Elevated blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs for a variety of reasons. Normally, the sugar level should not be higher than 5.5 mmol/l. The severity of hyperglycemia is determined by two main factors: the total amount of glucose in the blood and the rate at which it increases. In medical practice, the pathological condition in question is classified according to two criteria: fasting hyperglycemia and afternoon hyperglycemia.
Glucose is necessary for the cells of the human body, but if its level exceeds the norm, this can lead to irreversible consequences. The person himself may not notice the symptoms of this condition for a long time if it is mild. If the sugar level is significantly elevated, characteristic signs appear that are important to recognize in time and consult a doctor. In our clinic you can always get advice from competent specialists, take the necessary tests and undergo a course of treatment.
Causes of high blood sugar
High blood sugar may be associated with certain diseases:
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies;
- liver diseases;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- severe infectious diseases;
- obesity.
Diabetes mellitus is considered the most common cause of hyperglycemia, which is long-lasting and negatively affects almost all internal organs and systems of the body.
Factors that contribute to hyperglycemia that are not associated with pathologies of the body are also identified:
- overeating, predominance of simple carbohydrates in the diet;
- stress;
- severe premenstrual syndrome in women;
- alcohol abuse;
- hereditary predisposition.
Diabetes mellitus in children
Diabetes mellitus in children is a chronic disorder of carbohydrate metabolism, in which insulin production is disrupted and hyperglycemia develops. When the disease occurs, the child loses weight sharply, despite a good appetite, he is constantly tormented by thirst, and urination becomes more frequent. Typically, children are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, also called insulin-dependent.
Factors provoking the disease may be the following:
- genetic predisposition;
- viral infections, including measles, rubella, herpes;
- stress;
- artificial or mixed feeding, early introduction of cow's milk and grain crops, monotonous carbohydrate foods;
- surgical intervention;
- baby's weight at birth is 4.5 kg;
- excess weight, physical inactivity;
- diathesis;
- endocrine disorders, including Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, acromegaly, pheochromocytoma;
- pathologies of the digestive tract;
- autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, Libman-Sachs disease, periarteritis nodosa.
Recently, more and more often children are diagnosed with type 2 pathology, the main reasons being excess weight and obesity.
Associated symptoms
A pronounced increase in blood sugar levels manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, which are especially clearly visible in patients with diabetes:
- constant thirst and dry mouth;
- increased urge to urinate;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- increased appetite, weight gain or sudden weight loss (this symptom is typical mainly for patients with type 1 diabetes);
- skin itching, furunculosis, prolonged wound healing;
- increased blood pressure due to impaired renal function;
- increased irritability;
- drowsiness;
- apathetic state;
- difficulty concentrating;
- decreased vision;
- susceptibility to infectious diseases.
Having noticed such manifestations in yourself, you may suspect hyperglycemia, but only a qualified doctor will make an accurate diagnosis. In our clinic you can undergo a full range of examinations to identify acute and chronic diseases. An experienced endocrinologist will develop effective treatment tactics to eliminate pathological symptoms and return you to good health.
Diagnostics in our clinic
Diagnosis of hyperglycemia includes taking a medical history, analyzing clinical symptoms and a number of laboratory tests. A blood sugar test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. In some cases, it becomes necessary to repeat the analysis after a few days to exclude possible stress factors.
In modern medicine, several methods of testing blood for sugar are used:
- rapid test for determining the approximate glucose concentration - can be carried out at home, but does not provide one hundred percent accuracy;
- analysis for glycated hemoglobin - allows you to determine the average glucose level over a certain period of time (1-3 months);
- Glucose tolerance test is a comprehensive study that involves taking blood from a finger prick four times over two hours (on an empty stomach and after taking glucose).
In a healthy person, the glucose level is 3.5-5.5 mmol per liter of blood. An indicator of 6 mmol is considered a prediabetic state. If the glucose concentration exceeds this value, the doctor has reason to diagnose diabetes mellitus.
When performing a glucose tolerance test, a result of up to 7.9 mmol/l is considered as normal. Diabetes mellitus is indicated by a value of over 11 mmol per liter.
Principles of treatment
If you have high blood sugar, you will need treatment to avoid life-threatening conditions. The complex of therapeutic measures includes:
- adherence to the principles of proper nutrition;
- regular monitoring of blood sugar levels - for this you can purchase a special device for home use - a glucometer. It is recommended to carry out the test several times a day. Urgent consultation with an endocrinologist is required if sugar levels increase repeatedly over a short period;
- regular physical activity;
- weight normalization;
- regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels;
- taking medications to reduce blood glucose concentrations (insulin secretagogues, alpha-glucosiade inhibitors, etc.).
Treatment tactics are always selected individually depending on the reasons that led to the increase in blood sugar.
Irkutsk City Clinical Hospital No. 9
Memo for the patient:
What to do to prevent the development of hyperglycemia and diabetes.
Facts about hyperglycemia and diabetes:
- There is a new case of diabetes every 20 minutes in the United States, and every forty minutes in Europe.
- Currently, the prevalence of overt diabetes mellitus among the population of economically developed countries reaches 4-7%. However, mass surveys have shown that there are twice as many patients with latent forms of diabetes.
- In individuals whose body weight exceeds the norm by 20%, diabetes mellitus is detected 10 times more often than in the population. Among people with severe obesity, the incidence of diabetes increases 30 times. The combination of several risk factors has been shown to increase the likelihood of developing clinical diabetes mellitus by approximately 29 times.
- The mortality rate among patients with diabetes mellitus who have suffered a myocardial infarction is 1.5 - 2.5 times higher than in persons without carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) occurs when blood sugar levels rise above normal. This occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or it does not work as well as it should. Then glucose, the main source of energy, is not absorbed by the cells, the cells begin to “starve”, and weakness develops; blood sugar, on the contrary, rises and draws water from the cells - thirst appears; Due to metabolic disorders, small and large vessels of the brain, heart, kidneys and other organs are quickly affected, and immunity is impaired.
Check if you have any signs of diabetes?
- strong thirst;
- drowsiness;
- blurred vision;
- frequent urination;
- irritability;
- itching (especially in the perineal area);
- dry skin, pustules and boils;
- increased appetite;
- sticky urine.
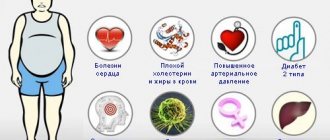
If blood glucose levels are too high, diabetes develops. In 95% of cases, this is type 2 diabetes, which occurs more often in people over 40 years of age who lead an unhealthy lifestyle. Look, maybe you also have risk factors for this dangerous disease?
- age over 45 years;
- diabetes mellitus in relatives;
- excess body weight;
- low physical activity;
- accidentally detected elevated glucose levels during examination;
- increased blood sugar during pregnancy and the birth of a large fetus;
- high blood pressure, above 140/90 mmHg;
- changes in cholesterol metabolism (low high-density lipoprotein levels ≤ 0.9 mmol/l and/or triglyceride levels ≥ 2.82 mmol/l);
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- suffered strokes, heart attacks.
If something has alerted you, then the only way to check whether you have diabetes or not is to do a blood test: determine your glucose level on an empty stomach and/or 2 hours after taking 75 grams of glucose. The frequency of examination depends on the risk group you fall into.
| Risk group | Frequency of examination |
| Persons over 45 years of age | At least once every 3 years; |
| Combination of 3 or more risk factors | At least once every 3 years; |
| Persons with prediabetes, especially those who are overweight | Once every 1-2 years |
Capillary blood glucose level
| Carrying out analysis | Norm | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
| On an empty stomach | 3,3-5,5mmol/l | 5,5-6,1mmol/l | > 6,1mmol/l |
| 2 hours after taking 75 grams of sugar or any time of the day | < 7,8mmol/l | 7,8-11,1mmol/l | >11,1mmol/l |
You can also check your risk of developing prediabetes or type 2 diabetes in the next 10 years using the following questionnaire:
- Age: up to 45 years (0 points), 45-54 years (2 points), 55-64 years (3 points), over 65 years (4 points).
- Body mass index - height (m) divided by body weight (kg) squared, for example, with a height of 165 cm and a weight of 73 kg, the index is 73: (1.65 m X 1.65) = 26.8 = 27 kg /m2: below 25 kg/m2 (0 points), 25-30 kg/m2 (1 point), more than 30 kg/m2 (3 points).
- Waist circumference - measured under the ribs at the level of the navel. Men: less than 94 cm (0 points), 94-102 cm (3 points), more than 102 cm (4 points). Women: less than 80 cm (0 points), 80-88 cm (3 points), more than 88 cm (4 points).
- How often do you eat vegetables, fruits or berries? Every day (0 points), not every day (1 point);
- Do you exercise regularly? Do you exercise 30 minutes every day or 3 hours during the week? Yes (0 points), no (2 points);
- Have you ever taken medications regularly to lower your blood pressure? No (0 points), yes (2 points).
- Have you ever had your blood sugar level higher than normal (during preventive examinations, during illness or pregnancy)? No (0 points), yes (5 points).
- Did your relatives have type 1 or type 2 diabetes? No (0 points), yes: grandparent, aunt/uncle, cousins (3 points), parents, brother/sister or own child (5 points).
TOTAL POINTS__________________________
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes over 10 years is:
| Total points | DM risk level 2 | Probability of developing type 2 diabetes |
| Less than 7 | Low risk | 1 in 100 (1%) |
| 7-11 | Slightly elevated | 1 in 25 (4%) |
| 12-14 | Moderate | 1 out of 6 (17%) |
| 15-20 | High risk | 1 out of 3 (33%) |
| more than 20 | Very high risk | 1 out of 2 (50%) |
- If you score less than 12 points, you are in good health and should maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- If you score 12-14 points, you may have prediabetes. You should ask your doctor about lifestyle changes.
- If you score 15-20 points, you may have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. It is advisable for you to check your blood sugar levels. You may need to change your lifestyle and may need medication to control your blood sugar levels.
- If you score more than 20, you most likely have type 2 diabetes. You should regularly check your blood sugar levels with a glucometer. You need to change your lifestyle and need medications to control your blood sugar levels.
Diabetes prevention should start in the kitchen.
About 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes are overweight, which weakens the effect of insulin. Therefore, the primary task in this situation is to reduce weight (not to the full norm, but 5-10% below the original) and maintain it at this level through continued dieting. This diet should be tasty, varied, not cause a feeling of hunger, but contain fewer calories than the patient consumed before; for this you just need to follow some rules:
These products should be sharply limited:
a) Severely increases blood sugar:
- Sugar, honey, dried fruits, fruit juices, confectionery, sweets, jam, lemonades (“Fanta”, “Pepsi”, etc.), natural kvass.
- Semolina porridge, mashed potatoes, heavily boiled porridge.
b) Contain a lot of calories:
- Butter, vegetable oil (especially in salads, vinaigrettes and when heating food), sour cream, mayonnaise, butter substitutes (Rama, etc.).
- Lard, sausages and sausages, sausages and pates, smoked meats, fatty meat, fatty fish, meat by-products (liver, liver), chicken legs, poultry skin.
- Fatty (“yellow” and processed) cheeses, cream, fatty cottage cheese.
- Nuts and seeds, pies and pies.
The consumption of these products should be halved:
- Bread (black or white), cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, etc.).
- Potatoes, pasta, corn and soy products, crackers, crackers (unsweetened), etc.
- Fruits: distribute throughout the day.
- Candies, waffles, etc.: as an “infrequent treat” (once a week).
- Acceptable in moderation: lean meat, fish, cottage cheese.
Increase consumption:
- Vegetables (but without added fat) in the form of vegetable side dishes : cabbage, cauliflower, carrots, beets, turnips, radishes, cucumbers, tomatoes, greens.
- Drinks without sugar: mineral water, tea).
| Physical activity to prevent diabetes Aerobic exercises are indicated, such as: walking, jogging, swimming, tennis, cycling, rhythmic gymnastics (promote more intense absorption of oxygen by the body and are beneficial for the heart and blood vessels). Aerobic physical activity ensures maximum oxygen delivery to organs and tissues, so they must be performed at a certain heart rate, which is calculated individually for each person.
|