Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. It develops under the influence of several factors that cause complete destruction and death of peripheral and central motor neurons. First, clinical paralysis develops, then muscle atrophy occurs. One muscle group after another is gradually involved in the pathological process. When the diaphragmatic muscles are affected, the patient loses the ability to breathe independently and requires artificial ventilation.
The disease is rare (statistically, it affects 2-5 people per 100 thousand people per year), and around the world it affects about 70 thousand people. It is also known that the disease is more often observed in men than in women, and the age of patients is usually over 50 years. The disease usually occurs in highly intelligent people and athletes who enjoy good health throughout their lives.
Currently, there is no single pharmacological agent that would cure ALS. Doctors at the neurology clinic provide symptomatic therapy with drugs registered in the Russian Federation. Due to the fact that clinical trials are conducted at the Yusupov Hospital, patients have a unique opportunity to be treated with the latest medicines that are not available in pharmacies. Specialists at the physical rehabilitation clinic use innovative techniques aimed at increasing muscle strength. If indicated, doctors in the intensive care unit perform artificial ventilation of the lungs using expert-class breathing apparatus.
Causes and mechanisms of development
Scientists believe that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- Autoimmune processes - phenomena in which the immune system perceives healthy cells as foreign elements and destroys them;
- Exposure to exotoxins - heat-labile proteins secreted by microorganisms;
- Excessive intake of calcium ions into nerve cells;
- Smoking.
Some researchers believe that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is hereditary. The disease can be inherited in an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant manner. In 15% of cases, patients were completely missing or had a defect in the gene that encodes an important enzyme, superoxide dismutase-1. It is part of the antioxidant system of the human body. Superoxide dismutase-1 converts superoxide (a radical oxidation product) into oxygen. Superoxide attacks nerve cells. The mechanism of development of the disease is based on a pathological abnormal association of protein molecules in the cytoplasm of motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord. With further progression of the disease, the following pathological processes occur:
- Skeletal muscles atrophy;
- The corticospinal and corticobulbar spinal tracts are degenerated;
- Motor neurons of the brain atrophy;
- The hypoglossal nerve and the anterior roots of the spinal cord become thinner.
Researchers have not yet established the reasons for the sudden onset of the process of destruction and death of motor neurons. Some scientists suggest that neurogeneration occurs under the influence of cellular and molecular processes. As a result of increased work of motor neurons, the release of glutamate increases. Excessive amounts of calcium accumulate in cells. It activates the breakdown of intracellular proteins. A large number of free radicals are released, including superoxide dismutase-1. They damage astroglia, microglia and motor neurons, causing their degeneration.
Expert opinion
Alexey Vladimirovich Vasiliev Head of the Research Center for Motor Neuron Disease/ALS, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a fatal disease that develops very slowly and is characterized by damage to motor neurons - muscles atrophy, paresis and paralysis of the limbs develop.The symptoms of ALS are similar to those of myopathy. The difference is that amyotrophic sclerosis is a disease of the central nervous system, and myopathy is muscular dystrophy. The main method for diagnosing ALS is electromyography, and MRI, biochemical blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid studies, and muscle biopsy are used as secondary methods.
Amyotrophic lateral syndrome is a very rare disease - no more than 5 people out of 100 thousand. This pathology is also called Charcot's disease or Lou Gehrig's disease, and was first described in the second half of the 19th century. Approximately 5% of cases are hereditary, and the genes responsible for this disease have already been identified.
Like other degenerative diseases of the central nervous system, Charcot's disease cannot be cured, you can only slow down its development. Of course, the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the better the syndromes can be stopped. The disease ends with complete muscle atrophy, the patient loses the ability to move and breathe independently.
Risk factors
The following risk factors have been identified:
- Heredity. 5-10% of people experience a hereditary form of ALS. For their children, the chance of developing the disease is 50%.
- Age. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis most often appears between the ages of 40 and 60 years.
- Floor. Before age 65, men are slightly more likely to suffer from ALS than women. After 70 years, the difference between the sexes is leveled.
It is possible that in some cases the negative impact of a polluted environment causes Lou Gehrig's disease. The reasons, therefore, lie in the disruption of the ecological balance.
In addition, some studies of the human genome have found numerous genetic changes that are common to all patients with hereditary ALS and to some people with unexplained Lou Gehrig's disease. It is possible that genetic changes are responsible for the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Environmental factors that may cause susceptibility to ALS include:
- Smoking. Cigarettes almost double the risk of developing neurological disorders. The longer a person smokes, the more dangerous this addiction poses. Quitting cigarettes can gradually reduce the increased risk.
- Exposure to lead. Some evidence suggests a link between ALS and long-term exposure to lead in the workplace.
According to statistics, people who served in the army are at risk. Science cannot yet answer exactly how military service affects the development of Lou Gehrig's disease, but the potential harm of the following factors is obvious: exposure to metals and chemical compounds, injuries, viral infections, increased physical activity.
Clinical forms
Depending on the level of damage to the central nervous system, neurologists distinguish the following types of ALS:
- Bulbar;
- Cervical;
- Chest;
- Lumbar;
- Diffuse;
- Respiratory (diaphragmatic).
Doctors also distinguish between the classic form of ALS, progressive bulbar palsy, primary lateral sclerosis, progressive muscular atrophy, and ALS-parkinsonism-dementia. According to the frequency of occurrence, there are sporadic (single) and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the form of ALS. As the disease progresses, the pathological process involves all muscles, and the symptoms will be the same for all forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The following general symptoms are characteristic of ALS:
- Fasciculations (muscle twitching) are one of the first symptoms of ALS, which may disappear on their own over time;
- Drooling, which occurs due to the accumulation of saliva in the mouth;
- Muscle weakness, developing due to the fact that the muscles are rapidly losing mass;
- Painful cramps and muscle spasms that cause difficulty during movement;
- Rapid fatigue, which occurs due to the fact that the muscles require more expenditure to perform normal actions;
- Pain that occurs during spasms, cramps, muscle twitching;
- Problems with swallowing, which lead to the patient losing the ability to eat;
- Cough and feeling of suffocation that occurs when saliva enters the respiratory tract;
- Problems with breathing, subsequently requiring the patient to be placed on artificial ventilation.
The patient also has problems with speech and communication. Psychologists at the Yusupov Hospital help patients cope with this problem. They teach communication using writing machines, computers, boards, tables. The patient's emotional lability requires special therapy. It may manifest itself as involuntary laughter or crying. Also, patients with ALS experience mood swings, develop depressive syndrome, and become irritable.
Violation of higher mental functions is manifested by impaired memory, thinking, and decreased intelligence. Experienced doctors at the neurology clinic and psychologists can help you cope with the problem. ALS does not affect vision, hearing, smell or touch. In patients, intestinal function and sexual function are not impaired, and the heart muscle is not affected.
Lumbosacral form
Lateral amyotrophic syndrome at the onset of the disease is manifested by weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities. First one leg gets sick, and after a while the other one hurts. Over time, tendon reflexes decrease and severe itching occurs.
As the disease progresses, the arm muscles are affected. They sharply decrease in volume. Then swallowing is impaired, the voice becomes nasal, and the tongue becomes thinner. The patient begins to choke and has problems eating. It is becoming increasingly difficult for him to chew. Then the sick person's jaw drops and he loses the ability to feed himself.
Another group of ALS symptoms indicates damage to both central and peripheral motor neurons. Weakness in the legs is combined with increased reflexes. Uncontrollable trembling often occurs. The same happens with the upper limbs. When neurons in the brain are affected, problems with chewing and swallowing occur. The patient's jaw drops, which prevents him from feeding independently. Sometimes the patient experiences bouts of uncontrollable laughter or crying.
Cervicothoracic form
ALS occurs when a peripheral motor neuron is destroyed. The patient develops weakness in the hand muscles. The hand begins to atrophy. At first, manifestations of the disease occur in one upper limb, but after a few months the other arm is also affected.
In the lower extremities, the pathological process proceeds differently. The leg muscles do not atrophy. Initially, an increase in reflexes is noted. Over time, pain and muscle weakness appear in the legs. By this time, the speech apparatus is impaired, weakness of the neck muscles appears - the head begins to hang. With the synchronous destruction of peripheral and central motor neurons, the muscles of the patient’s arms and legs atrophy, but reflexes are preserved.
At the onset of the patient’s bulbar form of ALS, the following symptoms occur:
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Articulation impairment;
- Choking while eating;
- Fasciculation and atrophy of the tongue;
- Nasal voice.
Problems with tongue movement make it difficult to pronounce sounds. When the central motor neuron is destroyed, psychosomatics are disrupted. The patient may show uncontrollable emotions: laughing or crying. Often he has an uncontrollable gag reflex for no reason. After some time, the strength of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities decreases, and they atrophy. Paresis (incomplete paralysis) develops.
High form
ALS develops when the central motor neuron is destroyed. In this form of the disease, along with muscle damage, the function of the nervous system is disrupted. The patient's mental health is impaired. He begins to remember information poorly, and his level of intelligence decreases significantly. Subsequently, dementia develops.
Diffuse form
lateral amyotrophic syndrome begins with the development of flaccid asymmetric tetraparesis (incomplete paralysis of all four limbs). Then bulbar syndrome joins in the form of dysphonia (speech disorder) and dysphagia (swallowing disorders). The respiratory form of the disease is very difficult. Due to respiratory failure, patients require urgent artificial ventilation.
Make an appointment
Difficulty absorbing food
When Lou Gehrig's disease (not to be confused with a football player named Eric Gehrig, whose statistics and physical characteristics differ significantly from those of Lou Gehrig and Fernando Ricksen) atrophies the muscles responsible for swallowing, patients can die from exhaustion and dehydration. There is also a significantly increased risk of food, liquids or saliva getting into the lungs, which can cause pneumonia. To prevent complications, an artificial feeding tube is used.
Forecast
It should be noted that the high and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are the most unfavorable - with them, the life expectancy of patients is significantly reduced. However, no matter what the first symptoms are, the disease quickly progresses, subsequently taking over the entire body, and the patient loses the ability to eat and move independently. Sometimes shortness of breath occurs - with physical activity and sometimes even without it. The patient feels a lack of air, which gives rise to panic. In the future, he may stop breathing on his own, and in order to provide him with oxygen, constant artificial ventilation will be needed. In some cases, at the end of the disease, difficulties with urination may appear. Due to atrophy, the patient loses weight.
Lateral atrophic sclerosis is accompanied by autonomic disorders: the limbs become noticeably cold, areas of the skin become stained, sweating and greasiness of the skin increases.
Life expectancy ranges from approximately 2 to 12 years, but most patients die within 5 years of diagnosis.
Breathing and physical therapy
Over time, the muscles weaken and breathing becomes more difficult. Doctors will check your breathing regularly and prescribe devices to help you sleep at night.
In some cases, patients choose to breathe through a ventilator. The doctor places a special tube into the surgical incision in the throat leading to the windpipe (tracheostomy) and connects the tube to a respirator.
A physical therapist deals with pain, gait, mobility, restraints, and equipment. Typically, patients with ALS are prescribed a set of gentle physical exercises aimed at maintaining normal cardiovascular function, muscle tone, and range of motion for as long as possible.
The patient may also need qualified psychological assistance.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is usually not immediately possible. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients. It includes the following research methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spinal cord and brain is the most informative method with which radiologists are able to visualize the degeneration of pyramidal structures and atrophy of the motor parts of the brain;
- Lumbar puncture - performed to obtain cerebrospinal fluid, in which laboratory technicians detect an increased protein content;
- Biochemical blood test - allows you to establish an increase in the level of CPK, ALT, AST, creatinine and urea;
- Neurophysiological diagnostic methods - electroneurography, electromyography, transcranial magnetic stimulation;
- Genetic analysis - identifying the gene that encodes superoxide dismutase - 1.
Neurological examination of patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis includes assessment of cranial nerve function, bulbar function, muscle tone according to the British Medical Research Council scale and movement disorders according to the Ashforth scale.
During magnetic resonance imaging of the neck with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, degenerative processes in the cranial nerves and atrophic changes in the anterior horns of the spinal cord are determined. Using electromyography, acute and chronic denervation is determined, which confirms damage to central neurons. The electromyogram shows the so-called “picket fence rhythm” - rhythmic fasciculations potentials. Electroneurography allows a non-invasive method to measure the speed of electrical impulses along nerve fibers. In the process of transcranial magnetic stimulation, the cerebral cortex is stimulated using short magnetic pulses. Both methods clearly show what neurodegenerative processes occur in the brain and spinal cord at this stage of the pathological process. Using additional research methods, doctors conduct differential diagnostics and determine which nervous function is impaired. The diagnosis of ALS is made by doctors at the neurology clinic if the following criteria are present:
- Signs of damage to the peripheral and central motor neuron;
- Data from electrophysiological and pathomorphological studies;
- Progression of the disease;
- Distribution of symptoms in one or more areas of innervation.
Knowledge and extensive experience, the use of the results of the latest diagnostic studies allows neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital to establish a diagnosis of ALS at an early stage of the disease.
What can you do yourself?
Once referred to a neurologist, it will likely take some time before the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
If you go to a specialized medical center, the examination may be assigned to several neurologists at the same time, as well as doctors of other profiles involved in the diagnosis and treatment of Lou Gehrig syndrome. The disease (the photo below shows Gehrig himself, whose career was cut short so suddenly due to a serious illness) always requires a serious, comprehensive approach.
You may have to wait a long time for a diagnosis, and the forced wait often leads to additional stress. Try to follow strategic recommendations that will allow you to profitably survive the diagnostic period:
- Keep a symptom diary. Before visiting a neurologist, start keeping a notebook or calendar in which you need to write down the time and circumstances in which you discovered any difficulties in walking, coordinating hand movements, speaking, or swallowing. Involuntary muscle movements also need to be recorded. These records will help identify a pattern of disease that will help make a diagnosis.
- Talk to experts. The trust between doctor and patient cannot be overstated when it comes to treating Lou Gehrig's disease (the photo above of the baseball player was taken before the disease). Try to establish trusting communication with all specialists involved in diagnosis and therapy.
Treatment
ALS therapy is ineffective in many cases. The goal of treatment is to slow the progression of the symptoms of the disease, increase the period during which the patient will be able to care for himself independently and will retain vital functions.
The only drug that is approved by the FDA (American Federal Administration for Supervision of Food and Drugs) is Rilutek, but it is not registered in the Russian Federation. Rilutek slows down the action of glutamate in brain cells, thereby improving the functioning of superoxide dismutase-1. The drug is prescribed to patients for life. Every three months, doctors monitor the level of liver transaminases. To prevent the death and improve the growth of nerve cells, patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis undergo stem cell transplantation.
To treat ALS, neurologists prescribe the following medications to patients:
- Prozerin is a drug that prevents the destruction of acetylcholine at neuromuscular synapses;
- Retabolil is an anabolic steroid that increases muscle mass;
- Vitamins A, B, C - to improve the conduction of nerve impulses.
When infectious complications develop, treatment is carried out with broad-spectrum antibiotics. Palliative therapy consists of eliminating dysphagia, dysarthria, muscle spasms, fasciculations, and depression. In the terminal stage of the disease, patients undergo endoscopic gastrotomy, tracheostomy and artificial ventilation. Thanks to the availability of modern equipment, the doctors of the intensive care unit of the Yusupov Hospital effectively support all the patient’s vital functions, which allows them to increase their life expectancy.
How to improve the patient's quality of life
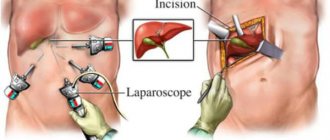
If patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis have problems chewing and swallowing food, they should prepare liquid and ground meals. Soups and porridges can be blended with a blender. When a patient loses the ability to swallow food on his own, surgeons at the Yusupov Hospital perform gastrostomy surgery. After this, food is introduced directly into the stomach through a tube inserted through a stoma in the anterior abdominal wall. In some cases, parenteral nutrition is carried out - mixtures that contain all the necessary ingredients are administered intravenously.
If speech is impaired, ALS patients lose the ability to speak. In this case, they can communicate with others using a printing device. Also for this purpose, systems with automatic sensors located on the eyeballs are used.
If the patient loses the ability to move independently, they resort to orthopedic devices, use special shoes, canes and strollers. The head is fixed with a special holder. As the disease progresses, the patient should be provided with a functional bed.
Forecast
The prognosis for the recovery of patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is pessimistic. Treatment of the disease is aimed at improving the quality and increasing the patient’s life expectancy. The only drug that affects the mechanism of development of the disease is not imported into the Russian Federation. The most unfavorable prognosis is for high and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Care and palliative therapy for patients suffering from ALS are provided at the neurology clinic and hospice of the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors in the intensive care unit use modern equipment to support the patient’s vital functions. To get complete information about the disease, the cost of treatment, and to make an appointment with a neurologist, call the contact center phone number. It works 24 hours a day without days off and lunch breaks.
Make an appointment
Goals of therapy
Currently, there are no effective treatments for this disease. Therefore, therapy is aimed at:
- slow down the progression of the disease and prolong the period of illness during which the patient does not need constant outside care;
- reduce the severity of individual symptoms of the disease and maintain a stable level of quality of life.