Lidocaine
Regional and local anesthesia should be carried out by experienced specialists in an appropriately equipped room with the availability of equipment and drugs necessary for cardiac monitoring and resuscitation, ready for immediate use. Anesthesia personnel. must be qualified and trained in anesthesia techniques and must be familiar with the diagnosis and treatment of systemic toxicities, adverse events and reactions, and other complications.
It should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis, epilepsy, chronic heart failure, bradycardia and respiratory depression, as well as in combination with drugs that interact with lidocaine and lead to increased bioavailability, potentiation of effects (for example, phenytoin) or prolongation of elimination ( for example, in hepatic or end-stage renal failure, in which lidocaine metabolites can accumulate).
Patients receiving class III antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, amiodarone) should be closely monitored and ECG monitoring, since the effect on the heart may be potentiated.
There have been post-marketing reports of chondrolysis in patients who received prolonged intra-articular infusion of local anesthetics after surgery. In most cases, chondrolysis was observed in the shoulder joint. Due to the many contributing factors and the inconsistency in the scientific literature regarding the mechanism by which the effect is realized, a cause-and-effect relationship has not been identified. Long-term intra-articular infusion is not an approved indication for the use of lidocaine. Intramuscular administration of lidocaine can increase the activity of creatine phosphokinase. which may complicate the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
Lidocaine has been shown to cause porphyria in animals and should be avoided in persons with porphyria.
When injected into inflamed or infected tissues, the effect of lidocaine may be reduced.
Before starting intravenous lidocaine, it is necessary to eliminate hypokalemia, hypoxia and acid-base imbalance.
Some local anesthetic procedures may cause serious adverse reactions, regardless of the local anesthetic used.
Conduction anesthesia of the spinal nerves can lead to depression of the cardiovascular system, especially against the background of hypovolemia, so caution should be exercised when administering epidural anesthesia to patients with cardiovascular disorders.
Epidural anesthesia can lead to hypotension and bradycardia. The risk can be reduced by pre-administration of crystalloid or colloid solutions. Arterial hypotension must be stopped immediately.
In some cases, paracervical blockade during pregnancy can lead to bradycardia or tachycardia in the fetus, which requires careful monitoring of the fetal heart rate (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
Administration to the head and neck area may result in inadvertent arterial entry leading to cerebral symptoms, even at low doses.
Retrobulbar administration may rarely result in entry into the subarachnoid space of the skull, resulting in serious/severe reactions including cardiovascular collapse, apnea, seizures, and temporary blindness.
Retro- and peribulbar administration of local anesthetics carries a low risk of persistent oculomotor dysfunction. The main causes include injury and/or local toxicity to muscles and/or nerves.
The severity of such reactions depends on the degree of injury, the concentration of the local anesthetic and the duration of its exposure in the tissues. In this regard, any local anesthetic must be used in the lowest effective concentration and dose. Lidocaine injection solution is not recommended for use in newborns. The optimal serum concentration of lidocaine to avoid toxicities such as seizures and arrhythmias has not been established in neonates.
Intravascular administration should be avoided unless directly indicated. Use with caution:
- in patients with coagulopathy. Therapy with anticoagulants (eg, heparin), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or plasma expanders increases the tendency to bleed. Accidental damage to blood vessels can lead to severe bleeding. If necessary, check bleeding time, activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and platelet count;
- patients with complete and incomplete block of intracardiac conduction, since local anesthetics can inhibit AV conduction;
-Patients with seizure disorders should be carefully monitored for CNS symptoms. Low doses of lidocaine may also increase seizure activity. In patients with Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, allergic and toxic reactions from the nervous system in response to the administration of local anesthetics may develop more often; -third trimester of pregnancy.
Lidocaine, solution for injection, 10, 20 mg/ml is not approved for intrathecal administration (subarachnoid anesthesia).
Compound
The solution for intravenous administration includes the active component lidocaine hydrochloride (monohydrate form).
An additional component is water for injection. The active component included in the injection solution is also lidocaine hydrochloride (monohydrate form), additional components are sodium chloride, water.
Spray 10% for topical use contains lidocaine , as well as additional components: propylene glycol, peppermint oil, 96% ethanol.
Eye drops contain lidocaine hydrochloride , as well as benzethonium chloride, sodium chloride, and water.
The gel for external use also contains a similar active substance.
Indications for use
A number of indications for the use of different forms of the drug are determined.
Indications for use intravenously and intramuscularly:
- for carrying out infiltration, spinal, epidural, conduction anesthesia ;
- for terminal anesthesia (also used in ophthalmology);
- for ventricular arrhythmias that are associated with glycoside intoxication;
- for the relief and prevention of the development of repeated ventricular fibrillation in patients with acute coronary syndrome, as well as repeated paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia .
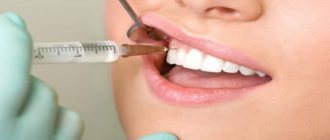
In dentistry, Lidocaine in ampoules is used for local anesthesia during surgical interventions in the oral cavity:
- when removing baby teeth;
- when opening superficial abscesses ;
- when removing bone fragments and suturing wounds;
- for anesthesia of the gums for the purpose of fixing a prosthesis or crown;
- in order to suppress or reduce the enhanced pharyngeal reflex during preparation for an x-ray examination;
- before removal or excision of an enlarged papilla of the tongue;
- before excision of benign superficial mucosal tumors;
- for opening salivary gland cysts and frenulectomy in children.
Application in ENT practice:
- before septectomy , electrocoagulation , resection of nasal polyps;
- for additional pain relief before opening a peritonsillar abscess ;
- as additional anesthesia before puncture of the maxillary sinus ;
- before tonsillectomy for the purpose of pain relief and reduction of the pharyngeal reflex (not used for adenectomy and tonsillectomy in children under eight years of age);
- for pain relief before washing the sinuses.
Use for examinations and endoscopy:
- for anesthesia, if necessary, insert a probe through the mouth or nose;
- for anesthesia before performing rectoscopy and if necessary, replacing catheters.
Application in obstetrics and gynecology:
- for the purpose of anesthetizing the perineum for episiotomy or treatment;
- for anesthesia of the surgical field during a number of surgical interventions;
- for anesthesia when suturing in case of abscesses ;
- for pain relief during excision and treatment of hymen rupture.
Application in dermatology:
- for anesthesia of mucous membranes before minor surgical operations.
Application in ophthalmology:
- for anesthesia, if necessary, use contact research methods;
- for pain relief during short-term interventions on the conjunctiva and cornea;
- during preparation for ophthalmological operations.
pharmachologic effect
Lidocaine - what is it?
Wikipedia indicates that lidocaine is a derivative of acetanilide in chemical structure. It has a pronounced antiarrhythmic and local anesthetic effect.
The pharmacological group to which the active substance belongs is local anesthetics .
Inhibits nerve conduction by blocking sodium channels in nerve fibers and nerve endings, thereby providing a local anesthetic effect.
If we compare the anesthetic effect of procaine , then lidocaine is 2-6 times superior to it. Also, its effects develop faster and last longer. How long the drug lasts depends on the interaction with other drugs. If the drug is used simultaneously with Epinephrine , then the effect lasts more than 2 hours. When applied topically, vasodilation is observed, but no local irritating effect is noted.
In the body, it stabilizes the cell membrane, blocks sodium channels, increases the level of membrane permeability for potassium ions, which determines its antiarrhythmic effect .
Under its influence, repolarization in the ventricles is accelerated, the fourth phase of depolarization in Purkinje fibers is inhibited, without affecting the electrophysiological state of the atria.
It does not have a significant effect on myocardial contractility and conductivity. The negative inotropic effect is slightly pronounced, it manifests itself for a short time and only if the drug is administered in large doses.
Contraindications for use
Lidocaine in ampoules should not be used by people who have the following diseases and conditions:
- severe bradycardia ;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- sinoatrial block;
- AV blockade of the second and third degree (exception - when a probe is inserted to stimulate the ventricles);
- heart failure in acute and chronic form;
- WPW syndrome;
- significant reduction in blood pressure ;
- cardiogenic shock;
- Adams-Stokes syndrome;
- retrobulbar administration (for people suffering from glaucoma );
- intraventricular conduction disorders;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- severe sensitivity to the components of the product.
Caution Lidocaine IV and for injection is prescribed for chronic heart failure , hypovolemia , arterial hypotension , sinus bradycardia , severe renal and liver failure, first-degree AV block, reduced hepatic blood flow, epileptiform convulsions .
The drug is also prescribed with caution to elderly and weakened people, adolescents and children under 18 years of age, and patients with high sensitivity to other amide drugs for local anesthesia.
It is also important to consider that the patient may have contraindications to a certain type of anesthesia.
It should be noted that the aerosol is contraindicated for use in plaster dentistry as an impression material, as there is a risk of aspiration .
Lidocaine price, where to buy
How much ampoules cost depends on the packaging and manufacturer.
The price of Lidocaine in 10% ampoules is 40-80 rubles per 10 pieces.
You can buy Lidocaine spray 10% for a price starting from 200 rubles. A numbing spray that contains lidocaine may be more expensive. The price of Lidocaine spray in Ukrainian pharmacies is on average 200 UAH. per package.
The price of Lidocaine gel is from 200 rubles per tube.
You can buy an aerosol, cream or ointment with lidocaine at any pharmacy.
A cathegel with lidocaine costs from 145 rubles.
buy a patch with lidocaine Versatis at a price of 530 rubles.
The price of lidocaine tablets depends on the drug and its manufacturer.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Cathegel with lidocaine gel for places.
approx. 12.5g syringe disposable. 5 pcs Montavit Pharmaceutical RUR 736 order - Lidocaine spray for local use. approx. 10% 650 doses 38g JSC Pharmaceutical Plant EGIS
RUB 322 order
- Lidocaine Velpharm solution for injection. 20mg/ml amp. 2ml 10 pcs. Welfarm LLC
77 RUR order
- Lidocaine solution for injection. 2% 2ml 10 pcs. OrganikaAO Organika
40 rub. order
- Cathegel with lidocaine gel 12.5 g Montavit Pharmaceuticals Fabrik GmbH
RUB 195 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Lidocaine-Vial (spray 10% 38g) Jewim Pharmaceutical (Shandong)
RUB 219 order
- Lidocaine (spray 10% 38g) FS.-Leksredstva
RUB 261 order
- Lidocaine (amp. 2% 2ml No. 10)Grotex LLC
116 RUR order
- Lidocaine (amp. 2% 2ml No. 10) Organics (Novokuznetsk Autonomous Okrug)
41 rub. order
- Lidocaine 2% ampoules 2ml No. 10Biosintez JSC
41 rub. order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Lidocaine 2% 2 ml No. 100 ampoules solution ZAT FZ Egis, Ugorshchina
661 UAH.order - Cathegel with lidocaine 12.5g N1 syringe tube urethral gel Pharmaceuticalutische Factory Montavit GmbH, Austria
72 UAH order
- Lidocaine-Darnitsa 2% 2 ml No. 10 solution
13 UAH order
- Cathegel with lidocaine 12.5 g No. 5 gel Pharmaceuticals Factory Montavit GmbH, Austria
410 UAH. order
- Lidocaine hydrochloride 2% 2 ml No. 10 solution
11 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Lidocaine ampoule Lidocaine 20 mg/ml amp. 2ml No. 10 Ukraine, Lubnyfarm PJSC
14 UAH order
- LIDOCAINE ampoule Lidocaine solution d/in. 2% amp. 2ml No. 100 Hungary, Egis
740 UAH. order
- LIDOCAINE ampoule Lidocaine solution d/in. 2% amp. 2ml No. 10 Ukraine, Health LLC
10 UAH.order
- Katedzhel with lidocaine gel Katedzhel with lidocaine gel urethra. spr-tube 12.5 g N 1 Austria, Montavit
93 UAH order
- LIDOCAINE liquid Lidocaine spray 10% 38g Ukraine, Zdorovye LLC
199 UAH order
show more
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
The highest concentration in the blood after intravenous administration is observed after 5-15 minutes, if the infusion is carried out slowly without a saturating initial dose, the maximum concentration is observed after 5-6 hours, and in people with acute myocardial infarction it can be achieved after a long time - up to 10 hours. Binds to plasma proteins by 50-80%. It is quickly distributed in the body and penetrates the placental and blood-brain barriers.
Metabolism mainly occurs in the liver; microsomal enzymes , resulting in the formation of active metabolites - glycine xylidide and monoethylglycine xylidide . People with liver disease have a slower metabolism. Excretion occurs in bile and urine.
If lidocaine cream or other agents are applied topically, absorption depends on the dose and also on the site where the lidocaine cream or gel is applied. Absorption is affected by the rate of perfusion in the mucosa.
There is good absorption in the respiratory tract, so care must be taken to prevent the administration of the drug in toxic doses.
After injections of lidocaine intramuscularly, almost complete absorption is noted. It is distributed quickly and binds to proteins, depending on the concentration of the active ingredient, by 60-80%.
The half-life depends on the dose administered, it is 1-2 hours.
If an aerosol is used, its effect appears within 1 minute and lasts 1-2 minutes. There is a gradual disappearance of the achieved decrease in sensitivity over 15 minutes.
Storage in medical institutions and pharmacies
| Medical institution | Storage organization |
| Pharmacy warehouse | Ventilated shelves. The air temperature is not higher than 25°C. |
| Pharmacy | Closed pull-out shelves or cabinet; The air temperature is not higher than 25°C. |
| Hospital, dentistry | Closed container in the closet; The air temperature is not higher than 25°C. |
Note: If the air temperature exceeds 25°C, then it is allowed to place the local anesthetic in a refrigerator with a temperature reading of 12°C .