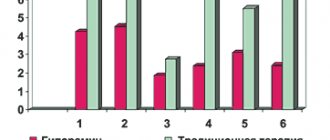
Release form
Transparent liquid without color:
- 100 ml of liquid in a bottle; 1, 10, 15, 24, 28, 30, 35, 48 or 36 bottles per carton.
- 200 ml of liquid in a bottle; 1 or 28 bottles in a cardboard box.
- 250 ml, 100 ml, 500 ml or 1000 ml liquid in a polymer container; one container in a plastic bag.
- 100 ml of liquid in a polymer container; 50 or 75 containers in a plastic bag.
- 250 ml of liquid in a polymer container; 24 or 36 containers in a plastic bag.
- 500 ml of liquid in a polymer container; 12 or 18 containers in a plastic bag.
- 1000 ml of liquid in a polymer container; 6 or 9 containers in a plastic bag.
White powder, odorless:
- 1 gram of powder in a bag, ten bags in a cardboard box.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Hemostatic drug, fibrinolysis blocker.
Chemical formula – H2N(CH2)5COOH.
Blocks the effects of plasminogen , suppresses the action of plasmin , and does not completely inhibit kinins . It has antiallergic activity and slightly enhances the antitoxic function of the liver.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is actively absorbed from the digestive tract. The highest concentration in the blood is reached after two hours. It is rapidly excreted in the urine, mainly unchanged. The half-life is approximately 2 hours.
Indications for use
The use of the medicine is justified in the following conditions and situations:
- prevention of bleeding during interventions on the liver, pancreas, lungs;
- prevention and treatment of menorrhagia and bleeding from internal organs, mucous membranes, erosions of the stomach and intestines, as well as during menstruation;
- hyperfibrinolysis of various origins, including those associated with the use of thrombolytic drugs and transfusion of canned blood products in large volumes;
- treatment and prevention of influenza and ARVI ;
- for the symptomatic treatment of bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia platelet dysfunction .
How does the drug work? What's included
ACC is present in the domestic pharmaceutical market in two forms:
- powder for oral administration;
- solution for infusion.
Each of them has its own indications for use and composition. But for the treatment of diseases of the ENT organs in children, the last form of release is mainly used - a solution.
It contains exclusively 5 percent aminocaproic acid, and saline and water for injection are used as solvents.
It is packaged in bottles of different sizes. But bottles of 100 and 250 ml are more common.
The drug is not produced in tablet form. But there are its analogues, presented on the market in the following dosage form: Tranexam, Tugina, Trenax, etc.
Such an extensive list of indications for the use of ACC is due to the large number of pharmacological properties of the drug. It provides:
- hemostatic effect, since it is one of the components of the blood coagulation system;
- antiallergic effect, as it plays an important role in the reactions of the immune system;
- decongestant effect, which is explained by blocking the development of allergic reactions;
- antiviral effect, due to binding to cell components and preventing the ability of viruses to produce substances necessary for their life.
It also reduces the permeability of vessel walls. But this cannot always be considered an advantage of the medication, since sometimes this effect can do a disservice.
For example, if there is a need for urgent administration of a certain drug, its absorption will be somewhat slowed down as a result of the continued effect of ACC.
But such a risk in case of pathologies of the ENT organs is minimal. The only thing that parents can note when using it to treat children is a slightly slower onset of effect when using local corticosteroids, which is incomparable to the positive effect of the drug on the strength of the vessels of the mucous membrane.
Thus, the effect of aminocaproic acid on the nasal mucosa is complex.
And although its use helps eliminate edema, it is not a vasoconstrictor. Therefore, addiction does not develop to it, which allows you to use the medication for an almost unlimited period of time until complete recovery.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Hematuria.
- Hypercoagulability, coagulopathy due to diffusion, intravascular disseminated coagulation , predisposition to thrombosis or thromboembolic disease .
- Kidney diseases with excretory dysfunction.
- Cerebral circulation disorders.
- Pregnancy or lactation .
It is recommended to use the drug with caution in case of valvular heart disease, arterial hypotension, hematuria, cryptogenic bleeding from the upper urinary tract, insufficiency of liver function, chronic insufficiency of kidney function, and age less than one year.
How to use for adenoids in children?
With adenoiditis, inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil occurs, as a result of which it swells and increases in size. Depending on the size of the tonsil, there are 4 degrees of adenoids, among which the 1st is considered the lightest, and the 4th is considered the most severe.
Typically, signs of the disease become apparent at 2–4 years of age, when the child begins to attend preschool institutions and encounter a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. They are:
- prolonged runny nose;
- constant snoring at night;
- mucus flowing down the back wall of the nasopharynx;
- attacks of dry cough, etc.
Not so long ago, removal of adenoids was considered the only way to treat pathology, but modern otolaryngologists and even popular pediatrician E. O. Komarovsky advise not to make such radical decisions until the age of 6–7 years.
By this age, with proper care of the child, timely treatment of acute respiratory infections and exacerbations of adenoiditis, the disease can regress on its own, that is, go away.
ACC, which is widely prescribed by otolaryngologists for adenoids, will help with this. It can be used as drops and an inhalation product.
The medication is especially effective in the initial stages of pathology. It helps eliminate swelling, which usually causes patients the greatest discomfort.
The use of the drug in the form of inhalation allows it to be delivered directly to the inflamed tissues of the pharyngeal tonsil, where drops cannot reach. This leads to the rapid elimination of the symptoms of adenoiditis and the subsidence of the inflammatory process.
ENT specialists are prescribed a 3-5-day course of inhalations in combination with corticosteroids, colloidal silver preparations, homeopathic remedies, etc. This is enough to relieve acute inflammation.[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
Instructions for use of Aminocaproic acid (Method and dosage)
Aminocaproic acid, instructions for use of solution
The solution is administered intravenously, drip. To achieve rapid action (for example, in acute hypofibrinogenemia ), up to 100 ml of a 5% solution is prescribed at 50-60 drops per minute for 20-30 minutes. In the first hour, 4-5 grams of the drug (about 100 ml) are administered, and then, if necessary, 1 gram (about 20 ml) per hour for another 8 hours or until the bleeding completely stops. If bleeding continues or bleeding occurs again, the drug is administered every 4 hours.
In pediatric patients, the drug is administered at the rate of 100 mg per kilogram of body weight per hour, and then at the rate of 33 mg per kilogram of body weight per hour; the highest daily dose is 18 grams per square meter of body surface area.
Daily dose:
- for adults equal to 5-30 g;
- for children less than 1 year old it is equal to 3 grams;
- for children 2-6 years old is equal to 3-6 grams;
- for children 7-10 years old it is 6-9 grams;
- For children over 11 years old, adult dosages are used.
For acute blood loss, the following dosages are used:
- children under 12 months are given 6 grams of the drug;
- children 1-4 years old are given 6-9 grams of the drug;
- children 5-8 years old are given 9-12 grams of the drug;
- Children 9-10 years old are given 18 grams of the drug.
The duration of treatment ranges from 3-14 days.
Aminocaproic acid, instructions for use of powder
After dissolving the powder in water, it is taken orally after or during meals. The daily dose for adult patients is divided into 3-6 doses, and for pediatric patients - into 3-5 doses.
With an average degree of increase in fibrinolytic activity, the drug is usually prescribed in a daily dose of 5-23 grams. Children under 1 year of age are prescribed a single dose of 0.05 grams per kilogram of weight (but not more than 1 gram). Daily dosage for children: up to 1 year is 3 grams, 1-7 years – 3-6 grams, 7-11 years – 6-9 grams. For adolescents (over 11 years old), the highest daily dose is 10-15 grams.
When treating acute bleeding , 5 grams of the drug are first prescribed, and then 1 gram once an hour (no more than 8 hours) until the bleeding completely stops. Daily dosage for pediatric patients with acute blood loss: up to 1 year is 6 grams, 1-5 years - 6-9 grams, 5-9 years - 9-12 grams, 10-11 years - 18 grams.
When treating subarachnoid hemorrhages, 6-9 grams of the drug are prescribed.
When treating traumatic hyphema, the drug is recommended at a dose of 0.1 grams per kilogram of body weight every four hours (up to 24 grams per day in total) for 5 days.
For uterine bleeding (metrorrhagia) associated with intrauterine contraceptives, and for menstruation, 3 grams of medication is prescribed every 6 hours.
To prevent and stop bleeding during dental interventions, adults are recommended to take 2-3 grams of medication up to 5 times a day. For adult patients, the average dosage is 10-18 grams of medication, and the maximum allowable is 4 grams. The duration of treatment is 3-14 days.
For influenza and ARVI , the medicine is used orally and topically. For oral use, 1 gram of the drug is first diluted in 2 tablespoons of a little sweet boiled water, resulting in a 5% solution.
This solution is prescribed orally in the following dosages:
- for children under two years old, 1-2 teaspoons (1-2 grams) four times a day, they are allowed to be added to drinks or food;
- children 2-6 years old: 1-2 tablespoons (2-4 grams) four times a day;
- children 6-10 years old 4-5 grams per day;
- Patients over 10 years of age are prescribed 1-2 grams up to 5 times a day.
Aminocaproic acid for the nose
It is also recommended to use the drug Aminocaproic acid in the nose (for a child or an adult), locally. Place a cotton swab into the nasal passage for 10 minutes every three hours, pre-moistened with a solution of 5% Aminocaproic acid, or, observing the specified frequency, instill 4-5 drops of the solution into the nasal passages. The drug can be used for inhalation by children and adults. In such cases, a nebulizer can be used for inhalation for the child.
In severe hypertoxic types of influenza or ARVI, the dosage of the drug is allowed to be increased to the maximum recommended at a given age with a moderate increase in fibrinolytic activity.
Aminocaproic acid, if necessary, can be used in combination with other antiviral drugs, interferon-containing agents and interferon inducers .
Intranasal instillation of Aminocaproic acid up to four times a day is advisable to carry out during the epidemic period for prevention.
The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the disease and is determined individually by the doctor.
Drugs similar in their pharmacological actions
Analogue drugs include products that are produced on the basis of tranexamic acid with antifibrinolytic, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects:
- Azeptil (Cyprus);
- Gesaksam (Ukraine/Germany);
- Gemotran (Ukraine);
- Neotranex (Italy);
- Trenaxa (India);
- Tramix (Ukraine);
- Sanghera (Ukraine);
- Tranestat (Russia);
- Transtop;
- Tugina (India);
- Cyclocapron (Ukraine).
Analogues based on aminomethylbenzoic acid:
- Pamba (Germany);
- Amben (Russia);
- Gumbix (India).
Analogs based on aprotinin – an antienzyme agent, a protease inhibitor:
- Kontrikal (Germany);
- Gordoks (Hungary);
- Aprotinin (Germany).
Aminocaproic acid is an affordable drug for all patients, regardless of their social status. The drug provides emergency assistance for nosebleeds and allergic reactions. The solution is used to treat runny nose in children with acute respiratory infections. The medicine has serious contraindications . It is not prescribed to patients with blood clotting disorders, patients with a history of strokes, heart attacks, or cerebrovascular accidents.
Aminocaproic acid price, where to buy
The price of Aminocaproic acid 5% 100 ml in Russia is 35-55 rubles, in Ukraine the price of this form of release is 12-26 hryvnia.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
LuxPharma* special offer
- Aminocaproic acid 50 mg/ml 5% vial.
100ml No. 1 1400 rub. order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Aminocaproic acid 0.5 No. 20 tablets PRAT "Fitofarm", Ukraine
25 UAH. order - Aminocaproic acid 5% 100 ml solution ZAT"Infusion", Ukraine
27 UAH order
- Aminocaproic acid 50 mg/ml 100 ml No. 1 PrAT solution” Pharmaceutical company “Darnitsa”, Ukraine
19 UAH order
- Aminocaproic acid 5% 100 ml solution Novofarm-Biosintez TOV, Novograd-Volinsky, Ukraine
18 UAH order
- Aminocaproic acid 5% 100 ml solution TOV "Yuriya-Pharm", Ukraine
28 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Aminocaproic acid infusion Aminocaproic acid solution for infusion. 50mg/ml 100ml vial. No. 1 Ukraine, Darnitsa ChAO
19 UAH order
- AMINOCAPRONIC ACID tablets Aminocaproic acid tablets. 0.5g No. 20 Ukraine, Fitofarm ChAO
29 UAH order
- AMINOCAPRONIC ACID Aminocaproic acid. 1g drinking №10 Ukraine, Health LLC
117 UAH. order
- AMINOCAPRONIC ACID infusion Aminocaproic acid solution inf. 5% 100ml Ukraine, Novofarm-Biosintez LLC
20 UAH order
- AMINOCAPRONIC ACID infusion Aminocaproic acid solution d/in. 5% 100ml Ukraine, Yuria-Pharm LLC
26 UAH order
show more