice as much as those who took a placebo.
Increased blood flow
In addition to improving muscle function, taking ATP supplements also promotes vasodilation, or widening of the arteries. Wider vessels mean more fuel—specifically, more oxygen and glucose—gets to active muscles faster. Vasodilation also helps remove metabolic waste products such as lactic acid and urea from muscle tissue and provides more nutrients to speed up muscle recovery.
Improved recovery
2022 study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition
, demonstrated that ATP supplementation helps prevent the depletion of ATP stores after intense exercise. Subjects who took the supplements also showed greater power than members of the placebo group during repeated Wingate anaerobic tests.
Do ATP supplements have side effects?
To date, there are no known side effects of taking adenosine triphosphate. But keep in mind that the longest ATP study lasted only 12 weeks. The effects of longer-term use of ATP supplements have not been studied.
Does ATP interact with other supplements?
ATP is safe to combine with other supplements. Moreover, sometimes this gives a positive synergistic effect and allows you to enhance the beneficial effects of supplements such as creatine and beta-alanine.
How much and in what form is it best to take ATP supplements?
ATP supplements are most often sold in tablet form; The ATP ingredient can also be found in some powder supplements. Health experts say that if you want to increase your ATP levels during exercise, your best bet is to take creatine monohydrate.
Regardless of supplement form, 400 mg of ATP should be taken to maximize benefits.
When is the best time to take ATP?
To date, there are no definitive research findings regarding the optimal timing and dosage of ATP supplementation. Existing research suggests that it is best to take 400 mg of ATP 30 minutes before the start of your workout. On days when you are not training, take AFL on an empty stomach 30 minutes before your first meal.
Instructions for use of ATF-Long
ATP-Long tablets, instructions for use
ATP-Long tablets are recommended to be taken sublingually (under the tongue) until completely absorbed. Reception is carried out regardless of food 3-4 times in 24 hours, in a single dose of 10-40 mg. The average period of taking the tablets is 20-30 days (further use is on the recommendation of a doctor). It is possible to repeat the course of treatment after 10-15 days. It is not recommended to exceed the maximum daily dose of 160 mg.
ATP-Long injection solution, instructions for use
ATP-Long injection solution is administered 1-2 times every 24 hours, intramuscularly, 1-2 ml, at a rate of 0.2-0.5 mg/kg.
Intravenous administration is carried out in the form of infusions (slowly) in a dose of 1-5 ml, at a rate of 0.05-0.1 mg/kg/min. Infusions are carried out in a hospital setting and under blood pressure control. The average duration of therapy is 10-14 days.
ATP systems[edit | edit code]
Consistent activation of energy systems during exercise
ATP reserves are sufficient only for the first 2-3 seconds of physical activity, but muscles can only work if ATP is available. For this, there are special systems that constantly synthesize new ATP molecules; they turn on depending on the duration of the load (see figure). These are three main biochemical systems:
1. Phosphagen system (Creatine phosphate) 2. Glycogen and lactic acid system 3. Aerobic respiration
Phosphagen system[edit | edit code]
When the muscles undergo short but intense activity (approximately 8-10 seconds), the phosphagen system is used - ADP combines with creatine phosphate. The phosphagen system ensures that small amounts of ATP are constantly circulating in our muscle cells. Muscle cells also contain a high-energy phosphate, creatine phosphate, which is used to restore ATP levels after short, high-intensity work. The enzyme creatine kinase takes the phosphate group from creatine phosphate and quickly transfers it to ADP to form ATP. So, the muscle cell converts ATP to ADP, and phosphagen quickly reduces ADP to ATP. Creatine phosphate levels begin to decline after just 10 seconds of high-intensity activity. An example of the use of the phosphagen energy system is the 100-meter sprint.
Glycogen and lactic acid system[edit | edit code]
The glycogen-lactic acid system supplies energy to the body more slowly than the phosphagen system and provides enough ATP for about 90 seconds of high-intensity activity. During the process, lactic acid is formed from glucose in muscle cells as a result of anaerobic metabolism.
Given the fact that in the anaerobic state the body does not use oxygen, this system provides short-term energy without activating the cardiorespiratory system in the same way as the aerobic system, but with saving time. Moreover, when muscles work quickly in anaerobic mode, they contract very powerfully, cutting off the supply of oxygen, as the vessels are compressed. This system can also be called anaerobic-respiratory, and a good example of how the body works in this mode is the 400-meter sprint. Typically, athletes are prevented from continuing to work in this manner by muscle soreness resulting from the accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues.
Aerobic respiration[edit | edit code]
If the exercise lasts more than two minutes, the aerobic system comes into play, and the muscles receive ATP first from carbohydrates, then from fats and finally from amino acids (proteins). Protein is used for energy mainly in conditions of hunger (diet in some cases). Aerobic respiration produces the slowest amount of ATP, but produces enough energy to sustain physical activity for several hours. This occurs because glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water freely, without being counteracted by, for example, lactic acid, as is the case in anaerobic work.
Interaction
Parallel use of cardiac glycosides increases the possibility of AV blockade .
Co-administration of magnesium can lead to hypermagnesemia .
Combination with Dipyridamole enhances the effect of ATP-Long, and with Aminophylline , Caffeine , Xanthinol Nicotinate , Theophylline , on the contrary, reduces its effectiveness.
ACE inhibitors , potassium and potassium-sparing diuretics increase the risk of hyperkalemia .
ATP-Long can enhance the antianginal effectiveness of calcium channel blockers , beta-blockers and nitrates .
Interactions of the drug Atf-long
ATP-Long cannot be used simultaneously with cardiac glycosides due to the increased risk of AV block. When used simultaneously with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium preparations and ACE inhibitors, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases, and with Magnerot and other magnesium preparations - hypermagnesemia. Dipyridamole enhances the therapeutic effect of the drug ATP-Long, and xanthinol nicotinate, caffeine, theophylline, aminophylline reduce it. ATP-Long can enhance the antianginal effect of β-adrenergic receptor blockers and nitrates.
special instructions
Both tablets and injections of the drug should be used with caution in conjunction with cardiac glycosides and in case of arterial hypotension and, due to the risk of AV blockade , as well as in diabetes mellitus , the patient’s predisposition to bronchospasm , fructose, sucrose-isomaltose, glucose tolerance disorders -galactose (for tablets).
Long-term use should be combined with monitoring plasma levels of magnesium and potassium .
During therapy, the consumption of caffeine-containing products should be limited.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Atf-long
When AV blockade is combined with other rhythm disturbances, the drug is not prescribed. With prolonged use of ATP-Long, it is necessary to monitor the level of potassium and magnesium in the blood. It is undesirable to use in cases of severe arterial hypotension. Prescribe with caution if you are prone to bronchospasms. ATP-Long should not be used simultaneously with cardiac glycosides due to the increased risk of AV block. Please note that the tablets contain small amounts of sucrose and lactose. During treatment with ATP-Long, it is necessary to limit the consumption of products containing caffeine (coffee, tea, cola drinks). Use during pregnancy and lactation. There are no clinical data on the safety and effectiveness of the drug during pregnancy and lactation, therefore its use by women during pregnancy is contraindicated. If it is necessary to use the drug during breastfeeding, breastfeeding should be stopped for the period of treatment. Children . Not used to treat children. The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving a vehicle or working with other mechanisms. There is no data on the ability of the drug ATP-Long to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or other mechanisms.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Vazonat
Phosphaden
Hawthorn fruit
Preductal
Meldonium
Angiosil Retard
Ranexa
Lily of the valley tincture
Neocardil
Rimecore
Triductane
Hawthorn tincture
Triductan MV
Trimectal MV
Trimectal
Neoton
Predisin
Trimetazidine
Tivortin Aspartate
Metamax
- Adexor;
- Vasopro;
- Dibikor;
- Vazonat;
- Cardazin;
- Kapikor;
- Coraxan;
- Cardimax;
- Mexicor;
- Metamax;
- Mildronate;
- Methonate;
- Neocardil;
- Preductal;
- Riboxin;
- Thiotriazolin;
- Triductane;
- Trimetazidine;
- Energoton , etc.
Reviews for ATF-Long
As a rule, reviews of ATP-Long are neutral and most likely this is due to the frequent use of this drug in combination with other drugs, the effects of which often overlap to such an extent that it becomes difficult to determine which drug has a positive effect on the body.
The same situation occurs with side effects and undesirable consequences.
If you have been prescribed this medication, you should rely on the doctor’s opinion and strictly follow his recommendations and instructions.
ATP - Adenosine Tri-Phosphoric acid[edit | edit code]
ATP formula
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate: adenine bound to three phosphate groups) is a molecule that serves as a source of energy for all processes in the body, including movement. Contraction of the muscle fiber occurs with the simultaneous breakdown of the ATP molecule, resulting in the release of energy that is used to carry out the contraction. In the body, ATP is synthesized from inosine.
ATP must go through several steps to give us energy. First, using a special coenzyme, one of the three phosphates (each of which provides ten calories) is separated, releasing energy and producing adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If more energy is required, the next phosphate is separated, forming adenosine monophosphate (AMP). The main source for the production of ATP is glucose, which in the cell is initially broken down into pyruvate and cytosol.
During rest, the reverse reaction occurs - with the help of ADP, phosphagen and glycogen, the phosphate group reattaches to the molecule, forming ATP. For these purposes, glucose is taken from glycogen reserves. The newly created ATP is ready for its next use. In essence, ATP works like a molecular battery, storing energy when it is not needed and releasing it when it is needed.
ATP structure[edit | edit code]
The ATP molecule consists of three components:
1. Ribose (the same five-carbon sugar that forms the backbone of DNA) 2. Adenine (connected carbon and nitrogen atoms) 3. Triphosphate
The ribose molecule is located in the center of the ATP molecule, the edge of which serves as a base for adenosine. A chain of three phosphates is located on the other side of the ribose molecule. ATP saturates the long, thin fibers containing a protein called myosin, which forms the basis of our muscle cells.
ATF-Long price, where to buy
The average price of ATF-Long is:
- tablets 10 mg No. 40 – 60 hryvnia;
- tablets 20 mg No. 40 – 90 hryvnia;
- ampoules 1 ml No. 10 – 25 hryvnia.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
LuxPharma* special offer
- ATP-long tablets 20 mg 40 pcs.
1850 rub. order
show more
Pharmacy24
- ATF-Long 0.01g No. 40 tablets PAT NEC "Borshchagivsky chemical and pharmaceutical plant", Kiev, Ukraine
58 UAH. order - ATF-Long 20 mg No. 40 tablets TOV FC Farkos, Ukraine
72 UAH order
- ATF-Long 0.02g No. 40 tablets PAT NEC "Borshchagivsky chemical-pharmaceutical plant", Kiev, Ukraine
85 UAH order