Manufacturer: SC Terapia SA
Active ingredients
- Not indicated. See instructions
Pharmacological action
- Not indicated. See instructions
- Description of the pharmacological action of Artroflex
- Composition of Artroflex
- Indications for use of the drug Artroflex
- Release form of the drug Artroflex
- Use of the drug Artroflex during pregnancy
- Contraindications to the use of the drug Artroflex
- Method of administration and dosage of the drug Artroflex
- Precautions when taking the drug Artroflex
- Storage conditions for the drug Artroflex
- Shelf life of the drug Artroflex
Description of pharmacological action
Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate sodium are involved in the biosynthesis of connective tissue, prevent the processes of cartilage destruction and stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue. Glucosamine - 2-deoxy-2-amino-D-glucose - stimulates the synthesis of proteoglycans (glucosaminoglycans and hyaluronic acid) of synovial fluid by chondrocytes; inhibits enzymes (collagenase, phospholipase A2, etc.) that cause destruction of cartilage tissue; suppresses the activity of lysosomal enzymes; prevents the damaging effect of corticosteroids on chondrocytes and the disruption of glycosaminoglycan synthesis induced by NSAIDs. Glucosamine stops the destruction of cartilage and reduces the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Chondroitin sulfate is a polysaccharide component of cartilage tissue proteoglycans with a repeating disaccharide unit: D-glucuronic acid N-acetyl-D-galactosamine sulfate. Participates in the construction of the basic substance of cartilage and bone tissue, inhibits enzymes that disrupt the structure and function of articular cartilage, and inhibits the processes of degeneration of cartilage tissue. Stimulates the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, promotes the regeneration of cartilage surfaces and joint capsule, increases the production of intra-articular fluid of the joints. Reduces associated inflammation, pain and increases mobility of affected joints. Clinical studies have confirmed that the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin enhances the positive effect on joint diseases.
Artiflex Ultra capsules, 60 pcs.
Avoid using Artiflex Ultra concomitantly with other NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, due to the increased risk of ulcers or bleeding, as well as other adverse reactions. Adverse reactions can be minimized by taking the lowest effective dose for the shortest amount of time necessary to control symptoms.
Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation, which may be fatal, with or without prior symptoms, has been reported for all NSAIDs at any time during treatment, regardless of a history of severe gastrointestinal complications.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation increases with increasing doses of NSAIDs, with a history of ulcers, including those complicated by bleeding or perforation, and in elderly patients. Such patients should begin treatment with the lowest available dose. Combination treatment with protective drugs (particularly misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) should be considered in these patients, as should patients who require concomitant use of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that may increase gastrointestinal risk.
Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disorders, especially elderly patients, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (in particular gastrointestinal bleeding) to the physician, especially in the early stages of treatment. Caution should be exercised when treating patients concomitantly receiving drugs that may increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and antiplatelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid.
If patients receiving ibuprofen develop gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration, treatment should be discontinued.
NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with a history of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, as their condition may worsen.
If acetylsalicylic acid is used to suppress platelet aggregation, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment with Artiflex Ultra.
There is evidence that drugs that inhibit COX/prostaglandin synthesis may impair female fertility through effects on ovulation. This can be corrected by stopping these medications.
The use of ibuprofen, especially in high doses (2400 mg/day) during long-term treatment, may be associated with a slight increase in the risk of arterial thrombotic complications (eg myocardial infarction or stroke). Low doses of ibuprofen (≤ 1200 mg/day) are not associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction.
For patients with uncontrolled hypertension, congestive heart failure, diagnosed coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease, long-term treatment should be prescribed by a physician only after careful analysis. In patients with significant risk factors for cardiovascular complications (such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking), long-term treatment with NSAIDs should be prescribed only after careful consideration.
Very rarely, severe skin reactions, some fatal, have been reported with NSAIDs, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Obviously, the highest risk of such reactions is in the early stages of treatment: the onset of such a reaction in most cases was observed during the first month of treatment. Treatment with ibuprofen should be discontinued at the first sign of skin rash, mucosal ulceration or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Ibuprofen may cause bronchospasm and asthma attacks or other hypersensitivity reactions. Risk factors for such reactions include pre-existing asthma, hay fever, nasal polyps, sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid or chronic respiratory diseases. This also applies to patients who experience allergic reactions to ibuprofen or other NSAIDs (in particular skin reactions, itching, urticaria).
Masking symptoms of underlying infections: Ibuprofen may mask symptoms of an infectious disease, which may delay the initiation of appropriate treatment and thereby complicate the course of the disease. This has been observed in bacterial community-acquired pneumonia and bacterial complications of chickenpox. When ibuprofen is used for fever or to relieve pain from an infection, monitoring for the infectious disease is recommended. In a non-medical setting, the patient should consult a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen.
It is not recommended to drink alcohol during treatment with Artiflex Ultra.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with:
- systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic connective tissue diseases - increased risk of aseptic meningitis;
- history of arterial hypertension and/or heart failure, which were accompanied by fluid retention and edema when using NSAIDs
- impaired renal and/or liver function; liver dysfunction increases the risk of renal toxicity and injury, as well as severe and potentially fatal liver reactions. For patients with liver or kidney disease, additional examinations are recommended before starting treatment: monitoring liver and kidney function and peripheral blood tests.
Long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to a dose-dependent decrease in prostaglandin synthesis and provoke the development of renal failure. Patients taking diuretics are at high risk; patients with impaired liver function, kidney function and/or cardiac disorders; elderly patients.
Features of the use of glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate
The drug should not be used in patients with hypersensitivity (allergy) to seafood.
An exacerbation of asthma symptoms is possible in patients with a history of bronchial asthma after starting treatment with glucosamine.
Rarely, edema and/or water retention in the body have been observed in patients with heart and/or renal failure. This may be due to the osmotic effect of chondroitin sulfate.
You should contact your doctor if your symptoms worsen after starting this drug.
Best before date
12 months
Vitamins with similar effects
- Betulanorm (Capsule)
- For the genitourinary system Life formula (Capsule)
- Coffeeberry (Capsule)
- Sana-Sol - Vitamin C (Oral tablets)
- Pancreavit (Capsule)
- St. John's wort (Oral tablets)
The description of vitamin Artroflex is intended for informational purposes only. Before starting to use any drug, it is recommended to consult a doctor and read the instructions for use. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions. Do not self-medicate; EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal. Any information on the project does not replace consultation with a specialist and cannot be a guarantee of the positive effect of the drug you use. The opinions of EUROLAB portal users may not coincide with the opinions of the site Administration.
Are you interested in Vitamin Artroflex? Do you want to know more detailed information or do you need a doctor's examination? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home . Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
Attention! The information presented in the vitamins and dietary supplements section is intended for informational purposes and should not be a basis for self-medication. Some of the drugs have a number of contraindications. Patients need to consult a specialist!
If you are interested in any other vitamins, vitamin-mineral complexes or dietary supplements, their descriptions and instructions for use, their analogues, information about the composition and form of release, indications for use and side effects, methods of use, dosages and contraindications, notes about the prescription of the drug for children, newborns and pregnant women, price and consumer reviews, or you have any other questions and suggestions - write to us, we will definitely try to help you.
Material and methods
The study included 358 patients with stage I–II OA of various locations.
Inclusion criteria:
1. Presence of one of the following symptoms:
- pain and crepitus in the knee joints,
- morning stiffness ≤ 30 min.
2. Presence of pain syndrome requiring drug therapy
- (40 mm or more on the visual analogue scale (VAS)).
3. The duration of the articular syndrome is no more than 10 years.
Exclusion criteria:
- High inflammatory activity,
- Reliable signs of another rheumatic disease,
- The presence of an ulcer of the gastric or duodenal mucosa in the acute stage,
- Severe concomitant pathology.
Taking into account the above criteria, 358 patients were included in the study. Of these, OA of the knee joints - 210 (59%) patients, polyosteoarthrosis - 97 (27%) patients, and OA of the hip joints - 51 (14%) patients (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1 Distribution of the sample of study patients by type of disease.
The average age of the patients was 54.5±2.02 years. The duration of the disease was on average 6.7±1.24 years.
The diagnosis of OA was established according to the criteria of Altman (1991). To determine the radiological stage of arthrosis, the classification of Kellgren and Laursen (1957) was used.
All 358 patients received complex therapy, including symptom-modifying fast-acting drugs (paracetamol/NSAIDs). As a structure-modifying slow-acting drug, patients received Flexinovo 1 tablet per day for 3 months. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed by the dynamics of joint pain using the Visual Analogue Scale and the Lequesne functional severity index over 3 months. Additionally, the number of patients who completely stopped taking painkillers was assessed.
Evaluation of results
Starting from the 1st month of treatment, patients of all three groups began to notice a decrease in pain and other clinical signs of the disease, but significantly more significant changes in indicators were observed in group I.
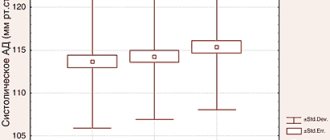
When analyzing the results of treatment in a group of patients with OA of the knee joints who received Flexinovo 1 tablet once a day for 3 months, there was a decrease in pain when moving according to VAS by the 3rd month of observation from 7.44 ± 1.51 to 3.3 ±0.96. In the same group, there was a significant decrease in pain at rest according to VAS from 3.44 ± 0.74 to 1.12 ± 0.31. The Lequesne functional index in this group of patients decreased from 6.6±1.19 to 4.35±0.49.
In group 2 of patients with polyosteoartosis, positive dynamics were also noted: a decrease in pain when moving according to VAS from 7.52±3.7 to 3.7±0.96 by the 3rd month of observation. At rest, pain in group 2 decreased from 3.37±0.81 to 1.41±0.54. The Lequesne functional index in this group of patients decreased from 6.5±1.36 to 4.5±0.51.
In group 3 of patients with OA of the hip joints, the pain index during movement decreased from 8.6±1.37 to 4.24±0.98, and the pain index at rest from 3.44±0.72 to 2.5±0. 81 by 3 month follow-up. At the same time, the Lequesne functional index also decreased from 6.8±1.23 to 5.3±0.81.
Thus, in all three groups, after 3 months of treatment, there was a significant decrease in the VAS pain index during movement (Fig. 2) and at rest (Fig. 3).
Rice. 2 VAS pain index when moving
Rice. 3 VAS pain index at rest
After three weeks of taking Flexinovo, the Lequesne index decreased in all three groups, but the most significant decrease in this indicator was noted in the knee OA group (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Lequesne functional index
Flexinovo made it possible to reduce or completely eliminate the use of traditional analgesics in patients of all three groups.
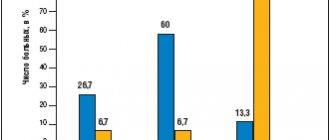
Three months after the start of therapy, 23% of patients were taking analgesics on demand, and 77% of patients were completely off pain medications (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5 Change in the proportion of patients taking NSAIDs while taking Flexinovo
The drug was well tolerated. Patients demonstrated high adherence to therapy. No side effects were identified when taking Flexinovo.
conclusions
- The use of Flexinovo, 1 tablet once a day for 3 months, in complex therapy of patients with OA of the knee joints, OA of the hip joints and polyosteoartosis reduces the severity of pain and the need for painkillers. Increases functional activity and quality of life of patients.
- Flexinovo is well tolerated. The use of Flexinovo, 1 tablet once a day for three months, is safe in terms of the development of side effects.
Thus, the data obtained confirm the effectiveness of Flexinovo in the complex therapy of OA of large joints and the feasibility of its use in general medical practice.
Literature:
- Rheumatology: national guide / Ed. E. L. Nasonova, V. A. Nasonova. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008; 573–588.
- 2.Peat G., McCarney R., Croft P. Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: a review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60;91–7.
- Khitrov N. A. Diversity and comorbidity of osteoarthritis: ways of treatment // Medical Council. - 2014. - No. 10. - p. 3 - 6.
- Svetlova M. S. Approaches to the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joints in the early stages of the disease // Medical Council. - 2012. - No. 2. - p. 3 - 9.
- Galushko E.A., Bolshakova T.Yu., Vinogradova I.B. and others. The structure of rheumatic diseases among the adult population of Russia according to epidemiological research. Nauch praktich rhevmat 2009;1:11–7.
- Ananyeva L P Symptomatic treatment of pain in rheumatic diseases // Consiliummedicum-2002 - T 4 - N 8 - P 416–425.
- Chichasova N.V. Treatment of pain in patients with osteoarthritis of various localizations // Attending physician. - 2014. - No. 7. p. 2 - 7.
- Jordan KM, Arden NK, Doherty M. EULAR recommendations 2003: an evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT) // Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:1145–1155.
- Luchikhina L.V. Arthrosis. Early diagnosis and pathogenetic therapy // M.: Medical Encyclopedia. - 2001. 139 p.
- Trentham DE, Dynesius-Trentham RA, Orav EJ et al. Full text of Harvard study effects of oral administration of type II collagen on rheumatoid arthritis // Science. - 1993. - Vol. 261. - P. 1727–1730.