Magne B6 oral solution in ampoules 10ml No. 10
Magne B6 solution.
Release forms
Solution.
INN
Magnesium lactate + magnesium pidolate + pyridoxine hydrochloride.
FTG
Magnesium preparation.
Description
Transparent brown liquid with a caramel odor.
Compound
One ampoule (10 ml) contains: Active substances: magnesium lactate dihydrate – 186 mg, magnesium pidolate – 936 mg (total magnesium content (Mg2+) is 100 mg (4.11 mmol)), pyridoxine hydrochloride – 10 mg. Excipients: sodium disulfite (E223), sodium saccharinate (E954), cherry-caramel flavor, purified water. Composition of cherry-caramel flavoring: alcoholates and alcohol tinctures of raspberry, orange, cocoa, black currant, extracts of coffee, Tonka beans, hemanthus and fenugreek, vanillin, ethylvanillin, maltol (E 636), piperonal, oxyphenylone, acetylmethylcarbinol, diacetyl, isoamyl acetate, gamma-nonalactone, ionones, methylisoeugenol, benzoic aldehyde, caramel (E 150), propylene glycol (E 1520). Pharmacotherapeutic group Mineral supplements. Magnesium-based products. ATX code: A12CC.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics Physiological aspects: Magnesium is predominantly an intracellular cation. It reduces the excitability of neurons and neuromuscular transmission of excitation, and takes part in many enzymatic processes. Magnesium is an essential element of organs and tissues: bone tissue contains half of the total amount of magnesium contained in the human body. Clinical aspects: Serum magnesium levels: - between 12 and 17 mg/L (1-1.4 mEq/L or 0.5-0.7 mmol/L): indicate mild magnesium deficiency - below 12 mg/L ( 1 mEq/L or 0.5 mmol/L): indicates severe magnesium deficiency. Deficiency can be: - primary, due to a congenital abnormality of magnesium metabolism, - secondary, due to • inadequate intake (severe malnutrition, alcoholism, total parenteral nutrition), • gastrointestinal absorption disorders (chronic diarrhea, gastrointestinal fistula, hypoparathyroidism), • excessive losses at the renal level (tubular disease, significant polyuria, diuretic abuse, chronic pyelonephritis, primary hyperaldosteronism, treatment with cisplatin). Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is involved in many metabolic processes in the body and in the regulation of nervous system metabolism. The biological properties of pyridoxine are provided by pyridoxal-5-phosphate, which is formed in the body with the participation of the enzyme pyridoxal kinase. Vitamin B6 improves the absorption of magnesium from the gastrointestinal tract and its penetration into cells, which determines the effectiveness of the combination of these substances. Pharmacokinetics Gastrointestinal absorption of magnesium salts occurs partly through a passive mechanism in which the solubility of the salt plays a determining role. The degree of this absorption does not exceed 50%. Excretion occurs primarily through urine.
Indications for use
This medicine contains magnesium and is used to correct a deficiency of this element in the body. A combination of a certain number of the following symptoms may indicate a magnesium deficiency: - Nervousness, irritability, mild anxiety, transient fatigue, mild sleep disturbances, - Signs of anxiety such as gastrointestinal cramps or rapid heartbeat (if the heart is healthy), - Muscle cramps, tingling sensation Prescribing magnesium may help relieve these symptoms. If no improvement is observed after one month of treatment, continuation of monotherapy with this drug is not advisable.
Contraindications
The use of the drug is contraindicated in the following cases: - hypersensitivity to one of the components - severe renal failure with creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/minute - co-administration with levodopa.
Precautionary measures
In case of concomitant calcium deficiency, the magnesium deficiency must be corrected before the calcium deficiency is corrected, i.e. before starting to take calcium supplements. In cases of severe magnesium deficiency and malabsorption, the intravenous route of drug administration should be chosen for treatment. This drug is indicated for oral administration. IT CANNOT BE INJECTED! In moderate renal impairment, caution should be exercised to avoid the risk associated with hypermagnesemia. Due to the presence of sucrose, the drug is contraindicated in cases of fructose intolerance, impaired absorption of glucose or galactose, or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency. Use with caution for gastric and duodenal ulcers and coronary heart disease. In case of severe liver damage, pyridoxine in high doses can cause deterioration of liver function. When pyridoxine is used in high doses (> 200 mg/day) for a long time (several months or in some cases years), sensory neuropathy may develop, which is accompanied by symptoms such as numbness and vestibular disturbances, tremors of the distal extremities and gradually developing sensory ataxia (impaired coordination of movements). These disorders are usually reversible and disappear after discontinuation of high doses of vitamin B6. The ampoules contain sulfite, which may cause or worsen allergic-type reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, in patients at risk. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction You must systematically inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking. Magnesium, not recommended combinations ■ Phosphorus or calcium salts These drugs inhibit the absorption of magnesium from the intestines. Combinations to consider ■ Oral tetracyclines An interval of at least 3 hours should be maintained between oral tetracyclines and magnesium due to reduced absorption of tetracyclines in the gastrointestinal tract. ■ Oral thrombolytic agents Magnesium weakens their effect. Magnesium reduces iron absorption. Vitamin B6, not recommended combinations ■ Levodopa When used simultaneously with levodopa, the effects of levodopa are reduced or completely inhibited. Vitamin B6, combinations that should be taken into account ■ Hormonal contraceptives When used simultaneously with hormonal contraceptives, the concentration of pyridoxine in the blood plasma may increase. ■ Diuretics When used simultaneously, the effect of diuretics is potentiated. ■ Isonicotin hydrazide, penicillamine, cycloserine When used simultaneously with isonicotin hydrazide, penicillamine, cycloserine, the effectiveness of pyridoxine may be reduced. ■ Phenytoin, phenobarbital When used simultaneously with phenytoin, phenobarbital, a decrease in the concentrations of phenytoin and phenobarbital in the blood plasma is possible.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnancy This medicine, if necessary, can be used at any stage of pregnancy. If, during treatment with the drug, you discover that you are pregnant, consult your doctor, who will decide whether you need to continue treatment. Breastfeeding period The use of magnesium and vitamin B6 contained in the drug is considered compatible with the lactation period. Data on this issue are limited by the maximum daily dose of vitamin B6. The recommended dose of vitamin B6 during breastfeeding is no more than 20 mg per day.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles or other machinery
There are no special recommendations.
Directions for use and doses
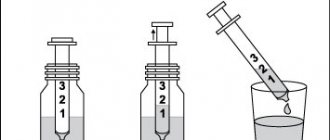
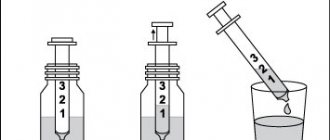
This drug is indicated for oral administration. IT CANNOT BE INJECTED! The contents of the ampoules should be diluted in half a glass of water. Adults: 3-4 ampoules per day, divided into 2-3 doses with meals. Children weighing over 10 kg (about 1 year of age and older): 10-30 mg/kg/day (0.4-1.2 mmol/kg/day), that is, 1-4 ampoules per day, divided into 2 -3 doses during meals. If you forget to take Magne B6, do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose! Treatment should be stopped after normalization of magnesium levels in the blood. ATTENTION: THE AMPOULES ARE SELF-PRESSING, DO NOT REQUIRE THE USE OF A NAILFISH! To open the ampoule, take it by the tip (you can first cover it with a piece of cloth) and break off the tip with a sharp movement. Follow the instructions shown in the picture!
Overdose
Oral overdose of magnesium usually does not cause toxic reactions if the kidneys are functioning normally. However, magnesium poisoning can develop in cases of kidney failure. Toxic effects depend on the level of magnesium in the blood, and their symptoms are as follows: - drop in blood pressure, - nausea, vomiting, - central nervous system depression, impaired reflexes, - ECG changes, - respiratory depression, coma, cardiac arrest and respiratory paralysis, - anuric syndrome . When taking a large dose, there is a risk of anuric syndrome. Treatment: rehydration, forced diuresis. In case of renal failure, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is necessary.
Side effects
Like all medicines, this drug may cause varying degrees of side effects in some people. - diarrhea - abdominal pain - skin reactions - allergic reactions Due to the presence of sodium disulfite (E 223) in this form of the drug (oral solution), there is a risk of allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, and bronchospasm. Reporting Adverse Reactions If you experience any adverse reactions, consult your doctor. This recommendation applies to any possible adverse reactions, including those not listed in the package insert. You can also report adverse reactions to the Adverse Drug Events Information Database, including reports of drug failure. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information about the safety of the drug.
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years. Do not take after the expiration date stated on the package.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Available without a prescription.
Package
10 ampoules of yellow glass type III, 10 ml capacity, with two or one break line at each of the two ends of the ampoule, along with instructions for use, in a cardboard box.
Buy Magne B6 oral solution in ampoules 10ml No. 10 in the pharmacy
Price for Magne B6 oral solution in ampoules 10ml No. 10
Instructions for use for Magne B6 oral solution in ampoules 10ml No. 10
Magne B6 for magnesium and vitamin B6 deficiency solution in ampoules No. 10
A country
France
The country of production may vary depending on the batch of goods. Please check with the operator for detailed information when confirming your order.
Compound
Solution for oral administration. Composition Active ingredients: magnesium lactate dihydrate** - 186 mg; magnesium pidolate** - 936 mg; pyridoxine hydrochloride - 10 mg; excipients: sodium disulfite - 15 mg, sodium saccharinate - 15 mg, cherry-caramel flavoring - 0.3 ml, purified water up to 10 ml.** - equivalent to the total magnesium content (Mg++) 100 mg Release form 10 ml of the drug in dark glass ampoules (hydrolytic class III EF), sealed on both sides, with a break line and the application of two marking rings on each side. 10 ampoules in a cardboard packaging insert along with instructions for use are placed in a cardboard box.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacodynamics Magnesium is a vital element that is found in all tissues of the body and is necessary for the normal functioning of cells and is involved in most metabolic reactions. In particular, it is involved in the regulation of the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction. The body receives magnesium through food. A lack of magnesium in the body can occur when the diet is disrupted or when the need for magnesium increases (with increased physical and mental stress, stress, pregnancy, use of diuretics). Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is involved in many metabolic processes and in the regulation of nervous system metabolism. Vitamin B6 improves the absorption of magnesium from the gastrointestinal tract and its penetration into cells. Serum magnesium content: - from 12 to 17 mg/l (0.5 - 0.7 mmol/l) indicates moderate magnesium deficiency; - below 12 mg/l (0.5 mmol/l) indicates severe magnesium deficiency. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption of magnesium in the gastrointestinal tract is no more than 50% of the dose taken orally. 99% of magnesium in the body is found inside cells. Approximately 2/3 of intracellular magnesium is distributed in bone tissue, and the other 1/3 is in smooth and striated muscle tissue. Magnesium is excreted primarily in the urine. At least 1/3 of the dose of magnesium taken is excreted in the urine.
Indications for use
Established magnesium deficiency, isolated or associated with other deficiency conditions, accompanied by symptoms such as: increased irritability, minor sleep disturbances; gastrointestinal cramps or rapid heartbeat; increased fatigue, pain and muscle spasms, tingling sensation.
Mode of application
Before taking the drug, you should consult your doctor. Adults are recommended to take 3-4 ampoules per day. Children over 1 year (body weight more than 10 kg) the daily dose is 10-30 mg magnesium / kg body weight (0.4 - 1.2 mmol magnesium /kg) or 1-4 ampoules. The daily dose should be divided into 2-3 doses, taken with meals. The solution from the ampoules is dissolved in? a glass of water. Treatment should be stopped immediately after normalization of magnesium concentration in the blood.
Interaction
Contraindicated combinations With levodopa: the activity of levodopa is inhibited by pyridoxine (unless taking this drug is combined with taking inhibitors of peripheral aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase). Any amount of pyridoxine should be avoided unless levodopa is taken in combination with peripheral aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitors. Combinations not recommended Concomitant use of drugs containing phosphates or calcium salts may impair intestinal absorption of magnesium. Combinations to consider When prescribing oral tetracyclines It is necessary to maintain an interval of at least three hours between oral administration of tetracycline and Magne B6®, since magnesium preparations reduce the absorption of tetracyclines.
Side effect
Immune system disordersVery rare (Contraindications—Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.—Severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/minute).—Phenylketonuria.—Children under 6 years of age (for the drug in tablet form) and up to 1 year ( for solution).— Simultaneous use of levodopa (see section “Interaction with other drugs”). With caution in moderate renal failure, as there is a risk of developing hypermagnesemia. Use during pregnancy and lactation Pregnancy Clinical experience of using the drug in a sufficient number of pregnant women women did not reveal any adverse effects on the occurrence of fetal malformations or fetotoxic effects. The drug Magne B6® can be used during pregnancy only if necessary, on the recommendation of a doctor. Breastfeeding Period Magnesium passes into breast milk. Use of the drug during lactation and breastfeeding.
Overdose
Symptoms With normal kidney function, an overdose of magnesium when taken orally usually does not lead to toxic reactions. However, in case of renal failure, magnesium poisoning may develop. Symptoms of overdose, the severity of which depends on the concentration of magnesium in the blood: decreased blood pressure; nausea, vomiting; depression of the central nervous system, decreased reflexes; changes in the electrocardiogram; respiratory depression, coma, cardiac arrest and respiratory paralysis; anuric syndrome. Treatment: Rehydration, forced diuresis. In case of renal failure, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is necessary.
special instructions
In case of severe magnesium deficiency or malabsorption syndrome, treatment begins with intravenous administration of magnesium preparations. In case of concomitant calcium deficiency, it is recommended to eliminate the magnesium deficiency before taking calcium supplements or dietary supplements containing calcium. With frequent use of laxatives, alcohol, strenuous physical activity and mental stress, the need for magnesium increases, which can lead to the development of magnesium deficiency in the body. The ampoules contain sulfite, which can cause or intensify the manifestations of allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, especially in patients at risk. When using pyridoxine in high doses (more than 200 mg per day) over a long period of time (several months or in some cases years), sensory axonal neuropathy may develop, which is accompanied by symptoms such as numbness, impaired proprioceptive sensitivity, tremors of the distal extremities and gradually developing sensory ataxia (impairments coordination of movements). These disorders are usually reversible and disappear after stopping taking vitamin B6. Attention: Self-breaking ampoules with Magne B6® do not require the use of a nail file. To open the ampoule, take it by the tip, having previously covered it with a piece of cloth, and break it off with a sharp movement, first from one pointed end, and then from the other, having previously directed the end of the ampoule, opened first, at an angle into a glass of water, so that the one being broken off by the second the tip of the ampoule was not above the glass. After breaking off the second tip of the ampoule, its contents will flow freely into the glass.