Directions for use and doses
Inside, after eating. Trichomoniasis: adults, 2 g once or 3 doses of 1 g every 12 hours (for example, morning, evening and the next morning) or 250 mg 2 times a day for 6 days. Children - 15 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 doses for 5–7 days.
Amebiasis: adults - 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-10 days; children - 20 mg/kg per day, divided into 2 doses for 5–10 days.
Giardiasis: adults - 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days; children - 15 mg/kg per day, divided into 2 doses for 5–7 days.
Infection caused by Gardnerella vaginalis: adults - 500 mg 2 times a day for 7 days or 2 g once.
Acute ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis (Vinceta gingivitis): adults - 500 mg 2 times a day for 2 days.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Naxojin
Antiprotozoal drug, nitroimidazole derivative. It is highly active against Trichomonas vaginalis and other protozoa, including Giardia intestinalis , Entamoeba histolytica and Lamblia intestinalis . The drug is also active against anaerobes such as Bacteroides spp ., Gardnerella vaginalis . The minimum trichomonacid concentration is 0.3–3 μg/ml. Naxojin is well absorbed after oral administration. When taken at intervals of 12 hours, 1 g 3 times, the concentration of the drug in the blood reaches 16 mcg/ml 3 hours after the first dose, 28 mcg/ml - 25 hours after the start of treatment and 7.5 mcg/ml - 12 hours after last appointment. After taking 1 g of Naxojin 3 times with an interval of 12 hours, its concentration in the vaginal secretion, determined 24, 48 and 72 hours after the start of treatment, was 129, 95 and 4 mcg/g, respectively. Naxojin is excreted from the body mainly through urine. The concentration of the drug in urine and vaginal secretions is higher than the trichomonasid concentration.
Experience with the use of naxogin for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis
AND
Sexually transmitted infections can lead to disruption of a woman’s reproductive health, severe congenital diseases of the fetus, damage to internal organs and systems with subsequent disability [1,2,6]. Complications such as miscarriage, amniotic infection, postpartum and post-abortion endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis, and abscess of the vaginal dome after hysterectomy are often encountered [1,6].
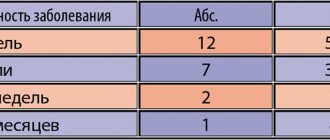
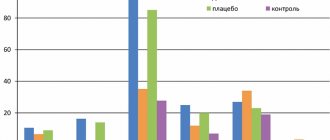
The term “bacterial vaginosis” (BV) was adopted at the 1st International Symposium on Vaginitis in Sweden in 1984 [4]. It belongs to diseases previously called “corynebacterial vaginitis”, “gardnerellosis”, “anaerobic vaginosis”. According to statistics, the dynamics of the incidence of BV in Russia in 1993–97 increased 4.1 times (see diagram).
Rice. 1. Dynamics of the incidence of bacterial vaginosis in Russia 1993-97. [6]
With BV, a change in vaginal microbiocenosis occurs: a sharp decrease and even complete disappearance of lactobacilli and the predominance of bacteroides, gardnerella, peptostreptococci, mobiluncus, mycoplasmas and other anaerobes. The development of BV is promoted by both endogenous factors (changes in hormonal status, decreased immunological reactivity, disruption of intestinal microbiocenosis), and exogenous (use of hormonal drugs, antidepressants, previous antibacterial therapy, use of intrauterine contraceptives, previous and concomitant inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract, frequent change of sexual partners) .
To treat BV, both topical and oral medications are prescribed. The most common are clindamycin and nitroimidazoles. Among the latter, naxogin (Nimorazol) from Pharmacia and Upjohn was proposed, which was the subject of our study.
In the methods of using any antiprotozoal drugs, there has recently been a tendency to produce as short-term and even single doses as possible. In particular, for naxojin, data are known on the treatment of BV with a single dose of 2.0 g. The effectiveness of the method was almost 78% [3]. The objective of this work was to evaluate the effectiveness of prolonged administration of naxogine in the treatment of BV.
Materials and methods
From September 1999 to February 2000, 39 women aged 22 to 55 years with BV were observed at the Gazprom clinic from September 1999 to February 2000. The selected group did not include women with inflammatory diseases of chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, herpesvirus, trichomonas and candidiasis etiology, women with organic diseases of the central nervous system, chronic liver and kidney diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and women receiving general or local vaginal therapy, as well as pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Diagnosis of BV was carried out according to the “Methodological materials for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases” [6], using well-established screening diagnostic tests. This complex includes four diagnostic tests:
• pathological nature of vaginal discharge in the form of homogeneous creamy, adherent to the vaginal mucosa and having an unpleasant odor;
• pH of vaginal discharge > 4.5;
• identification of “key” cells and microorganisms associated with BV by microscopy of wet unstained preparations of vaginal discharge and Gram-stained smears;
• positive amino test (appearance of a fishy odor when mixing equal amounts of vaginal discharge and a 10% KOH solution).
The diagnosis of BV was established in the presence of positive indications of at least 3 of the above criteria.
The clinical examination consisted of assessing anamnestic data, subjective and objective symptoms of the disease, and ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
In all cases, before and after treatment, bacterioscopic and bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge, cytological examination of smears from the endocervix and ectocervix, and colposcopic examination were carried out. It was also mandatory to study laboratory parameters: general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test (creatinine, urea, transaminases, bilirubin).
Naxojin was prescribed orally after meals, 1 tablet (0.5 g) 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours between doses for 6 days. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed 10–14 days and 3 months after completion of treatment. Simultaneously with the assessment of the effectiveness of naxojin, data on the tolerability of the drug were taken into account. Sexual partners were not treated. During treatment and follow-up, it was recommended to use condoms as contraception.
Results and discussion
In 1999, out of 3,581 women undergoing medical examination, BV was detected in 454, i.e. in 11.7%.
It was found that half of the women included in the study group had no complaints and considered themselves healthy. The rest complained mainly of discharge from the genital tract with a fishy odor, which was especially intensified after unprotected coitus, and itching and/or burning in the vulva and vagina.
Analysis of anamnestic data showed that for 24 of 39 patients with BV this diagnosis was established for the first time. The remaining 15 had previously been repeatedly treated for BV (metronidazole, tinidazole, clindamycin). The reasons for the relapses have not been established. Half of the women had previously received treatment for vulvovaginal candidiasis, ureaplasmosis (4), mycoplasmosis (2), chlamydia (3), trichomoniasis (2), genital warts of the vulva (8), cervical leukoplakia (3), cervical ectopia (5) . 5 women had used an IUD for contraception in the past 3–5 years.
During a microbiological study of vaginal discharge, microbial contamination characteristic of BV was detected in all participants in the study. At the same time, the microbial landscape was dominated by morphotypes of obligate anaerobes similar to bacteroides, peptostreptococci, Gardnerella vaginalis and (or) mobiluncus, “key” cells, etc. The number of lactobacilli was either counted in units in rare fields of view, or they were absent altogether.
When assessing leukocytosis in the material from the cervical canal, the absence of a pronounced leukocyte reaction was noted. Only 3 patients had leukocytosis up to 50–60 leukocytes in the field of view (against the background of an IUD).
Most authors believe that BV is not characterized by an inflammatory reaction of the vagina and symptoms of inflammation can only be detected during colposcopy. But sometimes the inflammatory reaction may be mild [4]. During a colposcopic examination, we identified small pinpoint inclusions of the “semolina” type after the Schiller test in only 4 patients. Of the concomitant diseases of the cervix, ectopia was found in 3 patients, leukoplakia in 6, Nabothian glands in 7, mosaic-like colpitis in 1, genital warts of the vulva and vagina in 3 patients.
During a cytological examination of smears from the endocervix and ectocervix, small- and coccobacillary flora was found in half of the women in the study group; a picture of inflammation was found in only 6 patients. In 7 women with already detected leukoplakia on the cervix, in 3 women ectopia was detected, 3 cases were due to papillomavirus infection.
The tolerability of the drug Naxojin was assessed based on the subjective feelings of the patients and the data of biochemical blood parameters. 3 out of 39 women had gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, heartburn, epigastric discomfort). One patient with chronic allergic dermatitis noted an exacerbation of the underlying disease in the form of a mild skin rash, which did not require discontinuation of the drug.
When studying biochemical blood parameters during treatment with Naxogin, no significant deviations from the norm were revealed.
In 5 out of 39 women, treatment with naxogin was complicated by vulvovaginal candidiasis. In these cases, subsequent local antifungal therapy with drugs such as ginalgin, terzhinan, pimafucin, etc. was required, with a positive effect.
In 32 out of 39 patients after treatment, examination of vaginal smears revealed mixed flora; in 2 women, rod flora was detected.
Considering the fact that with BV there is a change in the vaginal biotope, in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment and prevent relapses of the disease, all patients after treatment with BV were recommended for local vaginal use of eubiotics and probiotics (bifidumbacterin and lactobacterin, biosporin, etc.) for 10 days.
The treatment results are presented in the table.
As you can see, there was a very high and stable effect of curing BV - 3 months after treatment, the percentage of those recovered was 88.5. Conclusion
Naxojin is a highly effective treatment for BV. At the same time, the tested method of a prolonged course of treatment is more effective compared to a single dose of 2.0 g of the drug (88.5% and 77.8%, respectively). With the studied method, naxojin was well tolerated by patients: adverse reactions that did not require discontinuation of treatment were noted in only 4 out of 39 patients.
Naxojin is a highly effective treatment for BV. At the same time, the tested method of a prolonged course of treatment is more effective compared to a single dose of 2.0 g of the drug (88.5% and 77.8%, respectively). With the studied method, naxojin was well tolerated by patients: adverse reactions that did not require discontinuation of treatment were noted in only 4 out of 39 patients.
In order to prevent vulvovaginal candidiasis, it is advisable to simultaneously carry out local antifungal treatment.
For a more complete restoration of the vaginal biotope, it is advisable to use probiotics at the second stage of treatment. Literature:
1. Karpishchenko A.I., Kira E.F., Molchanov O.L. Journal of Obstetrics and Women's Diseases, 1998, No. 1, 65–69.
2. Aliev M.B., Dorovskikh R.A., Shvetsova E.V. and others. STI 1999, No. 5, 44–46.
3. Kisina V.I., Polishchuk N.A., Vakhnina T.E. and others. STI, 1999, No. 5,47–50.
4. Prilepskaya V.N. Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva. M., 1999, 316–325.
5. Krasnopolsky V.I. Pathology of the vagina and cervix. M., 1997, 82–86.
6. Methodological materials on the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. Ed. prof. K.K. Borisenko, Sanam Association, M., 1998, 3–5,105–107.
7. Sozaeva L.G. Correction of dysbiosis of the vaginal biotope with the spore probiotic biosporin. Author's abstract. Ph.D. diss, M., 1999, 3–9.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Naxodzhin
In order to prevent possible reinfection, it is recommended to treat both sexual partners simultaneously, even if one of them has no symptoms of the disease. During treatment with Naxojin and for 48 hours after stopping therapy, it is not recommended to drink alcohol. Patients with neurological diseases should be under medical supervision. In patients with severe impairment of liver and kidney function, the dose of the drug should be appropriately reduced. Due to the possible development of side effects, mainly when prescribed in a one-day regimen, it is recommended to avoid driving vehicles and working with potentially dangerous mechanisms for 48 hours after taking the drug.
Side effects of the drug Naxojin
Usually well tolerated, side effects are mild or moderate and do not require discontinuation of the drug. Nausea, heartburn, and sometimes vomiting are possible (taking the drug after meals helps minimize these effects). Cases of drowsiness, dizziness and skin reactions, diarrhea, metallic taste, dry mouth, coated tongue, glossitis and stomatitis have been reported. When taking metronidazole, which is a related compound to nimorazole, cases of pseudomembranous colitis, neuropathy (manifested by paresthesia) and epileptiform seizures have been rarely reported, which have been associated with high doses or prolonged use of the drug. Cases of transient moderate leukopenia, discomfort in the urethra and darkening of the urine have also been reported.