Vasoton (L-arginine), 0.5 g, capsules, 60 pcs.
L-arginine - amino-guanidyl-valeric acid - an amino acid that plays an important role in the urea formation cycle (neutralization of protein waste).
Provides nitrogen to the enzyme system that synthesizes nitroso group (NO), a substance that regulates arterial tone.
Vasoton™ (L-arginine):
- reduces blood pressure (treatment of hypertension) by reducing arterial muscle tension and dilating peripheral resistive arteries by improving the supply of nitric oxide;
- increases collateral blood flow to an occluded coronary vessel in patients with coronary heart disease;
— used in complex therapy and for the purpose of preventing atherosclerosis and its complications, to improve the functional state of the cardiovascular system;
— helps to improve the general condition of patients with coronary artery disease: reducing the frequency of angina attacks, reducing the amount of nitrates taken, increasing endurance to physical activity, as well as the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs;
- improves the rheological properties of blood, prevents the formation of blood clots, significantly reduces the risk of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques;
- participates in the production of growth hormone, which promotes growth intensity. This really allows short parents to ensure that their children become tall.
Vasoton™ (L-arginine) has a stimulating effect on the reproductive system equally in both men and women of all age groups:
- used to treat male infertility;
— increases the production of seminal fluid, spermatogenesis;
- stimulates potency and sexual activity;
- able to increase the strength and duration of blood supply to the genital organs; prolongs the time of sexual intercourse;
- enhances pleasant sexual sensations;
- makes orgasm longer;
- increases the frequency and intensity of orgasms.
Vasoton™ (L-arginine):
- promotes the production of serotonin or the hormone of joy, which improves mood, makes a person more active and resilient;
- stimulates the production of insulin, thereby helping to normalize blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes;
— improves liver function, especially recommended for cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, including after treatment of alcoholism, long-term use of medications;
- allows the body to quickly recover after heavy physical exertion, especially necessary for intensively training athletes after 30 years, when its natural secretion completely stops; reduces the number of free radicals;
— helps to increase muscle mass and reduce body fat mass with adequate physical activity;
- increases the cleansing potential of the kidneys;
- plays an important role in the urea formation cycle (purification of protein waste);
— activates the immune system, which is extremely important for immunodeficiency diseases (AIDS).
Vasoton. Possibilities of using Vasoton (L-arginine) in the treatment of diseases of internal organs
Metabolic therapy strategies are increasingly being used in modern drug therapy regimens. An example of this approach is the use of a nitric oxide donor, L-arginine, which has proven effective in treating a variety of diseases of internal organs. Currently, L-arginine is produced by various pharmaceutical companies, both domestic and foreign. One of the “new products” on our domestic market is the drug “Vazoton” (ZAO Altaivitamins, Russia), which contains the amino acid L-arginine. Vasoton is recommended to take 1 capsule (0.5 g) 2 times a day for 2–6 weeks. After 3–6 months, the preventive course can be repeated. Arginine (a-mino-s-guanidine valeric acid) is a diaminomonocarboxylic amino acid, the molecule of which, in addition to the amino group, contains an amidine group (NH2-C=NH). Arginine has the properties of a base (isoelectric point at pH = 10.76), forms colorless crystals, soluble in water. Arginine is part of almost all plant and animal proteins. Under the action of the enzyme arginase, as well as during alkaline hydrolysis, arginine breaks down into the amino acid ornithine and urea. This reaction plays an important role in the formation of urea in the liver of mammals. L-arginine is a natural L-isomer of the amino acid arginine, necessary for the synthesis of a number of proteins. The first serious scientific interest in this essential amino acid appeared in the mid-80s of the last century, when a series of experiments proved that L-arginine can stimulate the production of growth hormone. This effect allows us to classify this amino acid as a group of drugs that slow down the aging process. And it also underlies the extreme popularity of dietary supplements with arginine among professional athletes and people leading an active lifestyle. Vasotone (L-arginine) acts as a precursor to nitric oxide, which is released from endothelial cells and promotes vasodilation. The process of synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) from the amino acid L-arginine is a complex oxidative reaction catalyzed by a group of NO synthase enzymes in the presence of NADPH, calmodulin and other cofactors, which together form the L-arginine-NO system. Regulation of NO synthase activity occurs through the final product through feedback; NO is able to bind to the hemic group of the enzyme, thereby reducing its activity [1]. NO is one of the most important biological mediators involved in many physiological and pathophysiological processes. It is a secondary messenger unique in its nature and mechanisms of action in most cells of the body. In particular, NO is involved in the implementation of many important physiological functions, such as vasodilation, neurotransmission, reduction of platelet aggregation, immune system reactions, regulation of smooth muscle tone, memory, etc. [2]. The important role of nitric oxide in numerous biological processes in the body was the basis for naming NO Molecule of the Year in 1991 [3]. In 1980, the phenomenon of relaxation of pieces of aorta with intact endothelium in response to acetylcholine (ACh) was first described. This indicated the presence of a substance secreted by endothelial cells and affecting myocytes. The substance was named endothelium-dependent relaxing factor (EDRF). EDRF, through activation of soluble guanylate cyclase (GC) and subsequent synthesis of the second messenger cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), has been shown to induce relaxation of vascular smooth muscle. Later Palmer et al. identified EDRF as NO, which is produced by endothelial cells [4]. The effect of L-arginine on the cardiovascular system is complex and varied. The main mechanism of action in this case is the release of nitric oxide. L-arginine has the following effects: 1. Reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases by maintaining normal blood cholesterol levels. 2. Provides blood flow to the extremities. 3. Reduces diastolic pressure due to the expansion of peripheral resistive arteries by improving the supply of nitric oxide. 4. Increases collateral blood flow to an occluded coronary vessel in patients with coronary heart disease.
L-arginine is taken in doses of 2-3 g per day along with meals, or an hour and a half after meals, with a full glass of water. In a study by Kielar et al. It has been shown that regular administration of L-arginine helps to improve the general condition of patients with coronary heart disease, reduce the frequency of angina attacks, reduce the dose of nitro drugs, increase exercise tolerance, and also increase the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs [5]. In addition, L-arginine improves the rheological properties of blood, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis. According to Cylwik D. et al., long-term administration of L-arginine is accompanied by inhibition of collagen-induced platelet aggregation [6]. This information confirms that this amino acid has a pronounced antithrombotic effect. Numerous studies indicate that the administration of L-arginine to patients with heart failure is accompanied by a significant increase in blood flow in the coronary arteries during exercise, an improvement in the functional state according to the results of the measured walking test and in the level of quality of life. According to Gouvea SA et al., the hypotensive effect of oral administration of L-arginine in patients with renovascular hypertension is due not only to the release of NO, but also to the inhibition of angiotensin-II production [7]. Vasoton (L-arginine) is used in the treatment and prevention of liver diseases (cirrhosis and fatty hepatosis), this amino acid is involved in the cycle of transamination and removal of final nitrogen from the body, i.e. protein breakdown product. The body’s ability to secrete urea and excrete protein waste depends on the power of the “ornithine – citrulline – arginine” cycle. Vasoton helps improve liver function in case of hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, fatty infiltration of the liver, as well as with long-term use of medications. Vasotone (L-arginine) has a beneficial effect on the condition of the prostate gland, increases sperm production and increases blood flow to the genitals, creating conditions for a more stable and long-lasting erection. The drug is effective for erectile dysfunction, oligospermia, increases libido, potency, and stimulates spermatogenesis. In men, NO plays a critical role in the ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Some studies show that arginine at a dose of 2.8 g affects the production of a vasodilator in an amount sufficient to successfully combat the inability to erection, and daily intake of 3-4 g of this amino acid increases the specific sperm count [8]. The effects of this amino acid on the immune system are varied. L-arginine is known to stimulate the activity of NK cells, LAK cells (lymphokine activated killer cells) and T lymphocytes produced by the thymus. The experiment showed that split administration of high doses of arginine throughout the day leads to an increase in NK cell activity by 91%. According to Izgut-Uysal VN et al., the administration of L-arginine significantly increases phagocytosis by peritoneal macrophages, but this effect is more pronounced in middle and old age than in young people. Thus, L-arginine helps prevent age-related inhibition of the phagocytosis activity of peritoneal macrophages [9]. According to Song JX et al., parenteral administration of L-arginine as part of nutritional mixtures to patients with immunosuppression after surgery for colon cancer was accompanied by a significant increase in indicators such as the level of CD4 lymphocytes, NK cells, IL-2R and the CD4+// ratio. CD8+ [10]. It is the strengthening of the immune system that may explain the relationship between arginine intake and a decrease in the incidence of cancer. Ma Q. et al. It has been proven that the administration of L-arginine is accompanied by a decrease in the incidence of colon and mammary cancer induced by procarcinogens in laboratory animals. A possible mechanism of action explaining this effect should be considered nonspecific stimulation of the body’s immune system under the influence of L-arginine [11]. Vasoton (L-arginine) also has a beneficial effect on the endocrine system: - stimulates the production of somatotropic hormone, which helps reduce fat deposits, increase muscle mass, improve mood, makes a person more active, proactive and resilient; — in combination with glucose, activates the production of insulin (with a lack of L-arginine, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases); - affects the central nervous system (pituitary and pineal glands), indirectly affecting the production of pleasure hormones (endorphins, enkephalins). For this reason, Vasoton (L-arginine) is useful for anyone leading an active lifestyle. The drug allows the body to quickly recover after heavy physical exertion, which is especially important for intensely training athletes, while the cleansing potential of the kidneys increases. Side effects and contraindications Arginine can stimulate free radical processes, so it should be taken accompanied by antioxidants. Doses of several grams over a long period of time should not be recommended for those under 18 years of age. For arthritis and infections, taking arginine can exacerbate inflammation. In addition, arginine can cause or worsen a herpes outbreak, in these cases it should be taken along with lysine or other antiviral components. L-arginine is not recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women. L-arginine is not indicated for schizophrenia. Taking arginine in large doses is not recommended if a person currently has cancer - at least, this is the opinion of experts. Caution should be exercised when prescribing arginine-containing dietary supplements to patients with diabetes mellitus (or with impaired glucose tolerance), since hormonal changes caused by L-arginine intake can cause a significant increase in blood glucose levels in such people. However, Vasoton in a dose of only 0.5 g 2 times a day for 2–3 weeks, being quite gently incorporated into the body’s metabolic processes, does not, as a rule, have the above-mentioned side effects. So, Vasoton (L-arginine) is a highly effective dietary supplement that can be included in metabolic therapy and used to prevent a wide range of diseases of internal organs, as well as be prescribed to healthy people leading an active lifestyle.
The effect of the drug "Vazoton" on the reproductive and copulative functions of men
There has been a close relationship between cardiovascular diseases and erectile dysfunction. This is explained by the same risk factors for the development of the pathological condition: age, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc. The main cause of cardiovascular diseases and erectile dysfunction is impaired blood supply. Ischemia is also the main cause of damage to the spermatogenic epithelium and disruption of hormonal status, leading to infertility in men.
Relaxation of the muscular wall of arterioles under the influence of the endothelial relaxing factor NO - nitric oxide is important for normalizing blood flow and circulation of organs. It is one of the most important biological neurotransmitters involved in many physiological and pathophysiological processes. NO is produced by the endothelium and enters the cell through the plasma membrane, where, interacting with the enzyme guanylate cyclase (GC), it is converted into cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, which is enhanced by a decrease in the intracellular concentration of calcium ions. NO, in addition to vasodilation, reduces platelet aggregation and activates the immune system.
A large amount of experimental material confirms the enormous role of NO in improving blood flow in the coronary arteries, in the vessels of the lower extremities, in the cavernous bodies of the penis, and testicles. The precursor to nitric oxide is the essential amino acid L-arginine. It is vital for the body, since it supplies nitrogen to the system of enzymes that synthesize the nitro group NO, the main substance that regulates vascular tone throughout the arterial bed. L-arginine, being a donor of nitric oxide, ensures blood flow to organs, reduces diastolic pressure due to the expansion of peripheral arteries, increases collateral blood flow, improves the rheological properties of blood, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis. L-arginine plays an important role in the cycle of urea formation and the excretion of protein waste, improves liver function and prevents its fatty infiltration.
Currently, L-arginine is produced by various domestic and foreign pharmaceutical companies. Such a drug is “Vazoton” produced by a pharmaceutical company (Russia) with one hundred percent content of this essential amino acid.
A clinical study was conducted on the preventive and therapeutic effects of the drug "Vazoton" for reproductive and sexual disorders in men, as well as its homeostatic effect.
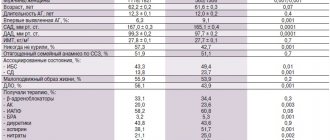
Treatment with Vazoton was carried out on 25 patients of active reproductive age (20–45 years) with secretory infertility in the absence of urogenital infection. 15 people reported problems of a sexual nature. The anamnesis revealed a decrease in libido in 5 patients, insufficient erection in 15 patients, and accelerated ejaculation in 7 patients. No severe somatic pathology was observed in anyone. When studying the ejaculate, combined changes in the spermogram were revealed: a decrease in sperm concentration (less than 40 million/ml), a decrease in actively motile forms (less than 25%), an increase in degenerative sperm (more than 50%). The level of total testosterone in 11 patients was between the average and lower limit of normal, in 15 – below the lower limit.
Vasoton was prescribed 1 capsule (0.5 g) 3 times a day. The course of treatment was 4 weeks. After completion of treatment, the level of total serum testosterone increased in 17 (68%) patients, by an average of 2±0.5 nmol/l, and remained unchanged in 8 (32%) patients. The ejaculate study was carried out after 4–5 days of sexual abstinence. The volume of ejaculate in 15 (60%) patients increased, on average, by 1.5 ± 0.8 ml, the concentration of sperm increased in 13 (52%) patients, on average, by 8 ± 2.3 million/ml. The number of actively motile sperm in the ejaculate of 17 (68%) patients increased, on average, by 7 ± 2.1%, and the number of weakly motile forms also increased. In 15 (60%) men, the number of degenerative forms of sperm decreased by an average of 5 ± 0.7%.
It should be noted that 22 (88%) patients noted an improvement in the psychophysiological state of sleep, memory, and attention. An increase in libido and sexual activity was found, the frequency of night-morning erections and the number of sexual acts increased, and the quality of orgasm improved. The total index on the International Scale of Erectile Function (IIEF) after treatment increased in patients with erectile dysfunction by an average of 3 ± 0.5 points. The total score on the “Quantitative Assessment of Male Copulative Function” (ICF), developed by O. B. Laurent and A. S. Segal in 1998, increased by an average of 4 ± 0.8 points. At the same time, the neurohumoral component of the copulatory cycle increased, on average, by 1.1 ± 0.3 points, the mental component – by 0.93 ± 0.1 points, the erectile component – by 0.95 ± 0.15 points, the ejaculatory component – by 1, 2 ± 0.2 points.
Throughout the entire course, no side effects were identified when taking Vazoton. Clinically significant changes were not revealed in the study of a general blood test, urine test, or biochemical blood test before and after treatment.
Thus, Vasoton is an effective remedy that has a stimulating effect on the reproductive and copulatory functions of men and can be used in complex or combination therapy and prevention of infertility and sexual dysfunction.