Indications for use
It has antiemetic, sedative and antitussive effects. The reaction to external stimuli decreases, as does psychomotor agitation, affective tension, the feeling of fear is suppressed, and a weakening of aggressiveness is noted. Teraligen is used as a sleeping pill, but in a general sense it is not. Neuroleptics simply induce drowsiness and speed up the onset of sleep. And this must be taken into account in certain specialties.
Teraligen may induce drowsiness and accelerate the onset of sleep
That is, the pharmacological use of Teraligen is quite wide. The medicine is available in the form of dark pink, film-coated tablets. It contains 5 mg of alimemazine tartrate.
Teraligen is effective for neurotic disorders due to trauma, intoxication, vascular disorders in combination with autonomic disorders, anxiety and mild depressive disorders.
This medicine is used to treat the following diseases:
- somatized mental disorders;
- states of excitement and anxiety against the background of somatic pathologies;
- sleep disorders of various origins;
The drug is used to treat mental disorders and depression
- psychopathy with asthenic and psychoasthenic disorders;
- anxiety-depressive conditions within the framework of borderline endogenous and vascular diseases;
- senestopathic depression;
- allergic reactions (symptomatic treatment);
- neuroses and neurosis-like conditions of endogenous and organic origin with a predominance of senestopathic, hypochondriacal, phobic and psychovegetative disorders.
Instructions for use of the drug Teraligen
Teraligen is taken orally, distributing the daily dose 3-4 times. It should be remembered that the effect of the drug begins 15-20 minutes after administration and lasts about 6-8 hours. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe a dosage of medication! Do not self-medicate, it is dangerous.
Recommended dosage for adults:
- For difficulty falling asleep: 5-10 mg 1 time per day, 30 minutes before bedtime;
- For anxiety: 20 mg 3-4 times a day;
- For psychotic conditions: 50-100 mg 4 times a day.
Recommended dosage for children over 7 years of age:
- For difficulty falling asleep: 2.5-5 mg 1 time per day, 30 minutes before bedtime;
- For allergies: 2.5-5 mg 3-4 times a day;
- For anxiety: 5-10 mg 3-4 times a day;
- For psychotic conditions: 15 mg 4 times a day.
Material and methods
20 patients (5 men and 15 women) took part in the clinical observation, 6 of them were over 65 years of age (1 man and 5 women), the average age was 50±16.39 years. All participants signed an informed consent to participate, and at the time of inclusion in the program, the clinical manifestations of their condition met the criteria for anxiety-depressive disorders (ICD-10 diagnosis: Other anxiety disorders - F41) with a severity of painful symptoms of at least 18 points on the anxiety scale Hamilton and at least 4 points on the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI, Clinical Global Impression Scale). Patients either did not have stable antipsychotic and antidepressant therapy over the past 3 months or did not demonstrate a sufficient response to therapy. The observation did not include patients with contraindications to the use of the drug Alimemazine and severe somatic diseases, consequences of severe brain damage.
The psychopathological structure of the patients' clinical status was dominated by manifestations of affective (anxiety) syndrome coupled with autonomic disorders. In 8 patients, anxiety and autonomic disorders were observed in the form of paroxysmal states, in the rest they were constantly present from the onset/exacerbation of the disease throughout its entire duration. At the time of inclusion in observation, all patients complained of difficulty falling asleep (signs of insomnia); many showed tearfulness, low mood, weakness and fatigue. Among the frequently occurring vegetative manifestations are headaches and dizziness, unsteadiness when walking, instability of blood pressure, tachycardia, sensation of hot flashes, “burning” in the body and head, numbness in the arms and legs, nausea, “lump in the throat”, various pain in the body, constipation and diarrhea, sweating, frequent urination.
The patients' condition was assessed initially (observation 1) and over time on the 12th and 30th days of therapy (observation 2-3). Efficiency assessment in dynamics was carried out 3 times on psychometric scales - Hamilton anxiety, Beck depression and Taylor questionnaire, and also analyzed the change in severity and improvement in status on scales of general clinical impression (severity of condition (CGI-S, Clinical Global Impression Scale - Severity of Illness) and from the second visit improvement (CGI-I, Clinical Global Impression Scale - Improvement)). Adverse events were also recorded in patients (in accordance with the general principles of reporting spontaneous messages in accordance with Federal Law 61, Article 64).
Therapy.
For therapy, the drug Alimemazine was used in the form of a solution for intramuscular administration (5 mg/ml, 25 mg in 5 ml), in the following dosage regimen: starting dose (day 1) was 12.5 mg (2.5 ml) 1 once a day (in the evening), on the 2-3rd day, as necessary, 25 mg (5 ml) once a day (in the evening), from the 4th day, as necessary, 50 mg per day. The average daily dose in 20 patients using Alimemazine solution from days 4 to 12 of therapy was 31.25 mg/day, most patients (n=17) took 25 mg/day, 2 at a dose of 50 mg/day and 1 patient 100 mg/day days To increase the effectiveness of relieving anxiety symptoms, the individual daily dose was increased in only one patient to 100 mg/day (50 mg 2 times a day). The issue of transferring to a tablet form (in a dose equivalent in milligrams) after 12 days of intramuscular injections of Alimemazine was decided with each patient individually; Taking into account the positive dynamics of the condition, good tolerability of the drug and the consent of the patients, it was decided to continue therapy with Alimemazin in tablet form (until the 30th day of treatment). Together with Alimemazine (solution), all patients received concomitant therapy with one of the antidepressants from the SSRI group (fluvoxamine 175 mg/day, sertraline 150 mg/day, escitalopram 15 mg/day) or SNRI (venlafaxine 150 mg/day), as well as 4 patients additionally took mood stabilizers (lamotrigine 200 mg/day). The choice of antidepressants was justified by the conditional predominance of anxiety or depressive symptoms in a given patient and the history of use of antidepressant therapy, if any, in the patient. The use of mood stabilizers was due to the presence of significant irritability and the observed cyclicality in the patients’ condition. In addition, all patients continued to take medications recommended for the correction of comorbid somatic diseases, for example, antihypertensive drugs, etc.
Contraindications
Teraligen is prohibited for use in the following cases:
- parkinsonism;
- myasthenia gravis;
- Reye's syndrome;
- hypersensitivity;
- simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors;
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- prostatic hyperplasia;
- severe liver and kidney diseases;
- children's age up to 7 years.
Teraligen is prohibited during pregnancy
Also, the drug is prescribed with caution when:
- suppression of bone marrow function;
- epilepsy;
- arterial hypotension;
- chronic alcoholism;
- jaundice;
- predisposition to urinary retention;
- open-angle glaucoma;
- obstruction of the bladder neck.
Teraligen
Clinical and pharmacological group
Antipsychotic drug (neuroleptic)
Contraindications
- - angle-closure glaucoma;
- - prostatic hyperplasia;
- - severe liver diseases;
- - severe kidney disease;
- - parkinsonism;
- - myasthenia;
- - Reye's syndrome;
- - simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors;
- - pregnancy;
- - period of breastfeeding;
- - children under 7 years of age;
- - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug should be used with caution in chronic alcoholism if there is a history of complications when using phenothiazine drugs, obstruction of the bladder neck, predisposition to urinary retention, epilepsy, open-angle glaucoma, jaundice, suppression of bone marrow function, arterial hypotension.
Dosage
The drug should be taken orally, dividing the daily dose into 3-4 doses.
The onset of action of the drug is after 15-20 minutes, the duration of action is 6-8 hours.
For adults, to achieve a hypnotic effect, 5-10 mg/day; to achieve an anxiolytic effect, 60-80 mg/day. For psychotic conditions - 200-400 mg/day.
Children over 7 years of age (depending on age and body weight) to achieve a hypnotic effect, 2.5-5 mg/day; as a symptomatic treatment of allergic reactions, 5-20 mg/day; to achieve an anxiolytic effect, 20-40 mg/day; in psychotic conditions, it is possible to increase the daily dose of the drug to 60 mg/day.
Side effects
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: drowsiness, lethargy, fatigue (occurs mainly in the first days of taking the drug and rarely requires discontinuation of the drug), paradoxical reaction (restlessness, agitation, nightmares, irritability); rarely - confusion, extrapyramidal disorders (hypokinesia, akathisia, tremor); increased frequency of night apnea, increased seizure activity (in children).
- From the senses: blurred visual perception (accommodation paresis), noise or ringing in the ears.
- From the cardiovascular system: dizziness, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia.
- From the digestive system: dry mouth, gastrointestinal atony, constipation, loss of appetite.
- From the respiratory system: dry nose, throat, increased viscosity of bronchial secretions.
- From the urinary system: bladder atony, urinary retention.
Other: allergic reactions, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis, increased sweating, muscle relaxation, photosensitivity.
The drug is usually well tolerated by patients. Side effects are rare and mild.
Overdose
Symptoms: depression of consciousness, increased adverse reactions.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Drug interactions
- Alimemazine enhances the effect of opioid analgesics, hypnotics, anxiolytic (tranquilizers) and antipsychotic (neuroleptics) drugs, as well as drugs for general anesthesia, m-anticholinergic drugs and antihypertensive drugs. The dose of alimemazine should be adjusted when used concomitantly with the above-mentioned drugs.
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with amphetamine derivatives, m-cholinomimetics, ephedrine, guanethidine, levodopa, dopamine, the effect of the latter is weakened.
- When alimemazine is used concomitantly with ethanol and drugs that depress the central nervous system, central nervous system depression is observed.
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with antiepileptic drugs and barbiturates, the threshold for convulsive readiness is reduced (dose adjustment of the drug is required).
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with beta-blockers, the concentration of the latter in the plasma increases (a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and arrhythmias is possible).
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with bromocriptine, the effect of the latter weakens and the concentration of prolactin in the blood serum increases.
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with tricyclic antidepressants and anticholinergic drugs, the m-anticholinergic activity of alimemazine is enhanced.
- With simultaneous use of alimemazine with MAO inhibitors and phenothiazine derivatives, the risk of arterial hypertension and extrapyramidal disorders increases (simultaneous use is not recommended).
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with drugs that inhibit bone marrow hematopoiesis, the risk of myelosuppression increases.
- With the simultaneous use of alimemazine with hepatotoxic drugs, the manifestations of hepatotoxicity of the drug increase.
special instructions
- During long-term treatment, a general blood test should be systematically performed and liver function assessed.
- Alimemazine may mask the ototoxic effect (tinnitus, dizziness) of co-administered drugs.
- To prevent distortion of the results of skin prick tests for allergens, the drug should be discontinued 72 hours before allergy testing.
- During treatment, false positive pregnancy test results are possible.
- During treatment you should not drink alcohol.
- Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
- During treatment with the drug, you should not engage in activities that require increased concentration.
Pregnancy and lactation
The use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Use in childhood
Contraindicated in children under 7 years of age.
For impaired renal function
The use of the drug is contraindicated in severe kidney disease.
For liver dysfunction
The use of the drug is contraindicated in severe liver diseases. During long-term treatment, liver function should be systematically assessed.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is available with a prescription.
Storage conditions and periods
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 3 years.
Release form, composition and packaging
Dark pink film-coated tablets with an embossed symbol on one side and a stripe on the other.
1 tab.
alimemazine tartrate
5 mg
Excipients: lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, refined sugar (sucrose), wheat starch, tapioca starch (tapioca), talc, magnesium stearate.
Shell composition: hypromellose, macrogol 6000, titanium dioxide, Osprey R110 pink dye, talc.
- 10 pieces. — cellular contour packages (1) — cardboard packs.
- 10 pieces. — contour cell packaging (2) — cardboard packs.
- 10 pieces. — contour cell packaging (5) — cardboard packs.
- 25 pcs. — cellular contour packages (1) — cardboard packs.
- 25 pcs. — contour cell packaging (2) — cardboard packs.
- 25 pcs. — contour cell packaging (5) — cardboard packs.
Side effects
Judging by the clinical data, patients taking Teraligen tablets tolerate the drug well. Therefore, the occurrence of side effects is rare. But if they do exist, then the list of side effects is as follows:
- From the genitourinary system: urinary retention, bladder atony.
- From the respiratory system: increased viscosity of bronchial secretions, dryness of the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx.
- Allergic reactions: urticaria, photosensitivity, allergic dermatitis, Quincke's edema.
- Laboratory indicators: false positive pregnancy test result.
- From the senses: decreased visual acuity, ringing and tinnitus. From the blood vessels and heart: arterial hypotension, cardiac arrhythmia, dizziness.
- From the digestive tract: dry mouth, intestinal atony, anorexia, constipation.
- From the nervous system: asthenia, drowsiness, fatigue, paradoxical reactions (including anxiety, nightmares, irritability and agitation), confusion. In addition, it is possible to develop increased frequency of sleep apnea, increased seizure activity, as well as extrapyramidal disorders (including akathisia, hypokinesia and tremor).
- Others: increased sweating, decreased bone marrow function, muscle relaxation.
In addition, alimemazine can distort the results of skin prick tests for various allergens. Therefore, if you are having an allergy test, you should stop taking the drug no later than 72 hours in advance.
Analogs of the drug Teraligen
Teraligen has no analogues for the active substance - alimemazine tartrate. Substitutes that have a similar pharmacological effect belong to the group of neuroleptics.
Remember that the attending physician must prescribe medications, as well as substitutes!
Remember that the attending physician prescribes medications or their analogues
Klopiksol
Clopixol tablets contain zuclopenthixol hydrochloride. Although this is in some sense a substitute for Teraligen, and they are similar in pharmacological action, Klopixol has a stronger antipsychotic effect. Thanks to this, Clopixol is more often used to treat serious mental health disorders: schizophrenia, hallucinations, paranoia, manic states, dementia.
Clopixol is contraindicated in comatose states, acute poisoning by barbiturates, alcohol, opiates, pregnancy and breastfeeding. Clopixol, unlike Teraligen, is better tolerated by patients. Side effects are similar to Teraligen, but occur even less frequently and are not as pronounced.
Conapax
It is also an antipsychotic drug based on thioridazine hydrochloride. Sonapax has a more pronounced antihistamine and anticholinergic effect compared to other neuroleptics. Indicated for use in those cases described in the instructions for Teraligen. But it can be used to treat children from 4 years of age. Conapax is contraindicated in comatose states, acute depression, porphyria, pheoxomocytoma, hematopoietic disorders, in the first trimester and in the last week of pregnancy, during lactation tions. Sonapax is well tolerated, it can be taken by children, and its price is lower than Teraligen.
Chloprothixene Zentiva
The main active ingredient of Sanofi Chloprothixene tablets is chlorprothixene. Medicines are indicated for the treatment of: psychoses, schizophrenia, depressive states, mental disorders during menopause and for diseases of the brain (traumatic brain injuries, enc ephalopathy), alcoholic delirium, sleep disorders caused by psychosomatic and neurotic disorders, insomnia due to burns, skin diseases, accompanied by itching. Contraindications for use: hypersensitivity, coma, poisoning with drugs that depress nervous activity. When taking tablets, in addition to the side effects characteristic of Teraligen, disorders of the mammary glands and reproductive organs are possible: galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, c decreased libido.
Pipolfen
This is a Hungarian analogue of Teraligen based on promethazine hydrochloride. It is often used as a sedative for postoperative pain (in combination with analgesics), allergic diseases and other cases. Pipolfen has a fairly large list of contraindications and age restrictions, so before treatment, be sure to consult a specialist and read the instructions.
Teraligen and alcohol
The combination of drugs and alcohol does not go away without leaving a trace; it can often lead to very serious consequences. You should be especially careful when taking psychotropic medications like Teraligen.
Teraligen should not be taken with alcohol!
The instructions attached to the medication clearly indicate that it is strictly forbidden to take it with alcohol, since it can only increase the severity and intensity of the underlying pathology.
The annotation for the drug indicates the side effects that occur when combining Teraligen + Alcohol:
- irritability and anxiety, nightmares and emotional overexcitement;
- drowsiness and excessive fatigue, lethargy;
- confusion;
- visual impairment, manifested by blurred perceived image;
- disorders such as tremor, an internal need to constantly move, or, conversely, a condition associated with insufficient movement activity;
- frequent cases of respiratory arrest during night sleep;
- extraneous sounds in the ears, frequent dizziness and fainting, decreased blood pressure;
- dryness of the mucous membranes in the mouth, nasal cavity, pharynx, lack of appetite, various allergic manifestations;
- tachycardia disorders, hyperhidrosis, disorders in bone marrow hematopoiesis;
- urinary retention;
- lack of normal tone in the muscular system of the gastrointestinal tract, bladder, as well as muscle relaxation, etc.
Remember that antipsychotic drugs have a strong effect on the central nervous system. Only a doctor can prescribe antipsychotics. In addition, a prescription is required to purchase such medications.
Results and discussion
Therapy with Alimemazine (solution) together with antidepressants from the SSRI and SNRI group determined significant positive dynamics in the reduction of anxiety and depressive disorders, sleep disorders and autonomic symptoms.
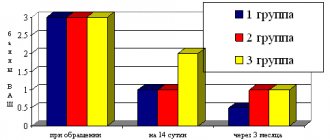
All patients experienced a significant decrease in the severity of both mental (already in the first half hour after the injection) and somatic components of anxiety (already in the first days of therapy), along with an improvement in the quality and duration of night sleep. It is worth noting that the parallel stabilization of vegetative symptoms affected both constant and paroxysmal manifestations. The most rapid reduction (already in the first 5-5 days of therapy) was observed among the following symptoms: sensation of hot flashes, “burning” in the body and head, numbness in the arms and legs, nausea, “lump in the throat”, various pain sensations in the body . Headaches and dizziness, blood pressure instability, sweating and frequent urination decreased in frequency and intensity closer to the 2nd week of therapy. The improvement in the clinical condition was reflected in a consistent decrease in the average total score of the anxiety level when assessed on the Hamilton scale, so by the 12th day it decreased by 33.7% (8.2 points, from 24.35 to 16.15 points), and also on the Taylor scale by 30.3% (by 9.5 points, a decrease from 31.4 to 21.9 points) (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The effect of using Alimemazine (solution for intramuscular use) on the reduction of depressive symptoms according to the Hamilton, Taylor and Beck scales (in points). When switching to a tablet form (in a dose equivalent to milligrams) after 12 days of intramuscular injections and continuing drug therapy (until the 30th day), a further progressive decrease in the severity of anxiety was observed. For example, on the Hamilton scale by the 30th day the decrease compared to the baseline was 55.4% (by 13.49 points, from 24.35 to 10.86 points), and on the Taylor scale by 50.0% ( 15.7 points, decrease from 31.4 to 15.7 points). All 19 patients who completed the study showed more than 50% improvement in anxiety.
The average decrease in the level of depression on the Beck scale by the 12th day was 20.8% (by 4.55 points, from 21.9 to 17.35 points), and with continued therapy with Alimemazine tablets by the 30th day by 35.4 % (by 7.76 points, from 21.9 to 14.14 points) (Fig. 1). The effect on depressive symptoms was predictably less rapid than on anxiety symptoms. However, it is worth noting that the effect on depression began from the first days of therapy and progressively increased, especially after the addition of the effect of antidepressants, which became more pronounced closer to the second week of therapy.
Similar dynamics were observed on the global clinical impression scale (Figure 2).
Rice. 2. Dynamics of severity and improvement of clinical condition during therapy with Alimemazine (solution for intramuscular use) according to the global clinical impression scale (improvement of condition - CGI-I and severity of condition - CGI-S). During drug therapy, the severity of the condition decreased by 26.7% (by 1.15 points, from 4.3 to 3.15 points) and on the 30th day by 56.0% (from 2.41 points to 1.89 points from the initial level), in addition, on the 12th day of therapy, an improvement was achieved to a level of 2.85 points on the 30th day by 35.4% (1.01 points, from 2.85 to 1.84 points ) (Clinical Global Impression of Severity and Improvement Scale, CGI-S CGI-I). Despite maintaining 1-2 points when assessed on the CGI-S scale, by the 30th day doctors noted extremely significant progress in the patients’ condition and an almost complete restoration of the patients’ functioning.
The use of a combination of antidepressants and Alimemazine made it possible to facilitate the initial stage of therapy, reducing the symptoms of nausea and anxiety associated with the use of SSRIs. Carrying out a detailed differentiation between the effects of Alimemazine and antidepressants was beyond the scope of this work and would require a significant increase in the sample and the formation of a control group, which is possible with more in-depth studies.
Only 1 patient dropped out of the observational program and did not complete the course of therapy, and this was not related to taking the drug. In general, all patients tolerated injection therapy with Alimemazine well and did not report significant side effects, regardless of age and gender. Among the most common side effects observed in patients were mild sedation the morning after injection of the drug in 4 participants, which was reduced by the 3rd day of therapy, as well as some hypotensive effect in 4 participants, which allowed them to reduce their antihypertensive therapy. The only negative point when ensuring continuity of therapy and continuing treatment with the oral form of Alimemazine (5 mg tablet) is some inconvenience for patients, which is associated with the transition to a large number of tablets required for administration and the corresponding achievement of the equivalent dose achieved with the drug solution.