Functions of the gallbladder
Gallbladder: schematic placement
The gallbladder is closely related to the liver, because it is in the liver that bile is produced, which is involved in the breakdown of a number of food components. A small bubble, 8 to 14 cm long and 3-5 cm wide, is a storage facility where up to 40 mg of liquid can be stored. At the request of the body, bile is transported through the common bile duct into the duodenum. The secretion produced in the liver and stored under it is involved in the breakdown of fats, ensures the transition from gastric to intestinal digestion, and neutralizes the effect of pepsin, which is so unfavorable for the pancreas. The acids contained in bile activate small intestinal motility, stimulate the production of mucus and hormones involved in digestion, and activate enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins.
Bile is also actively involved in excretory function. It removes up to 70 percent of cholesterol, bilirubin, some metals, glutathione and steroids from the body. The remaining approximately one-third of the cholesterol is reabsorbed by the intestines.
Liver bile
Hepatocytes produce bile constantly, 0.5–1 liters per day. 95–98% of liver bile consists of water and has an alkaline reaction. It contains bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, fatty acids, lecithin, ions Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, HCO3-, etc. The color of bile is due to bile pigments (bilirubin, etc.), which are formed from the breakdown products of red blood cells. It is bile pigments that color the intestinal contents brown. The role of bile in digestion is reduced to emulsification and breakdown of fats, which facilitates their digestion and absorption. Bile enhances intestinal motility.
Gallbladder diseases
But no matter how diligently nature (or God) took care of protecting a small but so important organ, man, through poor nutrition and not always a healthy lifestyle, did everything possible for the appearance of pathological processes and diseases in this organ, such as inflammation of the gallbladder, gallstones and polyps. Usually, inflammation of the gallbladder and cholelithiasis are concomitant, but which of the two diseases is primary, doctors disagree on this issue. How – you will learn about this and much more below.
Inflammation of the gallbladder, what is cholecystitis and why does it occur?
Clear localization of pain in gallbladder disease
Cholecystitis is the name of a pathological process that develops on the mucous membrane of the gallbladder. As a rule, this pathology affects older people, and women are twice as likely as men. The causes of this disease are:
- protozoa (giardia);
- microorganisms such as streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli and some others);
- worms.
Moreover, staphylococci and E. coli more often than others provoke inflammatory processes in the bile-forming organ, actively multiplying when the immune system is weakened. The infection enters it with blood or lymph from the intestines. Stagnant bile in the bladder or its ducts promotes the proliferation of microflora. Stagnation of bile secretion occurs for the following reasons:
- overeating – excessively high-calorie food changes the chemical composition of bile secretion;
- non-compliance with the diet (snacks in between, eating at night);
- sedentary work, lack of physical activity;
- hormonal changes in women (especially during pregnancy);
- age-related changes in the body, plus genetic predisposition;
- diabetes.
Inflammation in children can be caused by Giardia or Ascaris.
Classification of cholecystitis
Cholecystitis, like most inflammatory diseases, can be acute or chronic. Acute cholecystitis occurs within a quarter, chronic cholecystitis can last up to six months, at which time temporary remissions and improvements may occur. The disease is classified according to the severity of the inflammatory process:
- Catarrhal cholecystitis is characterized by external pathology of the mucous membrane of the organ, redness and swelling are observed on it;
- Phlegmonous cholecystitis fills all layers of the muscle tissue of the bladder with purulent exudate (consisting of dead leukocytes);
- Gangrenous cholecystitis is characterized by an inflammatory process with necrosis of gallbladder tissue.
Gallstones
Gallstones
Inflammation of the gallbladder can occur with or without the formation of stones. Cholecystitis without stones usually occurs in an acute form. Calculous cholecystitis, that is, inflammation with the presence of stones, is inherent in a chronic disease. Often, solid formations that form in the gallbladder clog the bile ducts, which leads to stagnation of bile and, accordingly, to inflammation. One of the reasons for the appearance of stones is the high cholesterol content of fatty foods. Sometimes small stones themselves pass through the ducts into the small intestine and are eliminated from the body, and then the pain disappears. Proponents of this theory believe that stone formation is primary and leads to cholecystitis, causing blockage of the bile canaliculi.
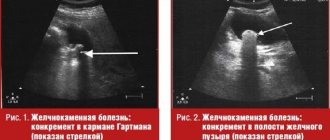
According to another theory, stones are formed as a consequence of cholecystitis, as a result of already formed stagnation of the secretion of the gallbladder. But both theories came to a consensus that cholesterol contained in excessively fatty foods is to blame for the pathologies of this organ. It is this substance that crystallizes and forms stones. Cholecystitis and the presence of stones in the bladder are diagnosed using ultrasound or x-ray. Most stones can reside in the gallbladder for several years without causing any problems. And the patient may not even be aware of their existence. If pain still occurs, or the presence of stones is detected during an examination for other reasons, the doctor may prescribe medications that dissolve solid formations. Such conservative treatment can last for several months, during which the patient is under the supervision of a doctor and undergoes regular examinations.
But if the duct is blocked, the circulation of bile is disrupted, and the development of acute cholecystitis begins. In such a situation, the doctor decides to remove the gallbladder, because an advanced disease can lead to rupture of the organ, or inflammation can affect the liver, diaphragm, or pancreas.
Treatment of gallstone disease
Treatment of gallstone disease is only surgical. Conservative treatment, taking choleretic drugs promotes the migration of stones from the gallbladder into the common bile duct and can cause acute biliary pancreatitis and obstructive jaundice.
Depending on the access and equipment used, cholecystectomy can be performed openly, laparoscopically through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall, and robotically using the DaVinci apparatus. Each method has its own indications and limitations.
Open cholecystectomy, this type of surgical intervention is indicated if there are contraindications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Such as severe cardiovascular or respiratory failure, abdominal adhesive disease, the presence of internal biliodigestive fistulas, Mirizzi syndrome.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the gold standard in the treatment of gallstone disease. This method is low-traumatic and provides excellent visualization and functionality. Modern high-tech equipment reduces the risk of intraoperative complications.
One of the options for laparoscopic surgery is robotic cholecystectomy using the DaVinci device. Allows you to isolate extrahepatic bile ducts with pinpoint accuracy, thereby protecting the patient from a dangerous complication - intersection of the common bile duct.
Special categories of patients
Elderly and senile patients require special attention. Many concomitant diseases can cause refusal of planned surgical treatment in favor of surgical treatment “for health reasons” in other clinics. Our clinic has accumulated extensive experience in providing care to patients of the older age group. After preoperative evaluation and preparation, older patients can expect to undergo surgical intervention.
Patients suffering from diabetes with a high body mass index require increased attention. Against the background of diabetes mellitus, the body's reparative capabilities are significantly reduced, which, along with severe pain and prolonged bed rest, can lead to a number of undesirable complications.
In both groups of patients, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the operation of choice, because minimally invasive access can significantly reduce surgical trauma and significantly speed up the process of patient activation. As a rule, you can get out of bed 3-4 hours after surgery. Thanks to early activation, the risk of developing cardiovascular complications and abdominal adhesive disease is significantly reduced. The use of special extended instruments allows laparoscopic surgery to be performed on patients with a body mass index of more than 40 kg/m2.
How is laparoscopic cholecystectomy performed?
The photographs show in detail the stages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
The picture shows the stage of mobilization of the neck of the gallbladder, its isolation from the adhesions with the duodenum.
In this image, using a laparoscopic instrument, the peritoneum in the area of the neck of the gallbladder is opened and the cystic duct is mobilized.
In this image, the cystic duct is highlighted and a clip is applied to it.
After applying two clips to the remaining part of the cystic duct and one to the outgoing part, it can be crossed.
After crossing the cystic duct, the cystic artery is isolated and clipped.
Now that the cystic artery has been crossed, all that remains is to separate the gallbladder from the bed and remove it from the abdominal cavity.
This image shows the separation of the gallbladder from its bed in the cervical region. Seemingly simple to perform, it requires very careful work to avoid liver damage.
The final stage of the operation. The gallbladder is separated from the bed and removed from the abdominal cavity.
What do gallbladder stones look like?
The photographs show removed gallbladders with extracted stones. The appearance of stones is varied. They differ in shape, size, appearance and structure.
In what cases is surgery justified?
The gallbladder plays an important role in the body, and its removal introduces an imbalance and forces the entire digestive system to rebuild. Therefore, the doctor tries to the last to preserve this small but so important organ. The decision to remove it is made only when its preservation threatens the patient’s life. Blockage of the ducts by stones can lead to rupture of the gallbladder and inflammatory damage to other organs - the liver, diaphragm, and intestines. The growth of polyps by 2 mm per year also indicates the possible degeneration of benign polyps into a life-threatening oncological tumor, and is therefore an indication for surgical intervention.
What is the pain with cholecystitis?
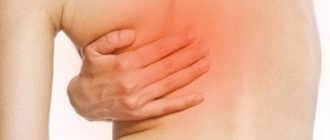
During attacks of this disease, a woman experiences severe cutting pain in the area of the right hypochondrium or in the epigastric region. The pain spreads throughout the right half of the body, extending from the neck to the shoulder blade. The pain can also move to the entire abdomen and intensify with every breath. During an exacerbation, nausea and vomiting with bile often occur. During an exacerbation of this disease, the skin is yellow and pale, the tongue is coated, and the mouth is dry. The abdominal wall in the upper part is motionless and hurts when pressed.
By the way, cholecystitis causes back pain.
Here it must be said that the same symptoms as cholecystitis may also occur in another disease. Unpleasant and cutting sensations in the chest and right shoulder blade are observed with coronary heart disease. The most important thing is to find out the reason that provokes those same pains. Exacerbation of cholecystitis occurs when consuming large quantities of unhealthy, fatty foods and other “forbidden” foods. A relapse of exacerbation may occur due to stress, nervous burnout and situations that affect the psyche and mental state in general. People suffering from cholelithiasis or pericholecystitis may experience an attack of illness due to severe physical exertion. An exacerbation can even be triggered by driving a car on bad roads with potholes, riding a bicycle or riding horses.
pain in the back and in the right hypochondrium due to cholecystitis
Jaundice that appears after an attack can have several causes. It usually appears with cholelithiasis, but can also appear with hypermotor dyskinesia. In some cases, with such diseases, white-gray stool is possible. This phenomenon will occur within a couple of days.
A person has a mild form of gallstone disease, an exacerbation appears and goes away unexpectedly. After some time after the attack, usually the next day, the patient recovers.