In this article we will tell you:
- Key functions of vitamin D
- Interaction with other elements
- Normal vitamin D content in the body
- Signs and causes of vitamin D deficiency
- Consequences of vitamin D deficiency in the body
- Consequences of hypervitaminosis (excess vitamin D)
- How to find out your vitamin D level
- Rules for taking vitamin D
- Vitamin D Rich Foods
- Vitamin D in cosmetology
Not every person knows why vitamin D is needed. But in vain. This element plays a very important role in the body. Unlike other vitamins, vitamin D acts as a hormone and every cell in the body has a receptor for it. Thanks to it, the skeleton is formed normally, immunity increases, blood pressure and heartbeat improve. Vitamin deficiency is manifested by frequent colds, hair loss, and depression. Experts estimate that about 1 billion people have low levels of vitamin D.
But an excess of vitamin does not lead to anything good, so you need to know the norm and check your level. To do this, you need to take special tests. After them, the doctor may prescribe vitamin D supplements. In addition, it is worth diversifying your menu with products rich in this vitamin. In general, prepare a piece of paper and a pen, there is a lot of useful information about vitamin D below.
Key functions of vitamin D
Vitamin D (calciferol)
– two substances similar in structure and action: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (colecalciferol or cholecalciferol).
Under the influence of sunlight, vitamin D3 is synthesized in the skin from provitamins (from food and synthesis from cholesterol). In the body, from these two forms (D2, D3), the active product of their transformation, calcitriol, is formed and used. It is formed in two stages: first in the liver and then in the kidneys.
The history of the discovery of vitamin D is associated with the study of retinol, or vitamin A. At the beginning of the 20th century, it was discovered that fish oil is rich in retinol. As an experiment, fish oil was given to dogs. After some time, scientists noticed that the animals stopped suffering from rickets, which was one of the main problems in pediatrics at that time.
Experts tried to link rickets with vitamin A deficiency, but Elmer McCollum, who discovered retinol, refuted this hypothesis. He conducted his experiments with dogs suffering from rickets: for some time, McCollum gave them fish oil with neutralized retinol. This prompted the scientist to think that the cure comes from some other substance, which is also contained in fish oil. This is how vitamin D was discovered at the beginning of the 20th century.
About a year later, scientists discovered that if food is exposed to ultraviolet light, the amount of vitamin D in it increases. Thus, it was established that the sun is the source of this valuable element.
Main functions of vitamin D
:
- Promotes normal skeletal formation.
- Ensures the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
- Promotes muscle tone.
- Increases immunity.
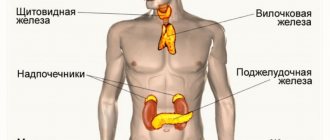
- Necessary for the functioning of the thyroid gland and normal blood clotting.
- Helps the body restore the protective membranes surrounding the nerves.
- Participates in the regulation of blood pressure and heartbeat.
- The connection between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune diseases and cancer is suspected and actively studied.
Which vitamin D is best for an adult to buy: drug rating
The rating will help you choose a vitamin preparation for everyone who needs an increased supply of cholecalciferol or wants to maintain health during the cold season. When compiling the TOP-6, the following parameters were taken into account:
- effectiveness of the drug;
- ease of use;
- price ratio with dosage and number of capsules (tablets, solution) in the package;
- reviews about vitamin D from customers.
The list of the best included 6 drugs that received maximum ratings in all respects.
No. 6 Prime Kraft, Vitamin D3 600 IU
The drug is inexpensive, but at the same time fully meets the expectations of buyers. It helps maintain bone strength, strengthens the immune system, and reduces the risk of osteoporosis and cancer. The supplement is available in capsules with a dosage of 600 IU - this amount is enough to cover the daily requirement for the “sunshine” vitamin.
Advantages:
- Pleasant taste.
- Large package of 90 pieces - can be drunk by the whole family.
- Convenient administration - one tablet per day.
- Affordable price of vitamin D for adults.
Flaws:
- Not suitable for the treatment of vitamin deficiency due to the low dosage.
No. 5 Chikalab, Vitamin and mineral complex Ca+Mg+Zn, D3, K2
Vitamin D – which one is better to buy for an adult man
? Pay attention to the complex supplement, which contains several useful components at once. Vitamin D has a positive effect on the condition of the prostate gland, zinc supports reproductive function. Calcium ensures bone strength, magnesium is responsible for the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, and vitamin B2 increases the digestibility of all components.
Advantages:
- 5 components included.
- 60 capsules per package - enough for a long time.
- An ideal complex for men's health.
- Capsule form - does not irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
Flaws:
- A long course of treatment is required.
No. 4 Natrol, Vitamin D3 5000 ME
The drug is suitable for those who need emergency measures to increase the level of vitamin D3 in the blood. One tablet contains 5000 IU of active ingredient - this amount is sufficient for the effective treatment of hypo- and vitamin deficiency. The drug improves the condition of bones and joints, supports the immune system, and regulates healthy cell growth.
Advantages:
- Prolongs youth by improving the condition of bones, teeth, skin and hair.
- Supports the immune system.
- Has a pleasant strawberry taste.
- One package contains 90 tablets - enough for a full course of treatment.
Flaws:
- Relatively high cost.
No. 3 Arnebia
The price of this vitamin D for adults is very affordable, and its effectiveness is confirmed by reviews. The supplement strengthens bone tissue and teeth, improves the condition of nails and hair, and promotes active growth of muscle tissue. Each tablet contains 5 mcg of cholecalciferol and 600 mg of calcium - this is 100% and 60% of the daily value, respectively.
Advantages:
- Combined effect of D3 and calcium.
- An unusual format in the form of effervescent tablets.
- Easy to digest without side effects.
Flaws:
- Small package – 20 tablets.
- Does not cover the daily calcium requirement.
No. 2 Vitamin D3 2000 IU Real Caps
The active substance of this drug is cholecalciferol in the amount of 2000 IU in one capsule. An increased dosage will help quickly restore vitamin balance in case of acute deficiency and reduced insolation. The product is easily absorbed and has a complex effect on the body - strengthens the heart muscle, increases bone strength, and serves as a prevention of cancer and osteoporosis.
Advantages:
- Fast therapeutic effect due to high dosage.
- Anti-cancer properties.
- The capsule form does not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
Flaws:
- Not suitable for prophylaxis or daily use.
Main types of vitamin D
Vitamins of group D (C27H44O3) are biologically active substances. According to their structure they are classified as sterols.
The group includes the following elements:
- D1
Chemical Formula: C56H88O2
Consists of two components: lumisterol and ergocalciferol. It is produced artificially. Does not play a significant role for humans and medicine.
- D 2
(ergocalciferol)
Chemical formula: C28H44O
A person can receive this element only through food. Also found in dietary supplements. Regulates the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
- D3
(cholecalciferol or colecalciferol)
Chemical formula: C27H44O
Of the entire group, this is the most active substance. Its sources for humans are food (fish, caviar, butter, cheese, chanterelle mushrooms) and sunlight
. Even five minutes of direct sunlight can be enough for the body to produce its daily requirement of vitamin D3.
We recommend
“Vitamins for sleep, against insomnia and obesity” Read more
- D4
(dehydrocholesterol)
Chemical formula: C28H46O
Contained in the skin. Under the influence of ultraviolet rays it turns into D3 in the epidermis.
- D5
(sitocalciferol)
Chemical formula: C29H48O
This is a synthetic analogue of vitamin D3, first produced in Chicago. Virtually non-toxic. Used in the treatment of cancer. It was found in nature in wheat oil.
- D6
(stigmacalciferol)
Chemical formula: C29H46O
The element is still being studied by specialists. It was synthesized from plants.
Types of Vitamin D
Vitamin D, or calciferol, is the general name for a group of biologically active substances - fat-soluble vitamins D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6. Two of them are beneficial for human health:
- ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and
- cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Ergocalciferol enters the body from the outside - along with plant foods (juices, grains, mushrooms). But cholecalciferol is synthesized by the body itself under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. This is why it is also called a “natural” vitamin. In addition, it is found in foods of animal origin - fatty fish, yolks, butter, etc. According to scientific research, D3 is approximately 30% more active in human life, which means that this particular type of calciferol is especially useful.
Metabolism of calceferol in the body
For vitamin D to start working in the body, it must go through two stages of activation, which will trigger its mechanism of action:
- In the liver, the substance interacts with enzymes and is converted into calcidiol (25 (OH) D3). It is based on the content of calcitriol in the blood serum that it is determined whether there is enough vitamin D in the body.
- At the second stage, the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol (1.25 (OH)2D3), is formed in the kidneys. It is of a steroid nature.
Calcitriol is responsible for the exchange of phosphate and calcium in the body. In intestinal cells, it stimulates the production of a special protein that transports calcium into the blood. And in the urinary tract it affects the muscles, enhancing the reabsorption of calcium.
The production of vitamin D in the human body is regulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH). The level of PTH is directly related to the amount of calcitriol, phosphorus and calcium: the more of these elements, the less parathyroid hormone and active enzymes are needed to replenish vitamin D.
After completing its work, vitamin D is converted by enzymes into an inactive substance (calcitroic acid metabolite), which is excreted from the body along with bile.
The question of the effect of vitamin D on the human body is still open. Scientists continue to study this substance. Perhaps in the near future new discoveries will be associated with it that can improve human life and health.
Absorption of vitamin D from food
Vitamin D is well absorbed from food. Its digestibility increases in the presence of fats and bile acids. Vitamin D is already found in fatty foods, so additional enrichment of the diet with fatty foods is not required.
As for bile acids, their presence in the gastrointestinal tract is not so much a matter of diet, but of health. If a person has good digestion and the liver secretes enough bile, there will be no problems with the absorption of vitamin D.
By the way, a healthy liver is also necessary for storing vitamin D. In the body, it accumulates in adipose tissue and the liver. During the cold season, when little calciferol is produced, its reserves are gradually consumed.
Interaction with other elements
The human body is a very complex system in which all elements are in constant interaction. And the health and general well-being of a person directly depends on how coordinated their work is. The effectiveness of vitamins can be enhanced by “helper molecules,” or cofactors. These are small compounds that are involved in biochemical processes. The most significant cofactors that enhance the effect of vitamin D include:
- Calcium
. As already mentioned, vitamin D controls calcium levels in the body. The mineral is well absorbed only with a sufficient amount of calcitriol. Therefore, these two substances are inextricably linked with each other.
- Magnesium
. This element performs many functions. For example, it is needed to convert food into energy. Magnesium is also involved in the absorption of calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium and vitamin D. Magnesium deficiency can be corrected not only with supplements, but also by including foods such as spinach, nuts, seeds, and whole grains in the diet.
- Vitamin K
. This element is responsible for bone health and also increases blood clotting, so it is simply necessary for the human body. If it is not there, people will begin to die from the slightest injury. Vitamins D and K work together when it comes to proper skeletal development. You can replenish your vitamin K reserves with foods such as kale, spinach, liver, eggs and hard cheese.
- Zinc
. Multifunctional element. With its participation, the body grows and develops, new cells are formed in it, infections are fought and fats, carbohydrates and proteins are fully absorbed. Zinc also facilitates the absorption of vitamin D and helps calcium enter bone tissue. A person can get this element through meat, vegetables and some grains.
- Bor
. A person needs very little of this substance, but it is still irreplaceable. Boron is involved in the metabolism and absorption of vitamin D. It is found in peanut butter, wine, avocado, raisins and some leafy vegetables.
- Vitamin A
. Controls protein synthesis. Together with vitamin D, it participates in the functioning of the genetic code. If a person lacks retinol, the functionality of vitamin D will be impaired. Vitamin A is found in carrots, mangoes, liver, butter, cheese and milk. Retinol is a fat-soluble substance and a powerful antioxidant. If it enters the body from plant foods, then it should be combined with fat-containing foods. This way retinol will be better absorbed.
Vitamin D: what is it good for, how to take it and is the sun so important?
82% of Russians experience vitamin D deficiency during the six autumn-winter months (and in some places longer). A deficiency of this vitamin can also be detected in mid-summer. And a few sunny days will not improve the situation. You can make up for the deficiency through food, nutritional supplements, and medications. To understand this issue on its merits, we turned to an expert - Ekaterina Gergesova, a consultant at the online medical laboratory Lab4U, a member of the Profile Commission of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in the specialty “Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics”. We also added a calculator to the article to calculate the dosage of vitamin D and a promotional code for laboratory testing with our partners.
What is vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin from the family of compounds (D1–D6). In this article we will talk about its most famous representatives - vitamins D1, D2 and D3.
Vitamin D is often called the "sunshine vitamin" because it is produced naturally in our skin when exposed to sunlight. Unfortunately, residents of most of Russia will not be able to “store” this vitamin during summer walks or vacations on the beach: the half-life of vitamin D from the body is about 15 days. But it is important not to go to extremes and take a conscious approach to monitoring vitamin levels. Together we will figure out what is needed for this.
Vitamin D in numbers:
Benefits of Vitamin D:
Important: an excess of a vitamin can be no less dangerous than a deficiency, so it is extremely important to know how necessary it is in each specific case. For this purpose, there is a test - 25-OH vitamin D - for the level of vitamin D in the blood. Based on this, the doctor determines the required dose—therapeutic or prophylactic—and makes recommendations.
It is recommended to check the level of vitamin D in the blood once every 6-12 months before starting to take medications - without analysis it is difficult to determine the optimal dosage. VkusVill customers can get tested for vitamin D in the Lab4U laboratory with an additional 10% discount using the promo code VkusD.
Daily intake of vitamin D:
Who needs vitamin D: risk groups
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency/Insufficiency
The main symptoms of vitamin D deficiency are:
- Bad mood,
- prostration,
- discomfort in bones and muscles,
- decreased visual acuity,
- increased sweating,
- frequent colds and acute respiratory viral infections.
As you can see, the symptoms are commonplace - many associate them with fatigue, seasonal ailments, stress and most often do not pay due attention to them. However, the consequences can be significant.
Research from the World Health Organization (WHO) confirms an increased risk of breast, colon, prostate, endometrial, ovarian, esophageal, stomach, pancreas, bladder, and kidney cancer due to vitamin D deficiency.
Another symptom - no longer so harmless in appearance - aches in the bones, muscles, problems with the spine, frequent fractures. When there is a lack or deficiency of vitamin D, most of the calcium and phosphorus that enters the body through food or supplements is not absorbed. Then the body begins to sacrifice bones - releasing these microelements from bone tissue. In young people, the limbs are more often affected, in older people - the spine. Bones become fragile and break (often with complications) even with minor impact. If we take into account that the approximate period of bone tissue renewal is 10 years, then the lack of vitamin D will remind itself for many more years.
Why the sun is not enough
To keep your vitamin D levels normal naturally, you need to:
1. live closer to the equator,
2. bask in the sun all year round, twice a week for 15–30 minutes,
3. do this during the daytime - from about 10:00 to 15:00,
4. have fair skin (the more melanin pigment in the skin, which is responsible for a dark complexion and bronze tan, the longer you need to be in the sun to get enough vitamin D).
Conditions 1 and 2 are not available to everyone. In Russia, most cities are located in places where solar UV radiation is not enough for the full synthesis of vitamin D. The further north the regions are, the fewer sunny days they experience per year (not to mention the subpolar and polar territories). In cloudy weather or in the shade, UV rays only partially pass through.
Condition number 3 is unsafe - as you know, the sun is most aggressive to the skin during these hours, increasing the risk of burns and more serious diseases. And sunscreen with SPF8 blocks the UV rays needed to produce vitamin D.
As for condition 4 , in general, it makes no difference what color the skin is if for six months of the year it is hidden under cloaks and fur coats. Therefore, it is possible and necessary to compensate for the deficiency of such a necessary vitamin for a person, primarily through nutrition.
What foods contain vitamin D?
Few foods are rich in vitamin D. There are two main forms:
- D2 - present in plants, fungi and yeast exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation;
- D3 - found in products of animal origin, fish is the richest in it.
Other animal products also contain vitamin D3, but in smaller quantities:
Vitamin D dosage forms
Increasing the level of vitamin D in the blood depends on the individual characteristics of the body. If sun exposure and diet are not enough, your doctor may prescribe vitamin D supplements.
Such preparations based on vitamin D3 and D2 can be considered natural. They are called “native”. They have low activity and low toxicity, being the basis for converting the vitamin into its active form. In adipose tissue, dosage forms of the vitamin can persist for about 2 months. In this regard, the time of day does not matter for taking medications. Moreover, it is possible to take high doses once a week and even once a month (follow your doctor's recommendations).
Native vitamin D can be taken on an empty stomach or with food - the fat content in accompanying products has virtually no effect on its absorption.
Which form of vitamin D should you choose?
Vitamin D is fat-soluble, so traditionally various natural oils have been used to deliver it: peanut, corn, soybean, sesame, olive.
Nowadays, various carriers are used, which, together with the vitamin, can be presented in the form of microemulsions, microcapsules, liposomes and micelle-forming compounds combined into a solution, tablets, capsules. In experimental studies, microcapsules showed better delivery and a longer lasting effect.
Oil solutions cause a greater increase in D in the blood compared to powder or ethanol based supplements. On the other hand, these differences are small and are important for people with intestinal diseases, overweight, etc. Each form has its own advantages: solutions are easier to swallow than capsules, and the latter are easier to dose.
Which vitamin D supplement to choose?
The two main forms of vitamin D are:
- vitamin D2 - ergocalciferol, comes from plants;
- vitamin D3 - cholecalciferol, animal origin.
Both play the same role in the body, but have slightly different molecular structures. Scientists are not yet sure which form is better. When advising people how much vitamin D they should get daily, the Russian Association of Endocrinologists does not differentiate between D2 and D3. However, if we are talking about vitamin D deficiency, it is recommended to replenish it with D3.
Do not choose the active metabolites of vitamin D and their analogues - calcitriol and alfacalcidol - on your own. They are used as prescribed by a doctor according to strict indications, under the control of calcium levels in the blood and urine, and the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood.
Dosage and regimen of vitamin D
Let's talk about the dosage for adults (depending on the test result), but first a few clarifications:
- We will talk about vitamin D in the form of colecalciferol.
- IU is the generally accepted international unit of measurement for matter.
- It is not recommended to take vitamin D in doses greater than 4,000 IU daily or 30,000 IU per week for more than 6 months without medical supervision.
- If you have underlying health conditions, such as obesity, impaired absorption of vitamin D, or others, you may need to increase your daily vitamin D intake (check with your doctor).
- And, of course, we are obliged to say: the interpretation of the results is for informational purposes only, is not a diagnosis and does not replace consultation with a doctor.
We do not recommend taking vitamin D without first getting tested and consulting with your doctor.
How to take vitamin D for children
- Children under 1 year of age should receive 400 IU (or 10 mcg) of vitamin D per day from the first days of life.
- Children over 1 year of age should receive 600 IU of vitamin D daily.
- It is important to consider sources of vitamin D in children: breast milk, breast milk substitutes, complementary feeding, sun exposure. If the analysis reveals a deficiency, be sure to consult a pediatrician - he will help you choose the drug, dosage and dosage regimen.
Should you take vitamin K along with vitamin D?
Vitamins D and K play an important role in the metabolism of calcium in the body.
Vitamin D:
- improves the absorption of calcium from food;
- releases calcium from bones into the blood if it is not enough from food. There, calcium is more important because it helps the heart beat, the lungs work, and the cells perform their tasks.
Vitamin K:
- activates the protein osteocalcin, which helps calcium enter the bones;
- activates a special GLA protein (MGP), which prevents excess calcium from accumulating in soft tissues (kidneys, blood vessels).
Excess vitamin D can lead to high levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia). Then calcium phosphate begins to accumulate in the lining of the blood vessels. Vitamin K helps prevent this. If you don't have enough calcium and you take vitamin D, vitamin K helps slow down the pumping of calcium from the bones into the blood. If you are taking vitamin D as recommended by your doctor based on test results, then taking vitamin K is likely not necessary.
Finally
As you can see, vitamin D plays a significant role in maintaining health. To keep its level at the optimal level, do not miss the opportunity to go to warm, sunny regions or just take a walk on a clear day. Eat more foods rich in this vitamin, especially fish. And do not neglect consulting a doctor and taking tests - this way you will know exactly how much vitamin D you need and in what form. Read about other important substances for our body in the material from the series of articles with nutritionists from VkusVill.
Want more expert content on healthy eating and nutrition? What would you like to know? Write questions in the comments!
Links to studies:
1. The Role of Vitamin D in Cancer Prevention
2. Prospective Study of Predictors of Vitamin D Status and Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Men
3. EFFECT OF HIGH-DOSE VITAMIN D REPLETION ON GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN AFRICAN AMERICAN MEN WITH PREDIABETES AND HYPOVITAMINOSIS D
4. Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: a birth-cohort study
5. Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc
6. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data
7. Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review
8. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Disease
9. Clinical recommendations. Vitamin D deficiency in adults: diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Normal vitamin D content in the body
Vitamin D is a vital substance for the human body, so its supply must be controlled. The daily intake depends on the person’s age:
| Age category | Daily requirement for vitamin D |
| Infants under 1 year | 7.5 – 10.0 mcg (400 – 500 IU) |
| Children from 1 to 5 years old | 10 mcg (400 IU) |
| Children from 5 to 13 years old | 2.5 mcg (400 IU) |
| Adults from 15 to 60 years old | 2.5 – 5.0 mcg (500 IU) |
| Adults over 60 years old | 10 – 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Pregnant and lactating women | 10 mcg (500 IU) |
Daily replenishment dose for vitamin D deficiency
:
| Desired level, NG/ML | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | |
| Current NG/ML level | 10 | 1000 | 2200 | 3600 | 5300 | 7400 | 10100 |
| 15 | 500 | 1700 | 3200 | 4900 | 7000 | 9700 | |
| 20 | 1200 | 2600 | 4300 | 6400 | 9100 | ||
| 25 | 600 | 2000 | 3700 | 5800 | 8600 | ||
| 30 | 1400 | 3100 | 5200 | 7900 | |||
| 35 | 800 | 2500 | 4600 | 7300 | |||
| 40 | 1700 | 3800 | 6500 | ||||
| 45 | 900 | 3000 | 5700 | ||||
| 50 | 2100 | 4800 | |||||
| 60 | 2700 | ||||||
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is a very common problem in Russia. After all, most of our territory is included in the zone of reduced insolation. In addition, vitamin D is synthesized by the body only if the sun's rays hit the skin at a certain angle, which is observed from 11 a.m. to 2 p.m. For children, this time may coincide with lunch or bedtime, while for adults it may be at work. Factors that lower vitamin D levels include constant use of sunscreen during the summer and bad habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Studies conducted in different regions of Russia have shown that vitamin D deficiency among Russian children under three years of age is approximately 24%, and its deficiency is 42%. And hypovitaminosis is especially acute in the winter period of the year - from late November to early March. Thus, more than 2/3 of children need additional vitamin D.
Symptoms in adults
Vitamin D deficiency can be detected through clinical and laboratory tests. The following symptoms should be a signal that it’s time to go to the doctor:
- chronic fatigue,
- irritability, nervousness,
- problems with stool
- sleep disorder,
- caries,
- decreased vision,
- bone loss and bone fragility,
- aching pain in bones and joints,
- increased sweating of the occipital region,
- cramps, nagging muscle pain,
- dryness, flaking of the skin,
- alopecia,
- loss of appetite, anorexia,
- overweight,
- frequent respiratory tract infections.
As we can see, the symptoms from this list are not specific. And based on them it can be difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, those who suspect they have calciferol vitamin deficiency should be tested for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH) D). If your level is in the range of 30-100 ng/ml, there is no need to worry. A reading of less than 20-30 ng/ml indicates vitamin D deficiency, and less than 10 ng/ml is diagnosed as a deficiency, in which case immediate action should be taken. Read more about the importance of vitamin D for women.
Symptoms in children
Calciferol is involved in the development of the embryo and the formation of innate immunity, so children should receive this vitamin even before birth, during the prenatal period. In childhood, when the child's skeleton, teeth and muscular structure are actively developing, adequate levels of vitamin D are very important. Symptoms of a deficiency of this vitamin in children include:
- increased tearfulness, excitability and sleep disturbances;
- growth retardation;
- slowing down the closure of the fontanel;
- weight loss;
- profuse sweating, especially during sleep;
- rickets, changes in the skeletal system (bent legs, enlarged head, flat back of the head, too convex forehead).
Read more about vitamin D for children.
At-risk groups
- Patients with liver, kidney and intestinal diseases. Vitamin D is activated in the liver and kidneys, so in people with diseases of these organs the process is disrupted.
- People with dark skin. A large amount of melanin in dark or tanned skin protects it from UV rays, which reduces the amount of cholecalciferol synthesized.
- Pregnant and lactating women. The developing skeleton of the embryo requires a large amount of calcium and calciferol - it receives them from the mother's body. During lactation, calcium is also washed out of the body, so nursing mothers, as a rule, do not have enough vitamin D and are recommended to take vitamin complexes.
- People over 60 years of age. With age, the absorption of fat in the intestines deteriorates, which affects the absorption of fat-soluble vitamin D.
- Overweight. Being a fat-soluble vitamin, calciferol dissolves in adipose tissue without having time to participate in a number of biochemical processes. Thus, the requirement for vitamin D is higher in obese people.
- Residents of the northern regions are practically deprived of sunshine, so they can replenish their supply of vitamin D only through food, dietary supplements and medications.
- Vegetarians. This is easily explained by the lack of animal foods containing vitamin D in their diet.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
At the beginning of the 20th century, many children suffered from rickets. This disease develops due to a lack of vitamin D. In adults, a deficiency of this element causes osteoporosis, intestinal obstruction, and weakened immunity.
Initial symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include weakness, sweating, irritability, decreased performance and appetite, sleep disturbances, dry and burning mouth.
Due to weakened immunity, a person begins to suffer from colds and infectious diseases more often. Impairments in the functioning of the immune system can even lead to the development of autoimmune and oncological pathologies.
With a deficiency of calciferol, a failure occurs in the synthesis of connective tissue, for example, cartilage. This can cause a person to experience pain in the joints and spine. Also, with a lack of vitamin D, collagen production is disrupted, and the skin begins to age faster.
Another problem is that when the body does not have enough calciferol, calcium begins to accumulate in it. Bones become very fragile and break easily, and teeth are destroyed.
Vitamin D is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses. Its deficiency leads to cuts in the smooth muscles of the intestines and obstruction. Multiple sclerosis, skeletal muscle damage, and blurred vision may also develop.
Lack of calciferol even affects the reproductive system. In women, the process of egg maturation stops, and in men, testosterone production decreases, which can lead to impotence.
Why does vitamin D deficiency occur?
Vitamin D deficiency may have the following causes:
• Insufficient intake of products containing it into the body. This is possible when following strict diets or in people who are vegetarians. • Diseases of the digestive system, especially the liver and biliary tract (disorder in the production of bile, which helps the body absorb the vitamin), as well as damage to the small intestine (impaired absorption of the vitamin). • Short exposure to the sun. In the cold season, when a person is rarely exposed to light and constantly wears warm clothes, the risk of hypovitaminosis is especially high.
Causes of vitamin D deficiency in the body
Why is the human body sorely lacking vitamin D? The reasons are obvious. This vitamin is synthesized in the skin in extremely small quantities and only under the influence of sunlight, but we spend little time in the sun, constantly staying indoors. And even on a long-awaited vacation on a sunny beach, we protect ourselves as much as possible from UVB rays with the help of sunscreens.
Vitamin D also enters the body with food, but, again, not always in sufficient quantities.
A deficiency of this vitamin is typical for those who suffer from diseases of the kidneys, liver and gallbladder, and experience digestive problems due to disturbances in the intestinal microbial environment (in this case, vitamin D is poorly absorbed from food and is less easily converted into its active form).
Fans of soda, dairy products and some other types of food rich in phosphates often face a lack of vitamin D. Excess phosphorus in the body interferes with the full absorption and use of vitamin D.
The human body has about 30 thousand genes, and among them only 2 thousand are affected by vitamin D. However, its deficiency creates a lot of problems: a person can develop various unpleasant diseases, the total number of which exceeds 200. This is a good reason to take care of the optimal level of vitamin D in the body.
Increased need for vitamin D
An increased need for calciferol occurs in pregnant and lactating women, in children and adolescents during periods of intensive growth and development. In old age, when natural physiological processes lead to increased fragility of bones, the human body also needs this vitamin more strongly.
The use of medium dosages of vitamin D is mandatory for women who have reached menopause: after the cessation of menstruation, the aging process becomes more active, including the bones begin to suffer significantly and a predisposition to fractures appears.
Consequences of vitamin D deficiency in the body
- Skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, etc.), increased sweating, problems with wound healing. There is clinical evidence that this is due to vitamin D deficiency.
- Partial baldness, hair loss. The correlation between poor hair condition and low levels of vitamin D has been proven for quite some time. Moreover, high doses of this vitamin have been successfully used to treat alopecia areata.
- Bleeding gums, increased caries, tooth loss, increased sensitivity of enamel, discomfort in the mouth.
- Weakened immunity and frequent cases of bacterial and viral infections. If you are constantly sick with ARVI and flu, the reason most likely lies in a lack of vitamin D. In children, its deficiency manifests itself in frequent pneumonia and bronchitis. In severe cases, an autoimmune disease may even develop.
- Increased fatigue, weakness.
- Problems with the musculoskeletal system: aching joint pain, osteoporosis, decreased muscle tone, cramps.
- Depressive conditions and other mental disorders. More than 600 studies have been conducted proving their connection with vitamin D deficiency.
Targeted nutrition tips
that will increase your energy level by 10 out of 10
From TOP nutritionists of the MIIN
Get tips
Thousands of studies have been conducted on the topic of hypovitaminosis D and its consequences, which include premature birth and slow fetal development, rickets in children, cardiovascular disorders, infertility, cancer, erectile dysfunction in men and endometriosis in women, various allergies, thyroid diseases glands, gestational diabetes and type 1 diabetes, autoimmune diseases. Even tooth decay and obesity are associated with low vitamin D levels!
Consequences of hypervitaminosis (excess vitamin D)
An overdose of vitamin D is almost more dangerous than a lack of it. In Soviet times, it was believed that it was better to have a mild form of rickets than an excess of calciferol.
Hypervitaminosis can be acute or chronic.
The acute form occurs in children if they have been taking vitamin D in high dosages for a long time. The condition may worsen due to increased sensitivity to the drug.
Symptoms of intoxication are as follows:
- lethargy, lack of appetite, constipation or diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Diarrhea and vomiting can lead to dehydration. This is very dangerous for a child’s body;
- headache, muscle and joint pain, cramps;
- increased body temperature and blood pressure, slow pulse, difficulty breathing.
The chronic form develops as a result of the use of calciferol in therapeutic doses for a long time, at least six months.
Its signs:
- lack of appetite, lethargy, decreased rate of weight gain or complete lack of weight gain;
- changes in bone tissue due to increased calcium content: rapid overgrowth of the large fontanelle, ossification of the sutures of the skull bones, partial ossification of the growth zone of long bones;
- increased calcium content in the blood, which leads to the fact that the mineral begins to be deposited on the walls of the blood vessels of internal organs: in the kidneys, heart, lungs, etc. This, in turn, disrupts their functioning.
Intoxication with calciferol has three forms, which depend on the severity: mild (without toxicosis), moderate (with moderate toxicosis) and severe (with severe toxicosis).
Mild intoxication may pass without a trace. After a severe form, complications can remain for life. Here, the greatest harm is caused by calcium deposits on the walls of blood vessels and in internal organs. The functioning of most body systems is disrupted. Children may develop chronic pyelonephritis and irregular teething.
In adults, an excess of calciferol leads to increased blood pressure and the development of cardiosclerosis, which in turn causes heart rhythm disturbances.
Excess vitamin D
Calciferol hypervitaminosis is a rarer phenomenon in our latitudes. The cause of calciferol oversaturation is often an overindulgence in vitamins. In this case, hypervitaminosis occurs, that is, a condition when the level of hydroxyvitamin D exceeds 100 ng/ml. Calcium salts begin to be deposited in muscles, internal organs, and skin, which negatively affects their condition and function. Hypervitaminosis provokes blurred vision, kidney failure and the appearance of stones. The passion of some young mothers for vitamins can lead to an excess of calciferol in the child’s body. Therefore, treatment and choice of medications for the child should be carried out as prescribed by the pediatrician. It takes into account the appearance of the newborn, as well as the type of feeding on which he is. For example, if you feed your child with milk formulas, then vitamin D is already included in their composition in the required amount, which means there is no need to use drugs to prevent its deficiency. While mother's milk, especially in winter, may contain insufficient amounts of this vitamin.
Among the signs of excess calciferol in children and adults:
- insomnia;
- frequent urination, diarrhea and vomiting;
- skin rashes;
- muscle cramps;
- irritability.
In addition, in children, an excess of vitamin D increases the symptoms of other diseases. Skin rashes or loose stools are sometimes mistaken for an allergy to vitamin D. In fact, it is simply an overdose that disrupts the liver and causes reactions similar to allergic ones.
How to find out your vitamin D level
To determine the level of vitamin D, a special blood test is taken - 25-OH. The blood is examined using high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS).
A number of laboratories instead use the ELISA method, which shows a lower degree of reliability (since it is, in principle, not intended to measure the level of vitamins D and captures many related metabolites, and the result is overestimated by 55%). If there are no laboratories nearby that accept analysis for 25-OH, you can also donate blood for ELISA, but you should remember the error of this method.
If the test result is less than 50 ng/ml, this indicates that the body is in great need of vitamin D and is deficient in it. An even lower figure, 35 ng/ml or less, indicates problems with the absorption of magnesium, calcium, zinc and other microelements from food, and if vitamin D drops below 20 ng/ml, this is a serious deficiency.
Blood test for vitamin D
A deficiency or excess of vitamin D has equally negative effects on the body. To maintain health and maintain the functions of all organs and systems, a certain level of the substance must be maintained. A special venous blood test will help determine how much vitamin D you need per day. Doctors will determine the microelement content in the body and then, based on general standards, select the required dosage of the drug or adjust the diet.
If the patient complains of soreness and deformation of the bones, frequent fractures, loss of appetite, the doctor prescribes a blood test for vitamin D. In addition to these symptoms, indigestion, prolonged exposure to sunless space, and analysis will be required before surgery on the bones or dental implantation.
An approximate breakdown of a blood test for vitamin D levels looks like this:
- normal levels range from 30 to 100 ng/ml or 75-250 nmol/l;
- slight deficiency from 10 to 30 ng/ml or 25-75 nmol/l;
- critical deficiency is below 10 ng/ml or below 25 nmol/l.
Only the doctor deciphers the tests and draws conclusions about prescribing the necessary treatment. This is usually done by an endocrinologist, sometimes a surgeon is involved. Additional tests and studies may be prescribed. For example, vitamin D deficiency is often caused by low vitamin E levels, increased liver enzymes, lack of sunlight, or poor diet.
Rules for taking vitamin D
Most domestic doctors recommend replenishing the deficiency of this valuable vitamin by taking it in doses of 400-800 IU. But this is too low a dosage, which is unlikely to have a noticeable effect. Even 5000 IU (a preventive dose of vitamin D for residents of the Northern regions) is not enough: it only allows you to reach the lower limit of the norm.
The optimal dosage for those suffering from hypovitaminosis D with an indicator of 20-40 ng is 10,000 IU daily for two to three months. This is an amount of substance approximately equal to that which would be produced by the human body under UV rays in 20-30 minutes (without SPF creams, of course). After a two to three month course, they are tested again, and if the vitamin level is restored, they switch to a lower dose - 4000-5000 IU (maintenance).
If the 25-OH analysis showed a result of 1-20 ng, then you need to take 20,000 IU of vitamin D every day, and then, within a month, 7,000-10,000 units. This is followed by monitoring, and if the dynamics are positive, the vitamin level is maintained with a prophylactic dose of 5000 IU, regardless of the time of year.
If the test results are above 40 ng, you need to take 7000 IU daily for one to one and a half months, and then maintain the vitamin level with a dose of 5000 units.
There are also higher dosages. They are prescribed, in particular, for tuberculosis and autoimmune diseases. Patients should take 30,000-40,000 IU per day for a long period (of course, under the supervision of a doctor).
We recommend
“Nutritious nutrition for children: from infants to school graduates” Read more
In general, correcting the situation with a lack of vitamin D in the body in 90% of cases turns out to be quite difficult. This vitamin is by no means harmless: long-term use of ultra-high doses (more than 40,000 units) is fraught with toxic effects and overdose. For people who have genetic mutations of VDR (genetic polymorphism of the receptors of this vitamin, which are present in almost every cell of the body), even such gigantic doses do not help to at least minimally improve the level of D. They have to take it in the form of injections. The same applies to people with gastrointestinal diseases.
Problems such as lack of cofactors, excess body weight, problems with intestinal flora, gall bladder, kidneys and liver slow down the treatment process. Pathogenic microorganisms also have an inhibitory effect:
- HIV. This virus binds to VDR(R) receptors and prevents them from converting vitamin D from food into the active form of D.
- Live Borrelia. Lyme/Borrelia reduces monocyte VDR by 50-fold.
- Epstein-Barr virus, or herpesvirus, reduces VDR by almost five times.
- Koch's bacillus and other mycobacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex that cause tuberculosis. The sensitivity of the receptors decreases by 3.3 times.
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) reduces VDR by 2.2 times.
- Acpergillus fumigus, often associated with cystic fibrosis.
- Helicobacter pylori.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonasaeruginosa).
Vitamin D receptors can be activated with the help of gamma-tocotrienols, Omega-3, Resveratrol, curcumin. These drugs work even with VDR mutations.
Learn more about NUTRILITE™ Vitamin D
Ultra-violet rays
The easiest and most natural way to increase your vitamin D levels is to spend more time in the sun. The ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight consists of three fractions of rays: UV-A, UV-B and UV-C. The synthesis of cholecalciferol requires B-fraction rays, which do not pass through the glass window. Therefore, it is recommended to catch them only in the fresh air. It should also be remembered that clouds and urban smog can retain up to 50% of ultraviolet radiation. The minimum duration of sunbathing should be 20-30 minutes a day from 11 a.m. to 2 p.m. Unfortunately, it is during these hours in the summer that you are most likely to get a sunburn. And the use of sunscreens with an SPF factor higher than 8 units block the production of vitamin D. Therefore, it is necessary to weigh the dangers and benefits of such tanning. If you can’t be in the sun, you can use a solarium. The rays of UV lamps are not equivalent to those of the sun, but they partially compensate for the deficiency of natural ultraviolet radiation. However, unreasonable use of a solarium can cause premature skin aging, pigmentation and even the appearance of melanoma.
Vitamin D Rich Foods
Among foods rich in vitamin D, fish is the leader. Calciferol is also found in whole milk and products made from it (cheese, butter), but in smaller quantities and in a form that is difficult to digest.
The main source of vitamin D is fish oil. 100 g of product contains 250 mcg of calciferol. This is 2500% of the daily requirement required by an adult.
The following is a list of dishes that contain vitamin D. The amount of calciferol in 100 g of product as a percentage of the daily intake is indicated in parentheses:
- Cod liver (1000%).
- Fatty herring (300%).
- Chum salmon (163%).
- Atlantic salmon (110%).
- Pink salmon (109%).
- Black caviar (80%).
- Egg yolk (77%).
- Tuna (57%).
- Chanterelle mushrooms – (53%).
As you can see, among the first are different varieties of fish. It contains more vitamin D than eggs or mushrooms. Therefore, housewives are recommended to cook fish dishes for their family more often. This way, both children and adults will receive the required amount of calciferol.
Below is a summary table of foods that contain vitamin D:
| Products | μg/100 g of product | Daily value for an adult, % |
| Fish: | ||
| Fish oil (from cod liver) | 250 | 2500 |
| Chum salmon | 16.3 | 163 |
| Mackerel | 16.1 | 161 |
| Milk products: | ||
| Butter | 1.5 | 13 |
| Ghee | 1.8 | 18 |
| Goat milk | 1.3 | 13 |
| Cheddar cheese | 1 | 10 |
| Swiss cheese | 1 | 10 |
| Processed cheese "Russian" | 0.74 | 7 |
| Eggs: | ||
| Egg yolk | 7.7 | 77 |
| Whole chicken egg | 2.2 | 22 |
| Quail egg | 1.4 | 14 |
| Mushrooms: | ||
| Chanterelles | 5.3 | 53 |
| Morels | 5.1 | 51 |
Who is Vitamin D3 suitable for?
Adults and children of any age need cholecalciferol - only the daily requirement differs. But there are risk groups that need increased intake of vitamin B3:
- pregnant and lactating women (the norm is from 800 to 1200 IU per day);
- vegetarians and fans of low-fat diets;
- persons with excess body weight (fat deposits interfere with the absorption of the vitamin compound);
- women during menopause and postmenopause;
- men and women planning to expand their family;
- athletes who engage in strength sports;
- residents of northern latitudes, where there is little sun;
- those with naturally dark skin;
- aged people.
Acute vitamin D3 deficiency is observed in each of us during the cold season - from October to March. At this time there is little sun, which means that too little cholecalciferol is produced to cover the daily requirement.
How much vitamin to take
For preventive purposes, adults are recommended to take 600-800 IU of vitamin D3 every day. The duration of the course is several months - throughout the entire season with a reduced level of insolation (exposure to sunlight).
For medicinal purposes, vitamin preparations are taken as prescribed by a doctor after determining the level of deficiency. The optimal concentration of cholecalciferol in the blood is considered to be in the range from 40 to 80 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/l). In case of acute deficiency, the daily dosage of the vitamin can reach up to 200 thousand IU, but in this case, treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
You can suspect a deficiency of a vitamin compound based on the following signs:
- increased fatigue;
- frequent colds;
- muscle pain;
- bone fragility;
- hair loss;
- increased tooth sensitivity.
What types of vitamins can you buy?
Vitamin D supplements are available in several forms:
- Pills. Convenient to take, suitable for long courses (you can drink it long after opening the package). The tablet is protected from the aggressive action of gastric juice by a special coating. But there may be difficulties with dosing this form if the prescribed dose differs from that indicated on the drug.
- Solution. The vitamin is available in the form of emulsions, liposomes, oil-based or water-based compounds. The liquid form is easier to dose and is better suited for children than others.
- Capsules. Recommended for people with inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Capsules with dense or liquid contents do not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines and do not cause side effects. The disadvantage of this form is the slow absorption of active substances.
- Jelly Bean. They have a pleasant taste, so they are suitable for both adults and children. But you need to take into account that the vitamin begins to interact with saliva while still in the oral cavity, so the effectiveness of the drug decreases.
To choose the best vitamin D for adults, you need to simultaneously consider both the dosage and the form of release. It’s good if one tablet/capsule/candy or measuring spoon will cover the daily dose of calciferol. A pleasant or neutral taste will be a good bonus.
Review of drugs containing vitamin D: summary table with prices
| Name | Price as of 2022 | Peculiarities |
| Aquadetrim | from 190 ₽ |
|
| Prime Kraft | 549 ₽ |
|
| Protein.Company, Vitamin D3 2000 IU | 899 ₽ |
|
| Minisan | 688 ₽ |
|
| Protein.Company, Calcium + Vitamin D3 | 699 ₽ |
|
| Wellness gummies Mixed Fruit | 1383 ₽ |
|
| Vitamir, Motherwort Forte D3 | 119 ₽ |
|
| Evalar, Vitamin D-Sun | 302 ₽ |
|
| Now Foods | 1189 ₽ |
|
| Arnebia | 239 ₽ |
|
| Cosmo–D3 | 562 ₽ |
|
| Natrol, Vitamin D3 5000 IU | 1249 ₽ |
|