In the human body, many metabolic processes occur every second. Remains of food and its components are excreted along with urine and feces. Some food components tend to color them, so sometimes you can see black stool.
Feces are the result of the processing of elements entering the human body, and by its qualitative characteristics it is always possible to assess the state of human health.
This reaction of the body in the form of black feces is often called “chernukha” or “melena” . In case of malfunctions in the body, the appearance of black feces is considered a dangerous signal from the body, which should alert a person.
Causes of dark stools
The reasons for the appearance of black feces can be different and its appearance does not always mean something bad. This phenomenon can occur in both women and men. Children are also not immune to black feces. All the reasons why stool turns black can be divided into two main categories:
- physiological;
- pathological.
Physiological causes are less dangerous and usually go away once the source of the problem is eliminated. Pathological ones are associated with dangerous changes in the body and often require medical intervention. The main factor in identifying the root cause is the general well-being of a person.
The body's reaction to foods
Black feces in humans can be a consequence of eating certain types of foods or a sudden change in diet.
In men with an addiction to drinking low-quality alcohol-containing liquids, black feces are a natural reaction of the body to poisoning.
Drinking large amounts of strong coffee or tea can give the feces a dark color.
Having foods high in calories in your diet can also cause black stools. Often a similar effect is observed when consuming the following products:
- beets;
- prunes;
- blood meat products;
- red grape varieties;
- red brands of wine.
Often, when people see dark-colored fibers in stool, they mistakenly perceive them as worms (helminths). In nature, such parasites have a completely different color, and the presence of such inclusions in the secretions is explained by a change in its color from the coloring pigments of food.
The body's reaction to medications
Black-green feces may appear after a course of antibiotic treatment, since when they are used, dead white blood cells accumulate in large quantities in areas of inflammation.
Taking painkillers containing salicylate can cause internal bleeding in an adult, which in turn leads to the appearance of dark stool.
Before using any medicine, it is recommended to study the instructions for its use, since a change in the color of the stool is necessarily indicated in the document as a possible side effect. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the consistency of feces after taking the drug.
If the stool is normal after taking the medicine, then you should not worry too much about its color. Diarrhea and loose stools during therapy are a signal of the need to consult a doctor for advice.
The black color can be caused by taking iron-containing medications and sorbents. This effect is observed when taking the following drugs:
- black activated carbon;
- Aspirin;
- De Nola;
- Ibuprofen.
Pregnant women may also experience black stools, which is associated with the use of a vitamin complex.
Digestive system problems and pathological changes
One of the common causes of black feces in newborns is swallowing a portion of blood during childbirth or getting it out of the nipples as a result of cracking.
More serious causes are associated with poor blood clotting, resulting in various types of bleeding.
The appearance of chernukha in adults may mean that this is a sign of serious problems in the digestive system.
In particular, this color appears due to the interaction of chromoprotein protein and hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach.
Black feces in an adult can appear as a result of bleeding in the body, provoked by various pathologies or surgical intervention.
Feces in newborns
Young mothers may be alarmed by their baby's black stool in the first hours after birth. A qualified doctor must prepare the woman in advance. Black stool in newborn babies is meconium. The baby's first bowel movements contain amniotic fluid, which the baby absorbed while still in the womb. Meconium has a viscous, sticky consistency and can stick to your baby's skin. In this case, feces are easily washed off with plain warm water. It is recommended to use boiled water to wash the newborn in the first days.
Original feces are usually passed for no more than two days. Then the baby's stool acquires a softer consistency and becomes light yellow or greenish. If black feces are observed in your baby for more than three days, you should definitely inform your doctor about it.
Provoking factors
The appearance of dark-colored feces is very often associated with the development of ulcerative pathological changes in the jejunum and stomach. Black feces may indicate cirrhosis, hepatitis B, A and C.
If the appearance of black feces is observed against the background of a person’s poor health, then you should urgently sound the alarm and do not delay a visit to a medical facility.
The following pathologies provoke the appearance of black stools:
- stomach ulcer;
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- tumor formations in the stomach (for example, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer);
- inflammatory process of the intestines and esophagus.
First aid for stomach bleeding
You cannot hesitate if the patient has red vomiting and black feces. What could cause these symptoms? Such signs will indicate the presence of heavy bleeding from the stomach. Taking the right steps before the ambulance arrives is of great importance. If the symptoms described above appear, the patient should be reassured and placed on a flat surface. An ice pack should be applied to the epigastric area. Such actions will help narrow the blood vessels, bleeding will become less intense.
If gastric bleeding is suspected, the patient should be prohibited from drinking and eating. Further treatment will be carried out by a qualified specialist in a medical facility.
Symptoms
Serious symptoms are abnormal behavior of the body and a person usually experiences the following symptoms:
- stomach pain;
- temperature increase;
- heartburn;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- bleeding from the anus.
Against the background of such a reaction of the body, anemia, constipation, and diarrhea may occur. Sometimes the appearance of black stool is a consequence of bleeding after surgery.
The disintegration of malignant tumors also leads to internal bleeding, leading to the coloring of stool in a rich black color.
The presence of viral or bacterial infections can also be a provoking factor for the appearance of chernukha.
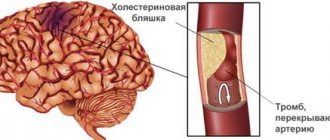
Esophageal varices or esophageal varices
Veins and arteries run along the walls of the esophagus, a long tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach. The vessels connect to the circulatory system of the abdominal organs, primarily the liver.
Esophageal varices
Heart and liver diseases lead to blood stagnation and increased pressure in the veins of the esophagus. Because of this, the vessels protrude into the lumen of the organ, the passage of food becomes difficult, and there is always a risk of injury from hard food or burns from alcohol. What pathologies can be complicated by VRVP:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatitis, often chronic;
- tumors;
- portal vein thrombosis;
- gall bladder and liver duct stones;
- chronic heart failure;
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- echinococcosis;
- cystic fibrosis.
Violation of the integrity of blood vessels leads to bleeding. It can be accompanied by only one manifestation - black loose stools or combine a set of other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting in the form of coffee grounds, abdominal pain, heartburn, belching.
Treatment of varicose veins of the esophagus is surgical - the doctor sutures, coagulates or cleaves the defect, thereby stopping blood loss. Before and during surgery, solutions are administered intravenously to normalize the electrolyte composition and maintain the volume of fluid circulating through the vessels.
Diagnostics
In the absence of obvious signs of illness, you can observe a change in the color of the stool for several days.
If the cause is the intake of coloring substances into the body along with foods, then after eliminating them from the diet, the color should normalize. If the problem persists for several days, you should consult your doctor for diagnosis.
Problems in the digestive system are indicated by the black color and smell of feces. At the same time, by the nature of the smell, you can determine the most likely problem area in the human body. The nature of the smell says a lot:
- putrefactive - problems in the digestive system associated with disruption of protein breakdown processes or chronic inflammation of the large intestine;
- rancid - problems with the digestive tract associated with pancreatic secretion or lack of bile in the intestines;
- sour - the presence of dyspepsia, that is, enzyme deficiency.
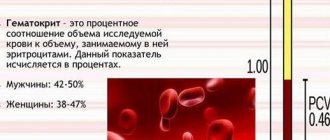
For diagnosis, a blood test is taken and a laboratory test is performed to determine the level of hemoglobin. A decrease in this indicator may indicate the presence of internal bleeding in the body.
To identify the general clinical picture, the attending physician prescribes a number of additional studies to assess the condition of the organs and the potential danger of bleeding. Most often carried out:
- research using a probe;
- MRI;
- CT;
- radiography;
- list of standard tests.
Such diagnostic methods make it possible to accurately determine the presence of pathological changes in the human body and develop therapeutic treatment tactics.
Survey
The patient is examined by a gastroenterologist; in the case of massive hemorrhage, a consultation with a surgeon is required. The diagnostic search in the presence of melena is aimed at quickly identifying the source of bleeding, and, if possible, eliminating it. A complex of instrumental and laboratory methods is used, which are necessary to study the state of the digestive tract, assess the severity of the patient’s condition and the degree of hemodynamic disorders. The most valuable for diagnostics are:
- X-ray examination
. A series of radiographs with oral contrast of the gastrointestinal tract with barium sulfate is an alternative to the endoscopic examination method. Using radiography, in 80-85% of cases it is possible to determine the location of the damage, but the technique is not always informative for establishing the etiology. - Endoscopy
. Endoscopy using a flexible probe is used not only to detect the site of hemorrhage, but also as a therapeutic method - special tools allow you to “cauterize” the bleeding vessel. In doubtful cases, a biopsy of altered areas of the mucosa is performed to verify the causes of melena. - Stool analysis
. In order to confirm the presence of blood in the stool, a three-fold Gregersen reaction is performed, which detects even a small amount of blood pigments. A standard coprogram must be performed, and bacteriological examination of stool is prescribed according to indications. - Coagulogram.
The results of the analysis of coagulation ability, the activity of the internal and external components of hemostasis are indicative of suspected hereditary hemorrhagic pathologies with impaired coagulation. To monitor the dynamics of the patient's condition, the study is done several times. - Blood tests
. All patients with melena are recommended to have a general blood test, which provides a rough estimate of the degree of blood loss for the development of further treatment tactics. To exclude concomitant diseases, a biochemical blood test and liver tests are necessary.
In case of massive bleeding and the impossibility of conducting a high-quality endoscopic examination, selective mesenteric arteriography is prescribed to visualize the exact location of the vessel damage. As a screening test for unclear etiology of melena, the radionuclide scanning method with labeled red blood cells is used.
To detect traces of blood in the stool, a stool occult blood test is prescribed.
Treatment
If the cause is the entry of coloring pigments into the body during the use of medications or after eating food, then to restore the color of stool it is enough to eliminate coloring products and medications.
In case of serious problems, the likelihood of needing hospitalization is very high. In some cases it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. If your condition suddenly worsens, you should immediately contact an ambulance service. Before the doctors arrive, the patient should not be given water or food; if possible, try to ensure recumbent rest.
For serious pathologies, the doctor can prescribe only two types of treatment - surgery and medication. Any therapy necessarily involves a low-calorie diet and bed rest.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is prescribed when pathological changes are detected, which result in bleeding, leading to the appearance of black stool. This treatment is aimed at excluding the root cause of the disease.
In a significant proportion of cases, the cause of black stool is somehow related to a disease of the digestive system. These types of pathologies include various types of gastritis.
Antral gastritis is associated with the presence of the bacterium Hilicobacter pylori in the human body, as a result of which the acidity of the gastric juice increases and the inflammatory process begins.
There are several types of the disease, some of which are considered a precancerous condition. In severe cases of the disease, gastric bleeding may occur, leading to the appearance of black stool.
Treatment of gastritis includes antibacterial therapy, taking drugs that reduce acidity and normalize the production of hydrochloric acid. Since today there are more than 10 varieties of this disease, the complex of medications is selected purely individually. The following drugs are often prescribed:
- antacids to neutralize hydrochloric acid - Gastal, Maalox, Rennie;
- antisecretory agents to reduce the level of gastric juice and acid - Ranitidine, Famotidine;
- inhibitors to suppress enzymes - Nexium, Ortanozol, Nolpaz;
- anticholinergic agents to suppress acid production - Gastrapecin;
- antibacterial agents - Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, Clarithromycin.
Gastritis is always associated with an acute inflammatory process that affects the lining of the gastric mucosa. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms.
The acute form responds well to treatment, which cannot be said about the chronic form. It is in the chronic form that gastric bleeding is characteristic, leading to the appearance of black stool.
Surgery
The appearance of black feces is very often observed in cancer. Their treatment involves a whole complex of treatments:
- drug therapy;
- radiation exposure;
- laser therapy;
- surgical intervention.
There are 4 stages of cancer in total. In the early stages, drug treatment and radiation therapy can be performed without surgery. Later stages in most cases require surgical intervention.
Peptic ulcer
Ulcerations on the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum often lead to damage to the blood vessels of the underlying layer - this is accompanied by blood loss of varying degrees. The patient may lose 20–30 ml daily from a small-diameter vessel or lose consciousness from profuse bleeding if there is a large ulcerative defect or larger arteries are affected.
Gastric ulcer on FGDS
Differences between gastric and duodenal ulcers:
| Sign | Stomach ulcer | Duodenal ulcer |
| Pain by location | In the epigastrium, 3–6 cm above the navel | Just above the navel |
| Pain by time of onset | Early – a few minutes after eating | 2 hours after eating |
| Age of onset | For most - from the age of 20 | Closer to 40 years old |
| Inheritance | Rarely | Often traced |
| Body mass | Often decreases | Doesn't change |
| Appetite | Reduced, often the patient refuses to eat because he is afraid of renewed pain | Saved |
| Response to hunger | pain | pain, but less pronounced |
Treatment can be surgical, conservative or combined. Surgery is indicated for large ulcers or defects of any size, but complicated by bleeding, malignancy, perforation, or penetration.
Conservative therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation, stopping the process, healing the mucosa and restoring its functions. For peptic ulcers, proton pump inhibitors, bismuth preparations, antibiotics, and astringents can be used.
Diet plays a big role. Everything irritating and traumatic is excluded - spicy, fried, salty, smoked, hard. Slimy porridges, neutral jelly, light soups, and stewed vegetables are optimal.
Complementary and alternative treatments at home
The main rule of treatment is moderation in diet and adherence to a correct lifestyle. For the treatment and prevention of diseases such as gastritis and ulcers, the fasting method can be used.
The therapeutic effect is achieved by maintaining a break in food intake, which allows the mucous membrane of the organs to recover. This method should be approached with caution and used only under the supervision of a physician.
Nutrition and supplements
Proper and balanced nutrition contributes to the normal functioning of the digestive system, failures in which lead to the appearance of black feces.
You should pay close attention to the calorie content of the food you eat and avoid spicy and salty foods as much as possible. Don't get carried away with fast foods and dry snacks.
It is recommended to provide the body with a balanced and proper diet, with a sufficient level of fruits and vegetables in the menu. The diet should include:
- dairy products;
- various types of cereals;
- bran;
- vegetables and fruits.
When preparing dishes, it is better to use the steam cooking method. Try not to eat foods that are too hot, as they provoke the formation of new foci of erosion in the stomach.
Do not overuse antibiotics. It is necessary to take such drugs only as prescribed by the attending physician in compliance with all rules and dosages according to the instructions.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics will ultimately lead to an imbalance of the intestinal microflora, which can lead to serious pathological changes in the future.
Folk remedies
The experience of traditional medicine is effectively used to prevent and eliminate the root cause of the appearance of black stools.
If black stool is caused by eating foods that stain the stool, time is the best remedy.
After a certain period and exclusion of these foods from the diet, the stool will acquire a natural color.
The use of one or another traditional medicine depends on the purpose of its use. For gastritis, it is effective to use:
- flax seeds;
- green apples;
- freshly squeezed potato juice;
- infusion of herbs chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow.
What is worth remembering when using such recipes is that you should not rely only on the effect of folk remedies; their use is justified only in combination with a course of medication.
Gastrointestinal Trauma
Accidental or intentional ingestion of foreign objects, seeds of berries and fruits, fish or meat bones often results in injury to the esophagus, stomach or intestines. Sharp edges cut into the mucous layer and can penetrate even deeper. As a result, not only blood loss occurs, but also severe inflammation often develops with the formation of edema.
Treatment of injuries can be conservative with the prescription of hemostatic, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, or surgical with suturing the wound and draining the source of inflammation.
Prevention
Only regular periodic examinations at a medical facility will help you avoid serious problems. It is better to prevent the disease in the early stages than to fight it after significant pathological changes in the body. It is recommended to undergo a routine examination at least 2 times annually.
It is worth knowing that pathological changes in a child’s body occur much faster than in an adult. At the first sign of problems, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible.
Women are required to visit a gynecologist. It is recommended to make such visits at least once a year.
There are the following recommendations regarding nutrition and lifestyle:
- reduce products that tend to color feces;
- review your diet, eliminate foods that are too high in calories;
- avoid overeating;
- do not indulge in fast food, fried and spicy foods;
- strives for a healthy lifestyle, does not smoke or drink alcoholic beverages.
Foods high in vitamins A, B, C, and E have an anti-cancer effect. Regular visits to the doctor, an active lifestyle, and proper diet will reduce the risk of serious pathologies in the future.
White diarrhea
Often occurs in children under one year of age. In this case, it can be caused by feeding with certain artificial formulas, overfeeding with milk, introducing new foods into complementary foods, an excess of hard-to-digest carbohydrates, and is sometimes observed during teething.
More serious causes of white diarrhea, which can occur in both children and adults: disorders of the gallbladder (partial or complete obstruction of the biliary tract), hepatitis (jaundice).
Whitening of the stool can be caused by medications that interfere with liver function (tetracycline, aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol, methotrexate, oral contraceptives, anti-tuberculosis drugs).
Forecast
Gastritis has become a common disease of our time, which is associated with the fast pace of modern life, irregular and poor-quality nutrition.
Experts say there has been a significant increase in this disease over the past 10 years. According to statistics, in developed countries, 95% of the population has problems with the digestive system.
People who drink large doses of alcohol and take corticosteroids are at risk. Pathological changes that occur in the body at advanced stages of the disease cause bleeding, the symptom of which is the appearance of black feces.
Treatment of gastritis in the early stages is effective and treatable. In advanced stages, the disease will cause significant complications:
- stomach ulcers;
- bleeding;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Esophageal cancer is a common disease in adults. If there is bleeding in the later stages of the disease, such people experience black stool.
The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the likelihood of a favorable prognosis in the treatment of the disease.
In total, there are 4 stages and each of them has its own healing process:
- first stage - 90%;
- second stage - 50%;
- third stage - only 10% live 10 years;
- stage four - life expectancy is no more than 6 months and there is practically no chance of cure.
Black feces can be the result of either a harmless reaction of the body or be a harbinger of serious problems that require immediate treatment.
Normal stool from a healthy person has a brown tint, and any deviations indicate an abnormal reaction of the body to the processes occurring in it.