The scourge of the 21st century is stress. His faithful companions: anxiety, excitement, neuroses, panic attacks, somatic manifestations (urticaria, skin itching, allergic dermatitis, eczema), sleep disturbances. It would seem that there’s nothing wrong with it, just rest and everything will pass. But if it does not go away, gets worse and disrupts the usual rhythm of life, then you need to consult a doctor. During drug treatment, doctors often prescribe a prescription for the anxiolytic (tranquilizer) Atarax, which is allowed even for children over one year of age.
Stress is a very common problem
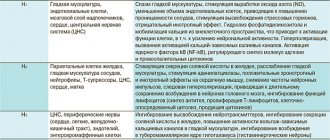
pharmachologic effect
Manufacturer: USB Pharma, Belgium
Release form: film-coated tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: hydroxyzine hydrochloride
Synonyms: Hydroxyzine
The drug contains hydroxyzine hydrochloride, which is a derivative of diphenylmethane. The substance reduces excitability, tension, anxiety and fear. The drug exhibits sedative, antihistamine, antiemetic effects. Atarax reduces muscle tension, relaxes the respiratory and digestive muscles, and also reduces itching in allergic diseases.
With long-term use of the drug there is no addiction or withdrawal syndrome.
Atarax for anxiety disorders (review)
Ryabokon I.V.
Anxiety is a state of fear and anxiety experienced by a person in anticipation of trouble. The causes of anxiety are varied: emotional instability, a sharp change in living conditions, the upcoming completion of a difficult task, etc. Anxiety may arise due to anticipation of a future threat (punishment or loss of loved ones). Typically, anxiety leads to defensive reactions. Anxiety is the result of frustration or its anticipation and is the primary psychological manifestation of stress. Z. Freud considered anxiety as a symptomatic manifestation of an internal emotional conflict caused by the fact that a person unconsciously suppresses sensations, feelings or impulses that are too threatening or irritating for him. With the emergence of anxiety, behavioral activity increases, the very nature of behavior changes, and additional physiological mechanisms of adaptation to changed conditions are activated.
Anxiety is a person’s tendency to experience a state of anxiety. Most often, a person’s anxiety is associated with the expectation of social consequences of his success or failure. Anxiety and anxiety are closely related to stress. On the one hand, anxious emotions are symptoms of stress. On the other hand, the initial level of anxiety determines individual sensitivity to stress. Like stress in general, the state of anxiety cannot be called unequivocally bad or good.
Sometimes anxiety is natural, adequate, and useful. Everyone feels anxious, restless or stressed in certain situations, especially if they have to do something unusual or prepare for it. For example, giving a speech in front of an audience or passing an exam. A person may feel anxious when walking down an unlit street at night or when lost in a strange city. This type of anxiety is normal and even useful, as it prompts you to prepare a speech, study the material before an exam, and think about whether you really need to go out at night all alone.
In other cases, anxiety is unnatural, pathological, inadequate, harmful. It becomes chronic, constant and begins to appear not only in stressful situations, but also for no apparent reason. Then anxiety not only does not help the person, but, on the contrary, begins to interfere with him in his daily activities.
The line between a “normal” stress response and a pathological anxiety disorder is often quite blurred, and it is difficult for a person to know when to seek professional help. These subsyndromal anxiety disorders are the most difficult to diagnose and often remain untreated, while having an extremely negative impact on the quality of life of the patient and those around him. It is believed that treatment options should be considered when anxiety about everyday events is beyond the patient's control. The following disorders may also be the reason for prescribing therapy: nervousness, fussiness, impaired concentration, irritability, sleep disturbance, symptoms of autonomic dysfunction.
In everyday medical practice, various herbal medicines, tranquilizers, barbiturates, antidepressants, and some antipsychotics are used to treat anxiety disorders.
One of the most powerful and quickly relieving sleep disorders and anxiety are benzodiazepine drugs. Among the disadvantages of treatment with benzodiazepines, the following should be mentioned: withdrawal syndrome (rapid resumption or transient increase in symptoms after discontinuation of the drug), the risk of addiction and the formation of drug dependence, impaired cognitive functions (attention, concentration, memory), and impaired coordination. Therefore, benzodiazepine drugs are not recommended to be taken for more than 2 weeks.
Hydroxyzine (Atarax) is neither a benzodiazepine nor a phenothiazine. The non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic Atarax (hydroxyzine) is a derivative of diphenylmetane, an antagonist of histamine H1 receptors.
Hydroxyzine is one of the oldest psychotropic drugs; it was introduced into clinical practice back in 1955. Atarax has a pronounced anti-anxiety, antihistamine, antipruritic and antiemetic effect. By reducing the concentration of histamine at the central level, it has the property of reducing anxiety, reducing aggressiveness and causing a persistent anxiolytic effect [2]. The drug acts within 15–30 minutes after oral administration (Cmax is noted 2 hours after taking the drug) and maintains this effect for 6–8 hours. Its main advantages are the absence of the “rebound” phenomenon, addiction (dependence), withdrawal symptoms and positive effect on cognitive function.
Hydroxyzine has been successfully used in a variety of areas of medicine: as a means of controlling tobacco smoking [3]; in pediatric dentistry [4]; for its intended purpose – for the treatment of anxiety neurosis (even in the era of the existence of such a nosological form) and for “mild” depression [5]; for behavioral and learning disorders in children [6]. Due to its antihistamine properties, hydroxyzine was used in allergology, to treat itching [7], and for urticaria pigmentosa (mastocytosis) in children [8]; in oncology [9]; in burn patients [10], in narcology [11] and in many other conditions.
Recently, there has been interest among researchers in the use of hydroxyzine in patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The prevalence of this pathology and the associated burden of social consequences in the current scientific literature appear to be quite significant. According to one review [E.G. Starostina. Generalized anxiety disorder and anxiety symptoms in general medical practice. Rus. honey. magazine 2004; 22 (222), 12: 1277] with reference to numerous foreign works, “GAD is among the top ten diseases with the greatest temporary disability and according to this indicator is on a par with coronary artery disease, diabetes, joint diseases, peptic ulcers, and mental disorders – with depression or even ahead of it.”
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled RCT for the treatment of GAD [17], the anxiolytic activity of Atarax at a dose of 50 mg (in 3 doses of 12.5 mg in the morning and afternoon plus 25 mg in the evening) was shown, which was manifested in a statistically significant, rapid and significant decrease symptoms of anxiety already at the end of the 1st week of treatment, which persisted for another 1 week after cessation of treatment (n=110; course duration 4 weeks; Hamilton-A score). In this case, there was no phenomenon of “rebound” or return of anxiety.
In another double-blind multicenter RCT [18], in which, along with placebo control, the benzodiazepine drug bromazepam was also used, it was shown that hydroxyzine used for 3 months was statistically significantly different from placebo and was as effective as the comparison drug. Moreover, with benzodiazepine, side effects of severe drowsiness were observed twice as often as with hydroxyzine (n = 334; dose of hydroxyzine 50 mg/day in 3 divided doses; bromazepam - 6 mg/day in 3 divided doses; improvement on the Hamilton-A scale >50 %; p<0.03 at the end of the 6th week and p<0.001 - after 12 weeks; the number of patients who responded to treatment: 40% at the 6th and 60% at the 12th week, respectively).
Another study [19] showed the effectiveness of Atarax (50 mg in 3 doses), comparable to that of the control buspirone (20 mg in 3 doses), with a statistically significant difference between Atarax and placebo on the 28th day of treatment (p<0.015) . There was no rebound phenomenon with abrupt withdrawal of both drugs (n=244; age 18–65 years).
In addition, one of the advantages of hydroxyzine is that, unlike benzodiazepines, it does not depress cognitive abilities [20] (triple crossover, double-blind RCT; comparing a single dose of 50 mg of hydroxyzine with a single dose of 2 mg of lorazepam and placebo; n = 9; healthy volunteers; 3-day interval before cross-over; assessment of cognitive functions 2–5 hours after taking comparator drugs).
Some studies have shown a positive effect of hydroxyzine on cognitive function [21] (comparison with lorazepam; double-blind multicenter RCT; n=30; GAD, Atarax 100 mg in 3 divided doses, lorazepam 4 mg in 3 divided doses; Beck score 28– th day of treatment). Unlike lorazepam, with the same anxiolytic activity, hydroxyzine restored cognitive function to normal limits.
Similar results were obtained in another, less conclusive study - an open RCT (A.E. Bobrov et al. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S.S. Korsakov. 1988; 2. GAD; n=50; outpatients; treatment course is 4 weeks, plus 2 weeks of follow-up).
Considering the characteristics of the drug (quick onset of action, good tolerability), lack of dependence and depression of the central nervous system make it an alternative drug to benzodiazepines in children and adolescents. In a study conducted at the Children's Psychiatry Center [23], Atarax was prescribed for various forms of mental illness in children and adolescents with manifestations of anxiety, irritability and insomnia-type sleep disorders, and its effectiveness was assessed. The study included 50 patients aged 5 to 18 years with various forms of mental illness, who were undergoing outpatient observation and treatment at the Children's Psychiatry Center. At the end of the 4th week of therapy, there was a decrease in the manifestations of anxiety and various fears noted earlier: falling asleep in the dark, staying at home in the absence of parents, fears of animals, noise of household appliances; in one case, a five-year-old boy could stay at home with a nanny without his parents (he had previously shown a pronounced affective reaction). In addition, all patients' sleep improved already in the second week of therapy, tearfulness, moodiness, and irritability were reduced. Simultaneously with the reduction of anxiety, the mood improved in 7 patients with a mixed anxious and depressive reaction caused by an adaptation disorder and with a mixed anxiety and depressive disorder, which was associated not with the direct antidepressant effect of Atarax, but with the comorbid dependence of anxiety and depression: anxiety was reduced - depression went away.
In a comparative study [22] of etifoxine and Atarax (hydroxyzine), the compared anxiolytics demonstrated high effectiveness in a wide range of psychopathological manifestations of adjustment disorders and generalized anxiety disorder. The results of therapy with etifoxine and Atarax showed the comparability of the clinical effect of the compared drugs, confirmed by a number of formalized indicators. The proportions of responders were comparable: 73.3 and 53.3% in the HARS assessment; 66.7 and 53.3% - as assessed by CGI-S for the groups receiving etifoxine and Atarax. The main clinical effect of the drugs in both groups was a decrease in the severity of manifestations of mental anxiety: the symptoms of internal tension (ethifoxine - in the 2nd week, Atarax - in the 3rd week), reactive (emotional) lability (one of the sub-items of “depressive mood”) were most quickly reduced "). In general, similar dynamics of cognitive anxiety were observed in both groups.
To summarize, we can reiterate that hydroxyzine (Atarax) has shown clear advantages over benzodiazepine anxiolytics in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Being as therapeutically effective as benzodiazepine anxiolytics, it does not produce rebound effects, does not depress cognitive function, and does not cause pathological dependence.
Literature:
1. Psychotropics 2000/2001 Lundbeck.
2. Krebs MO. Le trouble anxieux: cliniqu et implicacion neurobiologiques. La Revfue des Entretiens de Bichat 2001; 2 (5).
3. Turle G. An investigation into the therapeutic action of hydroxyzine/Atarax in the treatment of nervous disorders and the control of tobacco-habit. Brit J Psychiat 1958; 104: 82 rub. 33.
4. Lang L. An evaluation of the efficacy of hydroxyzine (atarax–vistaril) in controlling the behavior of child patients. J-Dent-Child 1965; 32, 4: 253–8)
5. R.Middlefell, K.Edwards Hydroxyzine/Atarax in the relief of tension associated with anxiety neurosis and mild depressive states. Brit J Psychiat 1959; 105:792–4.
6. Segal L, Tansley A. A clinical trial with Hydroxyzine (Atarax) on a group of maladjusted educationally subnormal children. J Mental–Science; Br J Psychiat from 1963; 1957; 103:677–81.
7. Rhoades R, Leifer K, Cohan R, Wittig H. Suppression of histamine-induced pruritus by three antihistaminic drugs. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1975 Mar.; 55, 3: 180–5.
8. Kettelhut B, Berkebile C, Bradley D, Metcalfe D. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of ketotifen versus hydroxyzine in the treatment of pediatric mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1989 May; 83, 5: 866–70)
9. Broder L, Lean N, Hilsenbeck S. A randomized blinded clinical trial comparing delta–9–tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and hydroxizine (HZ) as antiemetics (AE) for cancer chemotherapy (CT). PROC–AM–ASSOC–CANCER–RES; 1982; 23:514.
10. Vitale M, Fields–Blache C, Luterman. A Severe itching in the patient with burns. J burn care & rehabilitation 1991; 12, 4: 330–3.
11. Kaim S, Klett C, B. Rothfeld. Treatment of the acute alcohol withdrawal state: a comparison of four drugs. Agressologie: revue internationale de physio-biologie et de pharmacologie appliquees aux effets de l'agression, 1968; 9, 2: 305–8.
12. Chignon G. Le trouble Anxiete Generalise: du probleme diagnostique au defi therapeutique. Nervure J psychiat 1988; 11 (suppl.): 1–16.
13. Wittchen H–U, Jakobi F. Size and burden of mental disorders in Europe – a critical review and appraisal of 27 studies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2005; 15: 357–76; For details, see the February issue of our magazine).
14. Goodwin R, Gorman J. Psychopharmakologic Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder and risk of major Depression. Am J Psychiat 2002; 159:1935–7.
15. Goodwin RD, Jack M. Gorman. Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder with psychotropic drugs and the risk of major depressive disorder
16. Martin P. Coprescription, Antidepresseurs et anxiolytiques: consequences pratiques de la meilleure connaissance desmecanismes d'action putatifs des anxiolytiques. Actuel Psychiat 2001; 19 (1/2): 2–7.
17. Ferreri M, Hantouche T, M. Billardon. Interet de l'hydroxizyne dans des troubles d'anxiete generalisee: etude controlee en double aveugle versus placebo. L'encephale 1994; 20: 785–91.
18. Llorka P. et al. Efficiency and safety of hydroxysyne in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a 3-month double-blind study. J Clin Psychiatry 2002; 63:1020–7.
19. Lader Scotto J. A multicenter double–blind comparison of hydroxizine, buspirone and placebo in patient with generalized anxiety disorder. Psychopharmacology 1998; 139:402–6.
20. De Brabander A, Deberdt W. Effect of hydroxizyne on attention and memory. Human Psychopharmacology 1990; 357–62.
21. Samuelian J, Billardon M, Guillou N. Retentissment sur les functions cognitives de deux traits anxiolitiques chez des patients souffrant d'anxiete generalisee. L'encephale 1995; 21:147
22. Andryushchenko A.V., Beskova D.A., Romanov D.V. Psychopharmacotherapy of generalized anxiety (experience with the use of Strezam and Atarax) Mental disorders in general medicine No. 1; pp. 33–36
23. Rezakov A.A. Experience of using hydroxyzine (atarax) in children and adolescents. "PHARMIndex-Practik" issue 10; 2006, pp.37–39
Atarax - instructions for use
According to the instructions for use, Atarax is used to treat children from one year old and adults. The dosage of the drug and the regimen are determined individually and depend on the patient’s age, the severity of the disease and accompanying symptoms.
How to take Atarax: before or after meals
Tablets are taken orally regardless of food intake. Take the medication with a small amount of liquid.
The injection solution is used only for intramuscular administration. Subcutaneous, intravenous, and intra-arterial injections are prohibited.
Price of funds
Atarax (analogues without prescriptions can be purchased at any pharmacy) should be used only after consultation with a specialist who will select the optimal dosage taking into account the general condition of the patient.
| Name of the drug | Cost, rub.) |
| Atarax | 280 – 380 |
| Phenibut | 150 – 750 |
| Afobazole | 300 – 650 |
| Selank | 520 – 600 |
| Tenoten | 250 – 300 |
| loophole | 1000 – 1100 |
| Novo-passit | 210 – 400 |
| Persen | 240 — 460 |
You can purchase Atarax only with a prescription from your doctor. The analogues presented above are sold without prescriptions. Despite this, it is recommended to consult a specialist before using any medication.
Analogues of Atarax
There is a wide range of Atarax substitutes on the shelves of pharmacies. Medicines differ in composition, mechanism of action, and indications.
Analogs of Atarax, which are available without a doctor's prescription:
- Afobazole;
- Glycine;
- Novo-passit;
- Persen;
- Tryptophan Calm Formula;
- Motherwort extract.
Russian analogues of Atarax are represented by the following medicines:
- Bellataminal;
- Phenazepam;
- Amitriptyline;
- Chlorprothixene;
- Gidazepam;
- Teraligen;
- Paroxetine;
- Mexidol;
- Sibazon;
- Mälarena;
- Escitalopram;
- Picamilon;
- Azafen;
- Alprazolam;
- Hydroxyzine;
- Mebicar;
- Fluoketine.
Imported analogues of Atarks and their prices are presented in the table
| Name | average cost | Manufacturer country |
| Atarax | 310 | Belgium |
| Eglonil | 210-356 | France |
| Adaptol | 715 | Latvia |
| Strezam | 560-910 | France |
| Zoloft | 490-930 | Germany |
| Phenibut | 110 | Republic of Belarus |
| Grandaxin | 370-840 | Hungary |
| Clonazepam | 170 | Poland |
| Trittico | 740 | Italy |
| Elycea | 1150 | Slovenia |
| Sonapax | 280-450 | Poland |
| Donormil | 135-370 | France |
| Fevarin | 860-2300 | France |
| Paxil | 612 | Romania |
| Arcoxia | 520-1300 | Spain |
| Cipralex | 1100 | Denmark |
| Spitomin | 800 | Hungary |
Often patients are faced with the high cost of the drug or its absence in the pharmacy, then the question arises what can replace Atarax. The medication should be replaced by the attending physician.
Glycine
Manufacturer: LLC MNPK BIOTIKI, RF
Release form: sublingual tablets
Active ingredient: microencapsulated glycine
Synonyms: Glycised, Glycine Extra
A drug to improve metabolism in brain cells – Glycine. The medicine is an analogue of Atarax without side effects and exhibits a wide spectrum of action. The metabolite is used in the following cases:
- anxiety, tension, irritation;
- low performance;
- memory and attention disorders;
- sleep problems;
- consequences of brain injuries;
- hangover.
Glycine is approved for use in children from birth, pregnant and lactating women.
The main advantages of the analogue are:
- soft action;
- wide range;
- no adverse reactions;
- over-the-counter;
- affordable price.
The drugs differ in composition, mechanism of action, and indications. Atarax and Glycine can be used as part of complex treatment for a quick recovery.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of the drug:
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- porphyria;
- intolerance or hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- high sensitivity to cetirizine, piperazine derivatives, as well as ethylenediamine or aminophylline;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- impaired absorption of glucose and galactose;
- hereditary galactose intolerance.
Pregnant women should not use Atarax.
Atarax is used with caution in the following cases:
- myasthenia gravis;
- prostatic hyperplasia;
- difficulty defecating and urinating;
- dementia;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- predisposition to arrhythmia and seizures.
Atarax or Hydroxyzine – which is better, what is the difference
Manufacturer: Pharmproject, Russian Federation
Release form: film-coated tablets
Active ingredient: hydroxyzine hydrochloride
Synonyms: Hydroxyzine Canon, Atarax
Hydroxyzine is a Russian synonym for Atarax. The drugs have the same effect and indications. The substitute is used in children from 3 years of age and adults to eliminate attacks of anxiety, tension, during preparation for operations, and for allergic reactions. Adults are prescribed 50–100 mg at bedtime; for children, the dosage is calculated based on body weight.
Advantages of Atarax compared to its analogue:
- original drug (availability of studies);
- high efficiency;
- use in children from one year of age;
- positive reviews from doctors.
The medications are identical in composition and action. The neurologist decides which remedy to give preference to.
Atarax or Teraligen – which is better for anxiety and insomnia
Manufacturer: Valenta Pharmaceuticals, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: alimemazine
Teraligen is a tranquilizer drug. The analogue of Atarax is produced in simple and prolonged-release tablets, ampoules. Teraligen exhibits a mild sedative and anti-anxiety effect. The drug is prescribed as part of complex treatment for the following conditions:
- problems sleeping, insomnia;
- anxiety disorders;
- severe stress and acute reaction to it;
- behavioral disorders, dementia;
- neurasthenia and other neurological manifestations;
- allergies and itching.
The analogue is used in adults 1–2 times a day in the required dosage.
The drugs have a similar effect, but Teraligen has a wider range of indications.
Characteristics of the drug
Atacrax is available in 2 forms: injection and tablets. The main active ingredient is hydroxyzine. The drug and its analogues, which are sold without prescriptions, improve cognitive function and concentration.
For severe anxiety, which is accompanied by chronic insomnia, the active substance Atarax eliminates the symptoms of the condition, makes sleep sound and long, reducing the number of awakenings to a minimum. Due to the effect of the active component on certain areas of the subcortex of the brain, the drug has the ability to relax smooth muscles and skeletal muscles.
The drug is indicated for use in the following conditions:
- for somatic, neurological, mental pathologies in order to relieve excessive irritability, psychomotor tension and agitation;
- symptomatic treatment of withdrawal syndrome caused by chronic alcohol dependence;
- increased anxiety;
- a period of premedication to provide a sedative effect;
- treatment of itchy skin.
Conditions and pathologies in which Atarax is contraindicated:
- porphyria;
- hypersensitivity and intolerance to the components of the drug;
- hereditary galactose intolerance;
- angle-closure glaucoma.
The drug is not prescribed during pregnancy, breastfeeding or during labor. This is due to the fact that the active substance penetrates the placenta and negatively affects the intrauterine development of the unborn child.
Atarax is also able to relax the smooth muscles of the uterus, preventing it from contracting, which can negatively affect the process of labor. When breastfeeding, the active ingredient enters the baby's body with mother's milk, and the drug is contraindicated in children.
If any of the above pathologies and conditions are present, consultation with a specialist is necessary before use.
Atarax or Phenibut – which is better and more effective for adults
Manufacturer: Belmedpreparaty, Republic of Belarus
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: aminophenylbutyric acid
Synonyms: Noofen, Anvifen
An analogue of the drug Atarax is Phenibut, which belongs to the nootropics. The medication contains aminophenylbutyric acid. The active substance exhibits anti-anxiety, anticonvulsant effects, improves blood supply and the functioning of brain cells.
The analogue is used in adults and children over 8 years of age for neurasthenia, anxiety, stuttering, tics, and sleep problems.
Main benefits of Phenibut:
- prolonged action;
- effectiveness for insomnia;
- average cost;
- good reviews from pediatricians.
Atarax and the analog have the same effect on the central nervous system and do not cause addiction or withdrawal symptoms. The choice of drug is the prerogative of the doctor.
Comparison of addiction between Atarax and Hydroxyzine
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “o syndrome” in Atarax is quite similar to the similar values in Hydroxyzine. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Atarax has a fairly low value of the “syndrome”, however, the same as for Hydroxyzine.
Atarax or Grandaxin - which is better and stronger, what is the difference
Manufacturer: Egis, Hungary
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tofisopam
Grandaxin is a foreign analogue of Atarax. The medication belongs to the group of anxiolytic drugs and is used for neuroses, anxiety, apathy, obsessions, and chronic depression. Numerous reviews from gynecologists confirm the effectiveness of the analogue for premenstrual and menopausal syndromes.
Differences of Grandaxin:
- stronger action;
- effectiveness occurs on day 2;
- Can be used in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Medicines belong to the same pharmaceutical group, have identical effects on the body and are not addictive.
Atarax or Phenazepam – which is better for anxiety?
Manufacturer: Biosynthesis, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine
Synonyms: Elzepam
Phenazepam is a prescription analogue. The medicine has a complex effect on the human body. The substitute exhibits a hypnotic, sedative, anticonvulsant effect, and eliminates muscle tone. Phenazepam is effective for the following disorders:
- irritability, tension, anxiety;
- insomnia;
- obsessions, panic attacks, schizophrenia;
- alcohol addiction.
In addition, the analogue is used as a sedative before operations and other medical procedures.
Phenazepam has a stronger effect on the body and can be addictive. Which medicine is preferred depends on the severity of the disease, accompanying symptoms and the age of the patient.
Antidepressants
Should I take antidepressants for severe depression? Many people believe that such drugs are addictive. If previously drugs that could cause addiction and drug dependence were used in psychotherapy, today new generation drugs are used that affect the human body and psyche more gently and sparingly.
Among the reasons for mistrust in the use of antidepressants for depression is the fact that if the course of treatment is interrupted, a person may feel worse. If withdrawal symptoms occur, this indicates incorrect discontinuation of the prescribed drug. You should not perceive this reaction of the body as dependence on pills.
If you stop the artificial synthesis of brain neurotransmitters, their quantity in the human body will drop sharply. Patients feel that their depression or anxiety disorder is returning as anxiety increases. Any changes in your condition should be reported to your doctor. The specialist knows how to smoothly discontinue the prescribed medication. In combination with psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy works well, giving long-term results.
There are several groups of medications for anxiety and depression.
Tricyclic
The first group includes medications that have a three-cyclic structure; they are not sedatives and prevent the immediate breakdown of neurotransmitters (serotonin and norepinephrine). They do not disappear from the nerve endings, their synthesis increases, as does the amount of serotonin. These medications have a number of contraindications; they are not recommended for people who have kidney and liver diseases, glaucoma, atherosclerosis, or use of narcotic substances.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are monoamine neurotransmitters that regulate our emotions, as well as a number of processes in the brain: attention, cognitive functions, memory, arousal. Due to the inhibition of leasing, the amount of monoamines increases and their accumulation in nerve endings. Some groups of these drugs are contraindicated for pregnant women and people with work that requires concentration, as well as for hypertensive patients.
Selective serotonin uptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
The third group of drugs for the treatment of depression includes selective serotonin uptake inhibitors.
Medicines are prescribed to replenish “happiness hormones”. Do not think that this happens quickly; the process of restoration of neurotransmitters is gradual. SSRIs have one important advantage - when the drugs are abruptly stopped, there is no withdrawal syndrome. Contraindications to their use include diseases of the genitourinary system, as well as alcoholism and drug addiction. If a person has developed alcoholism due to depression, he should not take antidepressants, since alcohol increases the side effects of the medication for depression. Symptoms of the disorder may increase significantly and the condition may worsen. Quite often, psychological reasons cause the development of alcohol dependence; the risk of depression in alcoholics is several times higher than in healthy people. The first group of anti-depression drugs is especially dangerous to combine with ethanol, as this leads to a sharp increase in blood pressure.
Which antidepressant is best for anxiety and depression? Your doctor will answer this question; the choice of medications should always take into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Do you want to know about the cost of services?
8 call our specialist
Atarax or Afobazol – which is better?
Manufacturer: Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: fabomotizol
An over-the-counter analogue with a long-lasting effect is Afobazol. The medication exhibits an anti-anxiety effect and restores damaged nerve cell receptors. The substitute eliminates stress, tension, and insomnia. Afobazole is used as part of complex therapy for PMS, alcoholism, and smoking cessation. The medicine is prescribed for adults, 1 tablet three times a day.
If we compare the analogue and Atarax, the first drug has a gentler effect on the body, has no adverse reactions and can be used while driving.
Compatibility with other drugs
A separate issue when taking Atarax is its interaction with other medications. Thus, barbiturates, tranquilizers, opioid analgesics, ethanol-containing drugs, sleeping pills and any other drugs that depress the central nervous system, when taken simultaneously with the drug Atarax, enhance the effects. That is, lethargy, indifference, drowsiness and other effects will appear several times brighter and stronger. But if it is still necessary to take everything together, then the doctor monitoring the patient will draw up a dosage regimen and select an individual dosage for each drug.
Compatibility of other drugs with Atarax
The combination of Atarax + MAO inhibitors, anticholinergics is not recommended. Atarax is able to inhibit the action of epinephrine (adrenaline) and suspend the anticonvulsant effect of phenytoin.
Atarax has a destructive effect on the metabolism of substrate drugs for uridine diphosphate and glucuronyl transferase.
If you drink Cimetidine and Atarax at the same time, the concentration of hydroxyzine in the blood plasma will increase, but on the contrary, the concentration of metabolites will decrease.
As for cardiac glycosides, atropines, antihypertensive drugs, antiallergic drugs, Atarax does not in any way affect their functionality; the pharmacological effect provided.
However, it is worth remembering that it is better not to take drugs whose side effects indicate possible arrhythmia with Atarax. When they are mixed, there is a risk of prolongation of the QT interval and the development of ventricular tachycardia of the “pirouette” type.
Atarax or Adaptol – which is better?
Manufacturer: Olainfarm, Latvia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tetramethyltetraazabicyclooctanedione
Adaptol is an analogue of Atarax, which requires a prescription. The drug eliminates anxiety, stress, fear and anxiety. Adaptol does not cause a feeling of euphoria, does not impair coordination of movements and mental performance. The medication enhances the effect of sleeping pills. The drug can be used during the working day, before an exam or an important event.
Adaptol and Atarax have a similar effect on the body, but they differ in composition, indications and contraindications. Which medicine is best depends on the condition and accompanying manifestations.
Side effects
Since Atarax is a drug that acts on the central nervous system, it can sometimes cause suppression of certain functions or paradoxical stimulation. Also, when taking it, negative reactions from the body may occur:
- From the cardiovascular system: blood pressure rarely decreases, heart rate increases.
- From the point of view: decreased clarity of vision, impaired accommodation.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: a feeling of dry mouth, rarely - vomiting, nausea, problems with intestinal motility and, as a result, constipation.
- From the immune system: hypersensitivity, rarely anaphylactic shock may develop.
- From the urinary system: urine retention is rarely possible.
- From the respiratory system: rarely - bronchospasm and suffocation.
- Neurological disorders: drowsiness, headache, insomnia, dizziness, rarely – convulsions.
- Mental disturbances are rare: agitation, disorientation, and hallucinations are possible.
- Skin: itching, rash, rarely - swelling.
- General disorders: weakness, fever, fatigue.
Atarax or Stresam - which is better?
Manufacturer: Biocodex, France
Release form: capsules
Active ingredient: etifoxine hydrochloride
Stresam is an imported analogue of Atarax 25 mg. The drug is a tranquilizer, has a selective effect on the body with a mild sedative effect. Stresam is used for increased tension, excessive irritability, and anxiety.
Medicine occupies a special place in gynecology. The analogue is used in the complex treatment of menopause, menopausal syndrome, and PMS. Strezam is taken 50 mg 3 times a day. Duration of treatment is 4–6 weeks. A noticeable effect occurs after 10–14 days.
Comparison of the side effects of Atarax and Hydroxyzine
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Atarax has almost the same level of adverse events as Hydroxyzine. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Atarax are similar to Hydroxyzine: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
Atarax or Amitriptyline – which is better?
Manufacturer: OZONE, RF
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: amitriptyline hydrochloride
An analogue of Atarax that is cheaper than other drugs is Amitriptyline. The medicine is an antidepressant. The medicine has a wide spectrum of action. Amitriptyline eliminates anxiety disorders and has a sedative and analgesic effect. The substitute is used for the following pathologies:
- depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- psychosis, schizophrenia;
- bed-wetting;
- pain syndrome in chronic diseases.
Amitriptyline is prescribed as part of complex therapy for problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
The attending physician decides which medication to choose.
Indications
Indications for use of the drug are:
- relief of psychomotor agitation, tension, irritability in mental, neurological, somatic diseases;
- symptomatic treatment of withdrawal syndrome that occurs against the background of chronic alcoholism;
- anxiety;
- providing a sedative effect during premedication;
- therapy for itchy skin.
Why and why Atarax needs to be taken is determined by the attending physician. As a rule, taking Atarax is provoked by diagnosed skin diseases, which are accompanied by severe skin itching.
Atarax or Mebicar – which is better?
Manufacturer: Tatkhimpharmpreparaty, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tetramethyltetraazabicyclooctanedione
Synonyms: Adaptol
The anxiolytic drug Mebicar has a nootropic effect and improves the supply of nutrients to the body. The analogue eliminates tension, excitement, anxiety, but does not cause euphoria. Indications for taking Mebicar:
- neurotic disorders;
- psycho-emotional disorders;
- alcoholism, nicotine addiction.
The analogue is used as part of complex treatment of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.
The daily dosage of the substitute is 3–10 grams.
Atarax and Mebikar differ in composition, action, indications and limitations. Which drug is best depends on the severity of the disease and symptoms.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Atarax and Hydroxyzine
Atarax is more effective than Hydroxyzine - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is different.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Atarax is more pronounced, then with Hydroxyzine it is impossible to achieve this effect even in large doses.
Also, the speed of therapy is an indicator of the speed of the therapeutic action; Atarax and Hydroxyzine are also different, as is bioavailability - the amount of a drug reaching the site of its action in the body. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Atarax or Fluoxetine – which is better?
Manufacturer: Biocom, Russian Federation
Release form: capsules
Active ingredient: fluoxetine
Synonyms: Fluoxetine Canon
Fluoxetine and Atarax belong to different pharmaceutical groups and differ in action. The analogue is a receptor antagonist, reduces feelings of fear, anxiety, irritation, and improves mood. Fluoxetine is prescribed for depression of various natures, bulimia, and psycho-emotional disorders. The medication is taken 1 capsule per day, which must be swallowed whole.
The drugs differ in their active substance, principle of action and indications. A neurologist or psychiatrist decides which medication to give preference to.