Do liver steatosis need to be treated?
Very often, routine ultrasound diagnostics of the liver reveal diffuse changes in the liver such as steatosis (fatty hepatosis, fatty infiltration of the liver).
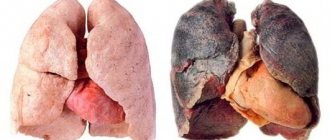
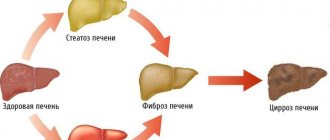
Liver steatosis is a common phenomenon for older people, most often accompanying the aging process, however, recently liver steatosis is also characteristic of young people, and even perhaps without accompanying excess weight? Of course, steatosis is a disease that is expressed in the fact that adipose tissue is formed inside the liver instead of liver tissue , which does not perform the function of the liver and differs from liver tissue in its structure by its high density. With steatosis, the amount of healthy liver gradually decreases and over time, the remaining healthy part will not be able to ensure the vital functions of the body. This stage of the disease is called cirrhosis of the liver and is difficult to treat.
The problem is complicated by the fact that the liver does not hurt, and even if it is seriously damaged, the patient does not have any complaints, with the exception of a possible feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium . Most often, heaviness and discomfort in the right hypochondrium with steatosis, as with other liver pathologies, are caused by an increase in its size.
Features of alcoholic liver disease
Liver dysfunction begins with alcoholic steatosis
. Doctors use this term to denote the phenomenon of fatty degeneration, which can be found in most alcohol addicts.
The prognosis for alcoholic liver steatosis is favorable only if, immediately after the onset of painful symptoms, a person consults a doctor and undergoes the prescribed treatment. A prerequisite for effective therapy is always a complete abstinence from drinking. If the patient does not comply, he will face cirrhosis or hepatitis in the near future.
Causes of liver steatosis
What is the cause of liver steatosis , why, according to statistics from the European Association of Hepatologists, is this disease widespread as an epidemic? The most common opinion is poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle. And this is a big mistake. The cause of steatosis is not an unhealthy lifestyle, but hormonal and metabolic changes; this is a disease that, in addition to lifestyle correction, nutrition and physical activity, also requires observation by a hepatologist and endocrinologist!
Literature:
- Gazatova N. D. Changes in cellular and humoral blood parameters in alcoholic liver fibrosis. Dissertation of a candidate of biological sciences: 14.03.03. Place of protection: Institute of Experimental Medicine. - Kaliningrad, 2022. - 23 p.
- Loginov A. S. Alcohol and liver. - M.: Higher School, 1987. - 94 p.
- Bakirov A. B. Chronic liver diseases. - Ufa: State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Bashkir State Medical University", 2009. - 118 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
Treatment of liver steatosis
Like any liver disease in which it is destroyed with a possible outcome in cirrhosis, treatment of steatosis is possible only with medications that act on the cause of the disease. In the case of steatosis, the cause of the disease is metabolic and hormonal disorders , which cause changes in the structure of the liver tissue. Internal fatty liver is always accompanied by a pathological flow of fat into the pancreas, heart and blood vessels, and kidneys. This life-threatening systemic disease is called metabolic syndrome.
Metabolic syndrome is treated by a hepatologist together with an endocrinologist , affecting both the causes of the disease and the consequence - steatosis. The result of treatment is always recovery if treatment is prescribed on time. In addition to drug correction of metabolic disorders, the treatment complex includes recommendations for proper nutrition and physical activity, which on their own, without treatment, do not produce results. The difficulty of treatment is due to the fact that the share of success in treatment depends on the behavior of the patients, which is why the patient’s serious awareness and desire to get results is so important.
Mechanism of disease development
Many people think that only drinks with a high alcohol content can cause liver problems. They consider wine, beer, and all kinds of alcoholic cocktails harmless. And this is a huge misconception. Frequent drinking and heavy drinking also lead to steatosis.
Under the influence of ethyl alcohol, the liver loses its ability to repair itself.
The enzymes necessary for ethanol oxidation begin to be produced in smaller quantities. In response, the concentration of acetaldehyde, an intermediate (toxic) breakdown product of alcohol, rapidly increases. It accumulates in tissues and organs, causes destruction of hepatocytes and leads to necrosis of liver structures.
Even if a person uses small portions of alcohol, but does it on an ongoing basis, problems will not be long in coming. The level of free fatty acids and triglycerides increases in hepatocytes. As a result, the liver begins to degenerate at the cellular level
.
For alcoholic liver steatosis:
- the production of protein compounds is blocked;
- the reaction of fat peroxidation accelerates, and abnormal foci of connective tissue form in the organ;
- local metabolism is disrupted;
- hypoxia appears;
- hepatocytes die.
Such changes contribute to the formation of cysts, which compress blood vessels and create conditions for the inflammatory process. From this moment on, full blood circulation in the organ becomes impossible.
Necessary examinations for prescribing and monitoring treatment of liver steatosis
To prescribe treatment for liver steatosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination that reveals the degree of liver damage and the severity of metabolic syndrome indicators. The modern equipment of our center allows us not only to detect fatty tissue in the liver, but also to calculate the percentage of normal healthy tissue in the liver and how much non-functioning fatty tissue! This is important for treatment tactics and prognosis for recovery.
The Fibroscan device with an additional sensor for assessing steatosis allows not only to quantify the fatty tissue in the liver according to the degree of steatosis from 0 to 3, but also allows you to measure the result of treatment, which in most cases leads to complete normalization of the liver structure (steatosis 0). Treatment is prescribed individually depending on the examination results. There is no common treatment regimen for all, since metabolic and hormonal disorders can be expressed differently.
How is the treatment carried out?
Since the disease is caused by excessive drinking, it needs to be treated under the guidance of not only a hepatologist, but also a narcologist. Typically, the therapeutic course begins with detoxification - hardware and medicinal
. If there is no severe withdrawal syndrome caused by quitting drinking, detox can be performed on an outpatient basis.
As soon as the patient’s body is cleared of alcohol and its toxic breakdown products, the addict is prepared for coding. The following options are possible here:
- Hypnosis. Involves placing a person into a state of deep hypnotic sleep. Afterwards, the doctor instructs him to completely abstain from “strong drinks.”
- Stress therapy according to Dovzhenko. It involves working with the depths of the subconscious. During the session, the patient is in a state reminiscent of a light doze. The doctor seems to reprogram the brain structures responsible for maintaining the craving for alcohol. Thanks to this, drinking ceases to interest the patient.
- Hardware programs. Requires special medical equipment. Laser encoding is used more often than others. During it, biologically active points of the human body are treated with laser beams, due to which alcohol addiction disappears. But the procedure must be repeated several times. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve sustainable positive dynamics.
For alcoholic hepatic steatosis, drug coding can also be used. Its essence is the subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular or oral administration of drugs that remove interest in alcohol and cause intolerance to it. But it is important to consider that all drugs have contraindications for use. Most of them are not suitable for severe liver disease. Therefore, the decision on the possibility of using coding drugs should be made by a narcologist together with a hepatologist.
To restore normal liver function in alcoholic steatosis, the following are used:
- Medicines including ademetionine.
With their help, it is possible to put the hepatobiliary system in order and restore healthy liver metabolism. - Products based on ursodeoxycholic acid.
This component reduces the concentration of triglycerides and improves bile production. Due to this effect, inflammation gradually disappears. - Preparations with essential phospholipids.
Accelerate the regeneration of liver cells, returning the liver’s ability to repair itself. - Hepatoprotectors of plant origin.
They have a general strengthening effect on the liver, reduce the severity of inflammatory processes and speed up the renewal of hepatocytes.
Drug correction for alcoholic liver steatosis should last at least three to six months. All this time, the patient must carefully monitor his health and eat properly. He will not be able to drink alcohol for the rest of his life.
Results of treatment of liver steatosis
Patient review:
» Dear Bella Leonidovna!
Dear Nelly Nikolaevna Tsurikova, Mushinskaya Kira Vladimirovna, girls at the reception, ultrasound diagnostic doctor, thank you all so much for organizing the treatment of my illness. You guys work wonders as a team! High-level professionals and people with a capital “P!” I am grateful to fate that I found your clinic, which really saved my life and changed it 180 degrees. Thanks to your efforts, qualifications and attention, I have become a completely healthy person. I lost 23.5 kg in 9 months, my liver has become a real factory that now works perfectly!
In general, I wish your team all the best. Do not stop! You really do a great job for people, help overcome serious illnesses.
On the eve of the New Year 2022, I would like to wish you health, family joys and love too! with best wishes, your patient from Kazan" >>> - Rustem 12/05/2018
Causes of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- Taking certain medications (hormones (glucocorticosteroids), estrogens, nefidipine, methotrexate, aspirin, diltiazem).
- Eating disorders (fasting, rapid weight loss, low protein diet).
- Surgical interventions (stomach and intestinal operations).
- External exposure to toxic substances (organic solvents, phosphorus, poisonous mushrooms).
- Intestinal diseases (inflammatory diseases, malabsorption, excessive growth of bacteria in the intestines).
- Insulin resistance is a decrease in the biological response to one or more effects of insulin.
The development of insulin resistance is facilitated by a hereditary factor - a predisposition to diabetes mellitus, detection of diabetes mellitus in close relatives, as well as excess caloric nutrition and low physical activity. These factors themselves contribute to increased obesity and fat accumulation in liver tissue. In approximately 42% of patients, risk factors for developing the disease cannot be identified.
Diet
You will have to avoid fatty, fried, and spicy foods. The diet is prescribed by a nutritionist based on the cause of steatosis. Exclude fried, smoked, spicy, legumes, and fatty meats from the menu.
For 2 kg of grated potatoes, 1 kg of ground liver or minced chicken, 4 tbsp. l. decoys. 150 g butter, herbs, salt to taste. Bake until it starts to spring back like a sponge cake. Grate the potatoes on a fine grater. For minced fish - on a coarse one.
For 1 kg of boiled rice, 300 g of soft butter. Mix butter with warm rice. Let cool. Add 600 g of cottage cheese, 6 eggs, 300 g of sugar. Mix thoroughly. A baking tray is greased with a thin layer of sunflower oil and sprinkled with breadcrumbs or flour.
Cut 1 large boiled beet into small cubes. Add some salt. Place in the refrigerator for an hour. Cut the boiled veal into large cubes. Steam raisins and prunes and grind in a meat grinder with a coarse mesh. For 0.5 kg of beets, 1 kg of meat, 200 g of raisins and prunes. Add some salt. Season with mayonnaise.
Beat a large layer of veal fillet. Mix cottage cheese with herbs and salt. Place on prepared veal. Place orange slices and fish fillets alternately. Make a roll. Secure with toothpicks. Wrap in foil. Bake for 40-50 minutes. If the cottage cheese is liquid, add 150 g of butter and 4 tbsp per 1 kg. l. decoys.
Watch the video menu for the week:
Fatty hepatosis of pregnant women
Separately, there is hepatic steatosis, which occurs without a significant cause in women bearing a child. Acute fatty hepatosis of pregnancy is diagnosed in one out of 13,000 women. 20–25% of cases end in death, according to foreign authors, and up to 60%, according to domestic sources.
The disease progresses quickly, over 2–3 weeks. Occurs mainly in late pregnancy - 32–36 weeks. The exact cause of this pathology has not yet been established.
Symptoms that may indicate acute fatty hepatosis in pregnant women: excessive vomiting, severe nervous disorders, general weakness, drowsiness.
The only treatment method is emergency delivery. Within 5 weeks after birth, the disease regresses.
Causes of fatty hepatosis
There are three main reasons for the development of hepatic steatosis:
- Obesity. If the body mass index exceeds 30, the likelihood of dystrophy is about 40%.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. Moreover, hepatosis can occur even in people who drink a little, but every day. There is a direct relationship between the duration of alcohol consumption and the severity of liver dystrophy and, as a consequence, the risk of developing cirrhosis.
- Long-term use of medications with hepatotoxic effects.
Less commonly, hepatosis develops against the background of diseases that occur with metabolic disorders; this category includes hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, myxedema, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, malignant neoplasms, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the absorption process is disrupted, etc. .
Liver dystrophy can be caused not only by obesity, but also by poor nutrition - overeating, abuse of fatty foods and foods containing hydrogenated fats and simple carbohydrates.
The disease is sometimes diagnosed in people who have a deficiency of enzymes involved in lipid metabolism (hereditary disease).
Most often, more than one factor leads to the development of steatosis. In most cases, there is a multifactorial factor, for example, the consumption of alcohol by a person who is eating poorly or taking toxic medications.
Diagnostic measures
Making a diagnosis based solely on clinical symptoms is impossible. When contacting a specialist, the doctor must first question the patient’s complaints and collect anamnesis. Particular attention should be paid to lifestyle, diet, profession, bad habits (drugs, alcohol), as well as concomitant diseases.
This is followed by a physical examination, during which the doctor:
- conducts an examination of the skin and mucous membranes, paying attention to color, the presence of rashes and swelling of the tissues;
- auscultation (listening) of the lungs and heart;
- palpation (palpation) of the lymph nodes and abdomen, during which the specialist detects hepatomegaly, as well as liver pain when pressing on the area of the right hypochondrium;
- measures temperature, blood pressure and heart rate.
After this, additional laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed:
- general clinical analysis - refers to routine. With steatosis, its indicators practically do not change;
- biochemistry is more informative, as it gives an idea of the severity of liver failure. Its assessment is based on the level of transaminases. Enzymes are located intracellularly, so after the destruction of hepatocytes they enter the blood in large quantities. In addition to ALT and AST, the doctor analyzes the content of bilirubin (total and fractions), protein and alkaline phosphatase;
- lipid profile, which includes five indicators. The transcript of the analysis presents total cholesterol, triglycerides and atherogenicity coefficient. It is calculated by a doctor to determine the ratio of factors contributing to steatosis to antiatherogenic indicators. The analysis also includes high-density lipoproteins (HDL), which are “good” because they remove cholesterol from cells into hepatocytes and with bile into the intestines. At the same time, LDL (“bad”) indicates a disorder of lipid metabolism, a high risk of fatty liver degeneration and the development of atherosclerosis;
Ultrasound - makes it possible to examine the liver and other internal organs, assess their volume, parenchyma and surface. Used for initial examination of patients;- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are more accurate methods for diagnosing liver diseases;
- targeted biopsy – used to make a final diagnosis. The material is collected under anesthesia, after which the liver tissue is subjected to histological analysis. Detection of fatty inclusions and fibrous fibers confirms steatosis.
Based on the histology conclusion, one can judge the severity and extent of the pathological process, as well as determine the prognosis for life.
With diffuse steatosis, the lesion covers almost the entire surface of the liver. Depending on the severity of changes in the parenchyma, several degrees of fatty degeneration of the organ are distinguished:
- the first is characterized by the appearance of areas with accumulations of fat droplets. Such groups can be located far from each other (in different parts of the organ), but there are many of them;
- the second is characterized by the development of intracellular obesity. During instrumental examination, moderately expressed altered areas with increased volume of hepatocytes due to lipid accumulations are visualized. In addition, there is a proliferation of connective tissue between cells;
- the third is manifested by a significant accumulation of fat in the intercellular space with the formation of cystic formations. Areas with connective tissue also become more pronounced, and stripes with strands of fibroblasts are clearly visualized. This stage often progresses to liver fibrosis.
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- proper nutrition, in particular limiting fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods;
- moderation in the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- taking medications correctly;
- regular physical activity.
Fat accumulation is often caused by excess weight due to a sedentary lifestyle. Scientists have proven that if you eat only fast food for 4 weeks, this disease will almost certainly occur. Student volunteers took part in the experiment. Moreover, the first signs appeared after 1 week of such nutrition. Therefore, nutrition and weight control are of great importance.
For prevention, hepatoprotectors should be used, especially during periods of increased load on the liver, for example, with prolonged alcohol consumption, antibiotic treatment, and following a diet aimed at weight loss.
Classification
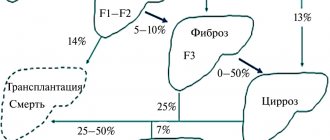
Based on etiology, hepatosis is divided into non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic steatosis. The first type of disease is diagnosed in only 7–10% of cases.
Hepatosis occurs:
- primary - caused by metabolic disorders, for example, obesity or hyperlipidemia;
- secondary – due to the impact on the body of external negative factors, which subsequently lead to metabolic disorders, for example, fasting, long-term use of corticosteroids, intestinal resection.
Doctors also take into account the characteristics of fat deposition, according to which hepatosis is divided into:
- diffuse;
- zonal;
- focal disseminated;
- pronounced disseminated.
Diagnostics
The clearest and clearest picture of the condition of the liver is provided by histological examination of the biopsy specimen. However, this invasive and fraught with complications procedure is insisted on in cases where the etiology of the disease is unknown. With alcoholism, such an examination simply makes no sense, since according to statistics, fatty liver degeneration is present in more than 90% of addicts.
Therefore, in most cases we are limited to:
- ultrasound examination;
- elastography to assess the density and structure of the parenchyma;
- a biochemical blood test with the mandatory determination of basic liver parameters, however, they are either unchanged or slightly increased;
- determination of lipid profile.
Important!
A biopsy is necessary if alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis or cirrhosis is suspected.
Disease severity
- mild: less than 30% of hepatocytes are affected;
- medium: up to 60% of cells are affected;
- severe: steatosis covers more than 60% of the liver parenchyma.