Cirrhosis of the liver (LC) is the final stage of many liver diseases, including chronic hepatitis, alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.1 This is the process of diffuse formation of connective tissue, which leads to dysfunction of the organ. Liver cirrhosis is irreversible; drug and non-drug treatment of liver cirrhosis is usually aimed at preventing the progression of the fibrosis process and preventing the development of complications.1 The prevalence of chronic hepatitis and fatty disease is growing, especially among people of working age - cirrhosis becomes not only medical, but also social and economically significant problem. The prevalence of the disease at the moment is more than 20 million.2 In the Russian Federation, about 200 thousand new cases of liver cirrhosis are registered annually. 2
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic progressive liver disease characterized by restructuring of the liver tissue and vascular bed, a decrease in the number of functioning liver cells (hepatocytes), proliferation of connective tissue, the appearance of regeneration nodes and the subsequent development of liver failure and portal hypertension.
In economically developed countries, liver cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of death between the ages of 35 and 60 years.
up
About the disease
The liver is one of the most important organs of the human body, ensuring the purification of toxins from the blood. The organ also takes an active part in digestion, carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism. It is not surprising that any malfunction of the liver negatively affects the entire body and the patient’s quality of life.
Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease, as a result of which liver tissue is replaced by connective tissue and the organ ceases to perform its function. Cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive disease that can lead to very serious, life-threatening consequences.
Sign up for a consultation
How does cirrhosis manifest?
For a long time, liver cirrhosis is asymptomatic or with minimal atypical manifestations. Weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance, irritability, tearfulness, touchiness, and a tendency to hysterical reactions appear.
Digestive disorders often occur: nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, intolerance to fatty foods and alcohol.
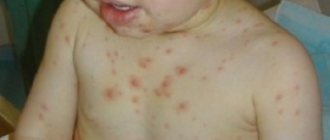
Characteristic signs of cirrhosis are heaviness and pain in the abdomen, mainly in the right hypochondrium, spider veins in the upper half of the body, redness of the palms, hemorrhages in the skin, bleeding of the mucous membranes. Complaints of itchy skin and joint pain are common.
Severe forms of the disease occur with severe impairment of liver function and life-threatening complications, primarily portal hypertension (increased pressure in the portal vein), leading to bleeding from the dilated veins of the esophagus, ascites, and hepatocellular failure.
up
Stage of the disease
The pathology has a chronic course with a gradual increase in symptoms and morphological transformations of the organ. Structural changes in the liver are classified according to the number and size of dead nodules formed in place of working hepatocytes. There are three degrees of damage: micronodular (the lesions do not exceed 0.3 cm in size), macronodular (the size of the lesions doubles), mixed (the presence of different-sized nodes).
The stage of pathology according to severity is determined according to the Child-Turcotte-Pugh rating scale:
- initial stage or compensated (class A);
- moderate or subcompensation (class B);
- decompensated or fatally severe (class C).
Child-Turcotte-Pugh Scorecard
The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination according to five criteria, with a certain number of points assigned. The total indicator indicates the stage of the disease. The final stage is the terminal (fourth) stage of the disease, which is inevitably followed by the death of the patient.
What are the causes of liver cirrhosis?
The most common causes of liver cirrhosis are:
- chronic viral hepatitis B (and D),
- hepatitis C,
- chronic alcoholism (alcoholic liver disease),
- metabolic disorders,
of which the main one is metabolic syndrome accompanied by fatty liver disease - non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In addition, cirrhosis is caused by hereditary diseases: hemochromatosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, etc., as well as autoimmune liver diseases, including primary biliary cirrhosis and toxic liver damage from industrial poisons and drugs.
up
Reasons for development
Cirrhosis is classified into several types, depending on the cause:
- Viral. Progresses due to untimely or incorrect treatment of hepatitis of viral etiology (A, B, C).
- Pharmacological (medicinal). Develops against the background of an overdose or prolonged use of certain types of medications.
- Toxic (in most cases, alcoholic). Occurs due to regular uncontrolled drinking. In terms of gender, this type is more typical for men.
- Metabolic and nutritional. It develops as a complication of chronic endocrine diseases associated with metabolic and hormonal imbalances (obesity, diabetes).
- Congenital. It is formed in the fetus during intrauterine development under the influence of teratogenic factors or due to unfavorable genetics.
- Biliary. Has two forms. Primary biliary cirrhosis occurs due to the destructive effects of cells of the own immune system (autoimmune factor). The secondary form develops as a result of severe pathologies of adjacent organs, most often the gallbladder and its ducts (the presence of stones, cysts, tumors, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the bile ducts).
- Cryptogenic. Diagnosed when the nature of the origin is unclear, when the exact causes cannot be established.
By age, pathology occurs more often in people in the 40+ category.
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
Liver assessment
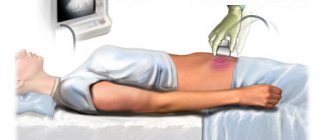
The diagnosis in the early stages of liver cirrhosis is difficult to establish, since there are often no pronounced changes in the liver. First of all, an ultrasound examination of the liver (ultrasound diagnostics) is performed, which makes it possible to identify diffuse changes in the liver tissue and an increase in its size (although this does not always happen). It is advisable to carry out Dopplerography of the vessels of the abdominal cavity to determine the width of the lumen of the vessels and the speed of blood flow. This allows us to determine the presence of signs of portal hypertension.
Important for characterizing the structural and functional state of liver cells is a biochemical blood test (ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, protein fractions), as well as a clinical blood test and coagulogram - blood clotting.
To accurately diagnose the degree of fibrosis, modern non-invasive (replacing biopsy) examination methods are used: elastometry (elastography) of the liver using the Fibroscan, Fibrotes, FibroMax apparatus. Liver damage is characterized by degrees from 0 to 4; 0 – healthy liver, 4 – cirrhosis.
Determining the cause of liver cirrhosis
First of all, it is necessary to do tests for hepatitis B and C viruses, since viruses are the most common cause of cirrhosis, especially in combination with alcohol. If viruses are not identified, then the search for the cause consists of excluding hereditary liver diseases, autoimmune indicators, as well as alcoholic liver disease, NAFLD and toxic liver damage.
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
The severity of cirrhosis is determined by the Child-Pugh scale, taking into account the severity of clinical and laboratory data, the main of which are the content of bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin in the blood, as well as the severity of encephalopathy and ascites. There are active and inactive cirrhosis, compensated and decompensated. Decompensated cirrhosis is characterized by the development of portal hypertension, the appearance of ascites, and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding.
up
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis begins with a clinical examination, which includes collecting complaints and examination.
During examination, the doctor may detect external signs of CP1:
- Redness on the palms and soles (palmaral erythema)
- Spider veins
- Reduction of hair in the armpits
- White nails
- Men with cirrhosis of the liver may experience gynecomastia, an enlargement of the mammary glands. The reasons for this are considered to be a reduced level of testosterone and an increased level of estradiol (the female sex hormone) in the blood due to various mechanisms: increased processes of aromatization of testosterone into estradiol, as well as increased production of globulin that binds sex steroids, and thus a decrease in the level of free testosterone.6 .7
Later, edema may appear, especially in the lower extremities, jaundice, and the development of ascites - accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity.
When palpating the abdomen, an enlarged liver is detected; it is often possible to palpate the nodal surface of the organ, the pointed edge. However, in the final stage of the disease, the size of the liver may decrease, and the spleen may increase.1 To confirm the diagnosis and establish the stage of the disease, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out, and calculated indices are also used.
Laboratory methods
- Standard biochemical tests that determine the level of bilirubin, total protein, prothrombin index, serum iron, ferritin and enzyme activity (AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase). These tests are nonspecific, their deviations can be observed in other diseases, but they help assess the degree of liver dysfunction.
- General clinical blood tests can reveal the presence of anemia, a decrease in the number of leukocytes, platelets, which can also be observed with cirrhosis.
- Tests for hepatitis viruses and other infectious agents may be ordered to determine the potential cause of the disease.
Calculation indices:
The use of test panels, such as FibroTest, FibroIndex, Hepascore, can be used to assess the stage of fibrosis. For example, the use of the Fibrotest score avoided biopsy in 50% of patients.2
To assess the severity of cirrhosis and predict survival, the Child-Pugh classification is most often used.2 The scale, which takes into account the results of laboratory tests and clinical manifestations, allows one to assess the degree of functional impairment and determine the stage of the disease. The higher the score, the worse the prognosis.2
Instrumental studies
In addition to needle biopsy, which is recognized as the “gold standard” for diagnosing fibrosis and cirrhosis, liver imaging methods play an important role in diagnosis. These include:
- Ultrasound of the liver, abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space. The most accessible and fairly informative method. Allows you to evaluate the anatomical and structural features, shape, size, vascular pattern. CP can be judged by an increase in the size of the liver and by its heterogeneous structure and uneven tuberous contour. Also, with liver cirrhosis, ultrasound may show signs of portal hypertension: ascites, dilation of portal veins, enlarged spleen.1
- CT, MRI (computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the liver) - by performing a large number of thin sections, it provides comprehensive information about the structure of the organ, the presence of fibrous nodes, false lobules, additional vessels, etc.
- Ultrasound elastometry (FibroScan device) can serve as an alternative to liver tissue biopsy, as it makes it possible to assess the density of the organ, which increases as the percentage of connective tissue increases.2
Only a comprehensive diagnosis can give a complete picture of the disease, so a combination of various methods is used, which sometimes have to be repeated several times.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
Treatment of liver cirrhosis is carried out with the aim of stopping or slowing down the progression of the disease and improving the quality of life.
The treatment program includes: therapeutic regimen and nutrition, drug treatment, prevention and treatment of complications.
Treatment results and prognosis depend on the severity of the disease.
With compensated cirrhosis, the functional state of hepatocytes is preserved, there are no signs of portal hypertension and disturbances in the protein-synthetic function of the liver. Treatment of cirrhosis at this stage of the disease is determined by the cause of the disease, depending on which specific therapy is prescribed. In addition, it is necessary to limit mental and physical stress.
If the cause of cirrhosis is viral hepatitis B or hepatitis C, then antiviral therapy is prescribed, which, as research in recent years has shown, not only suppresses the activity of the virus, but also has an antifibrotic and anticirrhotic effect.
For alcoholic cirrhosis (alcoholic liver disease), hepatoprotectors are prescribed, which, subject to complete abstinence from alcohol, make it possible not only to stop the progression of cirrhosis, but also help reduce the degree of fibrosis.
In case of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFL), adherence to the diet and rules of nutrition in combination with drug treatment, including hormonal disorders that cause liver damage, gives good results. It is possible to reverse the development of fibrosis and restore the functional and structural state of the liver.
A patient with liver cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation and the development of complications requires dietary, medicinal, and in some cases endoscopic and surgical treatment.
Decompensated cirrhosis is characterized by the development of severe complications, the main of which is portal hypertension, i.e. persistent increase in pressure in the portal system. This is manifested by splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach and bleeding from dilated veins, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites.
Various groups of drugs are used to treat portal hypertension: vasoconstrictors and vasodilators.
With the development of ascites, 50% of patients live for about 2 years, and only 25-50% of patients who do not respond to drug therapy survive 6 months. The goal of conservative therapy for ascites is to remove accumulated fluid from the body. For this purpose, a special salt-free diet and diuretics are prescribed.
In the terminal stage of liver cirrhosis, only a liver transplant can save the patient's life.
up
Liver cirrhosis - symptoms, signs, treatment, causes, nutrition and stages
Table of contents
- Classification
- Causes
- The first signs and degrees of cirrhosis in adults
- Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of liver cirrhosis
- Nutrition and diet for cirrhosis
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Liver cirrhosis is a serious chronic disease.
According to statistics, in developed countries it is
one of the six leading causes of death
for people aged 35 to 60 years. It kills about 50,000 people every year in the United States. In Russia, where the population is half as large, mortality from cirrhosis is comparable to American rates.*
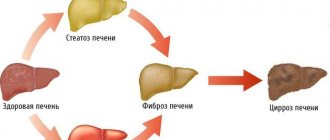
This disease is an extensive lesion of the liver, in which the tissues of the organ die and are gradually replaced by fibrous (connective) fibers. During the replacement process, the structure of the organ changes radically. Violation of the normal structure of the liver leads to the fact that it can no longer perform its functions. This is called liver failure.
Classification
Experts distinguish several types of liver cirrhosis.
For the reasons that led to the development of the disease, the following variants can be determined:
- Viral
- it is caused, for example, by hepatitis C and various biliary tract infections - Toxic
– caused by the consumption of alcohol, certain medications, food poisons and other substances that have a toxic effect on the body - Congenital
- represents the consequences of certain diseases that the patient’s parents suffered from, for example, hemochromatosis or tyrosinosis - Stagnant
- its origin is associated with circulatory failure - Metabolic and nutritional
– develops due to obesity, as well as in severe forms of diabetes mellitus
Separately, mention should be made of the group of liver cirrhosis of unknown etiology. We are talking about those cases when it is not possible to clearly determine the cause of the disease.
Causes
From the above it is clear that the occurrence and development of liver cirrhosis is due to many reasons. Most often, people get sick due to alcohol abuse.
According to various estimates, this reason accounts for from 40-50 to 70-80% of cases.*
The next most common factor influencing the occurrence and development of cirrhosis is exposure to viruses. Most cases are hepatitis C, but also hepatitis B.
In addition, cirrhosis is caused by:
- Biliary tract diseases
- Various intoxications - for example, chemical or medicinal
- Poor nutrition – first of all, chronic deficiency of vitamins and proteins in the diet
Cirrhosis caused by hereditary diseases is relatively rare. The same can be said about the disease of unknown etiology mentioned above, when it is not possible to determine the causes of its occurrence.
In about 50% of patients, liver problems are caused by a combination of different factors. For example, doctors often find cirrhosis caused by both binge drinking and hepatitis B.
The main peak incidence occurs in the age group over 40 years. Approximately 70-75% of those suffering from cirrhosis of the liver are men.
The first signs and degrees of cirrhosis in adults
First sign
the fact that a person’s liver is not all right – asthenovegetative syndrome. At the same time, the patient constantly feels tired, although there is no reason for this. He feels weak, becomes irritable and reacts sharply to completely innocent words or actions. He often has headaches.
Next, the so-called dyspeptic complex of syndromes. It includes:
- Nausea, which sometimes develops into vomiting
- Belching
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation
- Abdominal pain, aggravated by eating fried, pickled and fatty foods, as well as by drinking alcohol
- Reluctance to eat, up to complete lack of appetite for a long time
- Heaviness in the stomach
- Bloating
All of the above may indicate other diseases. Therefore, at this stage it is not always possible to clearly diagnose liver cirrhosis. Moreover, in about 20% of people who suffer from it, the true cause of the problem can only be determined after death.
There are three stages of the disease based on severity
- Initial
– symptoms either do not appear at all or are minimal - Clinical
– the symptoms are pronounced, and the doctor, when examining the patient, observes a typical picture of the disease - Terminal
– irreversible changes are detected, leading to death
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
In approximately 60% of patients
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis are quite noticeable. The specific picture largely depends on what stage the disease is at. But there are signs that are especially common.
The initial stage in most cases is not accompanied by biochemical disorders. But the disease progresses, and at the second stage the so-called hemorrhagic syndrome.
Main signs of hemorrhagic syndrome
- This:
- Bleeding from the gums and nose
- In women - uterine bleeding
- Hematomas (bruises) on the body that appear for unknown reasons
- Stomach and intestinal bleeding
- Ecchymoses are pinpoint subcutaneous hemorrhages that look like a rash.
At the same time, the patient increasingly feels weak. Irritability gradually gives way to apathy and indifference, memory and attention impairments appear. Possible problems with sleep: the patient suffers from insomnia at night, and feels drowsy during the day. Over time, coordination of movements is impaired, the patient experiences problems with writing, and his speech becomes less and less intelligible.
When examining a patient
The doctor may visually detect the following symptoms:
- The liver and spleen have increased in size
- On the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity there are dilated veins and spider veins
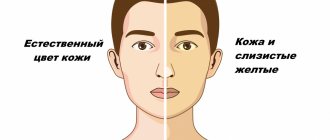
- The skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes have turned yellow
Complications
Liver cirrhosis can lead to various complications.
This could be, for example, bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus or pneumonia, peritonitis and other complications caused by infections. The following negative consequences often occur:
- Hepatic coma
is a disorder of the functions of the central nervous system, which manifests itself in a sharp decrease in the size of the liver, increasing drowsiness, disorientation, slowing down of thought processes and, ultimately, in the fact that the patient falls into a stupor, and then into a comatose state - Thrombosis in the portal vein system
- blood clots (blood clots) prevent free blood flow in the liver, which leads to cell death - Hepatorenal syndrome
- leads to impaired renal function, especially common in those who suffer from acute liver failure or alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver - Liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma
is a rapidly developing malignant tumor that is often associated with hepatitis C and hepatitis D
Liver cirrhosis is a dangerous disease in itself. But if complications occur, the risk of death increases significantly. So, with hepatorenal syndrome, if you do not start treating it on time, death occurs 10-14 days after the development of this complication.
Diagnostics
Experts recommend
Contact your general practitioner as soon as you think you have signs of liver cirrhosis. The doctor will refer the patient for laboratory tests. When he has the test results in hand, he will send the patient to a gastroenterologist or directly to a doctor specializing in liver diseases - a hepatologist. In some cases, for example, if signs of hepatic encephalopathy are detected, you will need to visit a neurologist. Also, when making a diagnosis, the following data are taken into account:
- History
- Visual inspection
- Instrumental diagnostics
Basic laboratory tests
which are carried out in case of suspected liver cirrhosis are:
- Liver complex biochemical tests
- it shows how well the liver performs its functions and helps to determine whether its activity is impaired - Complete blood count
- it is done because signs of cirrhosis may be a decrease in the number of leukocytes and red blood cells, as well as a noticeable decrease in hemoglobin levels - Coagulogram
- it needs to be done to find out if there are problems with blood clotting - A fecal occult blood test
helps identify hidden bleeding in the stomach and/or intestines. - Serological markers of viral hepatitis
are used to clarify the factors that could lead to the development of the disease - A blood test for alpha-fetoprotein
should be performed if liver cancer is suspected. - The level of creatinine and electrolytes
must be established to determine renal failure
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
If the patient is diagnosed with liver cirrhosis
, treatment can be carried out using different methods. The choice of a specific tactic is largely determined by the stage at which the disease is located and the reasons for which it arose. Specialists also take into account the individual characteristics of the patient. However, it is impossible to cure already formed cirrhosis. Modern medicine can only cope with the reasons due to which it arose.
Radical method of treating cirrhosis
- transplantation of the affected organ. They resort to it if there is an immediate threat to the patient’s life. In all other cases, medicinal methods are used. As a rule, the patient should adhere to a strict diet, and in case of alcoholic cirrhosis, it is necessary to eliminate the intake of alcohol in the body. The choice of medications depends on what type of cirrhosis doctors have to deal with. For example:
- For viral hepatitis, antiviral agents are used, in particular pegylated interferons
- For biliary cirrhosis associated with insufficiency of bile acids in the intestines, medications are used to narrow the bile ducts
- Autoimmune hepatitis can be treated with drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants)
Nutrition and diet for cirrhosis
Diet for the treatment of cirrhosis
is extremely important. Proper nutrition is both an excellent option for preventing the disease and a way to eliminate the causes that led to its occurrence. If there are no complications, the patient is prescribed a complete high-calorie diet. It necessarily contains proteins, fats and carbohydrates. However, it is necessary to exclude from the diet everything that irritates the digestive organs. First of all, this is:
- Alcohol
- Chemical additives
- Preservatives
If you have cirrhosis, you should refuse
from consuming foods that are:
- Spicy
- Sour
- Spicy
- Too salty
The diet must be prescribed by a specialist
which takes into account:
- Patient's eating habits
- Individual tolerance of products
- He already has diseases of the digestive system
The diet is modified if there are any complications of cirrhosis or other diseases.
To normalize metabolic processes in liver cells, the doctor may prescribe a vitamin complex. As for any medications, they must be used carefully. You should take only those pills that are prescribed by specialists and for which there are clear and unambiguous indications.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
- an important area of activity of the MEDSI clinic. We use effective modern techniques to eliminate the causes that influenced the occurrence of this disease and make the patient’s daily life more comfortable. Our clinic employs a team of international doctors. She takes a comprehensive approach to solving each specific problem. Any patient is guaranteed an individual approach: the doctor selects an examination plan, which is based on genetic factors, risk factors, concomitant pathologies, and medications taken.
Communication with doctors
starts with diagnosis. Experienced specialists who have the necessary laboratory equipment at their disposal will perform tests and study their results. Fast and accurate diagnosis is ensured thanks to the availability of the latest generation diagnostic equipment: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, video colonoscope, etc.
Our clinic specialists
They use cutting-edge techniques – fast track surgery and minimally invasive treatment. We have operating rooms equipped with the necessary modern equipment. Also we have:
- Reanimation and Intensive Care Unit
- Comfortable hospital with 3 meals a day, round-the-clock medical monitoring, single and double luxury rooms, toilets and showers
Don't forget: cirrhosis
is an extremely dangerous disease, and the sooner we begin treatment, the greater the likelihood that the threat to the body can be significantly reduced. MEDSI clinic staff are ready to answer your questions and provide the necessary advice.
You can make an appointment with a specialist 24 hours a day. Call us at +7 (495) 7-800-500.
* Sadovnikova I.I. Cirrhosis of the liver. Questions of etiology, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment / Breast Cancer Appendix “Diseases of the Digestive Organs” No. 2 dated November 4, 2003
Dietary recommendations for liver cirrhosis
For cirrhosis, prepare meals without salt, reduce the amount of free liquid and introduce foods rich in potassium.
Nutritional balance
The main parts of food are proteins, fats, carbohydrates, water, minerals and vitamins, which must be strictly balanced. The ratio between proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be 1:1:4. Animal proteins should make up about 60% of the total protein. Of the total fat, 20-25% should be vegetable oils as a source of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The balance of carbohydrates is expressed in the ratio of starch, sugar, fiber and pectin. Sugars should be represented by fruits, berries, dairy products, and honey. It is extremely important to maintain a balance of vitamins and minerals, which must be supplied to the body daily in accordance with daily requirements.
Diet
This is the number of meals and the interval between them during the day. For healthy people 3-4 times a day at 4-5 hour intervals. For some diseases, such as obesity, it is necessary to eat 5-6 times a day
up
What happens in the liver
The liver is a fundamental organ in the hepatobiliary system of the body. The functional responsibilities of the gland are:
- detoxification (cleansing) of the body from decay products, poisons and toxins;
- production and secretion of bile (a biochemical fluid, without which the process of digesting incoming food is impossible);
- breakdown of proteins and the release of amino acids essential for the body;
- formation of glycogen and its processing into glucose reserves;
- maintaining stable hormonal balance;
- participation in the process of hematopoiesis.
In cirrhosis, the ability of hepatocytes to regenerate (recovery) is blocked. Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, thin partitions (septa) are formed in the liver tissue. The cells, fenced on all sides by septa, gradually die off, turning into scars; the gland loses its ability to perform vital functions. It is impossible to start the destructive process in the opposite direction, so liver pathology cannot be cured.
Content:
- How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
- Classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- How long do people live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The human liver is the main organ that protects the body from the effects of poisons. It takes the brunt of alcohol and neutralizes toxins. In this difficult and sometimes unequal struggle, it itself is gradually being destroyed. As a result, inflammation develops - hepatitis, which, with continued alcoholization and the destructive influence of alcohol, turns into alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. This complication is life-threatening and, in the absence of sobriety and adequate treatment, leads to disastrous consequences. Therefore, the sooner the patient begins to get rid of this disease, the greater his chances of regaining health. Healing pathology is included in the tasks of the main course of anti-alcohol treatment. Hepatologists deal with advanced stages.
Symptoms of the initial stage
The initial period of the disease rarely proceeds in a forced mode. The patient may not be aware of the fatal disease until it passes from a latent stage to a more active one. Somatic signs of liver cirrhosis at an early stage are not pronounced. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all. This picture is observed because a person still has a compensatory mechanism, that is, liver cells not affected by pathology, trying to resist, work with double the load.
At the initial stage, the following symptoms may be observed:
- weight loss not due to intense exercise or changes in eating behavior;
- dysania (sleep disorder) or chronic sleepiness;
- loss of strength, causeless lethargy and asthenia (neuro-psychological weakness);
- loss of appetite (sometimes aversion to food);
- heaviness in the epigastric (epigastric) region;
- intense gas formation;
- alternating constipation (constipation) and diarrhea (diarrhea).
Later, a bitter taste in the mouth appears (usually after waking up) and discomfort, but not pain, in the right area of the abdomen. Such meager symptoms do not cause serious concern in people and rarely bring them to the doctor’s office. Signs of early cirrhosis are usually determined in patients with other chronic pathologies during a routine examination. As the disease progresses, symptoms intensify. The skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, and the legs swell. Hematomas appear on the body (without mechanical injuries).
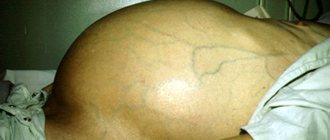
Complications develop: accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites, otherwise dropsy), with possible peritonitis of bacterial etiology, varicose dilation of the portal veins through which blood is delivered to the liver, and an increase in pressure in them (development of portal hypertension), which subsequently damages the renal apparatus (hepatorenal syndrome), threatening renal decompensation.
Photo of complications: portal hypertension accompanied by ascites
The most common consequences of cirrhosis are liver failure and carcinoma (liver cancer).
Treatment tactics for initial changes
Since liver cirrhosis is an incurable disease, the goal of conservative therapy is to slow down the process of transformation of hepatocytes, prolong the regenerative ability of the organ, relieve pain, and delay the development of complications. For the treatment of all types of cirrhosis, the following are used:
- medicines of the hepatoprotector group (herbal, essential phospholipid, animal) that have a protective and restorative effect on hepatocytes;
- vitamin preparations;
- bile acids of synthetic origin;
- diet therapy (limited diet and complete exclusion of alcohol);
- herbal medicine using traditional medicine;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, the main therapy is supplemented with:
- lipotropics, to regulate metabolic processes and prevent fatty infiltration of the gland (with alcoholic liver damage);
- steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex (in toxic and biliary cirrhosis);
- immunostimulating drugs (for the primary biliary type);
- diuretics, otherwise diuretics, in the presence of dropsy.
Therapy is carried out under regular monitoring of blood counts and ultrasound results. The treatment of cirrhosis is carried out by a therapist (at initial treatment), a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist - a specialist in the field of diseases of the hepatobiliary system. If surgical intervention is necessary, a surgeon joins in.
Basic drugs for the treatment of cirrhosis
| Group | Name of medicine |
| Essential phospholipids | Essentiale Forte N, Essliver, Fosfontziale, Phosphogliv, Eslidin, Enerliv |
| Herbal hepatoprotectors | Karsil, Dipana, Silimar, Liv -52, Cynarix, Bonjigar |
| Hepatoprotectors of animal origin | Hepatosan, Sirepar, Progepar |
| Bile acids of synthetic origin | Ursosan and its analogues: Ursofalk, Urdoxa, Ursodez |
| Amino acids or lipotropic substances | Heptral, Hepa-Merz, Lipoic acid, Betargin |
| Hormone-containing medications | Cortisone, Hydrocortisone |
| Vitamin complexes | Thiogamma, Berlition 300, Thiolepta, Thiolipon |
Which specific medications will be prescribed depends on the stage of the disease, the presence of complications and concomitant chronic pathologies. All medications are prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can be dangerous!
Classification
The disease is divided according to changes in the organ and severity. The following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- Small-knot.
- Large-knot.
- Mixed.
Stages of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver:
- Compensated – without pronounced symptoms.
- Subcompensated – with initial manifestations, but with preservation of functions.
- Decompensated – accompanied by partial and then complete failure of functioning.