Contraindications
When should you not use a drug like Valium? The effect of such a drug will not be as desired if you take it:
- with hypersensitivity;
- coma, shock;
- acute alcohol intoxication;
- acute forms of kidney and liver diseases;
- myasthenia gravis;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- in childhood up to 6 months;
- during breastfeeding and in the first trimester of pregnancy.
– with hypersensitivity;
– in coma, shock;
– in case of acute alcohol intoxication with weakening of vital functions;
– in case of acute intoxication with drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system;
– with myasthenia gravis;
– with angle-closure glaucoma;
– with severe COPD, acute respiratory failure;
– during pregnancy, lactation.
Interaction
It has anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects.
Negative side reactions are:
- addiction;
- development of such paradoxical reactions as anxiety, hallucinations, convulsions or insomnia;
- decreased reaction speed and concentration;
- deterioration of short-term memory;
- movement disorder in the form of ataxia, dysarthria;
- headache and dizziness;
- hypotension or bradycardia;
- long-term use can cause liver and kidney damage, intestinal atony, and reduce libido and potency;
- reactions at the injection site;
- “withdrawal” syndrome and aftereffects, manifested in decreased performance, muscle weakness;
- allergic reactions.
When a patient is prescribed this drug, it is important to inform them what Valium is, because it is a well-known psychotropic tranquilizer that has a number of side effects, including withdrawal syndrome and addiction. The attending physician, when prescribing it, is obliged to inform the patient about the possible negative effect on the body and offer other treatment options.
- Valium Roche causes potentiation of the effects of alcohol, anticonvulsants, hypnotics, antihistamines and hypotensive substances, neuroleptics, tricyclic antidepressants, general anesthetics, analgesics, muscle relaxants.
- Analeptics and psychostimulants can reduce the activity of Diazepam.
- Antacids reduce the rate, however, not the level of absorption of Diazepam.
- Isoniazid - prolongation of excretion and increase in blood concentration of Diazepam.
- Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation, for example, Cimetidine, Ketoconazole, Omeprazole, fluvoxamine, Fluoxetine, cause changes in pharmacokinetics and an increase in the duration of the clinical effects of Diazepam.
- Phenytoin is subject to changes in plasma concentration levels.
- Rifampicin - decreases the concentration of Diazepam in the blood.
- Erythromycin - slows down the metabolism of Diazepam in the liver.
The drug "Valium" causes potentiation of the effects of alcohol, hypnotics, anticonvulsants, hypotensive and antihistamines, as well as neuroleptics, general anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, muscle relaxants and analgesics.
Psychostimulants and analeptics can significantly reduce the activity of the drug "Diazepam".
Antacids reduce the rate, but not the level, of absorption of this drug.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors such as Cimetidine, Omeprazole, Ketoconazole, Fluoxetine and Fluvoxamine change the pharmacokinetics of the drug in question and also increase the duration of its clinical effects.
"Rifampicin" reduces con in the blood, and "Erythromycin" slows down its metabolism in the liver.
If you simultaneously take Valium with other types of psychotropic drugs, including drugs for injecting anesthesia, some of the barbiturates, phenothiazines, ethanol, a list of antidepressants, then its effect will increase. If you take it simultaneously with different types of muscle relaxants, the risk of apnea will significantly increase.
Pharmacokinetic interaction
If you take cimetidine or omeprazole for a long time, the clearance of Valium will decrease. Drugs that usually cause the induction of some of the liver enzymes, which also include antiepileptic drugs, will speed up the process of removing Valium from the patient's body.
We briefly reviewed the drug Valium, its dosage, indications and contraindications for its use. Return to the site again for new information about other drugs.
Indications for use
Valium is taken for anxiety disorders, dysphoria, insomnia, skeletal muscle spasms, in spastic conditions caused by damage to the spinal cord or brain (tetanus, athetosis, cerebral palsy), arthritis, bursitis, myositis, rheumatic pelvispondyloarthritis, chronic progressive polyarthritis, arthrosis, which accompanied by tension in the skeletal muscles, with angina pectoris, vertebral syndrome, and tension headaches.
According to the instructions, Valium is taken for alcohol withdrawal syndrome, if the patient is bothered by tremors, tension, anxiety, or severe agitation.
Valium can be included in the complex therapy of hypertension, gastrointestinal ulcers, disorders encountered in gynecology and obstetrics (psychosomatic, menstrual and menopausal), epilepsy, heart attack, eczema and other skin diseases accompanied by irritation and itching.
Valium is used as premedication before operations and diagnostic endoscopic procedures, and before general anesthesia.
There are reviews of Valium used in obstetrics: the drug is used to facilitate labor, premature birth (exclusively at the end of the 3rd trimester), and premature placental abruption.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Before turning to the mechanism of action of the drug, you should understand: “Valium - what is it?”
Valium is not described on Wikipedia, but it is a patented name for Diazepam, a drug from the benzodiazepine group that has enormous medical use.
Valium is a drug that, thanks to the anxiolytic activity of the active substance, relieves internal worries, fears, anxiety and tension. Diazepam has a dose-dependent effect on the central nervous system, that is, small doses (within 2-15 mg per day) cause a stimulating effect, and large doses (more than 15 mg per day) cause a sedative effect.
Overdose
The drug Valium is used orally.
The standard dose is 2.5-10 mg 2-3 times a day, maximum 60 mg per day.
Symptoms: confusion, drowsiness, paradoxical arousal, areflexia, decreased reflexes, stupor, deep sleep, decreased response to painful stimuli, dysarthria, nystagmus, ataxia, tremor, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, bradycardia, apnea, decreased blood pressure, severe weakness, collapse , coma, depression of respiratory and cardiac activity.
Treatment: gastric lavage, intake of enterosorbents, forced diuresis, symptomatic therapy, mechanical ventilation.
The list of symptoms of a Valium overdose is as follows:
- drowsiness;
- confusion;
- decreased reflexes;
- stunned;
- paradoxical arousal;
- areflexia;
- reduced pain threshold;
- dysarthria;
- deep dream;
- ataxia;
- nystagmus;
- bradycardia;
- tremor;
- shortness of breath and other respiratory problems;
- pronounced weakness;
- lowering blood pressure;
- collapse;
- depressed cardiac and respiratory activity;
- coma.
As treatment, the stomach is washed, diuresis is forced, activated charcoal is taken, symptomatic therapy is carried out, in particular, breathing rates and blood pressure are maintained. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
For an adult, the oral dose of Valium Roche ranges from 5 to 20 mg per day and is determined depending on the clinical picture and severity of symptoms. The maximum permissible single dose is no more than 10 mg. The course of treatment in case of anxiety is up to 6 weeks, after which you should contact your doctor to select the minimum maintenance dose. The drug is withdrawn gradually.
Parenterally, in emergency cases, 2 to 20 mg can be administered intramuscularly or intravenously. In the latter case, it must be administered slowly - at a rate of no more than 0.5–1 ml per minute.
It is accompanied by symptoms such as central nervous system depression of varying severity - from drowsiness to coma, and possible confusion, hypotension and respiratory depression.
Treatment when the patient is conscious is induction of vomiting and the use of activated charcoal; if unconscious, gastric lavage with a tube, symptomatic therapy, screening of vital signs, and fluid administration to enhance diuresis.
Barbiturates can be used to relieve agitation. A specific antidote is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist - Flumazenil.
Only an experienced specialist should prescribe the remedy in question. For an adult patient, the oral dose of the drug should be 5-20 mg per day. This amount of medication is determined depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, as well as the overall clinical picture.
The maximum possible single dose of the drug is no more than 10 mg. The course of therapy with this remedy in case of anxiety should last about 6 weeks. After this period, you should contact your doctor so that he can select the minimum maintenance dosage.
Side effects
Nervous system
From the very beginning of taking the drug, especially elderly patients may suffer from:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased concentration;
- ataxia;
- disorientation;
- unsteady gait;
- poor coordination of movements;
- lethargy;
- dulling of emotions;
- anterograde amnesia;
- rarely – headache;
- euphoria;
- depression;
- tremor;
- depressed mood;
- catalepsy;
- confusion;
- dystonic extrapyramidal reactions;
- weakness;
- hyporeflexia;
- dysarthria;
- extremely rarely - paradoxical reactions such as aggressive outbursts, fear, suicidal tendencies, anxiety, insomnia, etc.
Hematopoiesis
- Leukopenia.
- Neutropenia.
- Agranulocytosis.
- Anemia.
- Thrombocytopenia.
Digestive tract
- Dry mouth.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea.
- Decreased appetite.
- Vomit.
- Hiccups.
- Gastralgia.
- Constipation.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Jaundice.
The cardiovascular system
- Cardiopalmus.
- Tachycardia.
- Decreased blood pressure.
Genitourinary system
- Incontinence.
- Urinary retention.
- Kidney disorders.
- Increased or decreased libido.
- Dysminorrhea.
Types of allergic reaction to components
- Skin rash.
- Itching.
Effect on the fetus
- Teratogenicity.
- Depressed central nervous system.
- Breathing problems.
- Suppression of the sucking reflex in newborn infants.
Local reactions
- Phlebitis.
- Redness.
- Swelling.
- Pain.
Other reactions
- Addiction.
- Drug addiction.
- Depression of respiratory processes.
- External respiration dysfunctions.
- Visual impairment (diplopia).
- Bulimia.
- Loss of body weight.
- If you stop taking it abruptly, you will experience withdrawal syndrome.
- Irritability.
- Anxiety.
- Headache.
- Excitation.
- Excitement.
- Nervousness.
- Feeling of fear.
- Dysphoria.
- Increased sweating, etc.
Neurological disorders: drowsiness, increased fatigue, dizziness, decreased ability to concentrate, disorientation, ataxia, gait instability, poor coordination of movements, dullness of emotions, lethargy, slowed mental and motor reactions, headache, anterograde amnesia, euphoria, depression, depressed mood , tremor, catalepsy, dystonic extrapyramidal reactions, weakness, confusion, myasthenia gravis during the day, dysarthria, hyporeflexia, paradoxical reactions (psychomotor agitation, aggressive outbursts, fear, muscle spasms, suicidality, confusion, acute agitation, hallucinations, irritability, insomnia, anxiety).
Hematological disorders: leukopenia, agranulocytosis, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Digestive disorders: dry mouth, hypersalivation, gastralgia, heartburn, hiccups, nausea, decreased appetite, vomiting, constipation, liver dysfunction, jaundice, increased activity of liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase.
Cardiovascular disorders: palpitations, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia.
Genitourinary disorders: urinary incontinence, renal dysfunction, urinary retention, dysmenorrhea, increased/decreased libido.
Allergic reactions: itching, skin rash.
Effect on the fetus: central nervous system depression, teratogenicity (especially in the first trimester), respiratory failure, suppression of the sucking reflex.
Local reactions: phlebitis, venous thrombosis.
Storage conditions and periods
At room temperature.
Keep out of the reach of children.
solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration 10 mg/2 ml - 4 years.
5 mg tablets - 5 years.
tablets 10 mg - 5 years.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
In a place inaccessible to minor children. At room temperature.
No more than four years.
Store Valium solution at temperatures up to 25 degrees Celsius.
Release form
Diazepam is one of the items on the list of the minimum set of drugs determined by WHO. This remedy is used to treat the following diseases:
- anxiety;
- insomnia;
- epileptic seizures;
- muscle spasms;
- alcohol addiction.
The drug may be recommended for use in preparation for some medical procedures for the purpose of anesthesia or sedation of patients.
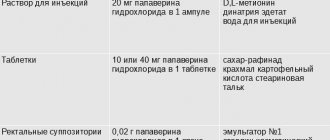
Valium is sold in the form of injectable solutions and tablets . As for the solution, 1 ml contains 5 mg of diazepam. Such medicines go on sale in quantities of 50 or 10 ampoules made of dark glass. Each holds 2 ml of solution. Ampoules are placed in cardboard packaging. The tablets contain 5 or 10 mg of diazepam and some other ingredients, which include:
- corn starch;
- anhydrous lactose;
- calcium stearate;
- gelatinized starch;
- dyes.
Reviews of Valium Roche
Valium is a fairly popular drug among patients, which is used as an anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant. According to reviews from most consumers, the medication in question turns out to be highly effective for various diseases, including epilepsy, sleep disorders, anxiety conditions, and so on. Also, taking it helps to reduce manifestations in the form of agitation, tremor and eliminate hallucinations.
However, there is no such remedy that would suit everyone. Some people who have used this drug have been unhappy. They note that the medicine begins to act only after a week. In addition, with prolonged use, the medication causes a large number of adverse reactions and leads to addiction.
Judging by reviews on the Internet on various forums and medical sites, the drug turns out to be effective for various diseases - epilepsy, anxiety, sleep disorders and others. Helps reduce symptoms such as tremor, agitation and eliminates hallucinations.
However, people who have used Valium note the inconvenience that the drug begins to act after a week and, with prolonged use, has a lot of adverse reactions, and also leads to addiction.
Kinetics
The medication "Valium", analogues of which are listed below, is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (when taken orally). In this case, absorption occurs by 75%, and the maximum concentration is reached after 1.5 hours.
The biological transformation of this medicine occurs in the liver. In this case, active metabolites with a half-life are formed. When prescribing the medication to infants, the effect is achieved after 30 hours, and for elderly and adults – after 100 and 48 hours, respectively. In case of liver pathologies, this indicator is extended to 4 days.
The drug in question is excreted from the human body mainly by the kidneys (90%) in the form of conjugates, as well as unchanged (2%) and together with feces (8%).
View gallery
Price, where to buy
The price for Valium Roche in Russia is not fixed, you can find private offers for 1000 rubles per package, but reliability and veracity are not guaranteed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m2_MA-IPaYQ
Regarding foreign sources, you can find information about the price of Valium Roche at 230 pounds sterling for 1000 tablets of 10 mg. However, in order to buy the necessary and high-quality drug, you should contact the help desk of your city, where you will be provided with information about the best prices and availability of this drug in pharmacies.
Similar drugs:
- Chlozepide Oral tablets
- Hydroxyzine Oral tablets
- Tranxene Capsule
- Rohypnol Injection solution
- Apo-Lorazepam Oral tablets
- Eunoctin Oral tablets
- Rohypnol Oral tablets
- Sirdalud Tablets
** The Drug Directory is intended for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions. Do not self-medicate; Before you start using Valium Roche, you should consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal. Any information on the site does not replace medical advice and cannot serve as a guarantee of the positive effect of the drug.
Are you interested in Valium Roche? Do you want to know more detailed information or do you need a doctor's examination? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home . Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
** Attention! The information presented in this medication guide is intended for medical professionals and should not be used as a basis for self-medication. The description of the drug Valium Roche is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended for prescribing treatment without the participation of a doctor. Patients need to consult a specialist!
If you are interested in any other drugs and medications, their descriptions and instructions for use, information about the composition and form of release, indications for use and side effects, methods of use, prices and reviews of drugs, or you have any other questions and suggestions - write to us, we will definitely try to help you.