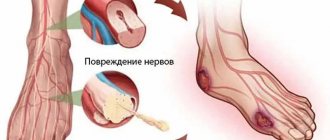
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most serious health problems in the world. One of the main complications of diabetes is a blood vessel disease called diabetic angiopathy. Impaired nutrition of the nerve trunks leads to the development of another problem in patients with diabetes - neuropathy.
Diabetic angiopathy
Diabetic angiopathy is a vascular lesion that occurs in people with diabetes. In diabetes, cholesterol and calcium gradually accumulate in the walls of the arteries, which leads to their obstruction and disruption of the blood supply to the tissues.
Diabetic angiopathy is divided into two main types: microangiopathy (damage to small vessels) and macroangiopathy (damage to large main arteries), and there is often a combination of both.
Macroangiopathy develops in the vessels of the heart and lower extremities, being essentially their malignant atherosclerosis.
Microangiopathy most often manifests itself in damage to the arteries of the eyes (retinal damage - diabetic retinopathy) or kidneys (diabetic nephropathy).
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur when the vessels in the nerve trunks are affected. Diabetic neuropathy most often develops in the nerves of the legs and feet.
Depending on the affected nerves, symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can range from pain and numbness in the extremities to complete loss of sensation in the feet and hands, with the development of lesions and purulent complications.
Diabetic neuropathy is a very common complication of diabetes. However, it is often possible to prevent diabetic neuropathy or slow its progression through strict blood sugar control and a healthy lifestyle.
Causes of diabetic angiopathy and neuropathy
It is known that diabetes mellitus causes hormonal and metabolic disorders, which cause the deposition of cholesterol plaques and inflammatory changes in the walls of blood vessels, which leads to the development and clinical manifestations of diabetic angiopathy. However, not all diabetics complain of manifestations of angiopathy. This complication of diabetes depends not only on the hormonal background of a particular patient, but also on his genetic characteristics.
Diabetics with high blood pressure, smokers, and alcohol abusers have more pronounced and malignant manifestations of diabetic angiopathy.
Long-term exposure to high blood sugar can damage fine nerve fibers, causing diabetic neuropathy. The main cause of nerve damage in diabetes is considered to be microangiopathy of the vessels supplying the nerves. Their blockade in diabetic angiopathy leads to a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients in the nervous tissue and to the death of nerve fibers.
Advantages of our clinic
The multidisciplinary clinic “Energy of Health” has experienced staff and the most modern equipment for diagnosing and treating various diseases. We provide each client with high quality medical services, which include:
- detailed examination to accurately determine the cause of complaints;
- consultations with narrow specialists directly in the clinic, as well as communication with foreign doctors if necessary;
- comprehensive treatment, selected in accordance with the indications and individual characteristics of the body;
- minor surgical operations directly in the clinic;
- own day hospital for maximum convenience;
- drawing up rehabilitation programs;
- affordable prices and services within the framework of voluntary health insurance.
Polyneuropathy is a dangerous complication of many conditions and diseases. You should not hope that the symptoms are limited to a simple tingling sensation; over time, the condition will worsen. Don’t delay seeing a doctor; sign up for a consultation with neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic.
Types of diabetic angiopathy
Diabetic nephropathy develops when the small arteries of the kidneys are damaged and leads to disruption of their function, up to the development of severe renal failure. Diabetic nephropathy is manifested by the appearance of protein in the urine, severe arterial hypertension, and increased levels of creatinine and urea in the blood.
Diabetic retinopathy develops when the retinal arteries are damaged. It is characterized by changes in the vessels of the fundus and hemorrhages in the retina. Can lead to retinal detachment and complete blindness.
Angiopathy of the lower extremities in diabetes mellitus develops through four stages:
- The first stage has no clinical symptoms, however, when examining the vessels, thickening of the arterial walls and their calcification can be detected.
- The second stage is manifested by the appearance of pain when walking over a certain distance (intermittent claudication)
- The third stage is characterized by the appearance of pain in the legs at rest, especially when lying horizontally. If you lower your legs, the pain decreases significantly.
- The fourth stage is manifested by the appearance of trophic ulcers and necrosis on the legs, and diabetic gangrene often develops. This condition is called diabetic foot syndrome.
Other problems
- Gastrointestinal problems
, especially mild symptoms of gastroparesis: mild intestinal upset, flatulence, nausea, vomiting. A light low-fat diet, limiting the consumption of fats and cell foods is necessary. If the symptoms are more severe, the endocrinologist will prescribe antibiotics, drugs that improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, agents that reduce stomach acid, and other medications. - Dizziness and weakness
. The patient should avoid sudden movements such as fast walking and heavy lifting. With low blood pressure, wearing special elastic socks and stockings, salty foods and taking hormones can improve the condition. For high blood pressure, special medications are needed. In case of muscle weakness and coordination problems, physiological procedures are also used. - Urinary tract infections
. Such diseases are treated with antibiotics. To prevent urinary tract infections, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids. If a person has urinary incontinence, they should try to go to the toilet at regular intervals, such as every three hours. - Erectile disfunction.
Men first need to rule out hormonal dysfunction by taking hormone tests. If hormones are normal, treatment for nephropathy is required. Erectile dysfunction caused by neuropathy can be treated with several methods that involve increasing blood flow to the penis. Local medications, procedures, vacuum devices, and implants are also used. - Dryness of the genital tract.
In women, neuropathy can cause vaginal dryness. In this case, vaginal lubricants are recommended.
Types of diabetic neuropathy
There are four main types of diabetic neuropathy. Most develop gradually, so this complication may not be noticed until serious problems arise.
Peripheral polyneuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form of diabetic neuropathy. First, problems with sensitivity develop in the legs, then signs of neuropathy may appear in the arms. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are often worse at night and may include:
- Numbness or decreased ability to feel pain or changes in temperature.
- Tingling or burning sensation.
- Sharp pain or cramps.
- Increased sensitivity to touch - for some people, even the weight of a sheet can be excruciating.
- Muscle weakness.
- Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankle.
- Loss of balance and coordination.
- Serious foot problems such as ulcers, infections, strains and bone and joint pain.
Autonomic neuropathy
The autonomic nervous system controls the heart, bladder, lungs, stomach, intestines, genitals and eyes. Diabetes can affect the nerves in any of these organs, which can cause:
- Problems with urination - urinary retention or incontinence due to damage to the autonomic innervation of the bladder.
- Constipation or uncontrolled bowel movements.
- Slowing of gastric emptying (gastroparesis), leading to nausea, vomiting, bloating and loss of appetite.
- Difficulty swallowing
- Impaired potency in men
- Vaginal dryness and other sexual disorders in women
- Increased or decreased sweating
Diabetic amyotrophy
Diabetic amyotrophy affects the large nerves of the limbs, such as the femoral and sciatic nerves. Another name for this condition is proximal neuropathy, which most often develops in older people with type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms usually occur on one side of the body and include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the hip or buttock
- Thigh muscle atrophy
- Difficulty getting up from a sitting position
Mononeuropathy
Mononeuropathy involves damage to a specific nerve. The nerve may be in the face, torso, or leg. Mononeuropathy is also called focal neuropathy. Most often found in older people.
Although mononeuropathy can cause severe pain, it usually does not cause any long-term problems. Symptoms gradually decrease and disappear on their own after a few weeks or months. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific nerve affected and may include:
- Double vision due to damage to the oculomotor nerve
- Facial paralysis with facial asymmetry
- Pain in the lower leg or foot
- Pain in the lower back or pelvis
- Pain in the anterior thigh
- Pain in the chest or stomach
- Weakness in the hand, with damage to the nerves of the brachial plexus.
Other studies
The doctor may also consider other tests necessary:
- Electromyography
- to determine the type and extent of nerve damage. A special device sends an electrical current to the nerve, and the electromyogram shows how the muscles respond to the electrical impulses delivered through the nerves; - Heart rate variability
. The doctor must know how the heart reacts to deep breathing, exercise, blood pressure and other changes; - Ultrasound examination of the pelvis and other systems
. Using ultrasound, the structural state of organs and some functions are assessed. For example, how the bladder works.
Electromyography
Pelvic ultrasound
Diagnosis of neuropathy and angiopathy
The diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy is based on symptoms, history, and clinical examination. During the exam, your doctor may check your muscle strength and tone, tendon reflexes, and sensitivity to touch, temperature, and vibration.
Additional diagnostic tests:
- Nerve conduction studies. This test checks how well the nerves in the arms and legs conduct electrical signals.
- Electromyography (EMG). Often performed in conjunction with nerve conduction studies, electromyography measures the electrical discharges produced in your muscles.
- Quantitative sensory testing. This non-invasive test is used to evaluate how responsive nerves are to vibration and temperature changes.
- Vegetative testing. The reaction of blood pressure in different body positions and the ability to sweat are assessed.
Complications
If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not eliminate the cause that caused the damage to the nerve fibers, neuropathy will steadily progress. Complications of the disease include:
- a significant decrease in muscle tone with subsequent muscle atrophy;
- loss of limb performance;
- development of extensive trophic ulcers requiring surgical intervention;
- loss of ability to move and self-care;
- chronic insomnia due to pain and the development of restless legs syndrome;
- depression and neuroses.
You can avoid complications if you consult a doctor for help in a timely manner and also follow preventive measures.
Make an appointment
Treatment of diabetic angiopathy
Compensation for diabetes mellitus is the basis of treatment for diabetic angiopathy. It is necessary to reduce blood glucose levels to normal values using glucose-lowering drugs; in severe cases of diabetes, it is necessary to use insulin therapy.
If objective signs of arterial damage (narrowing, calcification) are detected, it is advisable to constantly take angioprotectors (Vessel Due F), antithrombotic drugs (aspirin, Plavix), and vitamins.
Signs of severe angiopathy, with circulatory disorders in organs and limbs, should be the reason for active surgical treatment. In case of damage to the arteries of the leg, heart and kidneys, it is advisable to restore blood circulation using endovascular surgery methods (angioplasty and stenting). This will prevent the development of severe complications such as gangrene, myocardial infarction, and renal failure.
Diabetic angiopathy is a very dangerous disease that can be fatal. When the first symptoms of angiopathy appear, a patient with diabetes should immediately visit an experienced doctor specializing in this problem.
Pain management
Many painkillers help relieve the pain of nephropathy. For severe pain, a combination of several medications is prescribed. Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids and other medications are used for this purpose, although they all have side effects. Some of the painkillers are not recommended for older people and people with heart disease. As for over-the-counter pain relievers (paracetamol, ibuprofen), some experts advise patients not to take them because they are not enough to relieve neuropathic pain, but they have serious side effects.
Painkillers
External remedies are also used to relieve pain, especially effective for use on the ankles. The doctor may prescribe a cream containing capsaicin, lidocaine, nitrate spray, etc. In some patients, the condition is alleviated by alpha-lipolic acid, endotracheal oil and other means.
For patients with increased sensitivity to the feet and touching, for example, a blanket, a special device is used - a frame that holds the blanket in the air.
Some patients relieve pain with acupuncture, bio-communication, and physical therapy. But the effects of electrical stimulation on nerve pain, magnetic therapy, laser therapy and phototherapy have not yet been studied.
Symptoms
Diabetic neuropathy is characterized by extensive symptoms, nonspecific in the initial stages, which creates diagnostic difficulties.
In the acute version of the course, polyneuropathy is manifested by sudden sharp pain (“stab of a knife”, “puncture of a needle”) and an unbearable burning sensation in the hands and feet, the occurrence of pain during normal influences - touch, massage movements, application of external medications.
Chronic diabetic neuropathy is often completely asymptomatic and can be diagnosed during screening studies. Patients note that the most striking symptoms are numbness of the feet and a significant loss of sensitivity, due to which stability is impaired and the risk of sudden falls increases.
Due to the pain syndrome, sleep disorders and depression often develop, and patients are unable to work fully. Without treatment, the patient may find himself completely isolated from social life, he is threatened with a change in status - loss of profession, irreversible deterioration in the quality of life.
Statistics
Polyneuropathy is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus, developing in patients with type I diabetes in 54% of cases, in patients with type II diabetes in 45% of cases. In the general structure of polyneuropathies, the diabetic variant occupies 30%.
Diabetic polyneuropathy is detected in 10% of patients who are first diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (we are talking about type II).
An asymptomatic form is often found, so almost 50% of patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus do not report symptoms of polyneuropathy, which is detected only during instrumental studies or routine medical examinations.
Diabetic polyneuropathy in 20% of cases is manifested by severe pain, which is recognized as one of the most painful types of pain. It is the diabetic variant of polyneuropathy that is the indirect (indirect) cause of more than 50% of cases of non-traumatic amputations.