Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The active ingredient Betaloc reduces or eliminates the stimulating effect of catecholamines during stress and exercise, reduces myocardial contractility and cardiac output, reduces high blood pressure and heart rate. In addition, metoprolol reduces myocardial oxygen demand and prolongs diastole.
The drug may slightly increase TG levels and also slightly reduce HDL fractions and free fatty acid levels in the blood plasma.
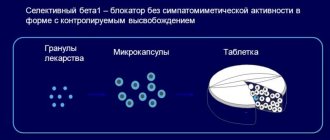
The tablets are characterized by a delayed release of the active substance, so the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma remains unchanged, which ensures a stable clinical effect for a day or more. The drug is better tolerated than its analogues, and the risk of developing unwanted side effects is significantly reduced.
Betaloc ZOK is completely absorbed. Absorption does not depend on the timing of meals. The degree of connection with blood plasma proteins is 5-10%. The active substance is metabolized in the liver to form three metabolites without beta-blocking activity.
About 95% of the drug is excreted in the urine, the remaining amount remains unchanged. The half-life averages 3-4 hours.
Composition and release form
The medicine belongs to the category of selective beta-blockers, the main active ingredient is metoprolol tartrate. Available in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous administration, additional components and concentration of the active component depend on the form of release.
The use of the drug reduces the risk of developing myocardial infarction and other complications in case of serious heart failure.
If symptoms of myocardial infarction appear, intravenous administration of Betaloc should be started as early as possible, optimally in the first 24 hours.
The mechanism of action of Betalok is based on blocking certain receptors that have a negative effect on the heart during physical and nervous stress.
The medicine prevents an increase in heart rate, an increase in myocardial contractility and an increase in blood pressure. The active substance normalizes heart function, reduces the likelihood of atrial fibrillation and flutter, which can lead to serious consequences.
Indications for use
What are Betaloc ZOK tablets for? First of all, they are prescribed to patients with:
- arterial hypertension;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- angina pectoris;
- functional disorders of the heart, which are accompanied by tachycardia .
As an element of therapy, the drug is used for chronic heart failure . In addition, Betaloc ZOK is used to reduce mortality and the likelihood of recurrent infarction after the acute phase of myocardial infarction , as well as as a prophylactic against migraine .
Betaloc ZOK or Bisoprolol - which is better, comparison
Manufacturer: Rapharma, Izvarino, Atoll, Russia
Release form: film-coated tablets
Active ingredient: Bisoprolol
Synonyms: Concor, Biprol, Biol, Bisogamma, Coronal, Niperten
You can replace Betaloc ZOK with Bisoprolol, which also selectively blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors, reduces the volume and force of cardiac output, reduces myocardial oxygen demand, and reduces heart rate.
Analogue Bisoprolol is the active component and international non-proprietary name of many drugs that have antianginal, antiarrhythmic and anti-ischemic properties. The half-life of Bisoprolol allows you to take the medicine once a day.
Reviews from cardiologists indicate the high effectiveness of the drug, regardless of the manufacturer and trade name, in the treatment of chronic heart failure, as well as stable angina and hypertension.
Contraindications
This drug is contraindicated in cases of atrioventricular block II-III degree, therapy with inotropic agents to activate beta-adrenergic receptors, sick sinus syndrome, peripheral arterial circulation disorders, heart failure in the decompensation phase, clinically significant sinus bradycardia , cardiogenic shock , as well as hypersensitivity to beta-adrenergic blockers and any component of the drug.
In addition, Betaloc ZOK is not suitable for patients with acute myocardial infarction with a heart rate less than 45 per minute, systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg. Art. or the duration of the P-Q interval on the ECG is more than 0.24 s.
Betalok zok tab p/o deputy vysv. 50 mg vial plast 30 pcs
Metoprolol is a CYP2D6 substrate, and therefore drugs that inhibit CYP2D6 (quinidine, terbinafine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, celecoxib, propafenone and diphenhydramine) may affect the plasma concentrations of metoprolol. The combined use of Betaloc® ZOK with the following drugs should be avoided:
Barbituric acid derivatives: barbiturates (study conducted with pentobarbital) increase the metabolism of metoprolol due to enzyme induction.
Propafenone: When propafenone was prescribed to four patients treated with metoprolol, an increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol was observed by 2-5 times, while two patients experienced side effects characteristic of metoprolol. This interaction was confirmed in a study on 8 volunteers. The interaction is likely due to the inhibition by propafenone, like quinidine, of the metabolism of metoprolol through the cytochrome P4502D6 system. Taking into account the fact that propafenone has beta-blocker properties, the joint administration of metoprolol and propafenone does not seem appropriate.
Verapamil: The combination of beta blockers (atenolol, propranolol and pindolol) and verapamil can cause bradycardia and lead to a decrease in blood pressure. Verapamil and beta-blockers have a complementary inhibitory effect on atrioventricular conduction and sinus node function.
The combination of Betaloc® ZOK with the following drugs may require dose adjustment:
Amiodarone: Concomitant use of amiodarone and metoprolol may result in severe sinus bradycardia. Given the extremely long half-life of amiodarone (50 days), a possible interaction should be considered long after discontinuation of amiodarone.
Class I Antiarrhythmics: Class I antiarrhythmics and beta-blockers may result in additive negative inotropic effects, which can lead to serious hemodynamic side effects in patients with impaired left ventricular function. This combination should also be avoided in patients with sick sinus syndrome and impaired AV conduction. The interaction is described using disopyramide as an example.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs weaken the antihypertensive effect of beta blockers. This interaction has been documented for indomethacin. It is likely that the described interaction will not be observed with sulindac. Negative interactions have been noted in studies with diclofenac.
Diphenhydramine: Diphenhydramine reduces the clearance of metoprolol to alpha-hydroxymetoprolol by 2.5 times. At the same time, an increase in the effect of metoprolol is observed.
Diltiazem: Diltiazem and beta-blockers mutually enhance the inhibitory effect on AV conduction and sinus node function. When metoprolol was combined with diltiazem, cases of severe bradycardia were observed.
Epinephrine (adrenaline): Ten cases of severe hypertension and bradycardia have been reported in patients taking non-selective beta blockers (including pindolol and propranolol) and receiving epinephrine (adrenaline). The interaction was also observed in the group of healthy volunteers. It is assumed that similar reactions can be observed when epinephrine is used together with local anesthetics if it accidentally enters the vascular bed. It is assumed that this risk is much lower with the use of cardioselective beta blockers.
Phenylpropanolamine: Phenylpropanolamine (norephedrine) in a single dose of 50 mg can cause an increase in diastolic blood pressure to pathological values in healthy volunteers. Propranolol mainly prevents the increase in blood pressure caused by phenylpropanolamine. However, beta blockers may cause paradoxical hypertension reactions in patients receiving high doses of phenylpropanolamine. Several cases of hypertensive crisis have been reported while taking phenylpropanolamine.
Quinidine: Quinidine inhibits the metabolism of metoprolol in a special group of patients with rapid hydroxylation (in Sweden approximately 90% of the population), causing mainly a significant increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol and increased beta blockade. It is believed that a similar interaction is typical for other beta-blockers, the metabolism of which involves cytochrome P4502D6.
Clonidine: Hypertensive reactions during abrupt withdrawal of clonidine may be exacerbated by concomitant use of beta-blockers. When used together, in case of discontinuation of clonidine, discontinuation of beta-blockers should begin several days before discontinuation of clonidine.
Rifampicin: Rifampicin may increase the metabolism of metoprolol, reducing plasma concentrations of metoprolol.
Patients concomitantly taking metoprolol and other beta blockers (eye drops) or monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should be closely monitored. While taking beta-blockers, inhalational anesthetics enhance the cardiodepressive effect. While taking beta-blockers, patients receiving oral hypoglycemic agents may require dose adjustment of the latter.
Plasma concentrations of metoprolol may increase when taking cimetidine or hydralazine.
Cardiac glycosides, when used together with beta-blockers, can increase atrioventricular conduction time and cause bradycardia.
Side effects
As a rule, when used correctly, the medicine is well tolerated by patients to whom it is prescribed. Side effects are minor or easily reversible.
Cardiovascular system: bradycardia , coldness of the extremities, increased manifestations of heart failure , orthostatic hypotension , cardiogenic shock , edema, pain in the heart, fainting, palpitations, first degree atrioventricular block arrhythmia .
Gastrointestinal tract: nausea , diarrhea , vomiting , abdominal pain, constipation .
Skin: rash, increased sweating.
Metabolism: increased body fat.
CNS: increased fatigue, headache , convulsions, problems concentrating, insomnia , dizziness , paresthesia , depression , drowsiness , nightmares.
Respiratory organs: shortness of breath , bronchospasm .
In rare cases, when taking the drug, the following are possible:
- gangrene;
- increased nervous excitability;
- memory impairment;
- hallucinations;
- anxiety;
- depression;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- hepatitis;
- hair loss;
- exacerbation of psoriasis ;
- liver dysfunction;
- photosensitivity;
- rhinitis;
- visual impairment;
- conjunctivitis;
- taste disturbances;
- irritation and/or dry eyes;
- tinnitus;
- arthralgia;
- thrombocytopenia;
- impotence , sexual dysfunction .
Instructions for use of Betaloc ZOK (Method and dosage)
Instructions for use of Betaloc ZOK include taking the drug once daily, regardless of meals (preferably in the morning). Tablets should not be crushed or chewed. During dosage selection, heart rate should be monitored.
Arterial hypertension : 50 mg per day (if the therapeutic effect is not achieved, the dose can be gradually increased to 100-200 mg per day, while Betaloc ZOK tablets, instructions for use, can be combined with other antihypertensive drugs).
Stable chronic heart failure of functional class III-IV : to begin with, a dosage is prescribed - 12.5 mg per day (1/2 tablet of 25 mg). If necessary, the dose is gradually increased, but this must be done strictly under the supervision of a doctor. After 14 days, the initial dosage is increased to 25 mg per day; after another 2 weeks, 50 mg per day can be prescribed. Thus, every 14 days the dose can be doubled until a maximum dosage of 200 mg is reached. However, the dose should not be increased until there is clear evidence that the patient is stable. Kidney function needs to be monitored.
Stable chronic heart failure of functional class II : at the beginning, a dose of 25 mg is prescribed. After the first 2 weeks, it can be increased to 50 mg per day, and then doubled every 14 days until a therapeutic effect is achieved. The maximum dosage is 200 mg per day.
For migraine prevention, 100–200 mg per day is prescribed.
For angina pectoris, 100–200 mg per day is prescribed (can be combined with other drugs for the treatment of angina pectoris).
For arrhythmia, 100–200 mg per day is prescribed.
Cardiac disorders with palpitations: 100 mg per day (if necessary, the dosage can be increased to 200 mg).
Betalok ZOK or Concor – which is better?
Manufacturer: Merck, Germany
Release form: film-coated tablets
Active ingredient: Bisoprolol
Synonyms: Biprol, Biol, Bisogamma, Coronal, Niperten
An analogue of Betaloc ZOK, the drug Concor also selectively blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors, providing hypotensive, antianginal and antiarrhythmic effects.
The medication slowly and gradually reduces blood pressure, the maximum effect occurs after two weeks.
Concor is used to treat hypertension, stable angina and chronic heart failure.
Therapeutic doses vary from 2.5 to 10 mg and are selected individually. When replacing, it should be taken into account that Concor 5 mg will be an approximate analogue of Betaloc ZOK 100 mg, but you should not change the dose yourself; be sure to consult your doctor.
For chronic heart failure, the dose is taken starting from 1.25 mg, gradually increasing to 5 or 10 mg per day.
Patient reviews are positive when using both drugs.
Overdose
There are cases where, at a dosage of 7.5 g, the drug caused severe intoxication with a fatal outcome in an adult. At doses of 1.4 and 2.5 g, respectively, there was moderate and severe intoxication.
An overdose of this drug can lead to respiratory depression, atrioventricular block I–III degrees, decreased blood pressure, heart failure, bradycardia , asystole , weak peripheral perfusion , cardiogenic shock , apnea . In addition, Betaloc ZOK in increased doses can cause impairment of consciousness, tremor , excessive sweating and fatigue, bronchospasm , vomiting, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia , renal impairment, loss of consciousness, convulsions, paresthesia , nausea, as well as esophageal spasm and hyperkalemia .
Initial signs of a drug overdose will be noticeable 20-120 minutes after administration.
Activated carbon is prescribed as treatment , as well as gastric lavage if necessary.
Depending on the manifestations of overdose, symptomatic treatment is carried out. So, you may need intubation and adequate ventilation, ECG monitoring, blood volume replenishment and glucose infusions. If necessary, Atropine (before gastric lavage) is administered intravenously 1-2 mg. For myocardial depression, Dobutamine or Dopamine . It is possible to use Glucagon intravenously at a dosage of 50–150 mcg per 1 kg of weight. In some cases, Adrenaline , terbutaline (to relieve bronchospasm ), as well as an artificial pacemaker, help. For arrhythmia and an extensive ventricular complex, a sodium solution is injected. Resuscitation measures may be necessary.
Interaction
When using the drug Betaloc ZOK and other beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, as well as MAO inhibitors and ganglion blockers, strict medical supervision is required.
The drug should not be combined with Propafenone , Verapamil . When taking Diltiazem and/or antiarrhythmic drugs, a negative ino- and chronotropic effect may develop. When using inhalational anesthetics, the cardiodepressive effect is enhanced.
It is possible that inducers or inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes may influence the content of the active substance Betaloc ZOK in the blood plasma. Its concentration is reduced when combined with Rifampicin or increased when taken simultaneously with Cimetidine , hydralazine , phenytoin , and serotonin .
When discontinuing clonidine, Betaloc ZOK must be discontinued several days before.
In combination with COX inhibitors, the antihypertensive effect of the drug may be reduced. Dosage adjustments of oral antidiabetic agents may also be necessary when administered concomitantly.
Betaloc® ZOK
Metoprolol is a CYP2D6 substrate. therefore, drugs that inhibit CYP2D6 (quinidine, terbinafine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, celecoxib, propafenone and diphenhydramine) may affect the plasma concentrations of metoprolol.
The combined use of Betaloc® ZOK with the following drugs should be avoided:
Barbituric acid derivatives: barbiturates (study conducted with pentobarbital) increase the metabolism of metoprolol due to enzyme induction.
Propafenone: When propafenone was prescribed to four patients treated with metoprolol, an increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol was observed by 2-5 times, while two patients experienced side effects characteristic of metoprolol. This interaction was confirmed in a study on 8 volunteers. The interaction is likely due to propafenone's inhibition, like quinidine, of the metabolism of metoprolol via the cytochrome P4502D6 system. Taking into account the fact that propafenone has β-blocker properties. Co-administration of metoprolol and propafenone does not seem appropriate.
Verapamil: The combination of beta-blockers (atenolol, propranolol and pindolol) and verapamil can cause bradycardia and lead to a decrease in blood pressure. Verapamil and β-blockers have a complementary inhibitory effect on atrioventricular conduction and sinus node function.
The combination of Betaloc® ZOK with the following drugs may require dose adjustment:
Amiodarone: Concomitant use of amiodarone and metoprolol may result in severe sinus bradycardia. Given the extremely long half-life of amiodarone (50 days), a possible interaction should be considered long after discontinuation of amiodarone.
Class I Antiarrhythmics: Class I antiarrhythmics and β-blockers may result in additive negative inotropic effects, which can lead to serious hemodynamic side effects in patients with impaired left ventricular function. This combination should also be avoided in patients with sick sinus syndrome and impaired AV conduction. The interaction is described using disopyramide as an example.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs reduce the antihypertensive effect of beta-blockers. This interaction has been documented for indomethacin. It is likely that the described interaction will not be observed with sulindac. Negative interactions have been noted in studies with diclofenac.
Diphenhydramine: Diphenhydramine reduces the clearance of metoprolol to α-hydroxymetoprolol by 2.5 times. At the same time, an increase in the effect of metoprolol is observed.
Diltiazem: Diltiazem and β-blockers mutually enhance the inhibitory effect on AV conduction and sinus node function. When metoprolol was combined with diltiazem, cases of severe bradycardia were observed.
Epinephrine (adrenaline): 10 cases of severe hypertension and bradycardia have been reported in patients taking non-selective beta-blockers (including pindolol and propranolol) and receiving epinephrine (adrenaline). The interaction was also observed in the group of healthy volunteers. It is assumed that similar reactions can be observed when epinephrine is used together with local anesthetics if it accidentally enters the vascular bed. It is assumed that this risk is much lower with the use of cardioselective beta-blockers.
Phenylpropanolamine: Phenylpropanolamine (norephedrine) in a single dose of 50 mg can cause an increase in diastolic blood pressure to pathological values in healthy volunteers. Propranolol mainly prevents the increase in blood pressure caused by phenylpropanolamine. However, beta-blockers may cause paradoxical hypertension reactions in patients receiving high doses of phenylpropanolamine. Several cases of hypertensive crisis have been reported while taking phenylpropanolamine.
Quinidine: Quinidine inhibits the metabolism of metoprolol in a special group of patients with rapid hydroxylation (in Sweden, approximately 90% of the population), causing mainly a significant increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol and increased beta-blockade. It is believed that a similar interaction is typical for other β-blockers, the metabolism of which involves cytochrome P4502D6.
Clonidine: Hypertensive reactions during abrupt withdrawal of clonidine may be exacerbated by concomitant use of beta-blockers. When used together, if clonidine is discontinued, discontinuation of β-blockers should begin several days before discontinuation of clonidine.
Rifampicin: Rifampicin may increase the metabolism of metoprolol, reducing plasma concentrations of metoprolol.
Patients concomitantly taking metoprolol and other β-blockers (eye drops) or monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should be closely monitored. When taking β-blockers, inhalational anesthetics enhance the cardiodepressive effect. While taking β-blockers, patients receiving oral hypoglycemic agents may require dose adjustment of the latter.
Plasma concentrations of metoprolol may increase when taking cimetidine or hydralazine.
Cardiac glycosides, when used together with beta-blockers, can increase atrioventricular conduction time and cause bradycardia.
Analogues of Betalok ZOK
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Biol
Metocard
Metozok
Nebilet
Nebilong
Betaxolol
Bisogamma
Aritel
Cordinorm
Vasocardin
Corvitol
Bidop
Bisoprolol
Nebivolol
Biprol
Bisoprol
Concor Cor
Lokren
Concor
Niperten
The following analogues of Betalok ZOK are sold in pharmacies:
- Betalok
- Egilok
- Metoprolol
- Metocard
- Metocore
- Serdol
- Azoprol Retard
- Vasocardin
- Corvitol
Reviews about analogues of Betalok ZOK are quite different. Some of them are almost as good as him, and some are of a fairly low level. So the price of analogs of this product, as well as their manufacturers, deserves special attention. To finally decide which medicine is best for each specific case, you should consult a doctor. In addition, before use, be sure to read the instructions.
Betaloc ZOK or Metoprolol – which is better?
Manufacturer: Vertex, Ozone, Pranafarm, Russia / Hemofarm, Serbia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: Metoprolol
Synonyms: Egilok, Metoprolol Teva, Metoprolol KRKA, Serdol, Metocard
Metoprolol is the active substance of Betaloc ZOK and all its synonyms, as well as its international non-proprietary name. In addition, there are many domestic drugs whose trade name is the same as the generic one.
The analog Metoprolol has the same properties - antihypertensive, antianginal and antiarrhythmic effects. According to doctors, the effectiveness of domestic analogues is no lower than that of imported drugs.
Reviews of Betaloka ZOK
Reviews of Betalok ZOK indicate that quite often after its use undesirable symptoms occur. Thus, patients often report cases of rhinitis . Some also complain of irregular pulse and unstable blood pressure. Because of this, specialists prescribe additional medications that are designed to eliminate these side effects. However, it should be noted that most people still tolerate this medication easily.
In addition, reviews of Betalok ZOK draw attention to the fact that the selection of dosages should be approached with particular care. The patient’s condition must be constantly monitored and the danger of deterioration must be eliminated in a timely manner.
Betaloka ZOK price, where to buy
The average price of Betaloc ZOK 50 mg is about 250 rubles, the price of 25 mg is about 150 rubles, and the average cost of 100 mg of the drug is about 400 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Betaloc ZOK tablets p.p.o.
with deceleration release 50 mg 30 pcs. Astra Zeneca AB/LLC Astra Zeneca Industries 284 rub. order - Betaloc ZOK tablets p.p.o. with deceleration release 25 mg 14 pcs. AstraZeneca AB / ZiO-Zdorovye / Astra Zeneca Industries LLC
146 RUR order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Betalok Zok (tablet p/o 100 mg No. 30)Astra Zeneсa/AstraZeneca Industries
RUB 383 order
- Betaloc Zok tablets 25 mg No. 14Astra Zenesa/AstraZeneca Industries
135 rub. order
- Betaloc Zok tablets 50 mg No. 30Astra Zenesa/AstraZeneca Industries
RUB 265 order
- Betalok Zok (tablet p/o 50 mg No. 30)Astra Zeneca/ZIO Health
RUB 279 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Betaloc Zok 100 mg N30 Astra Zeneca AB, Sweden
199 UAH order - Betaloc Zok 50 mg N30 tablets Astra Zeneca AB, Sweden
142 UAH order
- Betaloc Zok 25 mg No. 14 tablets Astra Zeneca AB, Sweden
80 UAH order