Pilonidal cyst (synonym - epithelial coccygeal duct) - refers to congenital anomalies of the development of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue. Localized in the sacrococcygeal region (intergluteal fold). The reason for the development is incomplete fusion of the rudimentary caudal ligament.
A piloidal or coccygeal cyst is more often found in men
Characteristic
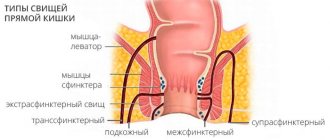
- It is a narrow passage in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Does not reach the anus and is not fused with the rectum (differential diagnosis with paraproctitis is required).
- The presence of one or more inlet openings (the cavity is not isolated from the external environment).
- The projection of the cyst may include skin appendages (hair, sweat or sebaceous glands).
- Correlation dependence on gender (occurs more often in men).
- It tends to become inflamed and purulent.
- Has a tendency to frequent relapses and transition to a chronic process.
- It may have an asymptomatic course, but does not undergo independent regression (resorption).
- The only radical treatment method is surgery.
POSTOPERATIVE REHABILITATION
The operation to remove a coccyx cyst is well tolerated. After surgery, most patients feel satisfactory. During this period, you will need to take painkillers and undergo a course of antibiotic therapy. After removing the bandage, baths with antiseptic compounds are prescribed. During the first postoperative month, heavy lifting and prolonged sitting should be avoided.
After surgery to remove a fistula on the coccyx has been performed, it is important to follow preventive measures. These include shaving hair near the wound, wearing non-pressure underwear made of natural materials, and high-quality hygiene of the intergluteal area.
Causes
The pathogenesis of the disease is based on a violation of the drainage of the epithelial tract (blockage of inlet openings) with a gradual accumulation of waste products in its cavity. This subsequently leads to suppuration and the formation of abscesses in the sacral region.
The causes of pilonidal cysts of the coccyx are usually divided into congenital and acquired.
| Cause | Factors |
| Congenital (the main theory of origin in Russian-language medical literature). | The disease is based on the processes of disembryogenesis (period of intrauterine development): 1. The theory of incomplete reduction of muscles and ligaments of the tail. 2. The theory of ectodermal invagination. Anomaly at the level of penetration of skin appendages into subcutaneous fatty tissue (incorrect formation of epidermal tissue and dermis). This theory is also typical for other similar pathologies with different localization (in the axillary region, between the fingers). 3. Neurogenic theory. It is assumed that the cyst is related to the formation of the terminal portion of the spinal cord (impaired regression of the terminal fragment). 4. The theory that connects the coccygeal tract with the coccygeal vertebrae (violation of their reverse development). |
| Acquired (the main theory of occurrence in the English-language medical literature). | In this case, the cystic formation is regarded as a purulent-septic process. Its occurrence is based on external and internal factors: 1. Mechanical injuries (abrasions, scratches, wounds). In this case, the skin defect will be the entry point for infection. Signs of suppuration do not appear immediately after infection (it has an asymptomatic course for a long time). 2. Failure to comply with hygiene rules. In newborns, diaper rash is a common cause of suppuration. 3. Specific types of profession that involve prolonged sitting (secretary, manager, programmer). 4. Inflammatory skin diseases (dermatitis). In this case, the effect is exerted by both mechanical irritation of the skin (microdefects are formed) and the action of the causative agent of the underlying disease. If the origin of the main pathology is based on an allergic or autoimmune process, then the opportunistic flora takes center stage (normally localized on the skin). 5. Decreased immunity. At the same time, the skin loses its barrier and protective function (opportunistic flora leads to the development of inflammation). 6. Traumatic injuries to the coccyx. In this case, the normal structure of the coccygeal tract may also be injured (change in direction, wounds, bruises), which serves as a basis for infection. 7. Inflammatory phenomena of skin appendages (sweat or sebaceous glands, hair follicles). In this case, inflammation of the coccygeal tract is secondary (based on a boil, carbuncle and other pustular skin diseases). With prolonged absence of treatment, the abscess can reach significant sizes and break outward with the formation of a secondary fistula or inward (anorectal tissue, spinal cord with the development of meningitis). |
Each theory is only an assumption as to the reasons for the appearance, since the exact cause has not been established.
CLINIC
As a result, patients report swelling of the perianal area, which, when inflamed, is accompanied by pain and palpation. Sometimes bleeding from the rectum is eliminated without pain. As a matter of fact, the patient may suffer from the consolidation of the inherited obstruction of the rectum or the mother may develop recurrent infections of the cervix of the inherited cervical obstruction. As Krizovo-Kuprikova teratoma directly affects the nerve pathways cauda equina
Or it metastasizes in the spinal cord, the patient may have maternal neurological scars, but it is even rare. With physical stimulation, similar perianal cysts will appear.
Brushes for anal passages/ducts.
As a matter of course, stench manifests itself as perianal pain, swelling and induration. These are spherical, smooth epidermal nodules, 1–2 cm in size. Most often, the stink is released in front of the anus.
Krizovo-Kuprikov's teratoma.
These drugs may be asymptomatic, but they may occasionally be detected during rectal examination. As a matter of fact, these soft tissues are localized presacral, ranging in size from 5 to 25 cm.
Dermoid brushes.
Typically, these are spherical rims with a size of 6–60 mm. The stench can be from the mother's sinus, which is what is called hair protruding. The problem is recurrent infection.
Epidermoid brushes.
These brushes are located near the dermis, and the stinking little bits lift the epidermis above themselves, creating thick, elastic dome-like structures with a yellowish-white color, which shifts within structures such as the hall. talk smarter. The stench can be found in the central canal, filled with keratin, and its diameter varies from several millimeters to 5 cm. More often than not, the stench is multiple. Over time, your brushes will become larger, and they may become inflamed and white.
Differential diagnosis must be carried out with pilonidal cysts, perianal abscesses, hemorrhoids and malignant tumors, hematomas due to trauma.
During diagnosis, pelvic computed tomography and transrectal ultrasonography provide valuable information. Endoscopic examination is required to exclude rectal cancer. In times of doubt, cytological examination can be taken instead of the brush removed by puncture.
Description
In the photo, external manifestations depend on the specific species:
- pilonidal cyst with abscess L05.0;
- pilonidal cyst without abscesses L05.9.
External manifestations in the first option:
- hyperemia in the coccyx area (severity varies widely from slight redness to a bright red spot);
- swelling of surrounding tissues;
- the contour is smooth and clear;
- pain on palpation (usually pain is a very local symptom that does not affect a large number of tissues);
- in some cases, when pressed, a small amount of pus may be released from the openings.
External manifestations in the second option:
- skin is not cheating;
- the swelling is insignificant (there is no edema as such);
- almost painless palpation;
- contoured using dyes;
- there is no discharge;
- The natural openings of the cyst are visually detected.
The different incidence and ratio of these two forms in different medical studies are given.
Pilonidal cyst of the coccyx: diagnosis
Diagnosis of a pilonidal cyst is usually not difficult. When making a diagnosis, experienced proctologists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account the results of a visual examination of the area of the intergluteal fold, digital rectal examination and other instrumental studies, which are carried out using the latest diagnostic equipment of the clinic:
- sigmoidoscopy, which allows you to determine the location of the cyst with maximum accuracy;
- probing the cyst - to determine the canal of the coccygeal passage;
- ultrasound examination - to clarify the location and extent of the process;
- radiography of the sacrum with contrast;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptoms
| Disease variant | Clinic |
| Uncomplicated option (no abscess) | Dull aching pain in the coccyx area. Sometimes the patient may complain of lower back pain without clear localization. General condition is satisfactory. There are no external changes. Minor itching may occur in the intergluteal space. |
| Complicated variant (abscess) | Acute pain (may have a shooting character, similar to the pain of radiculitis). A feeling of pulsation and swelling in the affected area. In severe cases, the patient cannot sit in a sitting position. The general condition is moderate. All typical symptoms of intoxication appear (fever, tachycardia, nausea/vomiting, weakness). When the abscess breaks out, fistulas form (heal only by secondary intention and for a long time) and the patient feels relief. The symptoms gradually disappear, but the disease does not go away completely. |
| Chronic variant (relapses are followed by a phase of remission) | The general condition is relatively satisfactory. The purulent focus does not form into a typical abscess, but immediately breaks out. This will explain the main symptom of such cysts - long-term non-healing fistulas and pronounced scar changes in the affected area. |
WHY DOES A FISTULA APPEAR?
The pathology is associated with a malfunction that occurs during the development of the embryo. The disease also manifests itself in patients who have a genetic predisposition to a specific form of the intergluteal fold and sacrococcygeal region.
There are certain factors that can trigger the activation of the disease. A fistula on the coccyx tends to appear against the background of:
- weakened immune system;
- lower back injuries;
- inflammation of the follicles;
- presence of infections in the body;
- increased hair growth in the sacrum area.
In some cases, the pathology is associated with a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, and poor personal hygiene. Sometimes the disease manifests itself after severe hypothermia.
Complications
In some cases, an abscess can develop into phlegmon (diffused purulent inflammation). This condition is an emergency and requires immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention (opening and draining the purulent cavity).
The abscess can also break out towards the spinal cord (bacteria enter the sinuses of the spinal cord and then along the ascending path to the brain). This leads to the development of meningitis and encephalitis with a corresponding clinical picture (an extremely dangerous complication). In this case, the patient feels relief in the area of the pilonidal cyst, since it is partially drained, but the general condition sharply worsens, focal and cerebral symptoms arise.
Conservative treatment
The following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine) for washing and treating the affected area.
- Antibiotics (Metronidazole, Cefuroxime) of local (gel, ointment) and general (tablets, IV, IM injections) action.
- Analgesics (Ketoprofen) to relieve pain.
- Antifungal agents (Fluconazole) if a fungal infection is suspected.
Drug therapy complements surgery but is not the primary treatment option.
Attention! Photo of shocking content. To view click on
.
Sometimes sclerotherapy is used - the introduction of sclerosing drugs (silver nitrate) into the cavity. The method is used relatively rarely due to low efficiency.
Surgery
There are several methods of surgical intervention (depending on the individual characteristics of the formation):
- Excision of the tract with suturing of the wound tightly (complications in the postoperative period are no more than 20%). Position on your stomach with legs apart. Dye is injected into the passage holes to reveal the structure. Next, the doctor uses a semicircular incision using a scalpel or electric knife to excise the tract along with the skin and subcutaneous fat. The wound is sutured tightly in layers. It is permissible to use various techniques - separate interrupted sutures, U-shaped ones.
- Excision of the tract with suturing of the edges of the wound to the bottom (it is best done in the acute phase of the disease in the presence of inflammation). The same bordering incision is made as in the previous version, highlighting all the branches of the epithelial tract. The passage is removed along with the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The tissues of the posterior wall and the upper areas on the lateral walls are partially excised with a scalpel. The edges of the wound are sutured to the surface of the sacrum and coccyx in a checkerboard pattern. Extremely low risk of relapse.
- Two-stage surgery . At the beginning of the operation, a puncture is performed at the site of the greatest fluctuation using a syringe. After this, the abscess is opened with a longitudinal incision. At the second stage, the coccygeal passage and its branches are partially excised within healthy tissue. The second stage is carried out on the 5-7th day, when the inflammation subsides. The wound is not sutured, but is kept open until granulation forms and gradually heals.
- Removal of the tract with wound plastic surgery using a skin flap . Used for frequent relapses and advanced cases of the disease. The cyst with all its branches, fistulas and altered skin is excised as a single block, right down to the sacral fascia. Skin flaps are cut at an angle to the edges of the wound, thereby ensuring good blood supply and mobility of the flap. The skin and subcutaneous fat are exfoliated down to the fascia. After movement, the triangular flap is fixed with separate sutures to the fascia and sutured from the caudal side. Do the same with other flaps.
- Subcutaneous excision (sinusectomy). They are used more often for chronic forms in remission (a large number of leaks, cavities, secondary holes caused by fistulas). Excision begins under the skin and goes from the primary to the secondary passages. Mandatory painting of the passage with a dye and the introduction of a special probe into its cavity. Subsequently, electrocoagulation of the stroke on the probe is performed. No suturing is performed.
Previously, a technique was used that involved opening and draining the abscess (management similar to abscesses), but this method is fraught with relapses in 80% of cases.
At the moment, high-tech methods using laser surgery are increasingly being used (it is a less invasive option and reduces the postoperative time of patient management).
TYPES OF PATHOLOGY
According to the clinical classification, there are four types of the disease:
| Uncomplicated epithelial coccygeal tract | It occurs latently, without pronounced symptoms. |
| Acute form of inflammation | It has two stages - infiltration and the stage of formation of a purulent abscess. |
| Chronic form of pilonidal cyst | It is characterized by the presence of three stages - infiltration, recurrent abscess, purulent fistula. |
| Remission of the inflammatory process | It occurs with weakening or complete disappearance of negative symptoms. |
Contact a specialist on time! Only with the help of timely and high-quality medical care will it be possible to avoid the transition of the disease to an acute or chronic stage.
CLINIC
Find the most common manifestation of illness is a painful, fluctuating fever in a kryzhovo-cuprica patient. In 50% of patients, the first manifestation of illness is a pilonidal abscess, localized cranial to the hair follicle. The most common symptoms are pain and purulent lesions at the sinus opening. In the early stages of illness, before the abscess has formed, cellulitis or foliculitis can be detected.
A differential diagnosis of pilonidal sinus is carried out with acute and chronic paraproctitis, hydradenitis and boils, as well as with syphilitic and tuberculous granuloma and osteomyelitis of the crustacean cyst.
The diagnosis of recurrent pilonidal disease is most often made after opening and draining the pilonidal abscess. In some cases, the pilonidal sinus is lost after an abscess opens and the wound closes, which implies a relapse. If hairs are lost in the wound, then a chronic inflammatory reaction leads to the process becoming chronic. This also corresponds to the anatomy of the intergluteal site, which represents the loss of hair from the sinus and a surgical wound.
Endoanal pilonidal sinus - near the anal opening, is rarely damaged. You should go in a caudal direction and work until the cracks are healed or not. In addition, you need to ensure that hair can be lost into the wound after surgical debridement of anal orifices. Hair can also grow in the normal anoderm and be caused by foreign body granules.
Polonidal disease
Kryzhovo-kuprikovy pilonidal sinus - widespread illness in young adults (frequency approximately 0.7%). Most often, it occurs in women between 15 and 30 years of age, after puberty, when the functioning of sebaceous glands and hair follicles, which flow into hair growth, is disrupted under the influence of state hormones. Especially in the age of 40 years, illness rarely occurs. In men, illness occurs 2–4 times more often, but in women, in whom it can occur at an earlier age (obviously, due to the earlier onset of puberty).
The pilonidal sinus can be found in different parts of the body, but most often its opening is found in the groin-cup area along the midline at intervals of approximately 5 cm from the anus. Sometimes a patient in this area may have multiple openings or secondary openings on the side of the midline. The sinus canal itself is smooth and covered with flat epithelium, leading to an empty space under the skin, which is covered with granulation tissue and filled with a ball of hair.
How should you prepare for surgery?
The night before hospitalization for surgical treatment, it is necessary to shave the sacrococcygeal and, if necessary, the gluteal region. It is possible to perform laser (Alexandrite or diode laser) or photoepilation a few days before hospitalization. However, the last two methods are ineffective for removing light hair. Another method of hair removal is electrolysis; it is more painful, but is suitable for all hair types. The effect after the procedures may not be achieved immediately, so it is better to perform them in advance - 14 days before the operation. Shaving, as an alternative to hair removal, will take you less time and money, but at the same time it may damage the skin, which can become a source of infection. No other special preparation is required for the operation; it will be enough to refuse food and liquids 8 hours before the operation.
Are there ways to prevent relapses/recurrences of the disease?
Despite the radical nature of the operations, there is always a risk of relapse of the disease. To reduce this risk it is recommended:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and features of postoperative wound care, which will be announced by medical personnel;
- shaving the sacrococcygeal area for 3 months after surgery;
- limiting sitting for 2 weeks and intense physical activity for 2 months after surgery.
- timely visits to the attending physician in the early postoperative period
LIKUVANNYA
Injections of phenol can be widely used in the treatment of pilonidal sinuses in Europe, both in cases of acute abscesses and in chronic illness. Introduce 80% of the phenol into the sinus, add 1 quill there and then remove it. After this, the sinus is scraped with a curette. This procedure can be repeated three times, and repeated courses of bathing, if necessary, can be completed at an interval of 4–6 days. The skin near the sinus is treated with phenol, which is the epidermis, with paraffin gel.
Phenol sterilizes the sinus and removes hair, which injections can be combined with local sinus excision. As a matter of course, the wound will heal in 4–8 days. The relapse rate becomes 9–27% and is similar to that observed after simple hanging and packing of a closed wound. Due to the intense inflammatory reaction of patients, they are deprived of one dose from the hospital, and it is then recommended to take clean baths and shin pads.
Based on the choice of method of surgical treatment, pilonidal disease is divided into three groups: acute pilonidal abscess, chronic pilonidal disease, complex or recurrent pilonidal disease.
For pilonidal abscess
it is opened, curettage and drainage are performed. If it is possible to drain it through the incision on the side in the middle line, the fragments of the wound deep in the fold between the sits will burn badly. An important element to note is that the lower leg hair grows near the wound and scar for up to 3 months.
It is necessary to put pressure on the patient so that the opening of the abscess does not guarantee the absence of relapse. If curettage is not performed, in 60% of patients the wound will continue to heal for 2 months, but in 40% of them a relapse occurs. The leaders believe that up to 85% of the sick will require radical treatment in the near future. Extension of the pilonidal sinus canal reduces the relapse rate to 15%. It is often impossible to reveal fragments of this before the first delivery, so it is recommended to stop giving it a little again a week after opening the abscess, if the swelling subsides.
Concept of chronic pilonidal sinus
There are patients in whom there is a pilonidal drainage abscess, as well as patients in whom there is chronic sinus disease without the development of an acute abscess. There are many approaches to surgical treatment of such patients. The first one lies at the superior sinus and lateral sinuses, straightening the empty space to the presacral fascia with the removal of hair, granulation tissue and detritus of the gastrointestinal tract and behind the help of a curette. The skin hangs sparingly. The wound is treated with a second tension of 5–8 tension. Bascom, having opened the opening of the sinus and its epithelial canal from a small incision with the primary suture, and opened the empty one and sanitized from the lateral incision - such a wound will heal faster and require less dressings. The method of asymmetrical cuts is to change the interstellar fold and eliminate the frictional forces that act on the edges of the wound at the interstellar fold. The wound can also be closed by moving the skin cap.
Few techniques for applying the primary suture are effective in the presence of infection and permanently suspended emptying, with a high incidence of infectious complications, frequent inability to apply tension, and a high rate of relapses (up to 38%). Although closing an open wound with a second tension is more likely, there are fewer relapses of illness (8-21%). The lower frequency of relapses is associated with the creation of a wide, flat scar, visible from the hair follicles. This protects against skin friction, hair penetration into the skin and follicular infection.
A compromise between these approaches is marsupialization, in which the edges of the wounds after the hanging sinus are sutured to the presacral fascia, and the wound is packed.
The problem is the treatment of recurrent pilonidal disease
or wounds of a folding shape after hanging sinus. Relapses often result from regrowth of hair in the scar at the interstitial site, accumulation of sweat and infection in it. This problem is solved by the methods of plastic surgery: the wound, granulation and scar tissue are left hanging, after which the wound is sutured with the first suture, liquidating the interstitial fold with a stitch of stiffening method. ів plastics of the skin (movement of V or Y-like clamps of the skin or skin-meat claptiv). According to the data of various authors, the frequency of relapses can be reduced to 1.3–20%.
LIKUVANNYA
The removal of perianal cysts is more surgical. Most teratomas can be removed from the krizhovy access; for radical treatment, it is recommended to remove the kurik. With very large swellings, there is a need for additional abdominal access. In three other types of cysts, they can be removed using transrectal access.
For teratomas, close monitoring of the patient after surgery is required to immediately detect relapse. For malignant teratomas, chemotherapy or exchange therapy is prescribed.